1.getevent命令使用
一般都是通过help来查询命令的使用方法,getevent命令也不例外
130|generic_x86:/ $ getevent -h
Usage: getevent [-t] [-n] [-s switchmask] [-S] [-v [mask]] [-d] [-p] [-i] [-l] [-q] [-c count] [-r] [device]
-t: show time stamps
-n: don't print newlines
-s: print switch states for given bits
-S: print all switch states
-v: verbosity mask (errs=1, dev=2, name=4, info=8, vers=16, pos. events=32, props=64)
-d: show HID descriptor, if available
-p: show possible events (errs, dev, name, pos. events)
-i: show all device info and possible events
-l: label event types and names in plain text
-q: quiet (clear verbosity mask)
-c: print given number of events then exit
-r: print rate events are received
其中最常用的参数就是:
-t: show time stamps—显示时间打印的时间
-l: label event types and names in plain text—这里表示把event事件类型名字打印出来
-r: print rate events are received—显示一下时间接受的速率
具体使用示例
127|generic_x86:/ $ gete -lrt
[ 171811.520824] /dev/input/event1: EV_ABS ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 00000000
[ 171811.520824] /dev/input/event1: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 00002fff
[ 171811.520824] /dev/input/event1: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00006a76
[ 171811.520824] /dev/input/event1: EV_ABS ABS_MT_PRESSURE 00000400
[ 171811.520824] /dev/input/event1: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000
[ 171811.560128] /dev/input/event1: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00006a43
[ 171811.560128] /dev/input/event1: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000 rate 25
[ 171811.563992] /dev/input/event1: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 0000305a
[ 171811.563992] /dev/input/event1: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00006a10
[ 171811.563992] /dev/input/event1: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000 rate 258
[ 171811.567507] /dev/input/event1: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 000069dd
[ 171811.567507] /dev/input/event1: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000 rate 284
示例解释打印对应的格式
[ 171811.520824] /dev/input/event1: EV_ABS ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 00000000
[事件打印时间] 具体节点文件名:事件类型 事件code 事件value
命令位置:
一般的命令都是在/system/bin下面,那么我们来/system/bin下找一个getevent
1|generic_x86:/system/bin $ ls -l | grep getevent
lrwxr-xr-x 1 root shell 7 2009-01-01 00:00 getevent -> toolbox
可以看到getevent命令是软连接的到toolbox的。
2.getevent源码分析
源码路径
system/core/toolbox/getevent.c
system/core/toolbox/toolbox.c
system/core/toolbox/tool.h
getevent命令链接到toolbox,那么入口函数就是toolbox的main函数了,就从toolbox的main函数开始讲起
以下是toolbox的源码分析,入口是main函数:
#define TOOL(name) int name##_main(int, char**);//这里会拼接名字
#include "tools.h"//这里内容其实就是TOOL(getevent) TOOL(getprop) TOOL(toolbox)
#undef TOOL
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
char* cmd = strrchr(argv[0], '/');
char* name = cmd ? (cmd + 1) : argv[0];//获取name就是getevent
for (size_t i = 0; tools[i].name; i++) {
if (!strcmp(tools[i].name, name)) {
return tools[i].func(argc, argv);//这里会调用到getevent_main
}
}
printf("%s: no such tool\n", argv[0]);
return 127;
}
这部分是getevent的源码,入口函数getevent_main函数
static struct pollfd *ufds;
static char **device_names;
static int nfds;
static void print_event(int type, int code, int value, int print_flags)
{
