😹 作者: gh-xiaohe
😻 gh-xiaohe的博客
😽 觉得博主文章写的不错的话,希望大家三连(✌关注,✌点赞,✌评论),多多支持一下!!
💒 流程控制

🚏 分支结构
🚀 if
- 根据判定的结果(真或假)决定执行某个分支的代码
🚬 if分支的三种结构
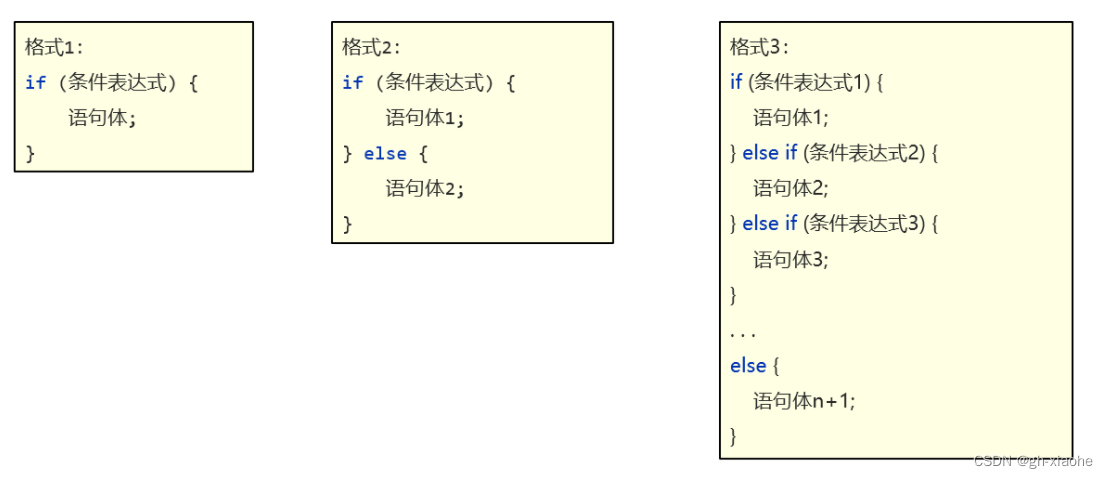
🚭 if第一种格式
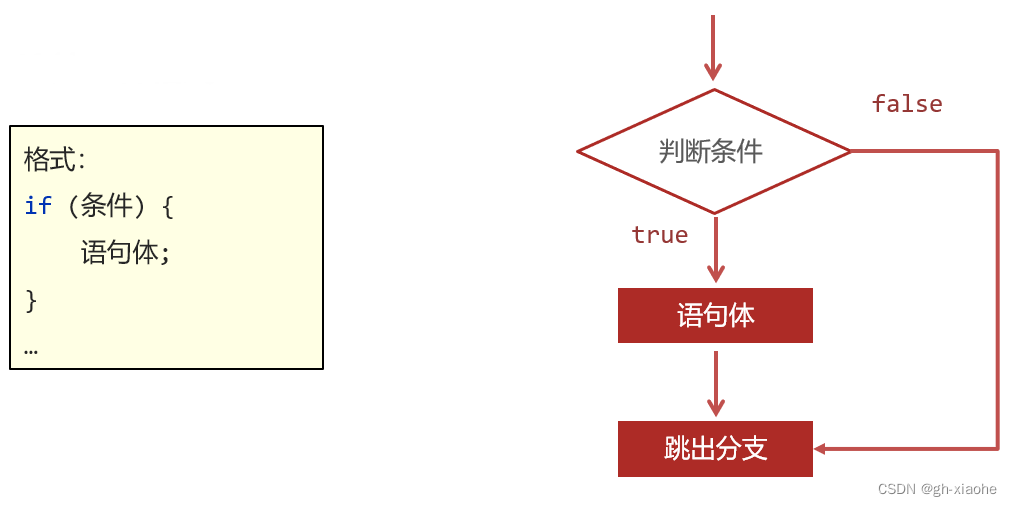
执行流程:
①首先判断条件表达式的结果,如果为true执行语句体,为 false 就不执行语句体。
注意事项:
- if 语句中,如果大括号控制的只有一行代码,则大括号可以省略不写。
🚭 if第二种格式
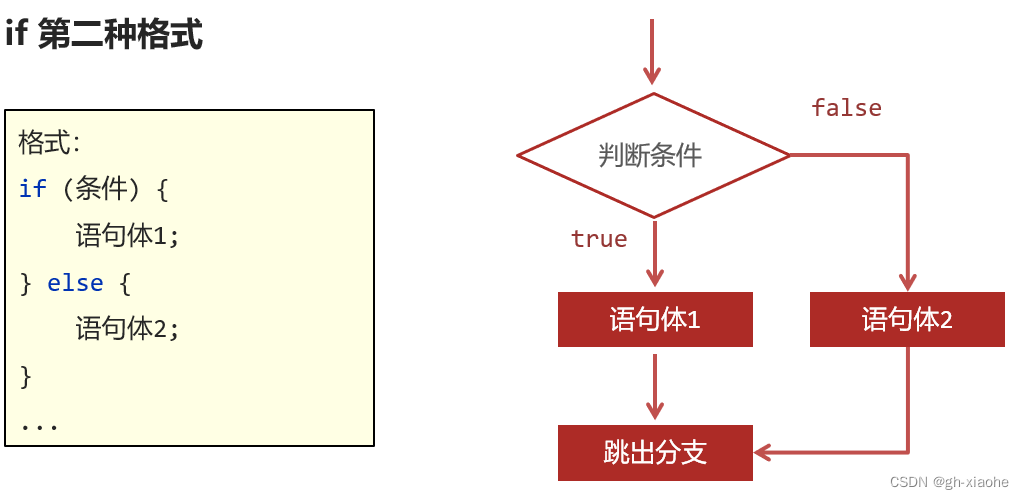
执行流程:
①首先判断条件表达式的结果,如果为true执行语句体1,为 false 就执行语句体2。
🚭 if第三种格式
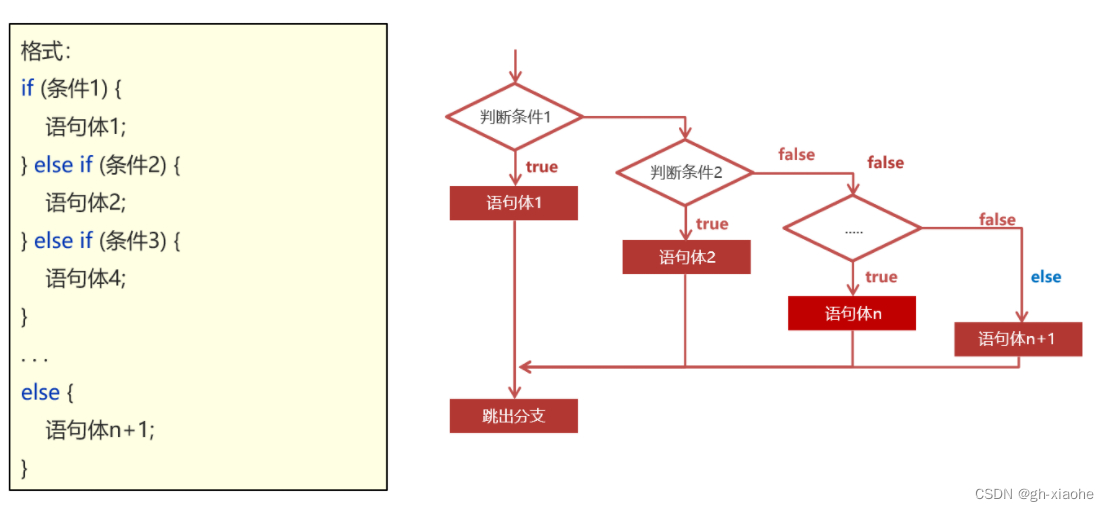
执行流程:

/**
目标:学会使用if分支结构解决问题,理解其流程。
*/
public class IfDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:心跳(60 - 100)之间是正常的,否则系统提示进一步检查
// 格式1: if(条件表达式){ 代码... }
int heartBeat = 30;
if(heartBeat < 60 || heartBeat > 100) { // || 表示或 一个条件为真,则执行后面的代码 如果左面的条件为假,则不执行后面的代码
System.out.println("您的心跳数据是:" + heartBeat +",您可能需要进一步检查!");
}
System.out.println("检查结束");
// 格式2: if(条件表达式){ 代码... } else { 代码... }
// 需求:发红包。
double money = 1;
// 发送一个1314.
