equals()方法、hashCode()方法的区别
在ImportNew上看到一篇文章8张图理解Java,下面详细地讲一下hashCode()方法:
- 如果两个对象相等(equal),那么他们一定有相同的哈希值。
- 如果两个对象的哈希值相同,但他们未必相等(equal)。
ImportNew原文的示例:
Java equals() and hashCode() Contract
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Apple {
private String color;
public Apple(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
//重写了equals方法
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj==null) return false;
if (!(obj instanceof Apple))
return false;
if (obj == this)
return true;
return this.color.equals(((Apple) obj).color);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Apple a1 = new Apple("green");
Apple a2 = new Apple("red");
//hashMap stores apple type and its quantity
HashMap<Apple, Integer> m = new HashMap<Apple, Integer>();
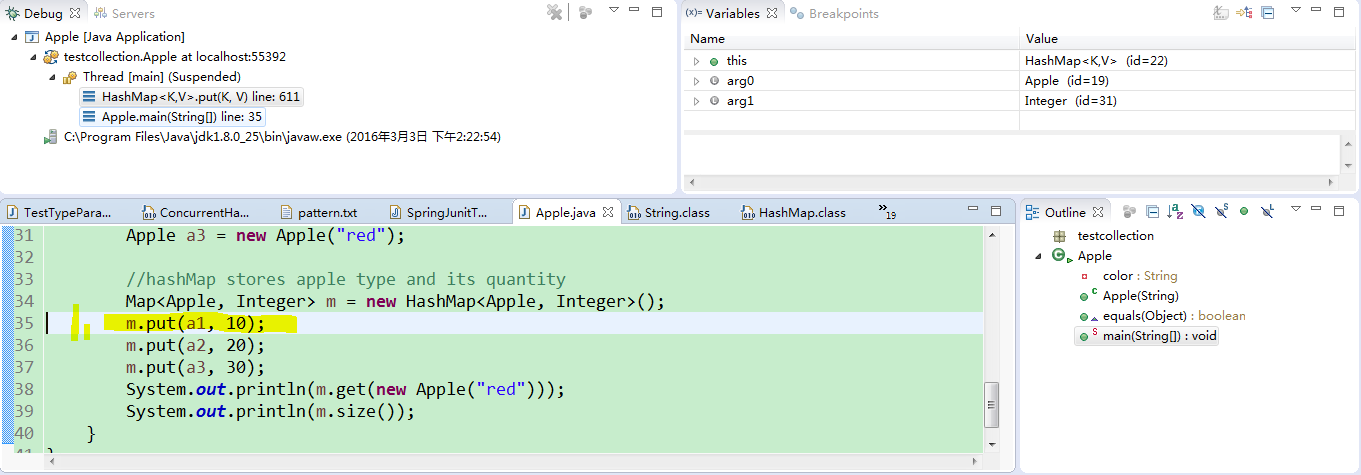
m.put(a1, 10);
m.put(a2, 20);
System.out.println(m.get(new Apple("green")));
}
}运行的结果是:null
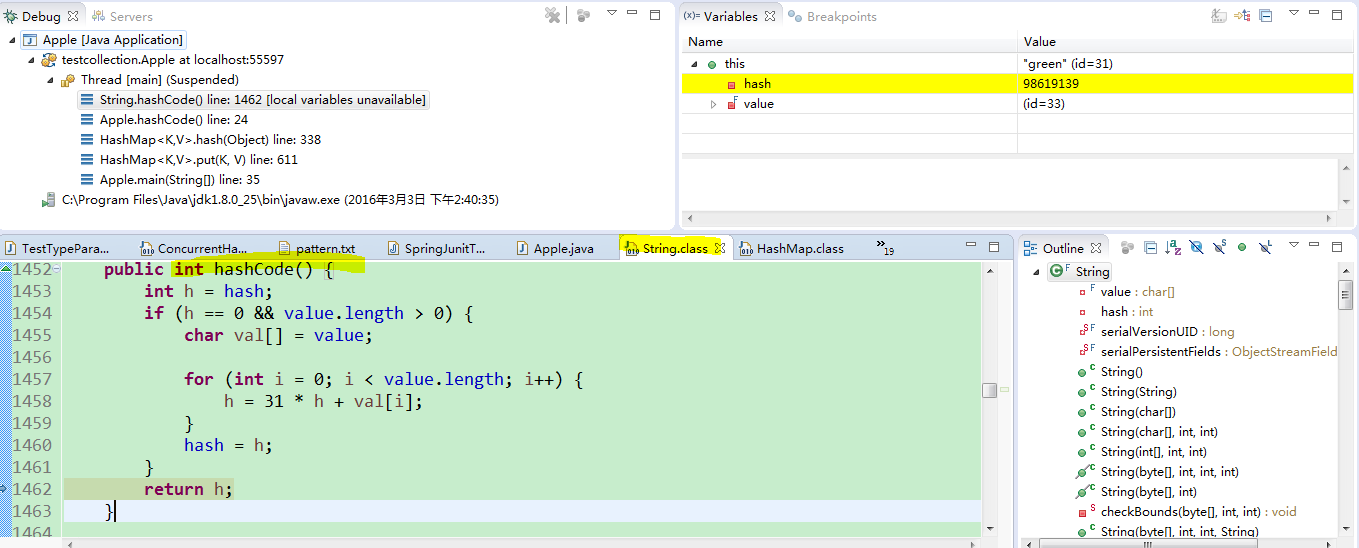
是因为没有重写hashCode()方法,大家可以debug跟进去调试看一下:
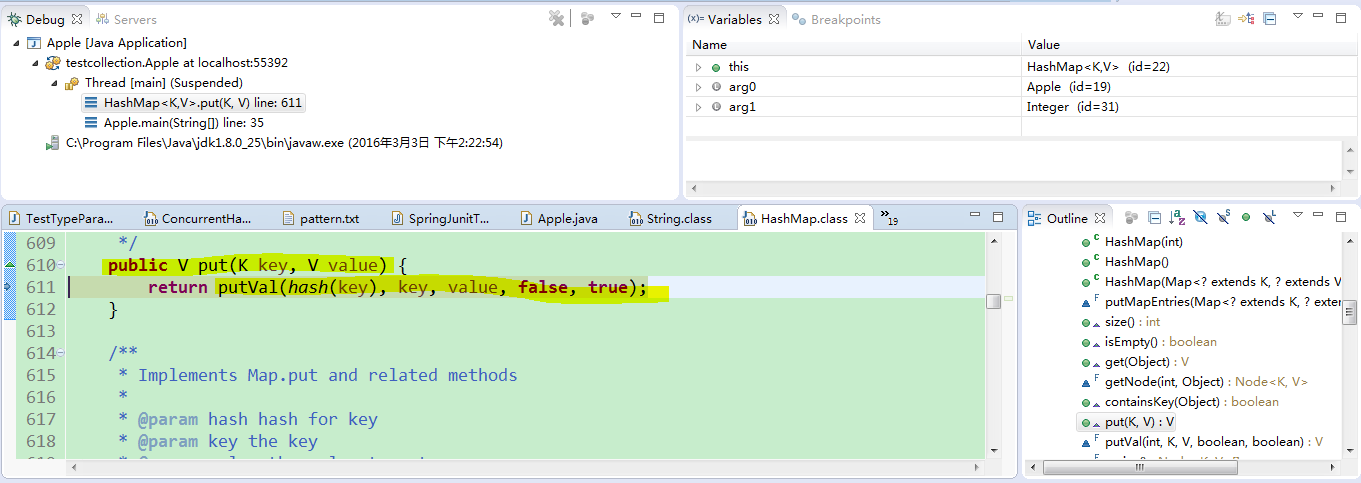
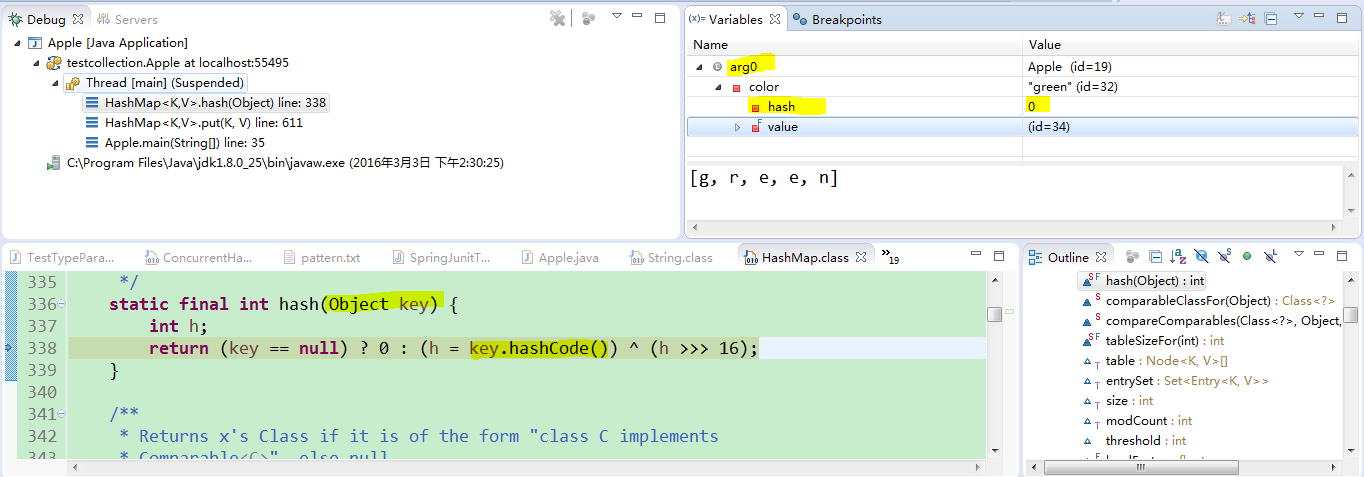
put操作的时候,里面会调用一个hash方法,而hash方法里会调用hashCode方法,如果你没有重写hashCode方法,那hash仍然为0
下面是重写了hashCode方法:
package testcollection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Apple {
