已定义的限制标记
Bean Validation v2.0的限制标记
Validation v2.0规范中已经定义了22个常用的标记。| 标记 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Null | |
| @NotNull | |
| @AssertTrue | 用于boolean或者Boolean,如果为null,认为是合法的,下同。当然我们可以和@NotNull同时使用。 |
| @Min | 允许BigDecimal,BigInteger,byte,short,int,long,但不允许float和double。 |
| @Max | |
| @DecimalMin | 除了@Min允许的,还允许CharSequence(String) |
| @DecimalMax | |
| @Negative | |
| @NegativeOrZero | |
| @Positive | |
| @PositiveOrZero | |
| @Size | CharSequence(String)的长度, Collection,Map, Array的size或长度,有两个参数:
|
| @Digits | 处理数字,允许整形、CharSequence(String),float,Float,double,Double。 |
| @Past | 支持Date和Calendar,从2.0版本起,支持Java 8的Instant, LocalDate, LocalDateTime, LocalTime, MonthDay, OffsetDateTime, OffsetTime, Year, YearMonth, ZonedDateTime。 |
| @PastOrPresent | |
| @Future | |
| @FutureOrPresent | |
| @Pattern | 是否符合我们定义的正则表达样式。下面是email样式的例子,当然在v2.0中,我们可以简单地使用@Email。regexp是必选,flags是可选。 |
| @NotEmpty | 不允许为null和empty,针对CharSequence,Collection,Map,Array |
| @NotBlank | 不允许null,只要有一个非空格的字符。针对CharSequence |
可选参数
可选参数:message
可选参数message:如果是{xxxx}的格式,可用于本地化,如果找不到,就作为一般性描述。如果没有大括号,就是一般性的描述。缺省的,内置的限制标记都有相应的{xxxx}说明,例如{javax.validation.constraints.NotNull.message}
可选参数:groups
可选参数groups:缺省为空,表示为default group。在不同的场景下,对有效值的限制会不同,通过groups来解决这个问题。@NotNull //不填写,相当于Default.class
private String screen0;
@NotNull(groups={Default.class,InterfaceOne.class}) //javax.validation.groups.Default
private String screen1;
@NotNull(groups=InterfaceOne.class)
private String screen2;
// 表明在InterfaceTwo.class和InterfaceThree.class的场景下只允许在3位整数和2位小数范围内,
// 但在InterfaceOne的场景下只允许在2位整数和2位小数范围内。
// 缺省不检查。
@Digits(integer = 2,fraction=2,groups={InterfaceTwo.class,InterfaceThree.class}) //这里要采用interface的类
@Digits(integer = 3,fraction=2,groups=InterfaceOne.class)
public double getPrice(){
return price;
}Set<ConstraintViolation<User>> violations = validator.validate(user,InterfaceOne.class);
Set<ConstraintViolation<User>> violations = validator.validate(user,Default.class,InterfaceOne.class);可选参数:playload
可选参数playload:在自定义的验证中用于携带元数据信息。
@XXX.List
每个类似都可以带List,例如@Max.List,例子如下。一般而言,我们不采用这种书写方式。@Digits.List( {
@Digits(integer = 2,fraction=2,groups={InterfaceTwo.class,InterfaceThree.class}),
@Digits(integer = 3,fraction=2,groups=InterfaceOne.class)
} )
public double getPrice(){ ... }hibernate validation提供的私有限制标记
在hibernate validator javadoc中查看org.hibernate.validator.constraints,在Bean validation之外还提供一下私有的限制标记,如CreditCardNumber,Currency,URL等。但需要注意,一旦采用这些私有,也就相当于绑定使用hibernate validator。
递归检查: @Valid
我们在User类中进行了检验。public class Team{
@NotNull
@Valid
private User user;
......
}运行时自动进行检查
增强编译时对验证标记的检查
限制检验不能应用于静态的,但在编译的时候不会报错。同样不会对一些限制的类型,例如 @Future加在了String上,编译时也不会进行报错。可以通过加入compile-time annotation processor来解决,如下。但这会自动打包到war中,不是我们运行时需要使用。一般而言,正式版本释放时,不加入这个jar包。<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator-annotation-processor</artifactId>
<version>6.0.2.Final</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>在接口而非实现上进行限制标记
/* 需要告知Spring的MethodValidationPostProcessor对方法进行验证,有两种方式:
➤ @ValidateOnExecution 标准方式,颗粒度更细,可以对类/接口、方法标记,但不能用于方法中的参数。如果要加上Group,需要加上@javax.validation.GroupSequence。
➤ @Validated Spring的方式,只能对类/接口标记,可以用于方法中的参数。对于Group,可以直接作为参数,例如@Validated({Default.class, Group1.class})。允许在同一Controller类(非Controller的不行)中,对不同方法参数使用不同group(对于标准方式,由于@GroupSequence只能加在类上,所以不能支持)。 */
@Validated
public interface EmployeeService {
/*【例子1】对方法的参数进行限制标记 */
Employee getEmployee(@Min(value=1L, message= "{validate.employeeService.getEmployee.id}") long id);
/*【例子2】对复杂的参数进行递归限制,提供多个限制标记 */
void saveEmployee(