if(money >= 1314){
System.out.println("您当前发送红包成功~~~");
}else {
System.out.println("您自己都没钱,就别发了~~");
}
// 格式3: if(条件表达式){ 代码...}else if(条件表达式){ 代码... } ... else{ 代码...}
// 绩效系统: 0-60 C 60-80 B 80-90 A 90-100 A+
int score = 199;
if(score >= 0 && score < 60){
System.out.println("您本月的绩效是:C");
}else if(score >= 60 && score < 80){
System.out.println("您本月的绩效是:B");
}else if(score >= 80 && score < 90){
System.out.println("您本月的绩效是:A");
}else if(score >= 90 && score <= 100){
System.out.println("您本月的绩效是:A+");
}else {
System.out.println("您录入的分数有毛病!");
}
}
}
🚬 考试奖励
需求:键盘录入考试成绩,根据成绩所在的区间,程序打印出不同的奖励机制
分析:
① 键盘录入考试成绩
② 由于奖励种类较多,属于多种判断,采用if...else...if格式实现
③ 为每种判断设置对应的条件
④ 为每种判断设置对应的奖励
public class IfTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
需求:键盘录入考试成绩,根据成绩所在的区间,程序打印出不同的奖励机制
分析:
① 键盘录入考试成绩
② 由于奖励种类较多,属于多种判断,采用if...else...if格式实现
③ 为每种判断设置对应的条件
④ 为每种判断设置对应的奖励
*/
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入考试成绩:");
int score = sc.nextInt();
if (score >= 95 && score <= 100) {
System.out.println("山地自行车一辆");
}else if (score >= 90 && score <= 94) {
System.out.println("游乐场玩一次");
}else if (score >= 80 && score <= 89) {
System.out.println("变形金刚玩具一个");
}else if (score >= 0 && score <= 79) {
System.out.println("胖揍一顿");
}else {
System.out.println("输入有误,请重新输入");
}
}
}
}
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-2aVHE2CB-1653185930843)(%E6%B5%81%E7%A8%8B%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.assets/image-20220522101342370.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/08d8e5fa6463406fbf2e4a226119f91a.png)
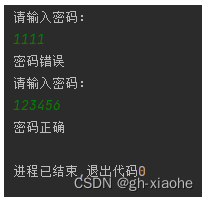
🚬 密码校验
需求: 键盘录入用户密码, 如果密码为 111111, 程序输出密码正确,否则输出密码有误
分析:
① 使用Scanner录入用户输入的密码,并使用变量接受
② 使用 if...else 组织程序逻辑
public class IfTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
需求: 键盘录入用户密码, 如果密码为 111111, 程序输出密码正确,否则输出密码有误
分析:
① 使用Scanner录入用户输入的密码,并使用变量接受
② 使用 if...else 组织程序逻辑
*/
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (;;) {
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.next(); // 录入密码
if (password.equals("123456")) {
System.out.println("密码正确");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("密码错误");
}
}
}
}
🚄 switch
- 也是匹配条件去执行分支, 适合做值匹配的分支选择,结构清晰,格式良好。

public class SwitchDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:学会使用switch分支结构,理解流程
// 周一:埋头苦干,解决bug 周五:今晚吃鸡
// 周二:请求大牛程序员帮忙 周六:与王婆介绍的小芳相亲
// 周三:今晚啤酒、龙虾、小烧烤 周日:郁郁寡欢、准备上班。
// 周四: 主动帮助新来的女程序解决bug
String weekday = "周二";
switch (weekday){
case "周一":
System.out.println("埋头苦干,解决bug ");
break;
case "周二":
System.out.println("请求大牛程序员帮忙");
break;
case "周三":
System.out.println("今晚啤酒、龙虾、小烧烤");
break;
case "周四":
System.out.println("主动帮助新来的女程序解决bug");
break;
case "周五":
System.out.println("今晚吃鸡");
break;
case "周六":
System.out.println("与王婆介绍的小芳相亲");
break;
case "周日":
System.out.println("郁郁寡欢、准备上班");
break;
default:
System.out.println("数据有误!");
}
}
}
🚬 总结
-
switch分支的格式、执行流程是怎么样的?

-
if、switch分支各自适合做什么业务场景?