const char *type_label, *code_label, *value_label;
if (print_flags & PRINT_LABELS) {
type_label = get_label(ev_labels, type);
code_label = NULL;
value_label = NULL;
switch(type) {
case EV_SYN:
code_label = get_label(syn_labels, code);
break;
case EV_KEY:
code_label = get_label(key_labels, code);
value_label = get_label(key_value_labels, value);
break;
case EV_REL:
code_label = get_label(rel_labels, code);
break;
case EV_ABS:
code_label = get_label(abs_labels, code);
switch(code) {
case ABS_MT_TOOL_TYPE:
value_label = get_label(mt_tool_labels, value);
}
break;
case EV_MSC:
code_label = get_label(msc_labels, code);
break;
case EV_LED:
code_label = get_label(led_labels, code);
break;
case EV_SND:
code_label = get_label(snd_labels, code);
break;
case EV_SW:
code_label = get_label(sw_labels, code);
break;
case EV_REP:
code_label = get_label(rep_labels, code);
break;
case EV_FF:
code_label = get_label(ff_labels, code);
break;
case EV_FF_STATUS:
code_label = get_label(ff_status_labels, code);
break;
}
if (type_label)
printf("%-12.12s", type_label);
else
printf("%04x ", type);
if (code_label)
printf(" %-20.20s", code_label);
else
printf(" %04x ", code);
if (value_label)
printf(" %-20.20s", value_label);
else
printf(" %08x ", value);
} else {
printf("%04x %04x %08x", type, code, value);
}
}
static void print_hid_descriptor(int bus, int vendor, int product)
{
const char *dirname = "/sys/kernel/debug/hid";
char prefix[16];
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *de;
char filename[PATH_MAX];
FILE *file;
char line[2048];
snprintf(prefix, sizeof(prefix), "%04X:%04X:%04X.", bus, vendor, product);
dir = opendir(dirname);
if(dir == NULL)
return;
while((de = readdir(dir))) {
if (strstr(de->d_name, prefix) == de->d_name) {
snprintf(filename, sizeof(filename), "%s/%s/rdesc", dirname, de->d_name);
file = fopen(filename, "r");
if (file) {
printf(" HID descriptor: %s\n\n", de->d_name);
while (fgets(line, sizeof(line), file)) {
fputs(" ", stdout);
fputs(line, stdout);
}
fclose(file);
puts("");
}
}
}
closedir(dir);
}
static int open_device(const char *device, int print_flags)
{
int version;
int fd;
int clkid = CLOCK_MONOTONIC;
struct pollfd *new_ufds;
char **new_device_names;
char name[80];
char location[80];
char idstr[80];
struct input_id id;
//打开devive对应的设备文件
fd = open(device, O_RDONLY | O_CLOEXEC);
if(fd < 0) {
if(print_flags & PRINT_DEVICE_ERRORS)
fprintf(stderr, "could not open %s, %s\n", device, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//做一些ioctl的操作
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGVERSION, &version)) {
if(print_flags & PRINT_DEVICE_ERRORS)
fprintf(stderr, "could not get driver version for %s, %s\n", device, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGID, &id)) {
if(print_flags & PRINT_DEVICE_ERRORS)
fprintf(stderr, "could not get driver id for %s, %s\n", device, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
name[sizeof(name) - 1] = '\0';
location[sizeof(location) - 1] = '\0';
idstr[sizeof(idstr) - 1] = '\0';
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGNAME(sizeof(name) - 1), &name) < 1) {
//fprintf(stderr, "could not get device name for %s, %s\n", device, strerror(errno));
name[0] = '\0';
}
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGPHYS(sizeof(location) - 1), &location) < 1) {
