第
1
章
Spring
中的
JdbcTemplate[
会用
]
1.1JdbcTemplate
概述
它是
spring
框架中提供的一个对象,是对原始
Jdbc API
对象的简单封装。
spring
框架为我们提供了很多的操作模板类。
操作关系型数据的:
JdbcTemplate
HibernateTemplate
操作
nosql
数据库的:
RedisTemplate
操作消息队列的:
JmsTemplate
我们今天的主角在
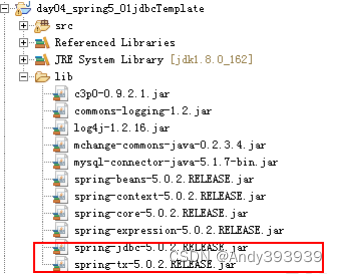
spring-jdbc-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar
中,我们在导包的时候,除了要导入这个
jar
包
外,还需要导入一个
spring-tx-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar
(它是和事务相关的)。
1.2JdbcTemplate
对象的创建
我们可以参考它的源码,来一探究竟:
public JdbcTemplate() {
}
public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
setDataSource(dataSource);
afterPropertiesSet();
}
public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource, boolean lazyInit) {
setDataSource(dataSource);
setLazyInit(lazyInit);
afterPropertiesSet();
}
除了默认构造函数之外,都需要提供一个数据源。既然有
set
方法,依据我们之前学过的依赖注入,我们可以在配置文件中配置这些对象。
1.3spring
中配置数据源
1.3.1
环境搭建
1.3.2 编写 spring 的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
1.3.3
配置数据源
我们之前已经接触过了两个数据源,
C3P0
和
DBCP
。要想使用这两数据源都需要导入对应的
jar
包。
1.3.3.1
配置
C3P0
数据源
导入
 到工程的
lib
目录。在
spring
的配置文件中配置:
到工程的
lib
目录。在
spring
的配置文件中配置:
 到工程的
lib
目录。在
spring
的配置文件中配置:
到工程的
lib
目录。在
spring
的配置文件中配置:
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring_day02"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="1234"></property>
</bean>
1.3.3.2
配置
DBCP
数据源
导入 到工程的
lib
目录。在
spring
的配置文件中配置:
到工程的
lib
目录。在
spring
的配置文件中配置:
 到工程的
lib
目录。在
spring
的配置文件中配置:
到工程的
lib
目录。在
spring
的配置文件中配置:
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:// /spring_day02"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="1234"></property>
</bean>
1.3.3.3
配置
spring
内置数据源
spring
框架也提供了一个内置数据源,我们也可以使用
spring
的内置数据源,它就在
spring-jdbc-5.0.2.REEASE.jar
包中:
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring_day02"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="1234"></property>
</bean>
1.3.4
将数据库连接的信息配置到属性文件中
:
【定义属性文件】
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///spring_day02
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123
【引入外部的属性文件】
一种方式
:
<!-- 引入外部属性文件: -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
</bean>
另一种方式
:
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
1.4JdbcTemplate
的增删改查操作
1.4.1
前期准备
创建数据库:
create database spring_day02;
use spring_day02;创建表:
create table account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40),
money float
)character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;
1.4.2
在
spring
配置文件中配置
JdbcTemplate
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置一个数据库的操作模板:JdbcTemplate -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring_day02"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="1234"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
1.4.3
最基本使用
public class JdbcTemplateDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取 Spring 容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据 id 获取 bean 对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//3.执行操作
jt.execute("insert into account(name,money)values('eee',500)");
}
}
1.4.4
保存操作
public class JdbcTemplateDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取 Spring 容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据 id 获取 bean 对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//3.执行操作
//保存
jt.update("insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)","fff",5000);
}
}
1.4.5
更新操作
public class JdbcTemplateDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取 Spring 容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据 id 获取 bean 对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//3.执行操作
//修改
jt.update("update account set money = money-? where id = ?",300,6);
}
}
1.4.6
删除操作
public class JdbcTemplateDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取 Spring 容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据 id 获取 bean 对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//3.执行操作
//删除
jt.update("delete from account where id = ?",6);
}
}
1.4.7
查询所有操作
public class JdbcTemplateDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取 Spring 容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据 id 获取 bean 对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//3.执行操作
//查询所有
List<Account> accounts = jt.query("select * from account where money > ? ",
new AccountRowMapper(), 500);
for(Account o : accounts){
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
public class AccountRowMapper implements RowMapper<Account>{
@Override
public Account mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Account account = new Account();
account.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
account.setName(rs.getString("name"));
account.setMoney(rs.getFloat("money"));
return account;
}
}
1.4.8
查询一个操作
使用 RowMapper 的方式:常用的方式
public class JdbcTemplateDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取 Spring 容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据 id 获取 bean 对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//3.执行操作
//查询一个
List<Account> as = jt.query("select * from account where id = ? ",