- if其实在功能上远远强大于switch。
- if适合做区间匹配。
- switch适合做:值匹配的分支选择、代码优雅。性能高,直接定位
🚬 switch的注意事项
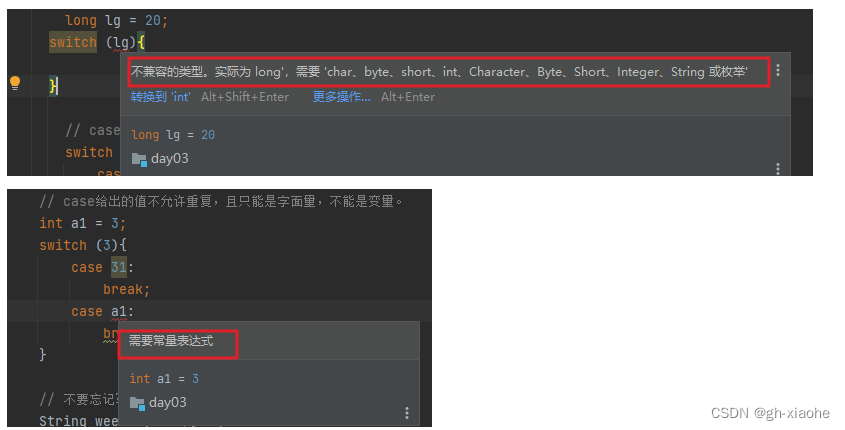
①表达式类型只能是byte、short、int、char,JDK5开始支持枚举,JDK7开始支持String、不支持double、float、long。(面试题)
原因:double、float数值在底层的运算不精确,long的范围太大。
②case给出的值不允许重复,且只能是字面量,不能是变量。
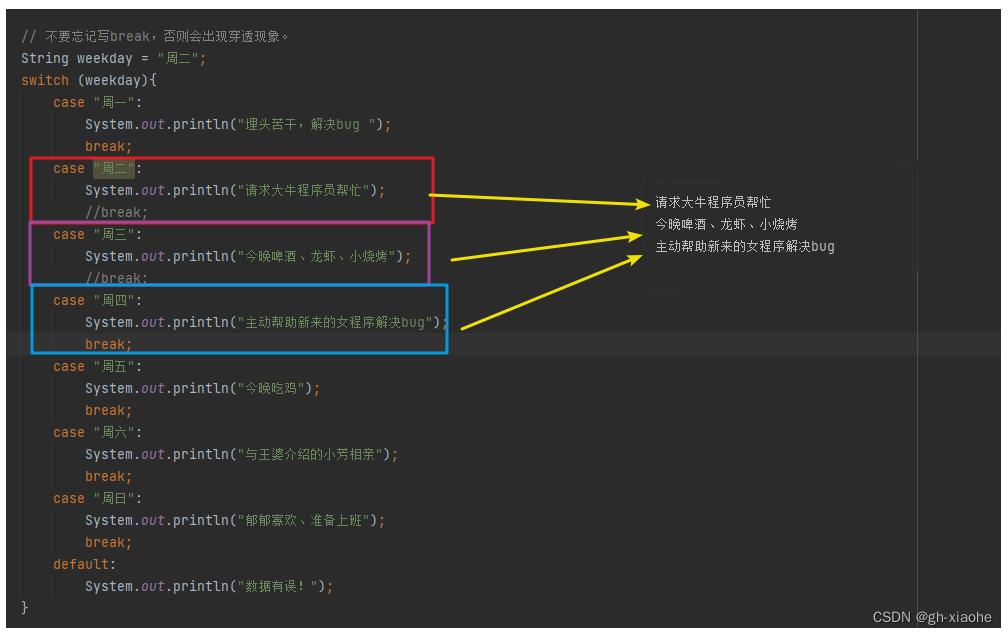
③不要忘记写break,否则会出现穿透现象。
public class SwitchDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:清楚switch的注意点。并在开发的时候注意。
// 表达式类型只能是byte、short、int、char,JDK5开始支持枚举,JDK7开始支持String、不支持double、float、long。
double a = 0.1 + 0.2;
System.out.println(a);// 0.30000000000000004 不等于0.3 不等于0.30000000000000004 非精确地运算
long lg = 20;
// switch (lg){
//
// }
// case给出的值不允许重复,且只能是字面量,不能是变量。
switch (3){
case 31:
break;
case 3:
break;
}
// 不要忘记写break,否则会出现穿透现象。
String weekday = "周二";
switch (weekday){
case "周一":
System.out.println("埋头苦干,解决bug ");
break;
case "周二":
System.out.println("请求大牛程序员帮忙");
//break;
case "周三":
System.out.println("今晚啤酒、龙虾、小烧烤");
//break;
case "周四":
System.out.println("主动帮助新来的女程序解决bug");
break;
case "周五":
System.out.println("今晚吃鸡");
break;
case "周六":
System.out.println("与王婆介绍的小芳相亲");
break;
case "周日":
System.out.println("郁郁寡欢、准备上班");
break;
default:
System.out.println("数据有误!");
}
}
}
🚬 switch的穿透性的应用场景
- 如果代码执行到没有写break的case块,执行完后将直接进入下一个case块执行代码(而且不会进行任何匹配),直到遇到break才跳出分支,这就是switch的穿透性。

public class SwicthDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:用户输入月份可以展示该月份的天数。
// 1、3 、5、 7 、 8、 10、 12月份是 31天
// 2月份是闰年为29天、非闰年为28天。
// 4 、6 、9、 11月份 是30天
int month = 7;
switch (month){
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
System.out.println(month +"是31天!");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(month +"月闰年为29天、非闰年为28天!");
break;
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
System.out.println(month +"是30天!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("数据有误!");
}
}
}
🚬 总结
- 什么情况下会出现switch穿透现象?
- case中没有写break。
- switch穿透性能解决什么问题?