private String color;
public Apple(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj==null) return false;
if (!(obj instanceof Apple))
return false;
if (obj == this)
return true;
String col = ((Apple) obj).color;
return this.color.equals(col);
}
//重写了hashCode方法
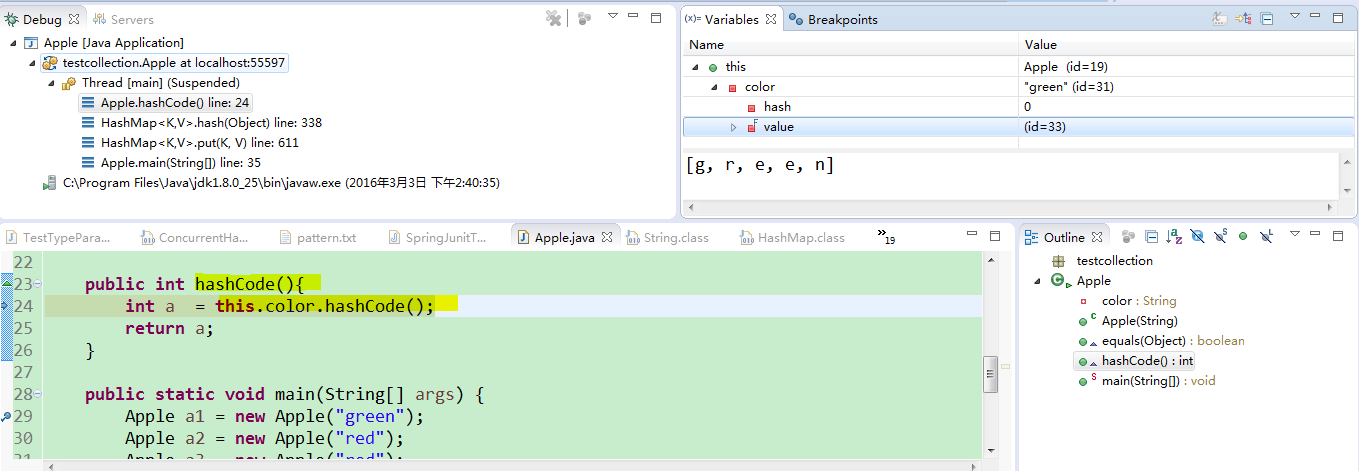
public int hashCode(){
int a = this.color.hashCode();
return a;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Apple a1 = new Apple("green");
Apple a2 = new Apple("red");
Apple a3 = new Apple("red");
//hashMap stores apple type and its quantity