new AccountRowMapper(), 55);
System.out.println(as.isEmpty()?"没有结果":as.get(0));
}
}
使用
ResultSetExtractor
的方式
:
不常用的方式
public class JdbcTemplateDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取 Spring 容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据 id 获取 bean 对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//3.执行操作
//查询一个
Account account = jt.query("select * from account where id = ?",
new AccountResultSetExtractor(),3);
System.out.println(account);
}
}
1.4.9
查询返回一行一列操作
public class JdbcTemplateDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取 Spring 容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据 id 获取 bean 对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//3.执行操作
//查询返回一行一列:使用聚合函数,在不使用 group by 字句时,都是返回一行一列。最长用的
就是分页中获取总记录条数
Integer total = jt.queryForObject("select count(*) from account where money > ?
",Integer.class,500);
System.out.println(total);
}
}
1.5
在
dao
中使用
JdbcTemplate
1.5.1
准备实体类
/**
* 账户的实体
*/
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Float money;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", money=" + money + "]";
}
}
1.5.2
第一种方式:在
dao
中定义
JdbcTemplate
/**
* 账户的接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 根据 id 查询账户信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer id);
/**
* 根据名称查询账户信息
* @return
*/
Account findAccountByName(String name);
/**
* 更新账户信息
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
}/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
* 此版本的 dao,需要给 dao 注入 JdbcTemplate
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer id) {
List<Account> list = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id = ?
",new AccountRowMapper(),id);
return list.isEmpty()?null:list.get(0);
}
@Override
public Account findAccountByName(String name) {
List<Account> list = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where name
= ? ",new AccountRowMapper(),name);
if(list.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
if(list.size()>1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一,不是只有一个账户对象");
}
return list.get(0);
}
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set money = ? where id = ?
",account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
}
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置一个 dao -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 注入 jdbcTemplate -->
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置一个数据库的操作模板:JdbcTemplate -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName"
value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring_day04"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="1234"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
思考:
此种方式有什么问题吗
?
答案:
有个小问题。就是我们的
dao
有很多时,每个
dao
都有一些重复性的代码。下面就是重复代码:
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}能不能把它抽取出来呢?
请看下一小节。
1.5.3
第二种方式:让
dao
继承
JdbcDaoSupport
JdbcDaoSupport
是
spring
框架为我们提供的一个类,该类中定义了一个
JdbcTemplate
对象,我们可以直接获取使用,但是要想创建该对象,需要为其提供一个数据源:具体源码如下:
public abstract class JdbcDaoSupport extends DaoSupport {
//定义对象
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//set 方法注入数据源,判断是否注入了,注入了就创建 JdbcTemplate
public final void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
if (this.jdbcTemplate == null || dataSource != this.jdbcTemplate.getDataSource())
{ //如果提供了数据源就创建 JdbcTemplate
this.jdbcTemplate = createJdbcTemplate(dataSource);
initTemplateConfig();
}
}
//使用数据源创建 JdcbTemplate
protected JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
//当然,我们也可以通过注入 JdbcTemplate 对象
public final void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
initTemplateConfig();
}
//使用 getJdbcTmeplate 方法获取操作模板对象
public final JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate() {
return this.jdbcTemplate;
}/**
* 账户的接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 根据 id 查询账户信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer id);
/**
* 根据名称查询账户信息
* @return
*/
Account findAccountByName(String name);
/**
* 更新账户信息
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
}/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
* 此版本 dao,只需要给它的父类注入一个数据源
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl2 extends JdbcDaoSupport implements IAccountDao {
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer id) {
//getJdbcTemplate()方法是从父类上继承下来的。
List<Account> list = getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where
id = ? ",new AccountRowMapper(),id);
return list.isEmpty()?null:list.get(0);
}
@Override
public Account findAccountByName(String name) {
//getJdbcTemplate()方法是从父类上继承下来的。
List<Account> list = getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where
name = ? ",new AccountRowMapper(),name);
if(list.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
if(list.size()>1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一,不是只有一个账户对象");
}
return list.get(0);
}
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
//getJdbcTemplate()方法是从父类上继承下来的。
getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set money = ? where id = ?