- 存在多个case分支的功能代码是一样时,可以用穿透性把流程集中到同一处处理,这样可以简化代码。
🚏 循环结构
循环条件
①初始化条件
②循环条件
③循环体
④迭代条件
🚀 for循环
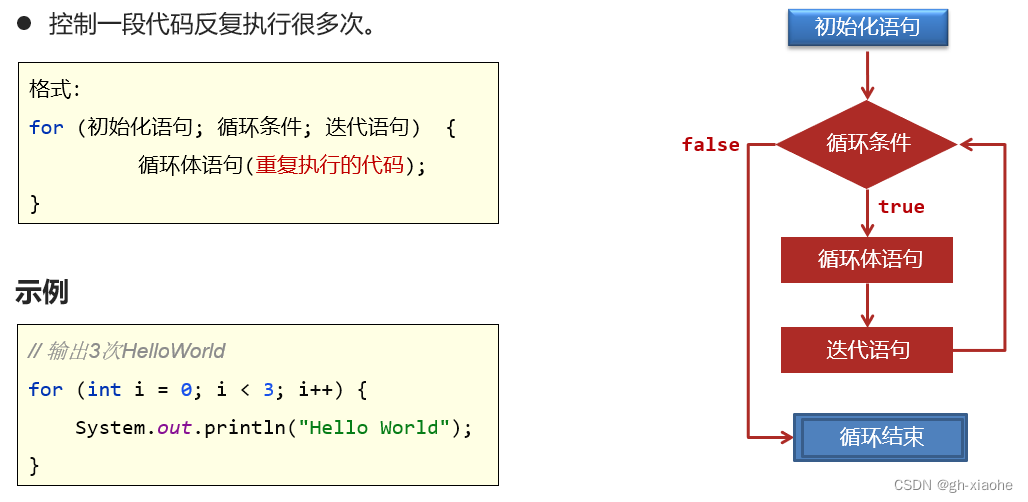
执行流程:

public class ForDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:学会使用for循环,并理解它的执行流程。
// 需求:输出3次HelloWorld
System.out.println("---------循环三次------------");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
System.out.println("--------从1 开始 < 5 循环 4 次-------------");
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
System.out.println("--------从1 开始 <= 5 循环 5次-------------");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
System.out.println("--------循环三次 i=1 i=3 i=5-------------");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i+=2) {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
}
}
🚬 总结:
- for循环格式和执行流程是什么样的?

🚄 for循环案例
🚬 案例一:求和
求1-5之间的数据和,并把求和结果在控制台输出
public class ForTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:计算1-5的和
// 2、定义一个整数变量用于累加数据求和
int sum = 0;
// 1、定义一个for循环找到 1 2 3 4 5
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
// i = 1 2 3 4 5
// 3、把循环的数据累加给sum变量
/**
等价于: sum = sum + i
i == 1 sum = 0 + 1
i == 2 sum = 1 + 2
i == 3 sum = 3 + 3
i == 4 sum = 6 + 4
i == 5 sum = 10 + 5
*/
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("1 到 5的和是:" + sum);
}
}
🚬 案例二:求奇数和
求1-10之间的奇数和,并把求和结果在控制台输出。
🚭 方式一
public class ForTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:求1-0的奇数和
// 3、定义一个求和的变量 累加奇数和
int sum = 0;
// 1、定义一个循环找到 1 2 3...10
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
// i 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
// 2、筛选出奇数
if(i % 2 == 1){
// i = 1 3 5 7 9
sum += i;
}
}
// 4、输出求和变量即可
System.out.println("1-10的奇数和是:" + sum);
}
}
🚭 方式二
public class ForTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 2、定义一个求和的变量 累加奇数和
int sum1 = 0;
// 1、定义循环找到 1 3 5 7 9
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i+=2) {
// i = 1 3 5 7 9
sum1 += i;
}
// 3、输出求和变量即可
System.out.println("1-10的奇数和是:" + sum1);
}
}
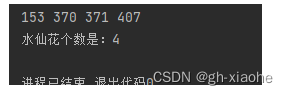
🚬 案例三:水仙花数
需求:在控制台输出所有的“水仙花数”,水仙花数必须满足如下2个要求:
1、水仙花数是一个三位数
2、水仙花数的个位、十位、百位的数字立方和等于原数
public class ForTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 100; i < 999; i++) {
int ge = i % 10;
int shi = i / 10 % 10;
int bai = i / 100;
int a = ge * ge * ge + shi * shi * shi + bai * bai * bai;
if (a == i) {
System.out.print(i+"\t");
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(); // 换行!
System.out.println("水仙花个数是:" + count);
}
}
🚒 while循环
🚬 总结 :
-
while循环的格式,执行流程是怎么样的?
-
什么时候用for循环,什么时候用while循环?
