Operating System
1. Process Description And Control
contents
-
Role of the Operating System
-
What is a process
-
Process Control Block
-
Advantages of Multiprogramming
-
Model
Two-State Model
Five-State Model
-
Scheduling
Role of the Operating System(OS)
- OS provides a convenient, feature rich, secure, and consistent interface of application to use.
- OS provides a uniform. abstract representation of resources that can be requested and accessed by application.
What is a process
program: A program is simply an exact formulation of an algorithm. Related Reference:
process: A process is a program in execution.Relative Reference
multiprogramming: CPU switches
execution of several programs. Relative Reference
Questions
How is multiprogramming seen by the CPU?
1) CPU executes machine instructions as dictated by the content of the program counter
2) Program counter can point to code of different programs without
making any differenceHow is multiprogramming seen by an individual program?
1) Program is executed as normal and consists of a sequence of machine instructions (trace)
2) Each process uses its own logical program counter to not interfere with execution progress of other processes
At each point in time, the logical program
counter of exactly one process is loaded into the real (and only once available) program counter of the CPU
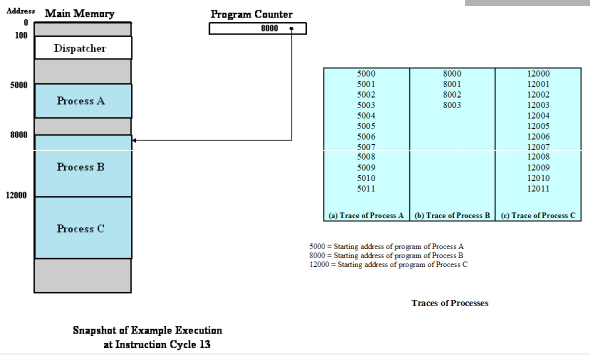
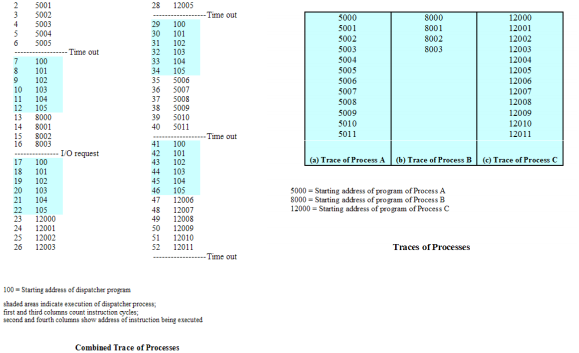
Trace of a Process:
- Sequence of instruction that execute for a process
- Dispatcher switches the processor from one process to another
Two essential elements of a process
Program code
PCB(Process Control Block)
PCB(Process Control Block)
Include:
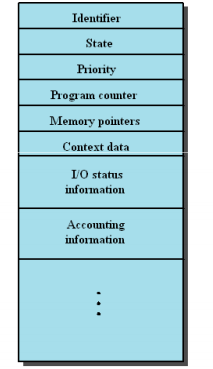
The data elements contained in a PCB fall into three general categories
Process Identification
PID(Process Identifier)
Identifier of the parent process
User IdentifierProcessor State Information
User-Visible Register
Register StatusProgram counter
Condition codes
Status informationStack Pointers
Subroutine Calling
Exception or Error Handling
Stack PointerProcess Control Information
Scheduling and States Information
Data Structuring
Process Privileges
…..
Advantages of Multiprogramming
Increasing utilization of components of a computer system.
CPU load
memory utilization
hard disk load
…….
Model
Two-State Model
Five-State Model
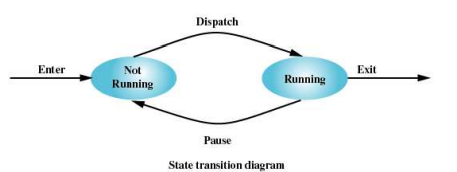
Two-State Model
A process can be specific two states:
Running
Not Running
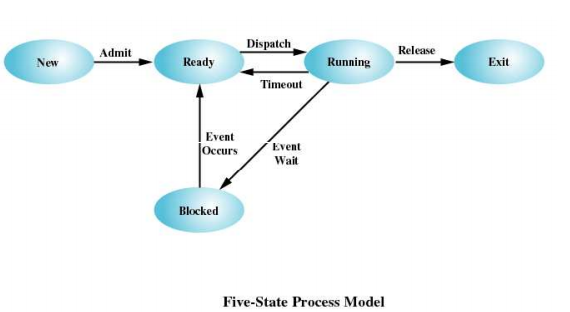
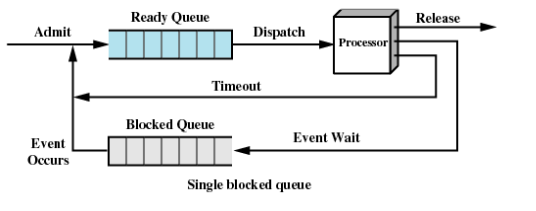
Five-State Model
Actual not all processes only have two states: Running and Not-Running. Often the process need to wait for a critical resource and be blocked state.
Therefore:
New(A new process is created)
Read(Process is waiting for CPU)
Running(Process is executing on CPU)
Blocked(Process is waiting for event)
Exit(Process is finished and being destroyed)
Scheduling
Operating systems with a simultaneous
execution of multiple processes must decide on the order and on the time of accessing resources by processes
When a computer is multiprogrammed it
frequently has multiple processes competing for the CPU at the same time•A a choice has to be made which process to run next
•the part of the operating system that makes this decision is called the scheduler
•the algorithm it uses is called the scheduling algorithm
•scheduling may involve both processes and threadsWhen to schedule
• a new process is created
- select the new one or keep the current one running
• a process terminates
- select and run another process, if any
• a process blocks (semaphore, I/O)
- dependencies btw processes may improve scheduling
• I/O interrupt
- run a waiting process
• hardware clock
- run the scheduler each clock interrupt or every k-th clock interruptScheduling: common goals
• fairness
- comparable processes should get comparable service (CPU time)
• policy enforcement
- different categories of processes may be treated differently
• balance
- try to keep all the part of the system busy when possibScheduling can be divided:
• non preemptive
- picks a process to run
- lets it run until it blocks, terminates or voluntary releases the CPU
- after clock interrupt, resume the process that was running before
• preemptive
- picks a process to run
- after a maximum amount of some fixed time suspends it (if still running)
- picks another process to run (if any available) requires clockScheduling: specific goals
• batch systems
- throughput
- turnaround time
- CPU utilization
• interactive systems
- response time/proportionality
• real-time systems
- meeting deadlines
- predictabilityScheduling in Batch Systems
• First-Come First-Served
• Shortest Job First
• Shortest Remaining Time NextScheduling in Interactive Systems
• Round Robin
• issues with Round Robin
• Priority Scheduling
……Scheduling in Real Time Systems
- hard-real time
- soft-real time
Reference: William Stallings, “Operating Systems - Internals and Design Principles”, Fifth Edition, Pearson Prentice Hall, 2005
个人笔记整理,转载请注明出处,谢谢!






















 885
885

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








