Java集合之JDK1.7HashMap原理解析
数据结构
- 数组 + 链表(单向链表)
- 元素插入方式:采用头插法
HashMap成员变量
在Java常用的集合中,首屈一指的Map,Map作为名词被翻译为"地图",当然旗下有很多的子类等等,此篇文章主要学习与了解HashMap,我们经过查看猿码,不难发现拥有如下成员变量:
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
{
// 默认初始化容量 16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
// 最大容量 2的30次方
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认加载因子 0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 创建一个空数组
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
// 数组初始化空数组
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
// 用以统计当前map中元素的个数
transient int size;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
* @serial
*/
// If table == EMPTY_TABLE then this is the initial capacity at which the
// table will be created when inflated.
int threshold;
// The load factor for the hash table 加载因子
final float loadFactor;
// 统计元素被修改的次数 且 不支持并发操作,在多线程的情况下会报ConcurrentModificationException
transient int modCount;
// 默认映射阈值
static final int ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD_DEFAULT = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// hash种子
transient int hashSeed = 0;
}
构造方法
无参构造
public HashMap() {
// 使用无参构造方法时,使用 默认初始化容量和默认加载因子
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
有参构造
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
// 指定初始化容量 + 默认加载因子
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
// 自定义初始化容量 + 自定义加载因子
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;//加载因子
threshold = initialCapacity; // 暂时初始化,后面会发现
init();
}
Put方法
/**
* Put方法:添加元素
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 当数组为空(空数组)时,则表示第一次添加元素
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
// 此处的threshold(即构造方法中的:threshold=initialCapacity)
inflateTable(threshold);
}
// 如果key为空,则添加一个key=null的value,单独处理
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 如果key不为空,则根据key获取hash值
int hash = hash(key);
// 根据hash值和数组长度,获取下标值i
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 取位置下标为i的数组元素
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
// 若hash = e.hash且 k = e.key 且 键值 key == k
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
// 创建变量值oldValue 保存当前node节点的值,作为oldValue
V oldValue = e.value;
// 将当前节点的值指向最新的值
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
// 返回oldValue值
return oldValue;
}
}
// +1
modCount++;
// 创建新节点node
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
inflateTable方法
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// 初始化容量为 2^n >= toSize
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
// 数组扩容时的阈值=(capacity * loadFactor)
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
// 初始化数组的大小
table = new Entry[capacity];
//
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}
addEntry方法
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 如果当前map的大小 大于或等于阈值threshold=(capacity * loadFactor) 且 当前下标bucketIndex不等于空时 进行扩容处理
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
// 数组大小扩容为原来的2倍
resize(2 * table.length);
// 标识扩容后 再次hash
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
// 扩容后 获取最新下标值
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
resize方法
void resize(int newCapacity) {
// 创建临时变量保存原数组大小 方便下边操作
Entry[] oldTable = table;
// 获取老数组的容量大小
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
// 创建新数组 大小为newCapacity
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
// 将原数组的值全部转移到新数组中
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
// 将当前table指向最新数组
table = newTable;
// 扩容阈值为: newCapacity * loadFactor
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
transfer方法
/**
*
* @param newTable
* @param rehash: 再次hash,由initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)决定
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
// 保存新数组的容量长度
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {// 当前节点e不为空
// 保存下一个节点 next
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
// 如果rehash为true,则需要进行再次hash
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
// 获取新数组的下标i
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
// 将e的next指向新数组i
e.next = newTable[i];
// 将下标为i的位置赋值为e
newTable[i] = e;
// 将节点e指向原来保存的next节点
e = next;
}
}
}
createEntry方法(采用头插法)
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 创建一个entry指向下标为bucketIndex的节点
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
// table[bucketIndex]完成赋值操作
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
// 大小+1
size++;
}
Get方法
public V get(Object key) {
// 如果key为null 则根据null值key获取最新的value
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
// key不为空 ,则获取entry节点
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
// 返回value(如果entry为空,则value为null,反之value = entry.getValue())
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
getEntry方法
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
// 因为size每添加一个元素之后会+1,因此若size为空,则元素为空,默认返回null
return null;
}
// 如果key为空时 hash=0,反之根据key获取hash值
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
// index i = indexFor(hash, table.length) 先获取下标值i
// 然后再从table中获取元素e,如果e不为空时,则需要遍历节点e以及next节点
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
// hash值相等且 key相等 或 (请求Key不为空且请求key值等于节点e的key)
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
// 返回节点e
return e;
}
// 没有找到对应的KEY值,默认返回null
return null;
}
modCount参数
代码执行逻辑
/**
* @author Mr.Gao
* @date 2023/1/3 11:00
* @apiNote: 开启两个线程来操作hashMap,一边put插入数据一边remove数据
* 对于单线程的hashmap是不会存在并发修改异常的
*/
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final Map<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>(10);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
hashMap.put("A", "1");
hashMap.put("A1", "11");
hashMap.put("A2", "12");
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
hashMap.put("B", "2");
hashMap.put("B1", "21");
hashMap.put("B2", "22");
}
}).start();
for (String key : hashMap.keySet()) {
if (key.equals("A")) {
hashMap.remove("A");
}
}
}
}
报异常ConcurrentModificationException

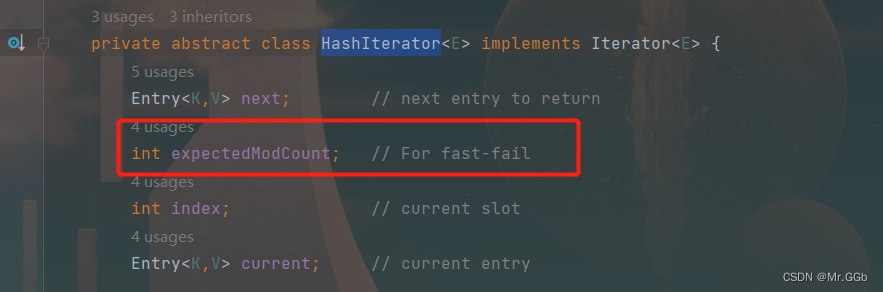
原因:因为hashMap中内嵌的迭代器Iterator,实际上调用的是迭代器重写的remove方法,从注释中可以发现为了快速失败,关键代码如下:
final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
// 如果modCount和期望的expectedModCount,则报出ConcurrentModificationException异常
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if ((next = e.next) == null) {
Entry[] t = table;
while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null)
;
}
current = e;
return e;
}
public void remove() {
if (current == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
Object k = current.key;
current = null;
HashMap.this.removeEntryForKey(k);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
问题小结
观察到此处可以发现java的1.7HashMap的一些问题:
- 1、不安全,Put方法和Get方法均为普通方法,任意一个线程均可操作map,
- 2、本身不支持多个线程操作执行一边foreach一边remove移除,否则会报并发修改异常ConcurrentModificationException。
- 3、经过阅读可以发现,元素插入时采用头插法,而采用头插法问题如下:
- 在put元素时,如果此时触发扩容,则在转移元素的时候顺序发生改变
- 在单线程情况下,put元素且触发扩容,是没有问题的
- 在多线程情况下,put元素且触发扩容,存在问题,由单向链表变更为环形链表(死循环)导致CPU飙升。






















 566
566











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