//fprintf(stderr, "could not get location for %s, %s\n", device, strerror(errno));
location[0] = '\0';
}
if(ioctl(fd, EVIOCGUNIQ(sizeof(idstr) - 1), &idstr) < 1) {
//fprintf(stderr, "could not get idstring for %s, %s\n", device, strerror(errno));
idstr[0] = '\0';
}
if (ioctl(fd, EVIOCSCLOCKID, &clkid) != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Can't enable monotonic clock reporting: %s\n", strerror(errno));
// a non-fatal error
}
new_ufds = realloc(ufds, sizeof(ufds[0]) * (nfds + 1));
if(new_ufds == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "out of memory\n");
return -1;
}
ufds = new_ufds;
new_device_names = realloc(device_names, sizeof(device_names[0]) * (nfds + 1));
if(new_device_names == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "out of memory\n");
return -1;
}
device_names = new_device_names;
if(print_flags & PRINT_DEVICE)
printf("add device %d: %s\n", nfds, device);
if(print_flags & PRINT_DEVICE_INFO)
printf(" bus: %04x\n"
" vendor %04x\n"
" product %04x\n"
" version %04x\n",
id.bustype, id.vendor, id.product, id.version);
if(print_flags & PRINT_DEVICE_NAME)
printf(" name: \"%s\"\n", name);
if(print_flags & PRINT_DEVICE_INFO)
printf(" location: \"%s\"\n"
" id: \"%s\"\n", location, idstr);
if(print_flags & PRINT_VERSION)
printf(" version: %d.%d.%d\n",
version >> 16, (version >> 8) & 0xff, version & 0xff);
if(print_flags & PRINT_POSSIBLE_EVENTS) {
print_possible_events(fd, print_flags);
}
if(print_flags & PRINT_INPUT_PROPS) {
print_input_props(fd);
}
if(print_flags & PRINT_HID_DESCRIPTOR) {
print_hid_descriptor(id.bustype, id.vendor, id.product);
}
//将open的fd赋值给pollfd
ufds[nfds].fd = fd;
//有事件的时候才触发
ufds[nfds].events = POLLIN;
device_names[nfds] = strdup(device);
nfds++;
return 0;
}
int close_device(const char *device, int print_flags)
{
int i;
for(i = 1; i < nfds; i++) {
if(strcmp(device_names[i], device) == 0) {
int count = nfds - i - 1;
if(print_flags & PRINT_DEVICE)
printf("remove device %d: %s\n", i, device);
free(device_names[i]);
memmove(device_names + i, device_names + i + 1, sizeof(device_names[0]) * count);
memmove(ufds + i, ufds + i + 1, sizeof(ufds[0]) * count);
nfds--;
return 0;
}
}
if(print_flags & PRINT_DEVICE_ERRORS)
fprintf(stderr, "remote device: %s not found\n", device);
return -1;
}
//读取/dev/input路径下面的节点内容变化
static int read_notify(const char *dirname, int nfd, int print_flags)
{
int res;
char devname[PATH_MAX];
char *filename;
char event_buf[512];
int event_size;
int event_pos = 0;
struct inotify_event *event;
res = read(nfd, event_buf, sizeof(event_buf));
if(res < (int)sizeof(*event)) {
if(errno == EINTR)
return 0;
fprintf(stderr, "could not get event, %s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
//printf("got %d bytes of event information\n", res);
strcpy(devname, dirname);
filename = devname + strlen(devname);
*filename++ = '/';
while(res >= (int)sizeof(*event)) {
event = (struct inotify_event *)(event_buf + event_pos);
//printf("%d: %08x \"%s\"\n", event->wd, event->mask, event->len ? event->name : "");
if(event->len) {
strcpy(filename, event->name);
if(event->mask & IN_CREATE) {
open_device(devname, print_flags);
}
else {
close_device(devname, print_flags);
}
}
event_size = sizeof(*event) + event->len;