",account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
}
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- 配置 dao2 -->
<bean id="accountDao2" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl2">
<!-- 注入 dataSource -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring_day04"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="1234"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
思考:
两版
Dao
有什么区别呢?
答案:
第一种在
Dao
类中定义
JdbcTemplate
的方式,适用于所有配置方式(
xml
和注解都可以)。
第二种让
Dao
继承
JdbcDaoSupport
的方式,只能用于基于
XML
的方式,注解用不了。
第
2
章
Spring
中的事务控制
2.1Spring
事务控制我们要明确的
第一:
JavaEE
体系进行分层开发,事务处理位于业务层,
Spring
提供了分层设计
业务层
的事务处理解决方案。
第二:
spring
框架为我们提供了一组事务控制的接口。具体在后面的第二小节介绍。这组接口是在
spring-tx-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar
中。
第三:
spring
的事务控制都是基于
AOP
的,它既可以使用编程的方式实现,也可以使用配置的方式实现。
我们学习的重点是使用配置的方式实现。
2.2Spring
中事务控制的
API
介绍
2.2.1 PlatformTransactionManager
此接口是
spring
的事务管理器,它里面提供了我们常用的操作事务的方法,如下图:

我们在开发中都是使用它的实现类,如下图:
真正管理事务的对象
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.
DataSourceTransactionManager
使用
Spring
JDBC
或
iBatis
进行持久化数据时使用
org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.
HibernateTransactionManager
使用
Hibernate
版本进行持久化数据时使用
2.2.2 TransactionDefinition
它是事务的定义信息对象,里面有如下方法:

2.2.2.1 事务的隔离级别

2.2.2.2 事务的传播行为
REQUIRED: 如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值)SUPPORTS: 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务)MANDATORY :使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常REQUERS_NEW: 新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。NOT_SUPPORTED: 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起NEVER: 以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常NESTED: 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行 REQUIRED 类似的操作。
2.2.2.3 超时时间
默认值是
-1
,没有超时限制。如果有,以秒为单位进行设置。
2.2.2.4
是否是只读事务
建议查询时设置为只读。
2.2.3 TransactionStatus
此接口提供的是事务具体的运行状态,方法介绍如下图:

2.3
基于
XML
的声明式事务控制(配置方式)重点
2.3.1
环境搭建
2.3.1.1
第一步:拷贝必要的
jar
包到工程的
lib
目录
2.3.1.2 第二步:创建 spring 的配置文件并导入约束
此处需要导入 aop 和 tx 两个名称空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
</beans>2.3.1.3 第三步:准备数据库表和实体类
创建数据库:
create database spring_day04;
use spring_day04;
创建表:
create table account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40),
money float
)character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;/**
* 账户的实体
*/
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Float money;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", money=" + money + "]";
}
}
2.3.1.4
第四步:编写业务层接口和实现类
/**
* 账户的业务层接口
*/
public interface IAccountService {
/**
* 根据 id 查询账户信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer id);//查
/**
* 转账
* @param sourceName 转出账户名称
* @param targeName 转入账户名称
* @param money 转账金额
*/
void transfer(String sourceName,String targeName,Float money);//增删改
}/**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer id) {
return accountDao.findAccountById(id);
}
@Override
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targeName, Float money) {
//1.根据名称查询两个账户
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targeName);
//2.修改两个账户的金额
source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money);//转出账户减钱
target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money);//转入账户加钱
//3.更新两个账户
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
int i=1/0;
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
}
}
2.3.1.5
第五步:编写
Dao
接口和实现类
/**
* 账户的持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 根据 id 查询账户信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer id);
/**
* 根据名称查询账户信息
* @return
*/
Account findAccountByName(String name);
/**
* 更新账户信息
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
}/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
* 此版本 dao,只需要给它的父类注入一个数据源
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl extends JdbcDaoSupport implements IAccountDao {
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer id) {
List<Account> list = getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where
id = ? ",new AccountRowMapper(),id);
return list.isEmpty()?null:list.get(0);
}
@Override
public Account findAccountByName(String name) {
List<Account> list = getJdbcTemplate().query("select * from account where
name = ? ",new AccountRowMapper(),name);
if(list.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
if(list.size()>1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一,不是只有一个账户对象");
}
return list.get(0);
}
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
getJdbcTemplate().update("update account set money = ? where id = ?
