Spring Boot 读取配置文件的方式可以分为
1. 注解
2. 获取 Spring Boot 的环境变量
来获取配置文件的信息,其中注解的方式又有集中表现形式。
第一步:创建 Spring Boot 工程( Maven 工程添加 Spring Boot 相应的依赖)。
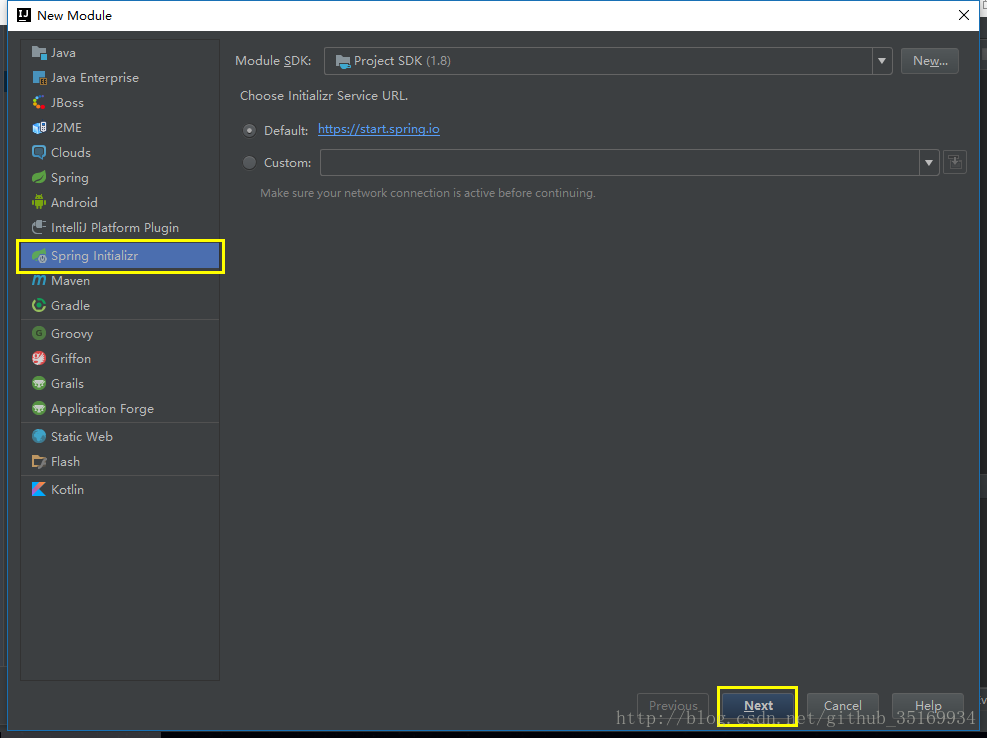
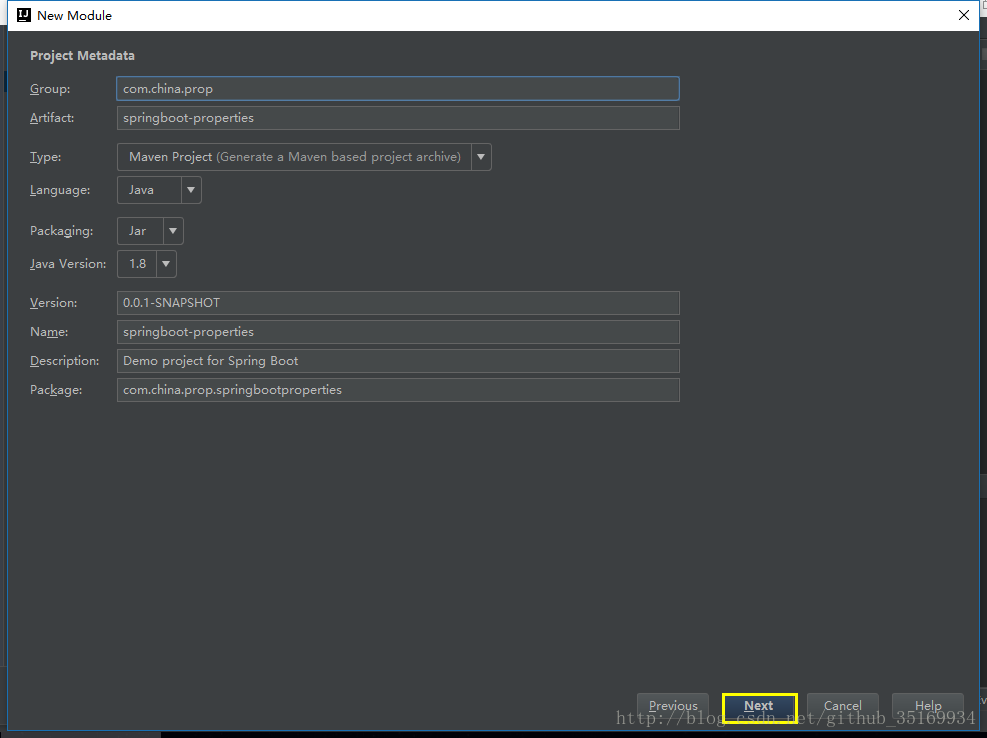
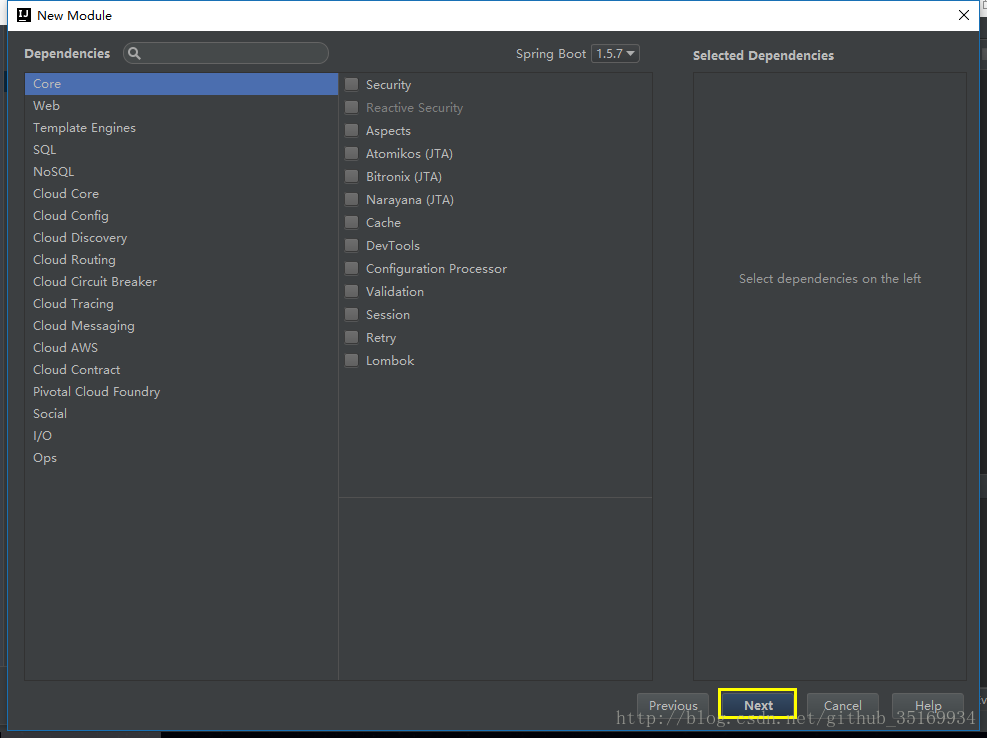
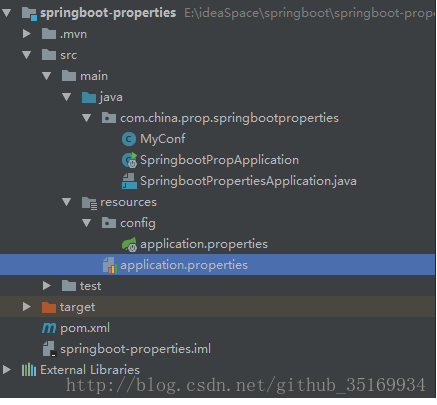
现在我们只是测试 Spring Boot 的 配置文件的读取,不需要其他的依赖,所以什么都没选,直接下一步 – 下一步 – 完成,项目目录结构如下:

此时的 application.properties 的内容为空
POM 文件内容为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.china.prop</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-properties</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>springboot-properties</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.7.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
POM 文件中的依赖是 IDEA 通过这种创建工程的方式给我们自动生成的。
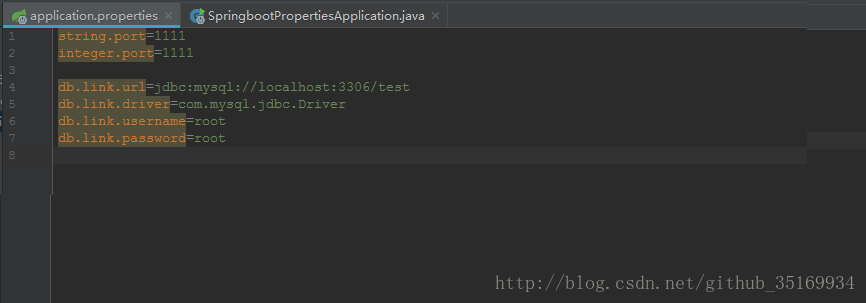
第二步:在配置文件中添加一些测试信息。
string.port=1111
integer.port=1111
db.link.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
db.link.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
db.link.username=root
db.link.password=root上面的配置变量仅仅是为了测试而添加的,不具有实际意义。string.port 与 integer.port 都是string 类型普通变量,这里只是做个名称区分而已。
一、 通过获取环境变量来获取配置参数
1.1. 主类
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootPropertiesApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取 Spring Boot 上下文
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(SpringbootPropertiesApplication.class, args);
// ctx.getEnvironment(); // 获取 边境变量
System.out.println("===========================================");