res -= event_size;
event_pos += event_size;
}
return 0;
}
//读取扫描路径下的节点
static int scan_dir(const char *dirname, int print_flags)
{
char devname[PATH_MAX];
char *filename;
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *de;
dir = opendir(dirname);
if(dir == NULL)
return -1;
strcpy(devname, dirname);
filename = devname + strlen(devname);
*filename++ = '/';
while((de = readdir(dir))) {
if(de->d_name[0] == '.' &&
(de->d_name[1] == '\0' ||
(de->d_name[1] == '.' && de->d_name[2] == '\0')))
continue;
strcpy(filename, de->d_name);
//devname获取到事件名称,如:/dev/input/event3
open_device(devname, print_flags);
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
//help的打印信息
static void usage(char *name)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s [-t] [-n] [-s switchmask] [-S] [-v [mask]] [-d] [-p] [-i] [-l] [-q] [-c count] [-r] [device]\n", name);
fprintf(stderr, " -t: show time stamps\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -n: don't print newlines\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -s: print switch states for given bits\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -S: print all switch states\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -v: verbosity mask (errs=1, dev=2, name=4, info=8, vers=16, pos. events=32, props=64)\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -d: show HID descriptor, if available\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -p: show possible events (errs, dev, name, pos. events)\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -i: show all device info and possible events\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -l: label event types and names in plain text\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -q: quiet (clear verbosity mask)\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -c: print given number of events then exit\n");
fprintf(stderr, " -r: print rate events are received\n");
}
//toolbox的转换过来的getevent命令的入口函数
int getevent_main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int c;
int i;
int res;
int get_time = 0;
int print_device = 0;
char *newline = "\n";
uint16_t get_switch = 0;
struct input_event event;
int print_flags = 0;
int print_flags_set = 0;
int dont_block = -1;
int event_count = 0;
int sync_rate = 0;
int64_t last_sync_time = 0;
const char *device = NULL;
const char *device_path = "/dev/input";
/* disable buffering on stdout */
setbuf(stdout, NULL);
opterr = 0;
//这个do{}while(1)循环其实就是用来解析参数的
do {
//读取getevent的参数
c = getopt(argc, argv, "tns:Sv::dpilqc:rh");
if (c == EOF)
break;
switch (c) {
case 't'://打印时间
get_time = 1;
break;
case 'n':
newline = "";
break;
case 's':
get_switch = strtoul(optarg, NULL, 0);
if(dont_block == -1)
dont_block = 1;
break;
case 'S':
get_switch = ~0;
if(dont_block == -1)
dont_block = 1;
break;
case 'v':
if(optarg)
print_flags |= strtoul(optarg, NULL, 0);
else
print_flags |= PRINT_DEVICE | PRINT_DEVICE_NAME | PRINT_DEVICE_INFO | PRINT_VERSION;
print_flags_set = 1;
break;
case 'd':
print_flags |= PRINT_HID_DESCRIPTOR;
break;
case 'p':
print_flags |= PRINT_DEVICE_ERRORS | PRINT_DEVICE
| PRINT_DEVICE_NAME | PRINT_POSSIBLE_EVENTS | PRINT_INPUT_PROPS;
print_flags_set = 1;
if(dont_block == -1)
dont_block = 1;
break;
case 'i':
print_flags |= PRINT_ALL_INFO;