",account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}
}/**
* 账户的封装类 RowMapper 的实现类
*/
public class AccountRowMapper implements RowMapper<Account>{
@Override
public Account mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Account account = new Account();
account.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
account.setName(rs.getString("name"));
account.setMoney(rs.getFloat("money"));
return account;
}
}
2.3.1.6
第六步:在配置文件中配置业务层和持久层对
<!-- 配置 service -->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置 dao -->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!-- 注入 dataSource -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring_day04"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="1234"></property>
</bean>
2.3.2
配置步骤
2.3.2.1
第一步:配置事务管理器
<!-- 配置一个事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 注入 DataSource -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
2.3.2.2
第二步:配置事务的通知引用事务管理器
<!-- 事务的配置 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
</tx:advice>
2.3.2.3
第三步:配置事务的属性
<!--在 tx:advice 标签内部 配置事务的属性 -->
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 指定方法名称:是业务核心方法
read-only:是否是只读事务。默认 false,不只读。
isolation:指定事务的隔离级别。默认值是使用数据库的默认隔离级别。
propagation:指定事务的传播行为。
timeout:指定超时时间。默认值为:-1。永不超时。
rollback-for:用于指定一个异常,当执行产生该异常时,事务回滚。产生其他异常,事务不回滚。
没有默认值,任何异常都回滚。
no-rollback-for:用于指定一个异常,当产生该异常时,事务不回滚,产生其他异常时,事务回
滚。没有默认值,任何异常都回滚。
-->
<tx:method name="*" read-only="false" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true" propagation="SUPPORTS"/>
</tx:attributes>
2.3.2.4
第四步:配置
AOP
切入点表达式
<!-- 配置 aop -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点表达式 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.itheima.service.impl.*.*(..))"
id="pt1"/>
</aop:config>
2.3.2.5
第五步:配置切入点表达式和事务通知的对应关系
<!-- 在 aop:config 标签内部:建立事务的通知和切入点表达式的关系 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt1"/>
2.4
基于注解的配置方式
2.4.1
环境搭建
2.4.1.1
第一步:拷贝必备的
jar
包到工程的
lib
目录
2.4.1.2 第二步:创建 spring 的配置文件导入约束并配置扫描的包
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 配置 spring 创建容器时要扫描的包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 配置 JdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置 spring 提供的内置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName"
value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_day02"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="1234"></property>
</bean>
</beans>2.4.1.3 第三步:创建数据库表和实体类
和基于
xml
的配置相同。略
2.4.1.4
第四步:创建业务层接口和实现类并使用注解让
spring
管理
/**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*/
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao;
//其余代码和基于 XML 的配置相同
}
2.4.1.5
第五步:创建
Dao
接口和实现类并使用注解让
spring
管理
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//其余代码和基于 XML 的配置相同
}
2.4.2
配置步骤
2.4.2.1
第一步:配置事务管理器并注入数据源
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
2.4.2.2
第二步:在业务层使用
@Transactional
注解
@Service("accountService")
