工作所需,要使用Java调用c/c++的动态库,实现Java程序使用动态库中的函数。
搜索了一番,常用的有JNI、JNA方法。
-
JNI(Java Native Interface)
JNI定义了一种公用的语法,当Java和c/c++都遵循这样的语法时就可以互相调用(也可调用汇编等其余语言)。JNI不能直接调用c/c++的库,必须使用java编写调用函数,生成C头文件,再利用C头文件编写C代码,生成动态库,最后JNI使用新生成的动态库完成执行。
过程繁琐,需增加改动Java和C/C++的程序。 -
JNA(Java Native Access)
JNA提供了一组Java工具类,用于在运行期间动态访问系统本地库(native library:如Window的dll)而不需要编写任何Native/JNI代码,省去了对c/c++程序的再封装。
最终决定选用JNA。
一、引入
JNA的引入很方便,使用maven直接导入即可。
<dependency>
<groupId>net.java.dev.jna</groupId>
<artifactId>jna</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
调用JNA有很多前提条件
二、前提条件
JNA有很多条件限制:
- JNA只能调用C方式编译出来的动态库,若是C++代码则需进行转换。如何用c的方式编译c++动态库,可见链接:c方式编译c++
- 使用中,Java和c/c++的系统版本必须一致,如都是32位或都是64位。
本文章全部使用64位版本
三、使用
扯了这么多,终于要开始调用了。免不了先查询文档:
API:http://java-native-access.github.io/jna/4.1.0/
github:https://github.com/java-native-access/jna
- 引入
Jna的样例中,基本都会定义一个接口,该接口链接c/c++动态库,生成一个实例,并定义了与动态库中一致的函数名称,用于后续调用。
举个栗子:
/******C端代码*********/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include "demo.h"
int hello()
{
printf("Hello world\n");
return 0;
}
将如上代码编译成动态库JnaLibrary.dll
编写Java端调用程序:
public interface Clibrary extends Library {
Clibrary instance = (Clibrary) Native.loadLibrary("JnaLibrary.dll", Clibrary.class);
//与动态库中的函数相对应
int hello();
}
//调用
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Clibrary.instance.hello();
}
}
编译执行,就会输出动态库的内容:Hello world
- 数据类型转换
要定义动态库中的函数,难免会涉及入参及出参,数据格式的处理就尤为重要。先了解Java与C之间的数据映射。
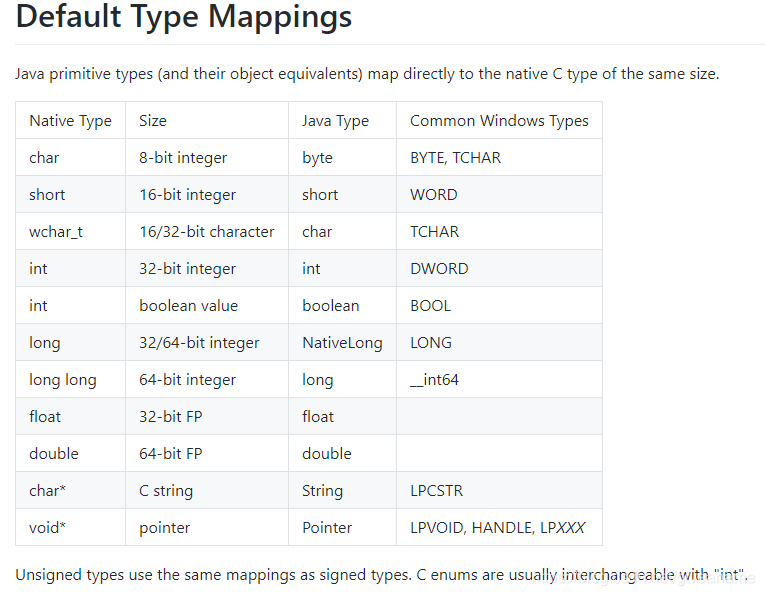
2.1 基本数据类型
根据对应表来定义即可
C端代码:
......(省略上述代码)
int basicTest(int a, float b)
{
printf("a=%d\n", a);
printf("b=%f\n", b);
return 100;
}
Java端代码:
public interface Clibrary extends Library {
Clibrary instance = (Clibrary) Native.loadLibrary("JnaLibrary", Clibrary.class);
int hello();
int basicTest(int a, float b, String pChar);
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=5;
float b = 1.5f;
int ret = Clibrary.instance.basicTest(a,b);
System.out.println("ret:"+ret);
}
}
输出结果:
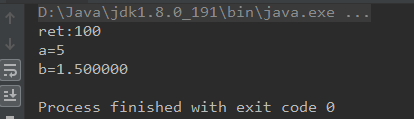
此处有个疑问:返回结果比动态库中函数更早输出了,希望有小伙伴能指点
2.2 指针和数组
说到C自然会用到指针,其转换也花了不少时间。Jna中专门定义了指针类型用来与c对应。
在C中指针与数组一直暧昧不清,传参时,形参定义一个指针,实参则要传入地址,而传一个数组的名称 == 传数组的首元素地址,github中就把两者放在一个demo中。
指针及数组:
eg:
c端代码
void arrayTest(char * pStr, unsigned char *puStr)
{
int i = 0;
printf("%s\n", pStr);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf("%c ", puStr[i]);
}
}
Java端:
......(省略其余代码)
//定义;其中char *直接使用String类型替代,unsigned char * 可转为byte[]数组
void arrayTest(String pStr, byte[] puStr);
//调用
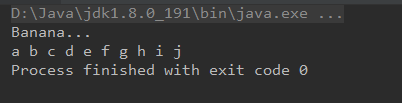
String str = "Banana...";
byte[] bytes = new byte[10];
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++){
bytes[i] = (byte)('a'+i);
}
Clibrary.instance.arrayTest(str, bytes);
输出:
基本数据类型指针
JNA中给基本数据类型int、float等直接提供了指针类
C端代码:
......(省略上述代码)