//获取字符串
System.out.println("String: " + (ctx.getEnvironment().getProperty("string.port") + 1111) );
//获取整数
System.out.println("Interger: " + (ctx.getEnvironment().getProperty("integer.port",Integer.class) + 1111 ));
System.out.println(ctx.getEnvironment().getProperty("db.link.url"));
System.out.println(ctx.getEnvironment().getProperty("db.link.driver"));
System.out.println(ctx.getEnvironment().getProperty("db.link.username"));
System.out.println(ctx.getEnvironment().getProperty("db.link.password"));
System.out.println("===========================================");
}
}1.2. 运行主类
===========================================
String: 11111111
Interger: 2222
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
root
root
===========================================可以看到配置文件中相同格式的port变量,可以获取到不同的格式数据。
- 1 新建 bean,通过注入环境变量来获取配置信息。
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyConf {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
public void show(){
System.out.println("===========================================");
//获取字符串
System.out.println("String: " +env.getProperty("string.port") + 1111);
//获取整数
System.out.println("Interger: " + (env.getProperty("integer.port",Integer.class) + 1111 ));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("db.link.url"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("db.link.driver"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("db.link.username"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("db.link.password"));
System.out.println("===========================================");
}
}2.2 改造主类并运行
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(SpringbootPropApplication.class, args);
MyConf myconf = (MyConf) ctx.getBean("myConf");
myconf.show();
ctx.close();
}结果:
===========================================
String: 11111111
Interger: 2222
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
root
root
===========================================二、通过注解获取配置文件信息
- 改造上面的 bean 配置类 MyConf:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyConf {
@Value("${string.port}") private int intPort;
@Value("${string.port}") private String stringPort;
@Value("${db.link.url}") private String dbUrl;
@Value("${db.link.driver}") private String dbDriver;
@Value("${db.link.username}")private String dbUsername;
@Value("${db.link.password}")private String dbPassword;
public void show(){
System.out.println("===========================================");
System.out.println("intPort : " + (intPort + 1111));
System.out.println("stringPort : " + (stringPort + 1111));
System.out.println("string : " + dbUrl);
System.out.println("string : " + dbDriver);
System.out.println("string : " + dbUsername);
System.out.println("string : " + dbPassword);
System.out.println("===========================================");
}
}- 运行主类可得:
===========================================
intPort : 2222
stringPort : 11111111
string : jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