@Transactional(readOnly=true,propagation=Propagation.SUPPORTS)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer id) {
return accountDao.findAccountById(id);
}
@Override
@Transactional(readOnly=false,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targeName, Float money) {
//1.根据名称查询两个账户
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targeName);
//2.修改两个账户的金额
source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money);//转出账户减钱
target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money);//转入账户加钱
//3.更新两个账户
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
//int i=1/0;
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
}
}
该注解的属性和
xml
中的属性含义一致。该注解可以出现在接口上,类上和方法上。
出现接口上,表示该接口的所有实现类都有事务支持。
出现在类上,表示类中所有方法有事务支持
出现在方法上,表示方法有事务支持。
以上三个位置的优先级:方法
>
类
>
接口
2.4.2.3
第三步:在配置文件中开启
spring
对注解事务的支持
<!-- 开启 spring 对注解事务的支持 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
2.4.3
不使用
xml
的配置方式
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringTxConfiguration {
//里面配置数据源,配置 JdbcTemplate,配置事务管理器。在之前的步骤已经写过了。
}
第
3
章
Spring5
的新特性[了解]
3.1
与
JDK
相关的升级
3.1.1 jdk
版本要求:
spring5.0
在
2017
年
9
月发布了它的
GA
(通用)版本。该版本是基于
jdk8
编写的,所以
jdk8
以下版本将无法使用。同时,可以兼容 jdk9
版本。 tomcat 版本要求
8.5
及以上。
注:
我们使用
jdk8
构建工程,可以降版编译。但是不能使用
jdk8
以下版本构建工程。
由于
jdk
和
tomcat
版本的更新,我们的
IDE
也需要同时更新。
(
目前使用的
eclipse 4.7.2)
3.1.2
利用
jdk8
版本更新的内容
第一:基于
JDK8
的反射增强
请看下面的代码:
public class Test {
//循环次数定义:10 亿次
private static final int loopCnt = 1000 * 1000 * 1000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//输出 jdk 的版本
System.out.println("java.version=" + System.getProperty("java.version"));
t1();
t2();
t3();
}
// 每次重新生成对象
public static void t1() {
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < loopCnt; i++) {
Person p = new Person();
p.setAge(31);
}
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("循环 10 亿次创建对象的时间:" + (e - s));
}
// 同一个对象
public static void t2() {
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
Person p = new Person();
for (int i = 0; i < loopCnt; i++) {
p.setAge(32);
}
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("循环 10 亿次给同一对象赋值的时间: " + (e - s));
}
//使用反射创建对象
public static void t3() throws Exception {
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
Class<Person> c = Person.class;
Person p = c.newInstance();
Method m = c.getMethod("setAge", Integer.class);
for (int i = 0; i < loopCnt; i++) {
m.invoke(p, 33);
}
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("循环 10 亿次反射创建对象的时间:" + (e - s));
}
static class Person {
private int age = 20;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
}
jdk1.8
版本(就是
JDK8
)运行时间如下:

当切换到 jdk1.7 版本之后,运行时间如下:

有此我们可以看出,在反射创建对象上,
jdk8
确实做了加强。
第二:
@NonNull
注解和
@Nullable
注解的使用
用 @Nullable
和
@NotNull
注解来显示表明可为空的参数和以及返回值。这样就够在编译的时候处理空值而不是在运行时抛出 NullPointerExceptions
。
第三:日志记录方面
Spring Framework 5.0 带来了
Commons Logging
桥接模块的封装
,
它被叫做
spring-jcl
而
不是标准的
Commons Logging
。当然,无需任何额外的桥接,新版本也会对