void pointerTest(int * pInt, float * pFloat)
{
*pInt = 10;
*pFloat = 12.34;
}
Java端代码:
定义:
//定义
......(省略上述代码)
void pointerTest(IntByReference pInt, FloatByReference pFloat);
//调用
......(省略上述代码)
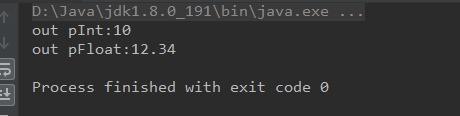
IntByReference pInt = new IntByReference();
FloatByReference pFloat = new FloatByReference();
Clibrary.instance.pointerTest(pInt, pFloat);
System.out.println("out pInt:"+pInt.getValue());
System.out.println("out pFloat:"+pFloat.getValue());
输出:
指向动态内存的指针
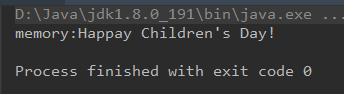
c中可以动态申请空间和赋值,Java使用Memory类与之相对应

c端代码:
//定义
void mallocTest(char *pszStr)
{
strcpy(pszStr, "Happay Children's Day!");
}
//调用
int main()
{
char *pStr = malloc(sizeof(char)*32);
mallocTest(pStr);
free(pStr);
return 0;
}
Java端代码:
//定义
void mallocTest(Memory pString);
//调用
Memory memory = new Memory(20);
Clibrary.instance.mallocTest(memory);
System.out.println("memory:"+memory.getString(0));
输出:
二级指针
Jna直接提供了PointerByReference类,有getValue()方法。
注意二级指针概念,其意是:指向指针的指针,因此PointerByReference.getValue()获取到的仍是一个指针类Pointer,再从该Pointer中获取值。
eg:
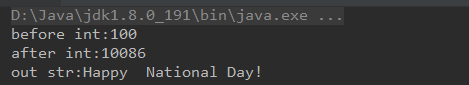
C端代码:
//定义
void doublePointTest(int ** ppInt, char ** ppStr)
{
printf("before int:%d\n", **ppInt);
**ppInt = 10086;
*ppStr = (char*)malloc(10 * sizeof(char));
strcpy(*ppStr, "Happy National Day!");
}
void freePoint(void *pt) {
if (pt != NULL) {
free(pt);
}
}
//调用
int main()
{
int a = 100;
int * pInt = &a;
char *pStr = NULL;
doublePointTest(&pInt, &pStr);
printf("after int:%d\n", *pInt);
printf("out str:%s\n", pStr);
//函数中动态申请内存,必须释放
freePoint(pStr);
system("pause");
}
Java端代码:
//定义
void doublePointTest(PointerByReference ppInt, PointerByReference ppStr);
void freePt(Pointer pt);
//调用
IntByReference intByReference = new IntByReference(100);
Pointer pInt = intByReference.getPointer();
PointerByReference ppInt = new PointerByReference(pInt);
PointerByReference ppStr = new PointerByReference();
try {
Clibrary.instance.doublePointTest(ppInt, ppStr);
System.out.println("after int:" + ppInt.getValue().getInt(0));
System.out.println("out str:" + ppStr.getValue().getString(0));
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
Clibrary.instance.freePoint(ppStr.getValue());
}
结果:
注意: C代码申请的内存不归Java管理,因此动态申请的内存必须手动释放,栗子中使用finally确保释放函数会被调用。
2020.6.30补充
三重指针
没想到三重指针说来就来了(╯‵□′)╯︵┻━┻ ,c中函数动态申请了一个二维数组并赋值,因此参数需传入一个三重指针获取其值。不多说,直接上demo
C端代码:
//函数定义
void obtain2DArray(float *** pppFloatOut, int * pLine, int *pColumn)
{
int line = 3, column=5;
float **ppFloatIn;
int i,j;
ppFloatIn = (float**)malloc(sizeof(float*)*line);
for (i = 0; i < line; i++) {
ppFloatIn[i] = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float*)*column);
}
for (i = 0; i < line; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < column; j++) {
