题目
Problem Statement
Treeland is a country with n cities, numbered 0 through n-1. Obviously, the topology of Treeland is a tree: there are exactly n-1 bidirectional roads, each connecting two cities in such a way that it is possible to travel from any city to any other city. You are given the description of the road network: the vector p with n-1 elements. For each valid index i, there is a road that connects the cities i+1 and p[i]. The distance between two cities is the smallest number of roads you need to use in order to travel from one city to the other. Rabbit Hanako had a trip in Treeland. She started her trip on day 0 in the city x[0] = 0. On each of the following m days she chose a city x[i] (possibly the same as her current city) and traveled there by using the only direct route. Each day she wrote down the distance she traveled - i.e., on day i she wrote down the distance d[i] between the cities x[i-1] and x[i]. After the trip was over, she constructed a set D that contained all values d[i] she wrote down. For example, if d[1], d[2], …, d[m] are {1, 0, 0, 1, 3, 5, 0} then the set D will be {0, 1, 3, 5}. You know that Hanako’s trip had the form described above, but you don’t know the value m and the values x[i]. You are given a vector < int> S. Check whether it is possible that S = D. In other words, check whether there are values m and x[1] … x[m] such that the set of distances D will contain exactly the same elements as the given vector < int> S. Return “Possible” if such a trip exists and “Impossible” if it does not.
Definition
Class:
JumpDistancesOnTreeEasy
Method:
isPossible
Parameters:
vector , vector
Returns:
string
Method signature:
string isPossible(vector p, vector S)
(be sure your method is public)
Limits
Time limit (s):
2.000
Memory limit (MB):
256
Stack limit (MB):
256
Constraints
p will contain between 1 and 50 elements, inclusive.
For each i, 0 <= p[i] <= i.
S will contain between 1 and 50 elements, inclusive.
Each element in S will be between 0 and |p|, inclusive.
For each i, S[i] < S[i+1].
Examples
0)
{0,1,1,0,4,4}
{2,4}
Returns: “Possible”
The tree is like:
0
/ \
1 4
/ \ / \
2 3 5 6One of the possible route is: 0, 2, 3, 6, 5. The distance for each day is {2, 2, 4, 2} so S = {2, 4}.
1)
{0,1,1,0,4,4}
{1,2,3,4,5}
Returns: “Impossible”
The maximal possible distance between any two cities is 4, so you will never have 5 in D.
2)
{0,1,1,0,4,4}
{3,4}
Returns: “Impossible”
3)
{0,1,2,3,4,0,6,7,8,9}
{2,4,6,8,10}
Returns: “Impossible”
4)
{0}
{1}
Returns: “Possible”
题意:
给你一棵树,所有的边距离为1,让你从根节点出发,经过若干个节点。将每次行走的距离记录下来记为集合D(去重)。现在给出集合S,问是否存在合法的路径使得D=S。
思路:
先跑一遍Floyd得出每个点之间的距离。如果存在某个点能到达的最大距离>=S的最大值,则显然只要到达该点就能满足题意,相反的,如果从根节点出发无法到达这种点,则无解。
代码:

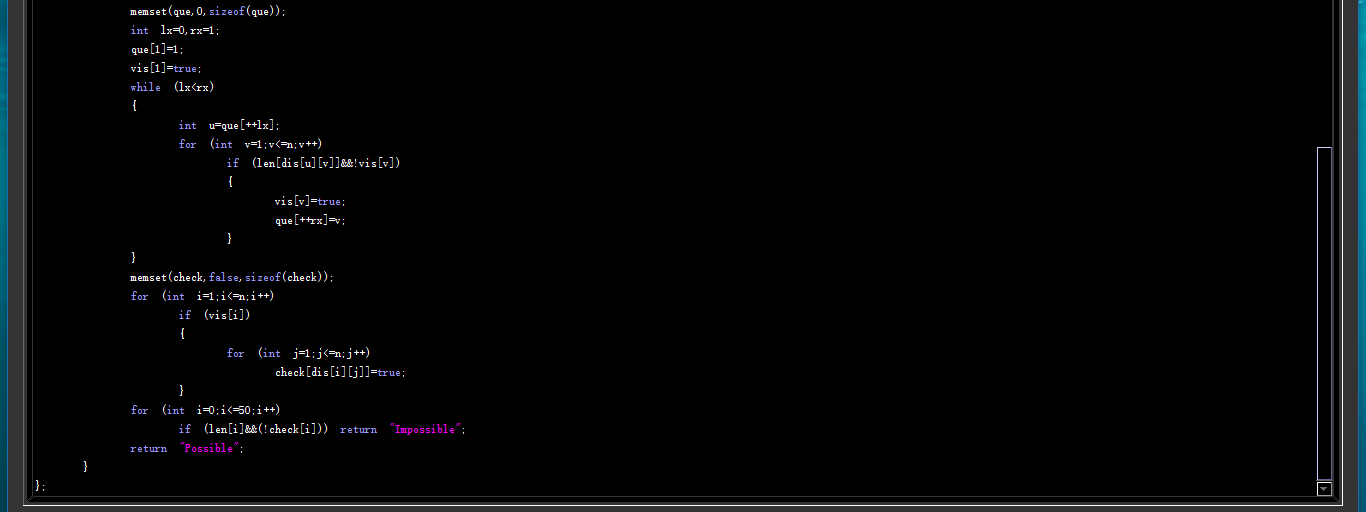
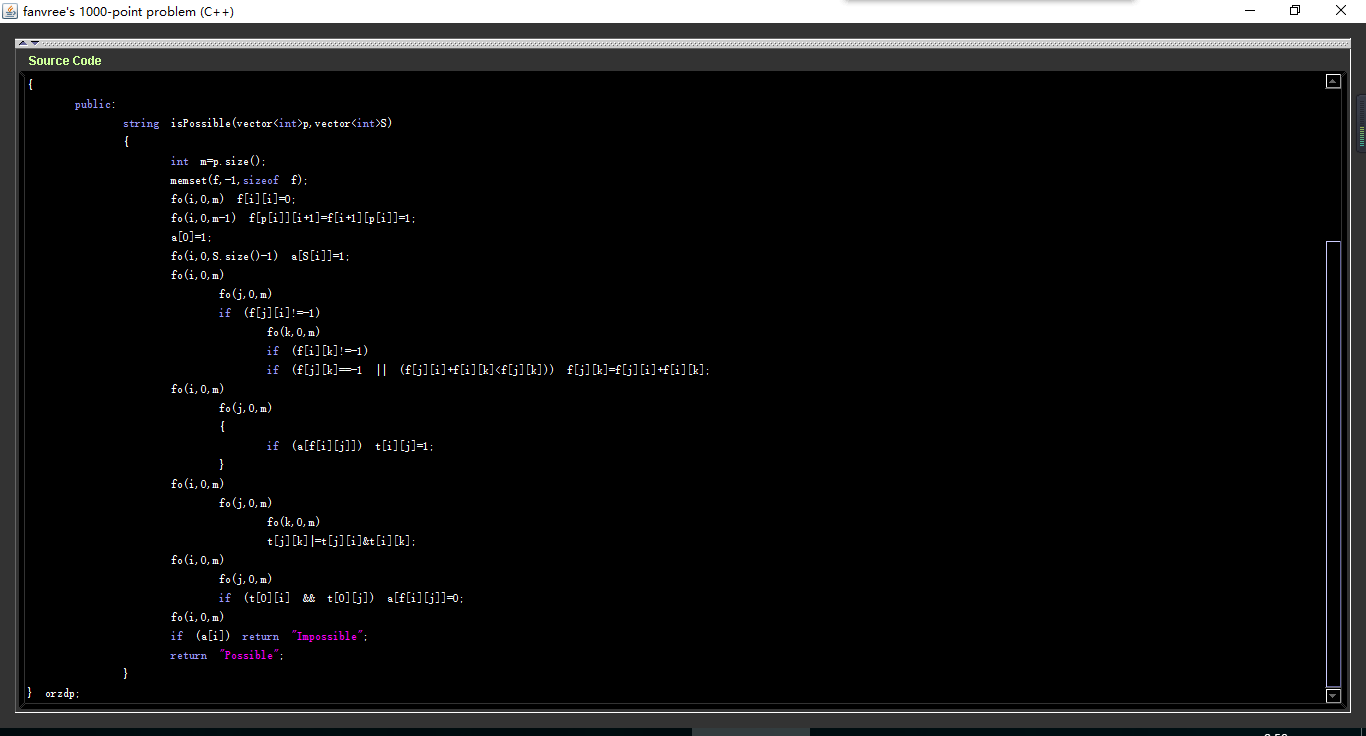
























 6599
6599











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