Log4j 2.x, SLF4J, JUL ( java.util.logging) 进行自动检测。
3.2
核心容器的更新
Spring Framework 5.0 现在支持候选组件索引作为类路径扫描的替代方案。该功能已经在类路径扫描器中添加,以简化添加候选组件标识的步骤。应用程序构建任务可以定义当前项目自己的 META-INF/spring.components 文件。在编译时,源模型是自包含的,JPA 实体和 Spring 组件是已被标记的。从索引读取实体而不是扫描类路径对于小于 200 个类的小型项目是没有明显差异。但对大型项目影响较大。加载组件索引开销更低。因此,随着类数的增加,索引读取的启动时间将保持不变。加载组件索引的耗费是廉价的。因此当类的数量不断增长,加上构建索引的启动时间仍然可以维持一个常数 , 不过对于组件扫描而言,启动时间则会有明显的增长。这个对于我们处于大型 Spring 项目的开发者所意味着的,是应用程序的启动时间将被大大缩减。虽然 20 或者 30 秒钟看似没什么,但如果每天要这样登上好几百次,加起来就够你受的了。使用了组件索引的话,就能帮助你每天过的更加高效。你可以在 Spring 的 Jira 上了解更多关于组件索引的相关信息。
3.3JetBrains Kotlin
语言支持
Kolin
概述:是一种支持函数式编程编程风格的面向对象语言。
Kotlin
运行在
JVM
之上,但运行环境并不限于 JVM
。
Kolin
的示例代码:
{
("/movie" and accept(TEXT_HTML)).nest {
GET("/", movieHandler::findAllView)
GET("/{card}", movieHandler::findOneView)
}
("/api/movie" and accept(APPLICATION_JSON)).nest {
GET("/", movieApiHandler::findAll)
GET("/{id}", movieApiHandler::findOne)
}
}
Kolin 注册 bean 对象到 spring 容器:
val context = GenericApplicationContext {
registerBean()
registerBean { Cinema(it.getBean()) }
}
3.4
响应式编程风格
此次
Spring
发行版本的一个激动人心的特性就是新的响应式堆栈
WEB
框架。这个堆栈完全的响应式且非阻塞,适合于事件循环风格的处理,可以进行少量线程的扩展。
Reactive Streams
是来自于
Netflix, Pivotal, Typesafe, Red Hat, Oracle, Twitter
以及Spray.io 的工程师特地开发的一个
API
。它为响应式编程实现的实现提供一个公共的
API
,好实现Hibernate 的
JPA
。这里
JPA
就是这个
API,
而
Hibernate
就是实现。
Reactive Streams API
是
Java 9
的官方版本的一部分。在
Java 8
中
,
你会需要专门引入依赖来使
用
Reactive Streams API
。
Spring Framework 5.0
对于流式处理的支持依赖于
Project Reactor
来构建
,
其专门实现了 Reactive Streams API。
Spring Framework 5.0
拥有一个新的
spring-webflux
模块,支持响应式
HTTP
和
WebSocket
客
户端。
Spring Framework 5.0
还提供了对于运行于服务器之上,包含了
REST, HTML,
以及
WebSocket
风格交互的响应式网页应用程序的支持。
在
spring-webflux
中包含了两种独立的服务端编程模型:
基于注解:使用到了
@Controller
以及
Spring MVC
的其它一些注解;
使用
Java 8 lambda
表达式的函数式风格的路由和处理。
有 了
Spring Webflux,
你现在可以创建出
WebClient,
它是响应式且非阻塞的,可以作为
RestTemplate
的一个替代方案。
这里有一个使用
Spring 5.0
的
REST
端点的
WebClient
实现:
WebClient webClient = WebClient.create();
Mono person = webClient.get()
.uri("http://localhost:8080/movie/42")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.exchange()
.then(response -> response.bodyToMono(Movie.class));
3.5Junit5
支持
完全支持
JUnit 5 Jupiter
,所以可以使用
JUnit 5
来编写测试以及扩展。此外还提供了一个编程以及扩展模型,Jupiter
子项目提供了一个测试引擎来在
Spring
上运行基于
Jupiter
的测试。
另外,
Spring Framework 5
还提供了在
Spring TestContext Framework
中进行并行测试的扩展。
针对响应式编程模型,
spring-test
现在还引入了支持
Spring WebFlux
的
WebTestClient
集成测
试的支持,类似于
MockMvc
,并不需要一个运行着的服务端。使用一个模拟的请求或者响应,
WebTestClient就可以直接绑定到 WebFlux
服务端设施。
你可以在这里找到这个激动人心的
TestContext
框架所带来的增强功能的完整列表。
当然,
Spring Framework 5.0
仍然支持我们的老朋友
JUnit!
在我写这篇文章的时候,
JUnit 5
还
只是发展到了
GA
版本。对于
JUnit4
,
Spring Framework
在未来还是要支持一段时间的。
3.6
依赖类库的更新
终止支持的类库
Portlet.Velocity.JasperReports.XMLBeans.JDO.Guava.支持的类库Jackson 2.6+EhCache 2.10+ / 3.0 GAHibernate 5.0+JDBC 4.0+XmlUnit 2.x+OkHttp 3.x+Netty 4.1+























 354
354











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