ppFloatIn[i][j] = i + j;
}
}
*pppFloatOut = ppFloatIn;
*pLine = line;
*pColumn = column;
return;
}
void free2Dppt(int line, int column, float **ppFloat)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < line; i++) {
if (ppFloat[i]) {
free(ppFloat[i]);
ppFloat[i] = NULL;
}
}
if (ppFloat) {
free(ppFloat);
ppFloat = NULL;
}
}
/**函数调用****************************************/
float **ppFloat;
int line, column;
obtain2DArray(&ppFloat, &line, &column);
printf("out line:%d column:%d\n", line, column);
for (int i = 0; i < line; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++) {
printf(" %f ", ppFloat[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
free2Dppt(line, column, ppFloat);
要注意,多重指针的本质都是指针,因此Jna调用中都可以将类型定义为Pointer,只是需区分函数所需的Pointer指向的内容。
Jna没有三重指针类型,但可以通过二维指针类型的方法getPointer()间接获取。
注意PointerByReference的getPointer()获得指向该类型的指针,getValue()方法获得其指向的值。
Java代码:
//方法定义
void obtain2DArray(Pointer pppFloatOut, IntByReference pLine, IntByReference pColumn);
void free2Dppt(int line, int column, Pointer ppFloat);
//调用
PointerByReference ppFloat = new PointerByReference();
Pointer pppFloat = ppFloat.getPointer();
IntByReference linePt = new IntByReference();
IntByReference columnPt = new IntByReference();
//通过获取二维指针的指针,得到三重指针
Clibrary.instance.obtain2DArray(pppFloat, linePt, columnPt);
int line = linePt.getValue();
int column = columnPt.getValue();
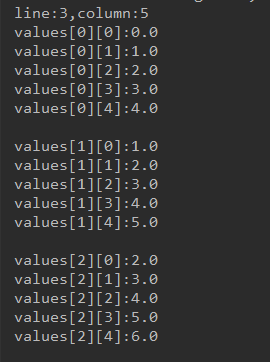
System.out.println("line:"+line+",column:"+column);
float[][] values = new float[line][column];
//输出一个3行5列的二维数组,即3个指向一行的指针,因此可获取指针数组;
// 注意getPointerArray方法必须指明指针数组的数量(此处是line = 3),否则返回的指针数组长度不定,有很多干扰值
Pointer[] pointers = ppFloat.getValue().getPointerArray(0, line);
for(int i=0;i<line;i++){
values[i] = pointers[i].getFloatArray(0, column);
}
for(int i=0;i<line;i++){
for(int j=0;j<column;j++)
System.out.println("values["+i+"]["+j+"]:"+values[i][j]);
System.out.println();
}
//传入PointerByReference的getValue()
Clibrary.instance.free2Dppt(line, column, ppFloat.getValue());
结果:
2.3 结构体、共用体
结构体需编写类继续Jna的Structure,并重写其 getFieldOrder() 方法,用于返回其成员名称。
该类还提供了两个接口 Structure.ByReference 和 Structure.ByValue,分别用于改写其指针和值的内容。
官方文档中,形参为指针时直接传入类,为结构体名称时传入ByValue接口,但试验其余方式也可。
1,传输结构体
eg:
c端代码:
typedef struct _rect
{
int index;
char info[16];
}Rect;
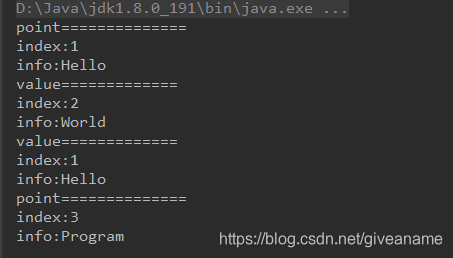
int readRect(Rect rect)
{
printf("value=============\n");
printf("index:%d\ninfo:%s\n", rect.index, rect.info);
return 0;
}
int readRectPoint(Rect * pRect)
{
printf("point==============\n");
printf("index:%d\n", pRect->index);
printf("info:%s\n", pRect->info);
return 0;
}
Java端代码:
...(省略其余代码)
public static class Rect extends Structure{
public int index;
public byte[] info = new byte[16];
public static class ByReference extends Rect implements Structure.ByReference{}