string : com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
string : root
string : root
===========================================- 指定配置文件,@PropertySource可以声明多个,
或者使用@PropertySources(@PropertySource(“xxx”),@PropertySource(“xxx”))。
2.1 新建配置文件 my.prop
aaa.a=111
aaa.b=222
aaa.c=3332.2 新建配置类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:config/my.prop")
public class PropConf {
@Value("${aaa.a}")
private String a;
@Value("${aaa.b}")
private String b;
@Value("${aaa.c}")
private String c;
public void show(){
System.out.println("a --- > " + a);
System.out.println("b --- > " + b);
System.out.println("c --- > " + c);
}
}2.3. 在主类中添加相应调用代码
PropConf conf = (PropConf) ctx.getBean("propConf");
conf.show();2.4. 结果:
a --- > 111
b --- > 222
c --- > 333改造一
可以改造上面的PropConf 类:添加@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “aaa”)
指定配置文件的前缀,生成giter 和 setter 方法来获取配置信息。
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:config/my.prop")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "aaa")
public class PropConf {
private String a;
private String b;
private String c;
public String getA() {return a;}
public void setA(String a) {this.a = a;}
public String getB() {return b;}
public void setB(String b) {this.b = b;}
public String getC() {return c;}
public void setC(String c) {this.c = c;}
public void show(){
System.out.println("a --- > " + a);
System.out.println("b --- > " + b);
System.out.println("c --- > " + c);
}
}运行主类可以获得同样的结果。
改造二
可以只声明 setter 方法:
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:config/my.prop")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "aaa")
public class PropConf {
private String a;
private String b;
private String c;
public void setA(String a) { this.a = a; }
public void setB(String b) { this.b = b; }
public void setC(String c) { this.c = c; }
public void show(){
System.out.println("a --- > " + a);
System.out.println("b --- > " + b);
System.out.println("c --- > " + c);
}
}运行主类也可以得到同样的结果:
a --- > 111
b --- > 222
c --- > 333=======================================
笔记1
上面获取配置文件的位置都是在 classpath 根目录下面的,Spring Boot 默认的配置文件地址有两个:(application.properties 为默认的配置文件名称)
1. classpath: 即放在resources里面。
2. classpath:config里面。
3. file:/
4. file:/config/
笔记2
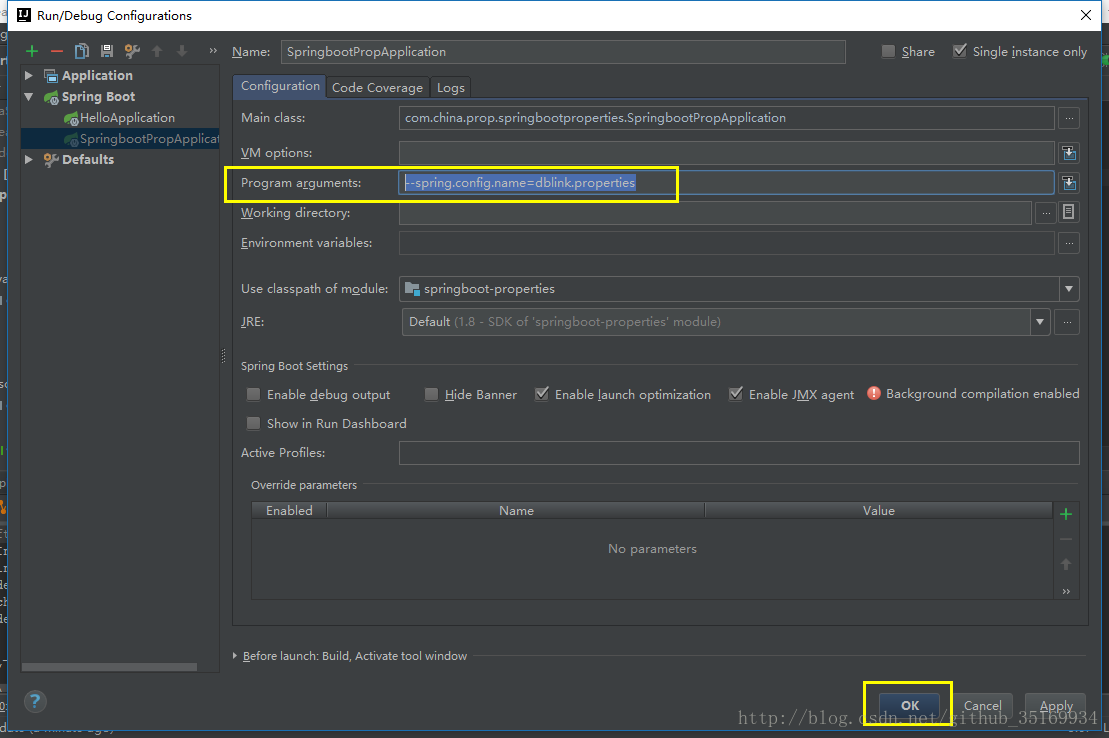
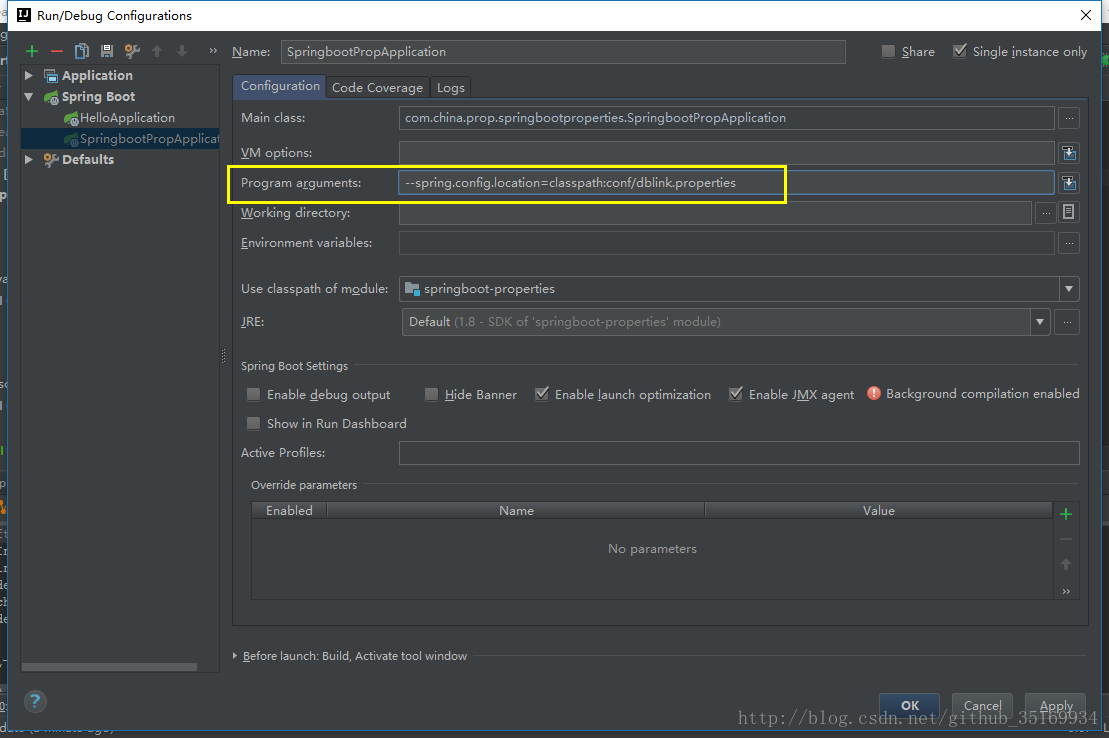
在系统系统时可以通过 –spring.config.name=xxx.properties 环境变量指定配置文件。
比如resources下有一个 dblink.properties,然后添加启动参数:
笔记3 应用启动可以指定配置文件地址
笔记4 Spring Boot 配置文件可以使用变量
笔记5 配置文件可以使用数组或者集合
- 在配置文件中添加集合信息
aaa.host[0]=127.0.0.1
aaa.host[1]=10.66.0.108
aaa.host[2]=10.66.0.111
aaa.host[3]=10.66.0.12
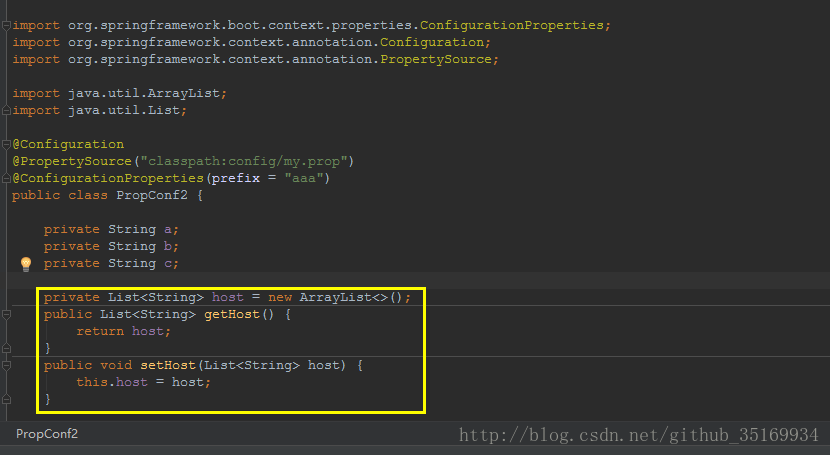
aaa.host[4]=10.66.0.134- 在配置类中注入参数
- 输出 host变量 可得:
[127.0.0.1, 10.66.0.108, 10.66.0.111, 10.66.0.12, 10.66.0.134]







 本文介绍SpringBoot中配置文件的两种读取方式:通过环境变量和注解。包括基本配置、不同数据类型的读取、指定配置文件及使用数组或集合。
本文介绍SpringBoot中配置文件的两种读取方式:通过环境变量和注解。包括基本配置、不同数据类型的读取、指定配置文件及使用数组或集合。

















 9203
9203

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