Map<Apple, Integer> m = new HashMap<Apple, Integer>();
m.put(a1, 10);
m.put(a2, 20);
m.put(a3, 30);
System.out.println(m.get(new Apple("red")));
System.out.println(m.size());
}
}
这样就有hash值了。
这样程序的结果是:30
ps:为什么是30呢?那20那个值还在不在?可以看到程序里
Apple a1 = new Apple("green");
Apple a2 = new Apple("red");
Apple a3 = new Apple("red");
//hashMap stores apple type and its quantity
Map<Apple, Integer> m = new HashMap<Apple, Integer>();
m.put(a1, 10);
m.put(a2, 20);
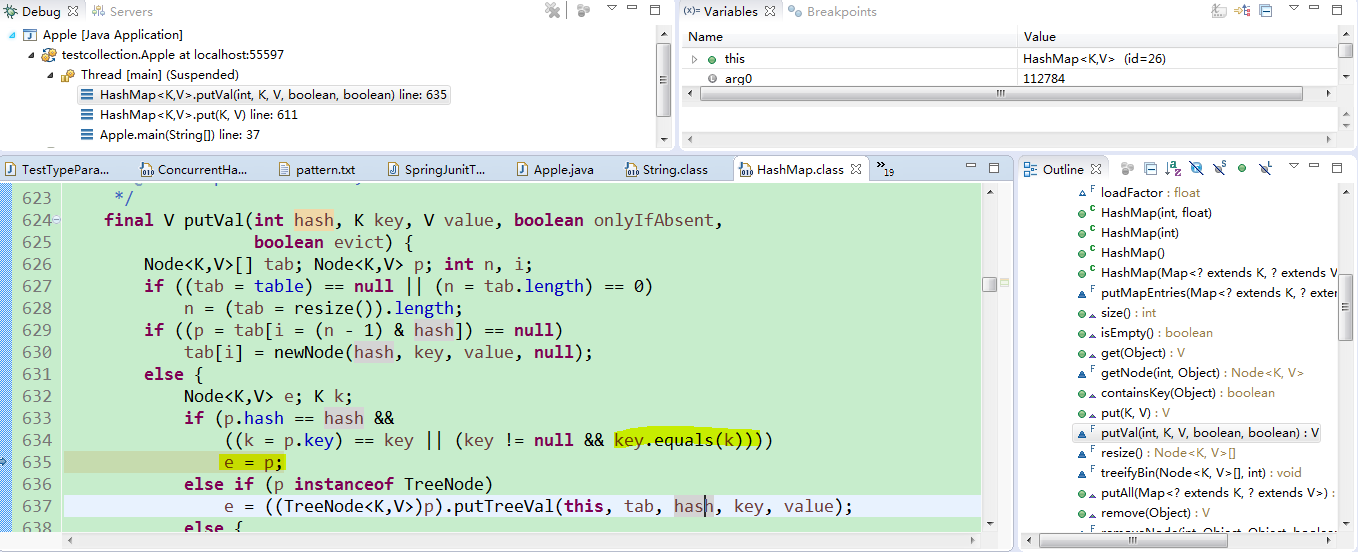
m.put(a3, 30);这里就涉及到HashMap的存储原理了,这里大家也可以debug跟踪源码看一看,就可以知道,因为也重写了equals方法,所以,30会替掉20,m.size()为2,map里面只有两个对象了。
那么如果没有重写equals方法呢?又会输出什么???