public static class ByValue extends Rect implements Structure.ByValue{
}
@Override
protected List<String> getFieldOrder(){
List<String> field = new ArrayList<>();
field.add("index");
field.add("info");
return field;
}
}
//文档demo
int readRect(Rect.ByValue rect);
int readRectPoint(Rect pRect);
//试验
int readRect(Rect rect);
int readRectPoint(Rect.ByReference pRect);
//调用时
//文档demo调用
Clibrary.Rect rect = new Clibrary.Rect();
rect.index = 1;
rect.info = "Hello".getBytes();
Clibrary.instance.readRectPoint(rect);
Clibrary.Rect.ByValue rectValue = new Clibrary.Rect.ByValue();
rectValue.index = 2;
rectValue.info = "World".getBytes();
Clibrary.instance.readRect(rectValue);
//试验内容
Clibrary.instance.readRect(rect);
Clibrary.Rect.ByReference rectReference = new Clibrary.Rect.ByReference();
rectReference.index = 3;
rectReference.info = "Program".getBytes();
Clibrary.instance.readRectPoint(rectReference);
输出结果皆正确
2,传输结构体数组:
eg:
c端代码:
int readRectArray(Rect *pRectArray) == 等同于 int readRectArray(Rect[] RectArray)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("pRectArray.index:%d\n", pRectArray[i].index);
printf("pRectArray.info:%s\n", pRectArray[i].info);
}
}
Java端调用:
//定义
void readRectArray(Rect[] rectArray);
//调用
Clibrary.Rect rectOne = new Clibrary.Rect();
//必须使用toArray方法,结构体数组才会是连续地址
Clibrary.Rect[] rectArray = (Clibrary.Rect[]) rectOne.toArray(5);
for(int i = 0;i<5;i++){
rectArray[i].index = i;
rectArray[i].info = "Hello".getBytes();
}
Clibrary.instance.readRectArray(rectArray);
3,获取返回的结构体数组
C代码:
Rect * obtainRectArray(int *pArrayNum)
{
int num = 5;
*pArrayNum = num;
Rect *pArray = (Rect*)malloc(num * sizeof(Rect));
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
pArray[i].index = i;
sprintf(pArray[i].info, "%s_%d","Hello",i);
}
return pArray;
}
//释放空间
void freeRect(Rect *pRect)
{
if(pRect)
{
free(pRect);
pRect= NULL;
}
}
Java代码:
//定义
Rect obtainRectArray(IntByReference arrayNum);
void freeRect(Rect[] rects);
//调用
Clibrary.Rect[] array = null;
try{
IntByReference numPt = new IntByReference();
Clibrary.Rect r = Clibrary.instance.obtainRectArray(numPt);
array = (Clibrary.Rect[]) r.toArray(numPt.getValue());
for(Clibrary.Rect rect :array){
System.out.println("rect.index:"+rect.index);
//必须使用Native.toString才能正常输出,使用rect.info.toString(),会输出异常信息
//如dll库中赋值了"Hello_1",输出会是"Hello_1 s n o w ",凑满了16个字节
System.out.println("rect.info:"+Native.toString(rect.info));
}
//使用Jna函数,也可以正常读取数组信息
Clibrary.instance.readRectArray(array);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
Clibrary.instance.freeRect(array);
}
————add 2020.7.3————
4,结构体中嵌套结构体
话不多说,上Demo
C端代码:
//结构体定义
typedef struct _rect
{
int index;
char info[16];
}Rect;
typedef struct _table
{
char tableName[32];
int rectNum;