- 功能上是完全一样的,for能解决的while也能解决,反之亦然。
- 使用规范是:知道循环几次:使用for;不知道循环几次建议使用:while。
- 不知道循环次数的情况下,建议使用while循环解决更专业。
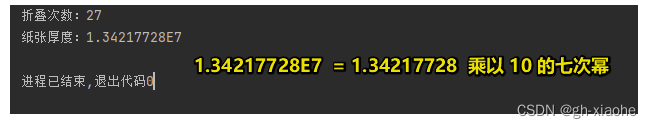
🚬 案例 :珠穆朗玛峰(世界最高峰8848.86米)
需求:
世界最高山峰是珠穆朗玛峰(8848.86米=8848860毫米),假如我有一张足够大的纸,它的厚度是0.1毫米。请问,折叠多少次,可以折成珠穆朗玛峰的高度。
思路:
这种不清楚要循环多少次的情况可以选择用while实现。
public class WhileTest6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:珠穆朗峰高度是8848860 纸张厚度 0.1 折叠纸张直到不低于珠穆朗峰位置,求折叠几次
// 1、定义变量记录山峰的高度 纸张的厚度
double peakHeight = 8848860; // 珠穆朗峰高度
double paperThickness = 0.1; // 纸张厚度
// 3、定义一个变量用于记录纸张折叠的次数
int count = 0;
// 2、定义一个while循环控制纸张进行折叠
while (paperThickness < peakHeight){
// 让纸张的厚度多一倍
paperThickness *= 2;
count++;
}
System.out.println("折叠的次数:" + count);
System.out.println("纸张的最终厚度:" + paperThickness);
}
}
🚤 do-while循环
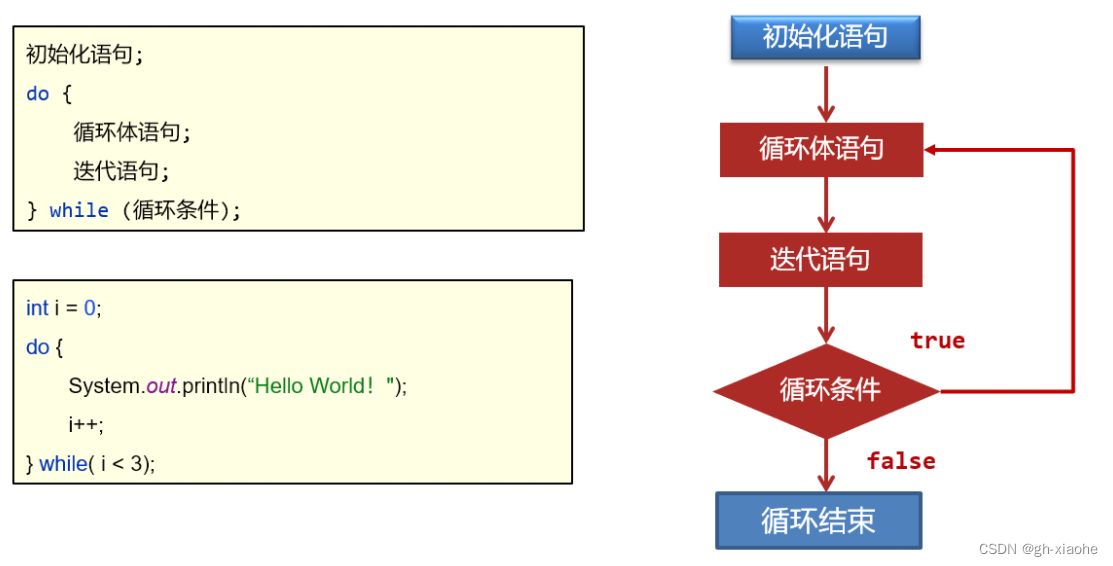
do-while循环的特点:一定会先执行一次循环体。
public class DoWhileDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:学会使用do-while循环,并理解其执行流程
int i = 0;
do {
System.out.println("Hello World");
i++;
}while (i < 3);
System.out.println(i); // 3
}
}
🚬 三种循环的区别小结
- for循环 和 while循环(先判断后执行)
- do…while (第一次先执行后判断)
- for循环和while循环的执行流程是一模一样的。
- 如果已知循环次数建议使用for循环,如果不清楚要循环多少次建议使用while循环。
- for循环中,控制循环的变量只在循环中可以使用。While循环中,控制循环的变量在循环后还可以继续使用。
🚗 死循环
- 一直循环的执行下去,如果没有干预不会停止下来
写法
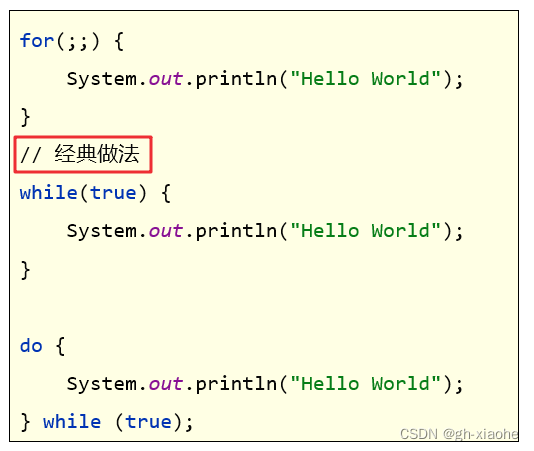
public class DeadForDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:学会定义死循环。
for ( ; ; ) {
System.out.println("Hello World~~~~");
}
// 经典写法
while (true) {
System.out.println("我是快乐的死循环~~~~");
}
do{
System.out.println("我是快乐的死循环~~~~");
}while (true);
}
}
🚬 案例:密码验证
需求:系统密码是520,请用户不断的输入密码验证,验证不对输出:密码错误,验证成功输出:欢迎进入系统,并停止程序。
分析:
定义一个整型变量记录正确的密码:520
使用while死循环,让用户不断输入数据,与正确密码比对:验证不成功输出:密码错误、验证成功输出:欢迎进入系统,并使用break结束当前循环的执行。
public class DeadForDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:学会定义死循环。
// for ( ; ; ) {
// System.out.println("Hello World~~~~");
// }
// 经典写法
// while (true) {
// System.out.println("我是快乐的死循环~~~~");
// }
// do{
// System.out.println("我是快乐的死循环~~~~");
// }while (true);
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
// 1、定义正确的密码
int okPassword = 520;
// 2、定义一个死循环让用户不断的输入密码认证
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请您输入正确的密码:");
int password = sc.nextInt();
// 3、使用if判断密码是否正确
if(password == okPassword){
