在网上看到一道面试题:LRU的cache设计,正好最近在学习memcached,于是很认真的研究了下这个问题
最笨的实现
一个数组,所有数据堆里边,每个数据维护一个时间(上一次被使用的时间),当查找某个数据的时候,遍历数组。当cache满的时候,需要遍历找到最久没变使用的记录,然后删除。这两个遍历充分暴露了这种实现的笨。
在网上搜了一下,看到大致有两种实现
1.直接利用linkedhashmap
2.使用hashmap+链表。
这两种思路是同一种思想,就是结合hashmap和链表进行存储
- hashmap可以实现快速查找
- 链表从表头到表尾是按从最近到最久访问的顺序维护的,这样当
需要失效最久未使用的时候直接把tail失效掉即可
linkedhashmap
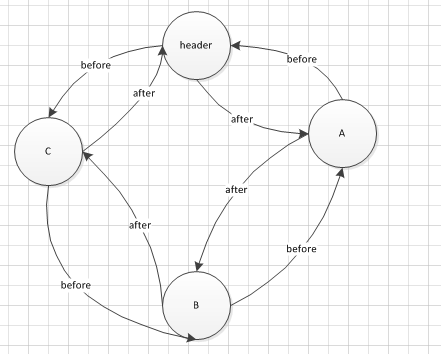
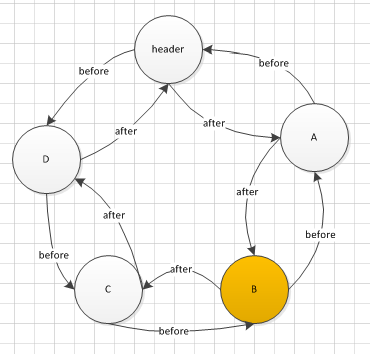
private transient Entry header;刚看到这边的时候想怎么只有header呢,按理说不应该维护header和tail么,后来经过研究,发现是一个环形的双向链表。so,header的before是链表头,header的fater是链表尾
put(D)后的数据结构
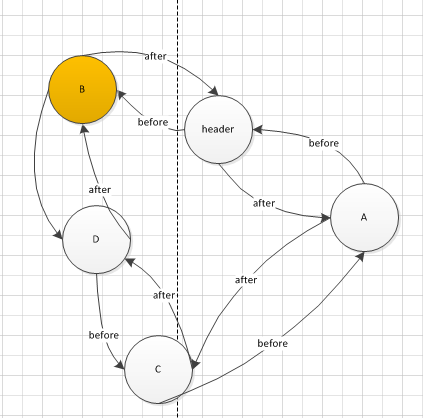
get(B)后,B在原位置删除,加到header的before的位置
private static class Entry extends HashMap.Entry
{
private void remove()
{
before.after = after;
after.before = before;
}
private void addBefore(Entry entry)
{
after = entry;
before = entry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}
//最关键的一个方法,实现按访问先后排序
void recordAccess(HashMap hashmap)
{
LinkedHashMap linkedhashmap = (LinkedHashMap)hashmap;
//accessOrder是否根据放入顺序排序的开关
if(linkedhashmap.accessOrder)
{
linkedhashmap.modCount++;
//先删除
remove();
//再加入header的before位置
addBefore(linkedhashmap.header);
}
}
Entry before;
Entry after;
}linkedhashmap 已经把最核心的基础准备好了
void addEntry(int i, Object obj, Object obj1, int j)
{
createEntry(i, obj, obj1, j);
Entry entry = header.after;
if(removeEldestEntry(entry))
removeEntryForKey(entry.key);
else
if(size >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
} protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry entry)
{
return false;
}removeEldestEntry方法默认是返回false,即不会删除链表尾的数据,这个地方需要重载一下这个方法
/**
* Created by liuzhao on 14-5-15.
*/
public class LRUCache2<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
private final int MAX_CACHE_SIZE;
public LRUCache2(int cacheSize) {
super((int) Math.ceil(cacheSize / 0.75) + 1, 0.75f, true);
MAX_CACHE_SIZE = cacheSize;
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return size() > MAX_CACHE_SIZE;
}
}hashmap+链表
package cache;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* Created by liuzhao on 14-5-12.
