我们首先来看一下什么是前向星.
前向星是一种特殊的边集数组,我们把边集数组中的每一条边按照起点从小到大排序,如果起点相同就按照终点从小到大排序,
并记录下以某个点为起点的所有边在数组中的起始位置和存储长度,那么前向星就构造好了.
用len[i]来记录所有以i为起点的边在数组中的存储长度.
用head[i]记录以i为边集在数组中的第一个存储位置.
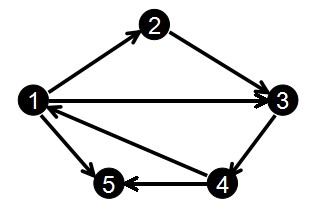
那么对于下图:
我们输入边的顺序为:
1 2
2 3
3 4
1 3
4 1
1 5
4 5
那么排完序后就得到:
编号: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
起点u: 1 1 1 2 3 4 4
终点v: 2 3 5 3 4 1 5
得到:
head[1] = 1 len[1] = 3
head[2] = 4 len[2] = 1
head[3] = 5 len[3] = 1
head[4] = 6 len[4] = 2
但是利用前向星会有排序操作,如果用快排时间至少为O(nlog(n))
如果用链式前向星,就可以避免排序.
我们建立边结构体为:
struct Edge
{
int next;
int to;
int w;
};其中edge[i].to表示第i条边的终点,edge[i].next表示与第i条边同起点的下一条边的存储位置,edge[i].w为边权值.
另外还有一个数组head[],它是用来表示以i为起点的第一条边存储的位置,实际上你会发现这里的第一条边存储的位置其实
在以i为起点的所有边的最后输入的那个编号.
head[]数组一般初始化为-1,对于加边的add函数是这样的:
void add(int u,int v,int w)
{
edge[cnt].w = w;
edge[cnt].to = v;
edge[cnt].next = head[u];
head[u] = cnt++;
}初始化cnt = 0,这样,现在我们还是按照上面的图和输入来模拟一下:
edge[0].to = 2; edge[0].next = -1; head[1] = 0;
edge[1].to = 3; edge[1].next = -1; head[2] = 1;
edge[2].to = 4; edge[2],next = -1; head[3] = 2;
edge[3].to = 3; edge[3].next = 0; head[1] = 3;
edge[4].to = 1; edge[4].next = -1; head[4] = 4;
edge[5].to = 5; edge[5].next = 3; head[1] = 5;
edge[6].to = 5; edge[6].next = 4; head[4] = 6;
很明显,head[i]保存的是以i为起点的所有边中编号最大的那个,而把这个当作顶点i的第一条起始边的位置.
这样在遍历时是倒着遍历的,也就是说与输入顺序是相反的,不过这样不影响结果的正确性.
比如以上图为例,以节点1为起点的边有3条,它们的编号分别是0,3,5 而head[1] = 5
我们在遍历以u节点为起始位置的所有边的时候是这样的:
for(int i=head[u];~i;i=edge[i].next)
那么就是说先遍历编号为5的边,也就是head[1],然后就是edge[5].next,也就是编号3的边,然后继续edge[3].next,也
就是编号0的边,可以看出是逆序的.
模板代码1:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int M = 4444;
int d[M],head[M],vis[M];
struct nod{
int nex,to,w;
}eg[M];
typedef pair<int,int> P;
int cnt=0;
inline void add(int u,int v,int w){
eg[cnt].to=v;
eg[cnt].w=w;
eg[cnt].nex=head[u];
head[u]=cnt++;
}
void dijkstra(int s){
priority_queue<P,vector<P>,greater<P> >que;
d[s]=0;
que.push(P(0,s));
while(!que.empty()){
P p = que.top();
que.pop();
int v=p.second;
if(d[v]<p.first) continue;
for(int i=head[v];~i;i=eg[i].nex){
nod e=eg[i];
if(e.w+d[v]<d[e.to]){
d[e.to]=e.w+d[v];
que.push(P(d[e.to],e.to));
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int t,n;
scanf("%d %d",&t,&n);
memset(d,inf,sizeof(d));
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){
int u,v,cost;
scanf("%d %d %d",&u,&v,&cost);
add(u,v,cost);
add(v,u,cost);
}
dijkstra(1);
printf("%d\n",d[n]);
return 0;
}模板代码2(优化):
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_V = 200010;
const int MAX_E = 2000010;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int V,E,cnt;
int heap[MAX_V],dis[MAX_V];
struct Edge{
int to,next,cost;
}rng[MAX_E];
void add(int u,int v,int cost){
rng[cnt].to = v;
rng[cnt].next = heap[u];
rng[cnt].cost = cost;
heap[u] = cnt++;
}
struct Rule{
bool operator()(int &a,int &b)const{
return dis[a] > dis[b];
}
};
inline int read()
{
int X=0,w=1; char ch=0;
while(ch<'0' || ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') w=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0' && ch<='9') X=(X<<3)+(X<<1)+ch-'0',ch=getchar();
return X*w;
}
void Dijkstra(int a_){
memset(dis,INF,sizeof(dis));
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,Rule > q;
dis[a_] = 0;q.push(a_);
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.top();q.pop();
for(int k=heap[u];k != -1;k = rng[k].next){
int &v = rng[k].to;
if(dis[v] > dis[u] + rng[k].cost){
dis[v] = dis[u] + rng[k].cost;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
int main(void){
cnt = 0;
memset(heap,-1,sizeof(heap));
V = read(),E = read();
int x,y,z;
for(int i=1;i<=E;i++){
x = read(),y = read(),z = read();
add(x,y,z);
}
Dijkstra(1);
if(dis[V] == INF){
printf("-1\n");
}
else
printf("%d\n",dis[V]);
return 0;
}
























 465
465

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








