基数排序又是桶排序的改进,基数排序根据每个位数只包含10个数,开辟10个桶,通过对位数低到高地计数数组元素每个位数的数值(类似于计数排序),划分到对应桶中完成排序。
时间复杂度分析:
假设k为数据的最大位数,每一次扫描数组元素进行桶分配,时间复杂度为O(n)。从个位排到最大位数k,需要进行k次桶分配,则时间复杂度始终为O(n*k)。
空间复杂度:
和桶排序类似,需要申请k个桶,总共要分配n个数,空间复杂度为O(n+k)。
应用:
对于十进制整数来说,基数排序是非常高效的。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {31, 5, 6, 2, 10, 17, 41};
System.out.print("排序前:");
arrPrint(arr);
RadixSort(arr);
System.out.print("排序后:");
arrPrint(arr);
}
// 基数排序
//
private static void RadixSort(int[] arr) {
radixsort(arr, arr.length - 1, maxBit(arr));
}
// maxBit函数:计算数组的最大位数
// 具体方法为:先找到数组最大值max,之后反复除10,每次除不尽就在digit中累计+1,
// 直至除max到max=0,此时digit的值就为数组arr的最大位数。
// 本实例中max为41,最大位数digit=2。
private static int maxBit(int[] arr) {
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (max < arr[i])
max = arr[i];
}
int digit = 0;
while (max != 0) {
digit++;
max /= 10;
}
return digit;
}
// 基数排序函数
// 输入为待排序数组arr,数组arr的最大位数digit,在本示例中digit=2
//
// 第一层for循环,从位数1遍历到arr存在的最大位数digit,如当digit=2时,d遍历1和2.
//
// 第二层第一个for循环,计数数组count所有元素归零。
//
// 第二层第二个for循环,从左到右遍历数组arr,遍历元素为arr[i],使用getDigit函数
// 获取arr[i]元素第d位的数值,记为j(比如31的第1位数值为1,第2位的数值为3)。
// 那么j必然分布为0-9,正好是count的索引,则count[j]加1。类似于计数排序,使用count数组
// 记录数组arr中第d位数字出现的数值j的出现次数,比如d=1时,遍历到31,j=1,则count[1]位置加1。
//
// 第二层第三个for循环,类似于计数排序,遍历计数数组count,将count的前一个位置计数
// 结果累加到后一个位置计数结果中,此时count的元素,表示在arr中,小于等于对应第d位数值
// 为count当前索引的元素的数量,(如count[1]=3,表示arr中,小于等于第d位数值为1的元素
// 的数量为3)。
//
// 第二层第四个for循环,如同计数排序,倒序遍历arr的元素arr[i],getDigit函数获取arr[i]
// 的第d位数值j,以j为索引获取count中的计数值count[j],那么count[j] - 1表示arr中,
// 除了自己(arr[i])以外的,第d位数值小于等于j的元素的个数。