System.out.println("登录成功了~~~");
break; // 可以理解结束当前所在循环的执行的
}else {
System.out.println("密码错误!");
}
}
}
}
🚲 循环嵌套
- 循环中又包含循环

🚬 嵌套循环的特点
- 外部循环每循环一次,内部循环全部执行完一次。
public class ForForDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:理解嵌套循环的执行流程
// 场景:假如你有老婆,然后你犯错了,你老婆罚你说5天,每天3句我爱你。
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("----" + "说我爱你" + i + "天" + "------");
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
System.out.println("\t"+"我爱你" + i + "句");
}
}
}
}
🚬 练习1
需求:打印给定的图形
public class ForForDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("--------------------------");
/**
*****
*****
*****
*****
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println(); // 换行
}
System.out.println("************************");
/**
*
**
***
****
*****
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i + 1; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
🚬 练习2
需求:打印 9 * 9 乘法表
public class ForForDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("打印九九乘法表");
/**
打印 9*9 乘法表
*/
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print(i + "*" + j + "=" + i * j + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
🚏 跳转关键字:break、continue(面试题)
🚀跳转控制语句介绍
-
break : 跳出并结束当前所在循环的执行。
-
continue: 用于跳出当前循环的当次执行,进入下一次循环。

🚬 示例1
public class BreakAndContinueDemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:理解break 和 continue的作用。
// 场景:你犯错了,你老婆罚你做5天家务,每天都是洗碗。
// 但是洗碗到第三天后心软了 原谅你了不用洗了
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("快乐的洗碗~~~~");
if(i == 2) {
break; // 跳出并结束当前循环的执行~~
}
}
// continue 跳出当前循环的当次执行,进入循环的下一次
// 场景:你犯错了,你老婆罚你做5天家务,
// 每天都是洗碗。但是洗碗到第三天后心软了 原谅你了不用洗了 但是依然不解恨 继续洗第4天 5天
for (int i = 1; i <= 5 ; i++) {
if(i == 3){
continue; // 立即跳出当次执行,进入循环的下一次!
}
System.out.println("洗碗:" + i);
}
}
}
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-BdD3G6vb-1653223997840)(%E6%B5%81%E7%A8%8B%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.assets/image-20220522205058803.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8c956aec6d2a400a9994b23777b9babd.png)
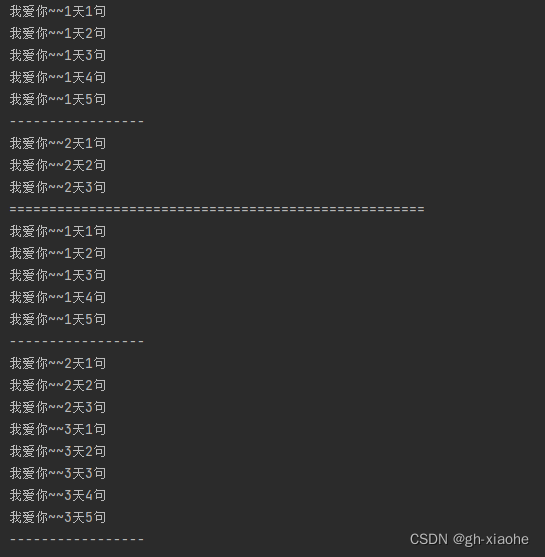
🚬 示例2
public class BreakAndContinueDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:理解break和continue操作外部循环。
// 场景:假如你有老婆,你老婆罚你说3天,每天5句我爱你,但是说到第二天的第3句就心软了,以后都不用说了!
