Create & Access SQLite database using Python
Estimated time needed: 15 minutes
Objectives
After completing this lab you will be able to:
- Create a database
- Create a table
- Insert data into the table
- Query data from the table
- Retrieve the result set into a pandas dataframe
- Close the database connection
SQLite is a software library that implements a self-contained, serverless, zero-configuration, transactional SQL database engine. SQLite is the most widely deployed SQL database engine in the world.
Task 1: Create database using SQLite
In [1]:
#Install & load sqlite3 #!pip install sqlite3 ##Uncomment this code only if you are working in a local environment to install sqlite3 import sqlite3
In [2]:
# Connecting to sqlite
# connection object
conn = sqlite3.connect('INSTRUCTOR.db')
Cursor class is an instance using which you can invoke methods that execute SQLite statements, fetch data from the result sets of the queries. You can create Cursor object using the cursor() method of the Connection object/class.
In [3]:
# cursor object cursor_obj = conn.cursor()
Task 2: Create a table in the database
In this step we will create a table in the database with following details:
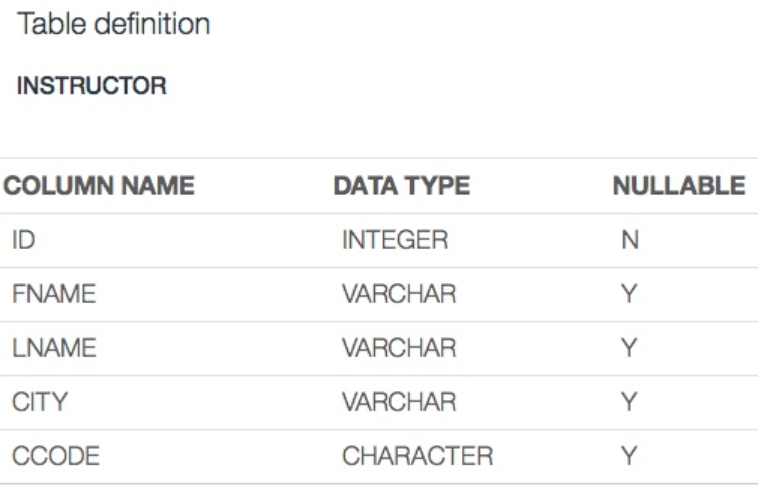
Before creating a table, let's first check if the table already exists or not. To drop the table from a database, use the DROP query. A cursor is an object that helps execute the query and fetch the records from the database.
In [4]:
# Drop the table if already exists.
cursor_obj.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS INSTRUCTOR")
Out[4]:
<sqlite3.Cursor at 0x7f6923339c70>
Dont worry if you get this error:
If you see an exception/error similar to the following, indicating that INSTRUCTOR is an undefined name, that's okay. It just implies that the INSTRUCTOR table does not exist in the table - which would be the case if you had not created it previously.
Exception: [IBM][CLI Driver][DB2/LINUXX8664] SQL0204N "ABC12345.INSTRUCTOR" is an undefined name. SQLSTATE=42704 SQLCODE=-204
In [5]:
# Creating table
table = """ create table IF NOT EXISTS INSTRUCTOR(ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, FNAME VARCHAR(20), LNAME VARCHAR(20), CITY VARCHAR(20), CCODE CHAR(2));"""
cursor_obj.execute(table)
print("Table is Ready")
Table is Ready
Task 3: Insert data into the table
In this step we will insert some rows of data into the table.
The INSTRUCTOR table we created in the previous step contains 3 rows of data:

We will start by inserting just the first row of data, i.e. for instructor Rav Ahuja
In [6]:
cursor_obj.execute('''insert into INSTRUCTOR values (1, 'Rav', 'Ahuja', 'TORONTO', 'CA')''')
Out[6]:
<sqlite3.Cursor at 0x7f6923339c70>
The output you will get something as: sqlite3.Cursor at 0x27a1a491260 which means mySql database has sqlite3.Cursor object at 0x27a1a49126 as output in table. But you may get the different number.
Now use a single query to insert the remaining two rows of data
In [7]:
cursor_obj.execute('''insert into INSTRUCTOR values (2, 'Raul', 'Chong', 'Markham', 'CA'), (3, 'Hima', 'Vasudevan', 'Chicago', 'US')''')
Out[7]:
<sqlite3.Cursor at 0x7f6923339c70>
Task 4: Query data in the table
In this step we will retrieve data we inserted into the INSTRUCTOR table.
In [8]:
statement = '''SELECT * FROM INSTRUCTOR'''
cursor_obj.execute(statement)
print("All the data")
output_all = cursor_obj.fetchall()
for row_all in output_all:
print(row_all)
All the data (1, 'Rav', 'Ahuja', 'TORONTO', 'CA') (2, 'Raul', 'Chong', 'Markham', 'CA') (3, 'Hima', 'Vasudevan', 'Chicago', 'US')
In [9]:
## Fetch few rows from the table
statement = '''SELECT * FROM INSTRUCTOR'''
cursor_obj.execute(statement)
print("All the data")
# If you want to fetch few rows from the table we use fetchmany(numberofrows) and mention the number how many rows you want to fetch
output_many = cursor_obj.fetchmany(2)
for row_many in output_many:
print(row_many)
All the data (1, 'Rav', 'Ahuja', 'TORONTO', 'CA') (2, 'Raul', 'Chong', 'Markham', 'CA')
In [10]:
# Fetch only FNAME from the table
statement = '''SELECT FNAME FROM INSTRUCTOR'''
cursor_obj.execute(statement)
print("All the data")
output_column = cursor_obj.fetchall()
for fetch in output_column:
print(fetch)
All the data
('Rav',)
('Raul',)
('Hima',)
Bonus: now write and execute an update statement that changes the Rav's CITY to MOOSETOWN
In [11]:
query_update='''update INSTRUCTOR set CITY='MOOSETOWN' where FNAME="Rav"''' cursor_obj.execute(query_update)
Out[11]:
<sqlite3.Cursor at 0x7f6923339c70>
In [12]:
statement = '''SELECT * FROM INSTRUCTOR'''
cursor_obj.execute(statement)
print("All the data")
output1 = cursor_obj.fetchmany(2)
for row in output1:
print(row)
All the data (1, 'Rav', 'Ahuja', 'MOOSETOWN', 'CA') (2, 'Raul', 'Chong', 'Markham', 'CA')
Task 5: Retrieve data into Pandas
In this step we will retrieve the contents of the INSTRUCTOR table into a Pandas dataframe
In [13]:
import pandas as pd
#retrieve the query results into a pandas dataframe
df = pd.read_sql_query("select * from instructor;", conn)
#print the dataframe
df
Out[13]:
| ID | FNAME | LNAME | CITY | CCODE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Rav | Ahuja | MOOSETOWN | CA |
| 1 | 2 | Raul | Chong | Markham | CA |
| 2 | 3 | Hima | Vasudevan | Chicago | US |
In [14]:
#print just the LNAME for first row in the pandas data frame df.LNAME[0]
Out[14]:
'Ahuja'
Once the data is in a Pandas dataframe, you can do the typical pandas operations on it.
For example you can use the shape method to see how many rows and columns are in the dataframe
In [15]:
df.shape
Out[15]:
(3, 5)
Task 6: Close the Connection
We free all resources by closing the connection. Remember that it is always important to close connections so that we can avoid unused connections taking up resources.
In [16]:
# Close the connection conn.close()
Summary
In this tutorial you created a database & table in Python notebook using SQLite3. Then created a table and insert a few rows of data into it. Then queried the data. You also retrieved the data into a pandas dataframe.






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








