Alice’s Cube
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 1948 Accepted Submission(s): 639
Problem Description
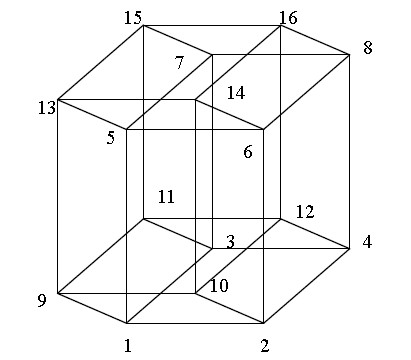
Alice has received a hypercube toy as her birthday present. This hypercube has 16 vertices, numbered from 1 to 16, as illustrated below. On every vertex, there is a light bulb that can be turned on or off. Initially, eight of the light bulbs are turned on and the other eight are turned off. You are allowed to switch the states of two adjacent light bulbs with different states (“on” to “off”, and “off” to “on”; specifically, swap their states) in one operation.
Given the initial state of the lights, your task is to calculate the minimum number of steps needed to achieve the target state, in which the light bulbs on the sub cube (1,2,3,4)-(5,6,7,8) are turned off, and the rest of them are turned on.
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of the input contains an integer T, meaning the number of the test cases. There are about 13000 test cases in total.
For each test case there are 16 numbers in a single line, the i-th number is 1 meaning the light of the i-th vertex on the picture is on, and otherwise it’s off.
For each test case there are 16 numbers in a single line, the i-th number is 1 meaning the light of the i-th vertex on the picture is on, and otherwise it’s off.
Output
For every test cases output a number with case number meaning the minimum steps needed to achieve the goal. If the number is larger than 3, you should output “more”.
Sample Input
3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case #1: 0 Case #2: 1 Case #3: more
bfs的套路
1,首先正难则反,因为终止状态已经确定了,就是0000000011111111,所以可以终止状态往前搜索(3步即可)。
2,标记,用数字的二进制表示哪些状态已经被访问过了,一个bool vis[1<<16]的数组即可
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int a[17];
int step;
};
node h;
bool vis[1<<16];///2^16
int st[1<<16];
int data[17][4]={
{0,0,0,0},
{2,3,5,9},
{1,4,6,10},
{1,4,7,11},
{2,3,8,12},
{1,6,7,13},
{2,5,8,14},
{3,5,8,15},
{4,6,7,16},
{1,10,11,13},
{2,9,12,14},
{3,9,12,15},
{4,10,11,16},
{5,9,14,15},
{6,10,13,16},
{7,11,13,16},
{8,12,14,15}
};
int getstate(int a[]){
int sum=0;
int r=1;
for(int i=1;i<=16;i++){
sum+=(a[i]*r);
r*=2;
}
return sum;
}
void bfs(){
queue<node> qq;
h.a[1]=0;h.a[2]=0;h.a[3]=0;h.a[4]=0;
h.a[5]=0;h.a[6]=0;h.a[7]=0;h.a[8]=0;
h.a[9]=1;h.a[10]=1;h.a[11]=1;h.a[12]=1;
h.a[13]=1;h.a[14]=1;h.a[15]=1;h.a[16]=1;
h.step=0;
vis[getstate(h.a)]=true;
st[getstate(h.a)]=0;
qq.push(h);
while(!qq.empty()){
node top;
top=qq.front();
qq.pop();
if(top.step==3){
continue;
}
int temp[17];
//memcpy(temp,top.a,sizeof(temp));
for(int i=1;i<=16;i++){
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
memcpy(temp,top.a,sizeof(temp));
if(temp[i]!=temp[data[i][j]]){
swap(temp[i],temp[data[i][j]]);
if(vis[getstate(temp)]){
continue;
}else{
vis[getstate(temp)]=true;
st[getstate(temp)]=top.step+1;
node newnode;
memcpy(newnode.a,temp,sizeof(temp));
newnode.step=top.step+1;
qq.push(newnode);
}
}
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int T;
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
bfs();///end state fix
int cas=1;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
int sum;
int s[17];
for(int i=1;i<=16;i++){
scanf("%d",&s[i]);
sum=getstate(s);
}
if(vis[sum]){
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",cas++,st[sum]);
}else{
printf("Case #%d: more\n",cas++);
}
}
return 0;
}






















 927
927

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