OUT:
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++) {
System.out.println("我爱你~~" + i + "天" + j + "句");
if(i == 2 && j == 3){
break OUT; // 指定跳出外部循环,并结束外部循环了!
}
}
System.out.println("-----------------");
}
System.out.println("====================================================");
// continue可以指定结束外部循环的当次执行,进入外部循环的下一次执行
// 场景:假如你有老婆,你老婆罚你说3天,每天5句我爱你,但是说到第二天的第3句就心软了,当天
// 不用说了,但是依然不解恨,第3天还是要说的。
OUT:
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++) {
System.out.println("我爱你~~" + i + "天" + j + "句");
if(i == 2 && j == 3){
continue OUT;
}
}
System.out.println("-----------------");
}
}
}
🚏 案例技术:随机数Random类
🚀Random随机数技术
- 作用:用于在程序中获取随机数的技术。
🚄 使用步骤
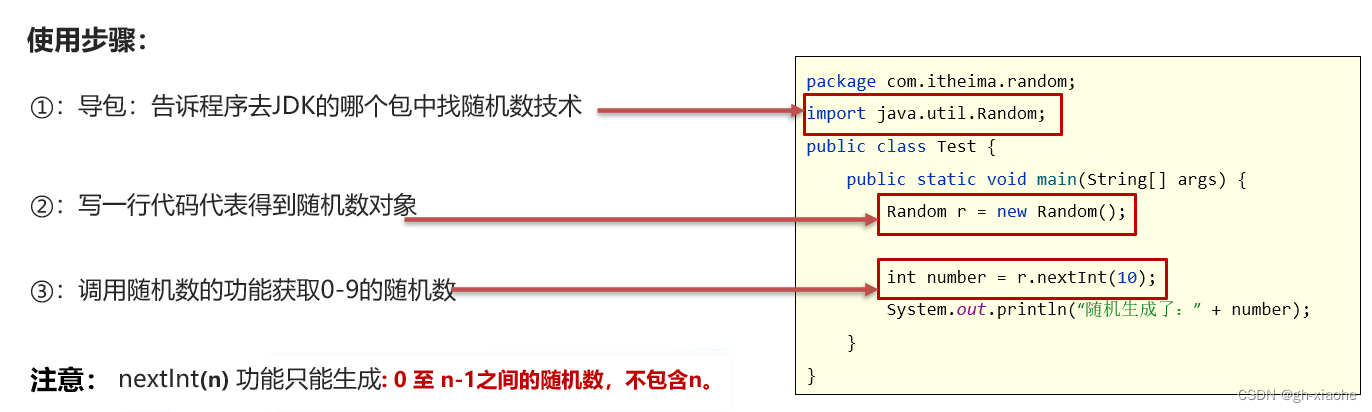
🚒 Random生成随机数的特点
- nextInt(n)功能只能生成:0 – (n-1)之间的随机数
🚤 Random生成区间随机数的技巧:减加法。

🚬 案例
public class RandomTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、随机一个幸运号码 1- 100之间 (0 - 99) + 1
Random random = new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(100) + 1;
System.out.println("幸运号码:" + i);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入一个1-100之间的数字:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = scanner.nextInt();
if (num == i) {
System.out.println("恭喜你,中奖了!");
break;
}else if (num > i) {
System.out.println("太大了,再试一次!");
}else {
System.out.println("太小了,再试一次!");
}
}
}
}
🚬 拓展 Random 的实现类
public class RandomGenerator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Random 实现 RandomGenerator 接口 中的 nextInt() 方法 生成随机数 的一个区间
Random random = new Random();
int randomNumber = random.nextInt(10, 20); // [10, 20) 左闭右开
System.out.println("The random number is: " + randomNumber);
}
}
JDK查看
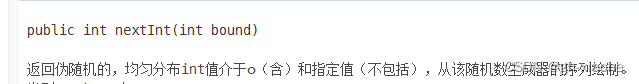
🚗 总结
- Random随机数类生成需要几步,具体是什么样的?
- 导包:import java.util.Random;
- Random r = new Random();
- int number = r.nextInt(10);
- Random随机数如何生成 65 – 91之间的随机数?
- 65 – 91 => (0 - 26)+ 65
- int number = r.nextInt(27) + 65;
























 218
218











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