*/
public class LRUCache1<K, V> {
private final int MAX_CACHE_SIZE;
private Entry first;
private Entry last;
private HashMap<K, Entry<K, V>> hashMap;
public LRUCache1(int cacheSize) {
MAX_CACHE_SIZE = cacheSize;
hashMap = new HashMap<K, Entry<K, V>>();
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
Entry entry = getEntry(key);
if (entry == null) {
if (hashMap.size() >= MAX_CACHE_SIZE) {
hashMap.remove(last.key);
removeLast();
}
entry = new Entry();
entry.key = key;
}
entry.value = value;
moveToFirst(entry);
hashMap.put(key, entry);
}
public V get(K key) {
Entry<K, V> entry = getEntry(key);
if (entry == null) return null;
moveToFirst(entry);
return entry.value;
}
public void remove(K key) {
Entry entry = getEntry(key);
if (entry != null) {
if (entry.pre != null) entry.pre.next = entry.next;
if (entry.next != null) entry.next.pre = entry.pre;
if (entry == first) first = entry.next;
if (entry == last) last = entry.pre;
}
hashMap.remove(key);
}
private void moveToFirst(Entry entry) {
if (entry == first) return;
if (entry.pre != null)
{
entry.pre.next = entry.next;
}
if (entry.next != null) {
entry.next.pre = entry.pre;
}
if (entry == last) {
last = last.pre;
}
if (first == null || last == null) {
first = last = entry;
return;
}
entry.next = first;
first.pre = entry;
first = entry;
entry.pre = null;
}
private void removeLast() {
if (last != null) {
last = last.pre;
if (last == null) first = null;
else last.next = null;
}
}
private Entry<K, V> getEntry(K key) {
return hashMap.get(key);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Entry entry = first;
while (entry != null) {
sb.append(String.format("%s:%s ", entry.key, entry.value));
entry = entry.next;
}
return sb.toString();
}
class Entry<K, V> {
public Entry pre;
public Entry next;
public K key;
public V value;
}
static void lruCache1() {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("===========================LRU 链表实现===========================");
LRUCache1<Integer, String> lru = new LRUCache1(5);
lru.put(1, "11");
lru.put(2, "11");
lru.put(3, "11");
lru.put(4, "11");
lru.put(5, "11");
lru.put(5, "12");
System.out.println(lru.toString());
lru.put(6, "66");
lru.get(2);
lru.put(7, "77");
lru.get(4);
System.out.println(lru.toString());
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
lruCache1();
}
}memcached的实现
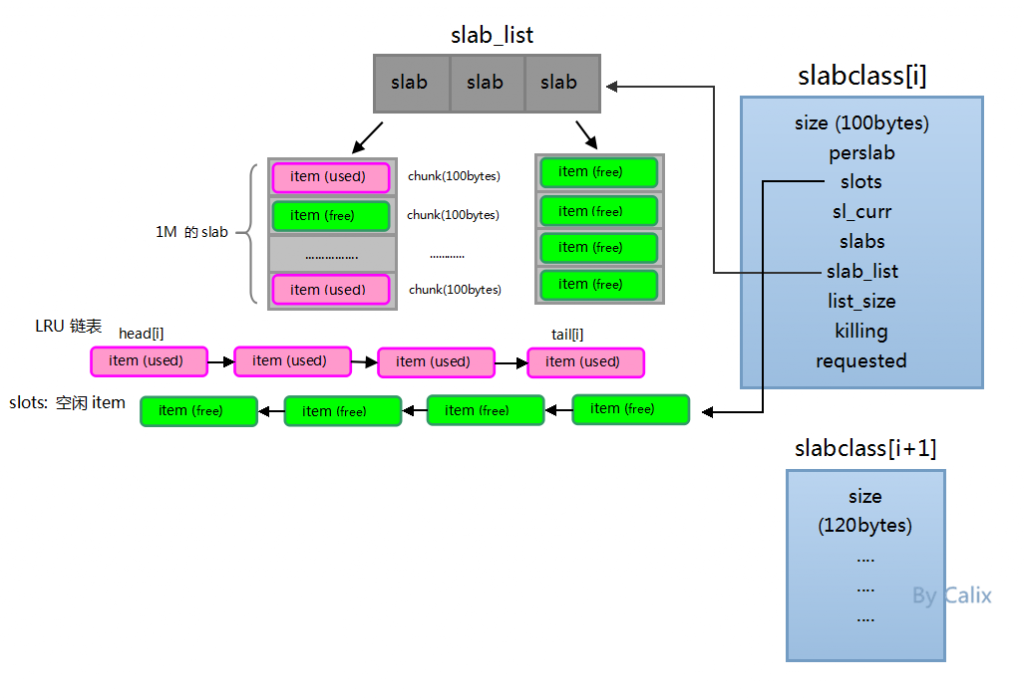
使用内存保存数据总会有满的情况,满就得淘汰,而memcached中的淘汰机制是LRU(最近最少使用算法 ),所以每个slabclass都保存着一个LRU队列,而head[i]和tail[i]则就是id为i的slabclass LRU队列的头部和尾部,尾部的item是最应该淘汰的项,也就是最近最少使用的项。























 7569
7569











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