print_flags_set = 1;
if(dont_block == -1)
dont_block = 1;
break;
case 'l'://打印事件类型
print_flags |= PRINT_LABELS;
break;
case 'q':
print_flags_set = 1;
break;
case 'c':
event_count = atoi(optarg);
dont_block = 0;
break;
case 'r'://打印事件的接收速率
sync_rate = 1;
break;
case '?':
fprintf(stderr, "%s: invalid option -%c\n",
argv[0], optopt);
case 'h'://打印help的信息
usage(argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
} while (1);
if(dont_block == -1)
dont_block = 0;
if (optind + 1 == argc) {
device = argv[optind];
optind++;
}
if (optind != argc) {
usage(argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
//用来记录监听的事件个数,可以直观的理解为pollfd的数组大小
nfds = 1;
//pollfd数组
ufds = calloc(1, sizeof(ufds[0]));
//使用intoify监听"/dev/input"路径下的节点变化,如usb,keyboard的热插拔事件
//这里只是初始化一个fd,还并未开始真正的监听
ufds[0].fd = inotify_init();
//监听POLLIN事件
ufds[0].events = POLLIN;
//监听具体的某个事件,如getevent /dev/input/event3会进入
if(device) {
if(!print_flags_set)
print_flags |= PRINT_DEVICE_ERRORS;
res = open_device(device, print_flags);
if(res < 0) {
return 1;
}
} else {
if(!print_flags_set)
print_flags |= PRINT_DEVICE_ERRORS | PRINT_DEVICE | PRINT_DEVICE_NAME;
print_device = 1;
//将fd和device_path映射上,该目录下有create或者delete的操作时就会触发POLLIN事件
res = inotify_add_watch(ufds[0].fd, device_path, IN_DELETE | IN_CREATE);
if(res < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "could not add watch for %s, %s\n", device_path, strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
//扫描"/dev/input"路径下的所有事件节点,放入pollfd中
res = scan_dir(device_path, print_flags);
if(res < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "scan dir failed for %s\n", device_path);
return 1;
}
}
if(get_switch) {
for(i = 1; i < nfds; i++) {
uint16_t sw;
res = ioctl(ufds[i].fd, EVIOCGSW(1), &sw);
if(res < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "could not get switch state, %s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
sw &= get_switch;
printf("%04x%s", sw, newline);
}
}
if(dont_block)
return 0;
while(1) {
//int pollres =
//开启监听工作,监听的fd有事件来到的时候唤醒继续往下执行,没有事件的时候阻塞
poll(ufds, nfds, -1);
//printf("poll %d, returned %d\n", nfds, pollres);
if(ufds[0].revents & POLLIN) {
//监听到/dev/input下发生事件
read_notify(device_path, ufds[0].fd, print_flags);
}
//按键,触摸的事件
for(i = 1; i < nfds; i++) {
if(ufds[i].revents) {
if(ufds[i].revents & POLLIN) {
res = read(ufds[i].fd, &event, sizeof(event));
if(res < (int)sizeof(event)) {
fprintf(stderr, "could not get event\n");
return 1;
}
//打印event事件
if(get_time) {
printf("[%8ld.%06ld] ", event.time.tv_sec, event.time.tv_usec);
}
//打印event事件名
if(print_device)
printf("%s: ", device_names[i]);
//打印event的type,code,value
print_event(event.type, event.code, event.value, print_flags);
if(sync_rate && event.type == 0 && event.code == 0) {
int64_t now = event.time.tv_sec * 1000000LL + event.time.tv_usec;
if(last_sync_time)
printf(" rate %lld", 1000000LL / (now - last_sync_time));
last_sync_time = now;
}
printf("%s", newline);
if(event_count && --event_count == 0)
return 0;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
3.getevent命令设计思想
其实getevent命令最核心的就是使用poll机制来监听fd事件
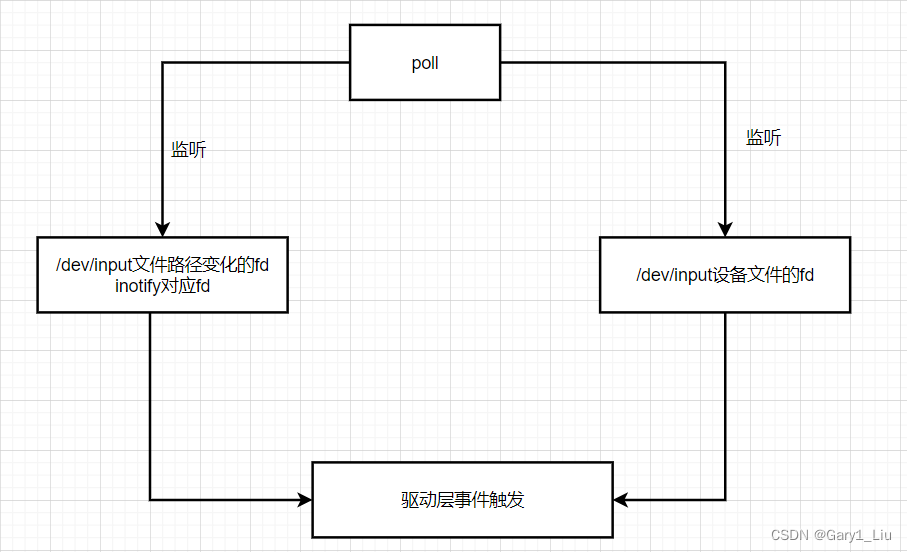
至此,getevent命令相关的使用,源码和设计思想分析完毕。s’s’ssss





















 3434
3434











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