输出
null
3
m.put(a1, 10);
m.put(a2, 20);
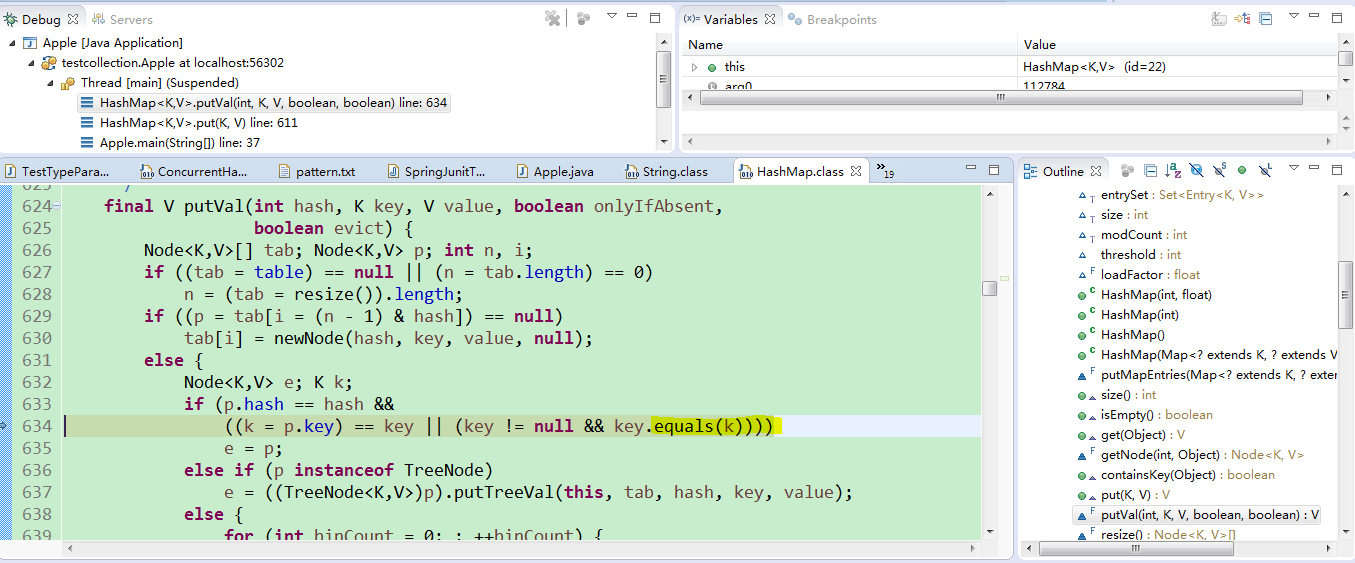
m.put(a3, 30);当put a1和a2之后,put a3时,里面会调用equals方法:
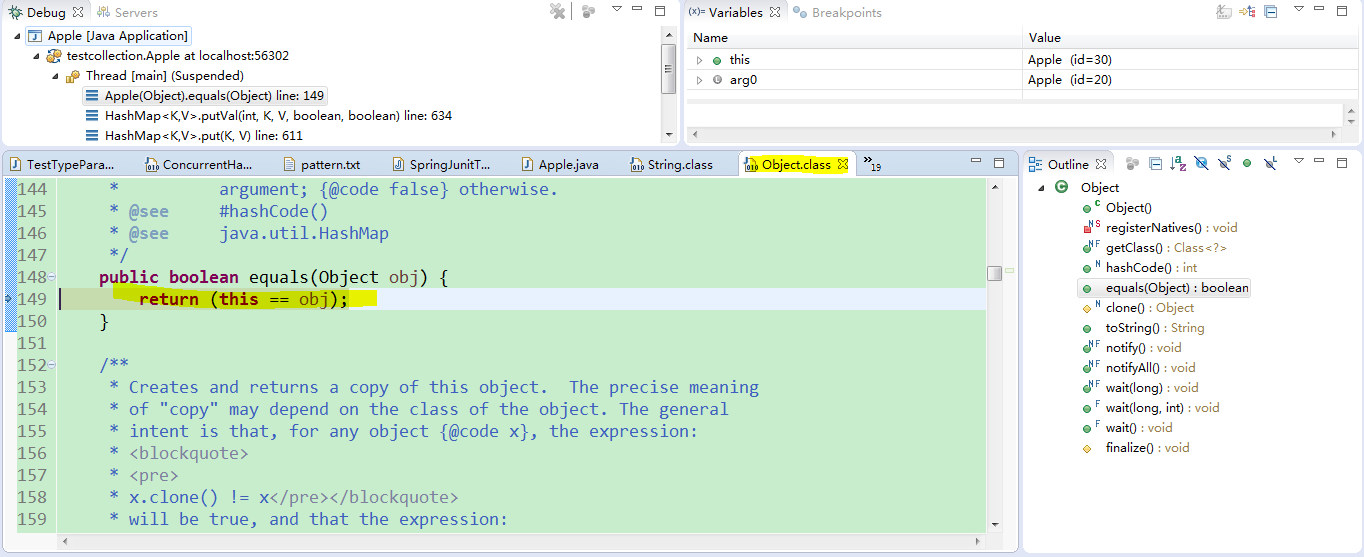
而这个equals方法是Object里面的方法,并不是String类里面的equals方法,所以肯定是不等的
所以可以得出结论了:
- 两个对象相等,那么一定是equals的,并且hashCode是相等的;
- 如果两个对象的hashCode相等,那也不一定相等






















 148
148

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