@NotNull(message = "{validate.employeeService.saveEmployee}")
@Valid Employee employee);
/*【例子3】对返回值进行限制 */
/* 一般而言,我们不会在返回值限制那里加上message,如果代码写得正确,应能避免违限,出现违限,表明是代码的问题。 */
/* 在返回值上限制,告知调用者不存在null的情况。 */
@NotNull
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees();
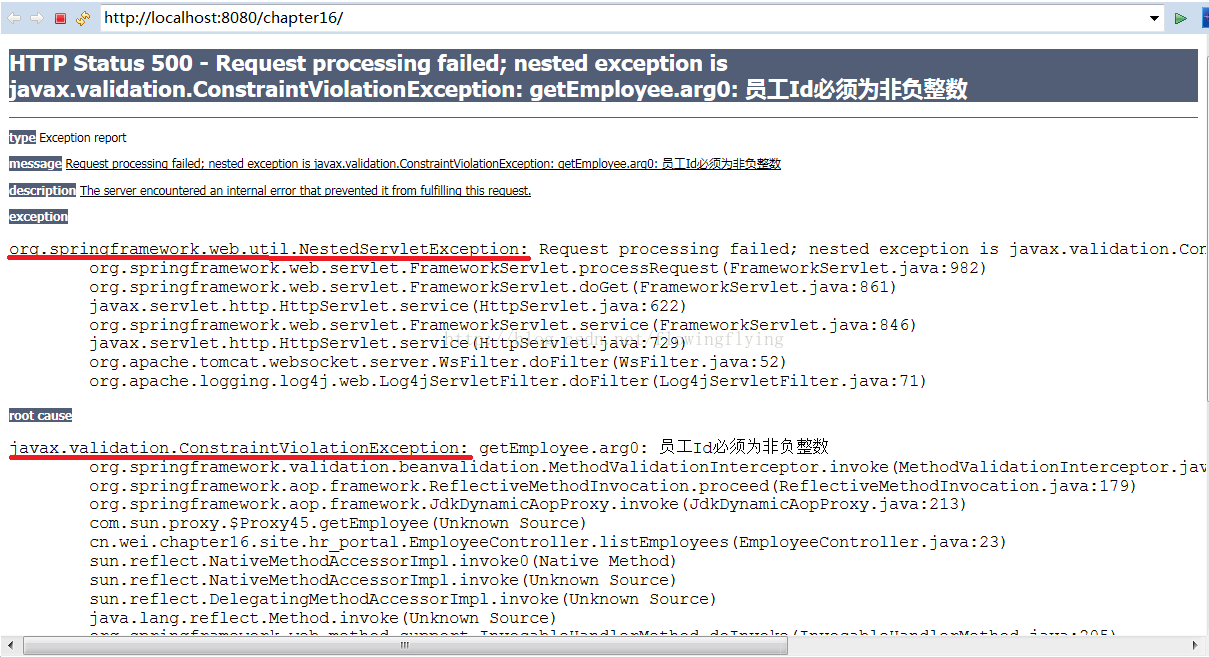
}如果在实现上,如果出现了方法的输入或者输出违反限制,将会抛出异常javax.validation.ConstraintViolationException,如果这个方法是在controller中调用,我们又没有对其进行捕获处理,则在返回一个500的错误页面,如下:
在控制器的方法使用参数限制
参见的是对输入的form中的参数进行限制。假定form的数据定义为EmployeeForm,里面的属性有若干限制。public class EmployeeForm {
@NotBlank(message = "{validate.employee.firstName}")
private String firstName;
@NotBlank(message = "{validate.employee.lastName}")
private String lastName;
private String middleName;
// ...... getters and setters ......
}@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Inject private EmployeeService employeeService;
//GET:显示输入框
@RequestMapping(value = "/create", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String createEmployee(Map<String, Object> model){
model.put("employeeForm", new EmployeeForm());
return "employee/create";
}
//POST:请求添加员工
//@Valid表示对EmployeeForm参数进行递归验证,然后再执行方法,验证限制的违反将放入Errors中。
@RequestMapping(value = "/create", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ModelAndView createEmployee(Map<String, Object> model, @Valid EmployeeForm form, Errors errors){
//【1】当输入参数不符合要求时,返回employee/create,同时将错误显示在页面上。相关的jsp为:
// <form:input path="firstName" />
// <form:errors path="firstName" cssClass="errors" />
if(errors.hasErrors()){
//model.put("employeeForm", form);//实际上model已经具有这些信息,无需重复传递
return new ModelAndView("employee/create");
}
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setFirstName(form.getFirstName());
employee.setLastName(form.getLastName());
employee.setMiddleName(form.getMiddleName());
//【2】调用了具有方法参数限制的方法。
// 将会抛出ConstraintViolationException异常,对异常进行处理
try{
this.employeeService.saveEmployee(employee);
}catch(ConstraintViolationException e){
model.put("validationErrors", e.getConstraintViolations());
return new ModelAndView("employee/create");
}
return new ModelAndView(new RedirectView("/", true, false));
}
}<%--@elvariable id="validationErrors" type="java.util.Set<javax.validation.ConstraintViolation>"--%>
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<html>
<head>
<title><spring:message code="title.create.employee" /></title>
<style type="text/css">
.errors {
color:#CC0000;
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2><spring:message code="title.create.employee" /></h2>
<c:if test="${validationErrors != null}"><div class="errors">
<ul>
<c:forEach items="${validationErrors}" var="error">
<li><c:out value="${error.message}" /></li>
</c:forEach>
</ul>
</div>
</c:if>
<form:form method="post" modelAttribute="employeeForm">
<form:label path="firstName">
<spring:message code="form.first.name" />
</form:label><br />
<form:input path="firstName" /><br />
<form:errors path="firstName" cssClass="errors" /><br />
<form:label path="middleName">
<spring:message code="form.middle.name" />
</form:label><br />
<form:input path="middleName" /><br />
<form:errors path="middleName" cssClass="errors" /><br />
<form:label path="lastName">
<spring:message code="form.last.name" />
</form:label><br/>
<form:input path="lastName" /><br />
<form:errors path="lastName" cssClass="errors" /><br />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form:form>
</body>
</html>相关链接: 我的Professional Java for Web Applications相关文章



























 2965
2965

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