// 第d位数值小于等于j的元素的个数为count[j] - 1,那么arr[i]在排序后数组中就应该排名
// 第count[j] - 1位,所以直接bucket[count[j] - 1] = arr[i]即可。排序完count[j]位置累减
//
// 第二层第五个for循环,将桶中元素按顺序传arr。
private static void radixsort(int[] arr, int len, int digit) {
final int radix = 10;
int j = 0;
int[] count = new int[radix];
int[] bucket = new int[len + 1];
for (int d = 1; d <= digit; d++) {
for (int i = 0; i < radix; i++) {
count[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) {
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
count[j]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i < radix; i++) {
count[i] += count[i - 1];
}
for (int i = len; i >= 0; i--) {
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
bucket[count[j] - 1] = arr[i];
count[j]--;
}
j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++, j++) {
arr[i] = bucket[j];
}
}
}
// getDigit函数
// 返回数字x中第d位的数值.比如x=31, d=1时,返回1(31中第1位的数值为1)
private static int getDigit(int x, int d) {
return (x / ((int) Math.pow(10, d - 1))) % 10;
}
// 辅助函数:将int[] 打印出来
private static void arrPrint(int[] arr) {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
str.append("[");
for (int v : arr) {
str.append(v + ", ");
}
str.delete(str.length() - 2, str.length());
str.append("]");
System.out.println(str.toString());
}
}
本实例的动画演示如下:
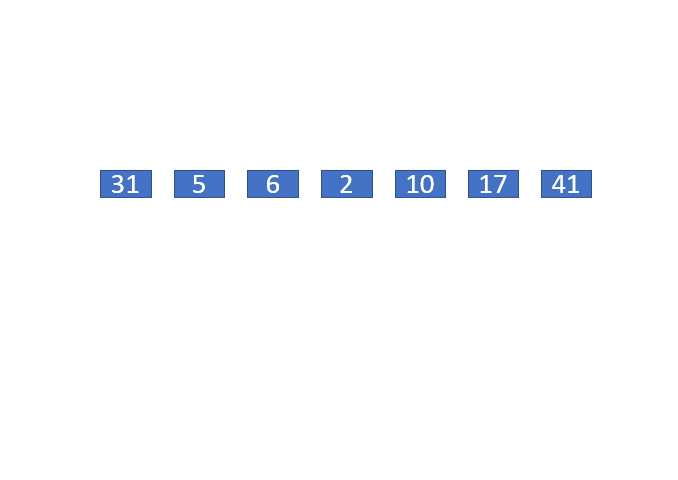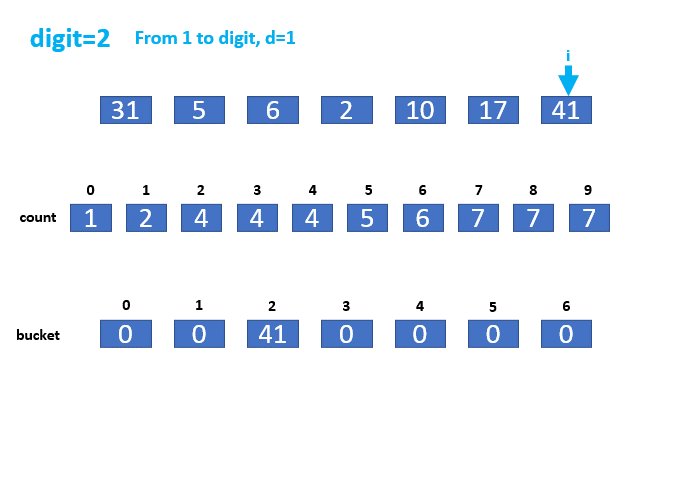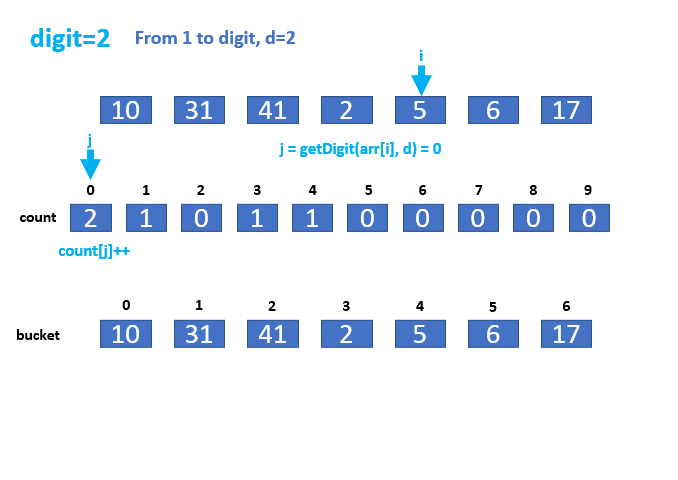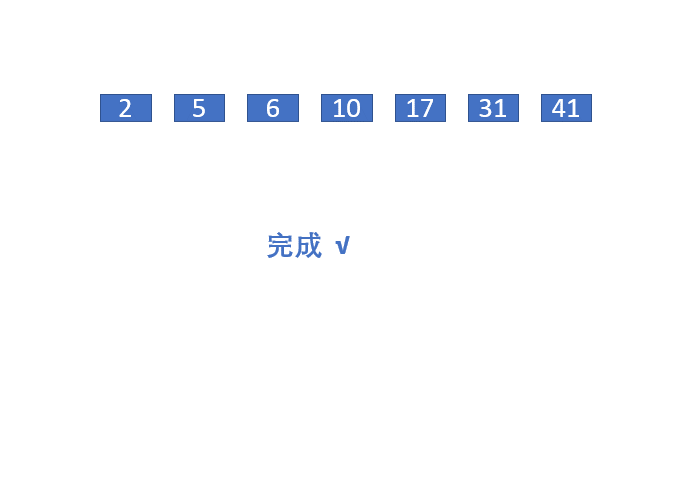


























 1356
1356











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