Rect *pRectArray;
}Table;
//函数定义
void obtainTable(Table *pTable, char *pTableName)
{
Table table;
strcpy(pTable->tableName, pTableName);
int num = 5;
pTable->rectNum = num;
Rect *pArray = (Rect*)malloc(num * sizeof(Rect));
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
pArray[i].index = i;
sprintf(pArray[i].info, "%s_%d", "Hello", i);
}
pTable->pRectArray = pArray;
return ;
}
void freeTable(Table *pTable)
{
if(pTable->pRectArray)
{
free(pTable->pRectArray);
pTable->pRectArray = NULL;
}
}
//函数调用
Table table;
obtainTable(&table, "A table");
printf("name:%s\n", table.tableName);
int num = table.rectNum;
printf("num:%d\n", num);
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
printf("index:%d\n", table.pRectArray[i].index);
printf("info:%s\n", table.pRectArray[i].info);
}
freeTable(&table);
Java端代码:
//结构体定义
class Rect extends Structure{
public Rect(){}
public int index;
public byte[] info = new byte[16];
public static class ByReference extends Rect implements Structure.ByReference{}
public static class ByValue extends Rect implements Structure.ByValue{}
@Override
protected List<String> getFieldOrder(){
return Arrays.asList("index", "info");
}
}
class Table extends Structure{
public byte[] tableName = new byte[32];
public int rectNum;
//此处需使用结构体指针
public Rect.ByReference pRectArray ;
public Table(){}
public static class ByReference extends Table implements Structure.ByReference{}
public static class ByValue extends Table implements Structure.ByValue{}
@Override
protected List<String> getFieldOrder(){
return Arrays.asList("tableName", "rectNum", "pRectArray");
}
}
//方法定义
void obtainTable(Table pTable, String tableName);
void freeTable(Table pTable);
//方法调用
Clibrary.Table table = new Clibrary.Table();
try{
Clibrary.instance.obtainTable(table, "A table");
Clibrary.Rect rectArray[] = (Clibrary.Rect[]) table.pRectArray.toArray(table.rectNum);
System.out.println("table_name:"+Native.toString(table.tableName));
for(int i=0;i<table.rectNum;i++){
System.out.println("index:"+rectArray[i].index);
System.out.println("info:"+Native.toString(rectArray[i].info));
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
Clibrary.instance.freeTable(table);
}
输出结果:

注明:以上样例——函数返回结构体数组
指针,是JNA的API文档demo,其中byte[]信息必须用Native.toString(byte[])才能正确输出。
四、Tips
最后附上调试、部署时总结的一些经验;
0,上文提到的2个前提条件
1,在idea下调试运行时,将动态库按照系统和位数,在resources下创建相应目录,即可根据系统位数自动加载。
或者新建目录,并将该目录设置为resources属性,同样可行。
如我在项目中创建了library目录,并将其设置为resouces属性


2,当动态库放置于这些文件夹或系统目录时,Clibrary接口的动态库可省去固定路径和后缀名
否则要写固定路径和全名:

3,设置编码
c里面没有原生字符串,Windows下的LPCTSTR实际上是一个字节数组指针,JNA进行LPCSTR -> String映射的时候会先将LPCSTR映射为byte[],再根据系统属性"jna.encoding"的值返回new String(byte[],jna.encoding),反之亦然。
当"jna.encoding"为null时Java会以默认的UTF-8进行编码,如果这个本地库是非Unicode的就会产生乱码。
可知:
Jna默认使用utf-8编码,若动态库中需要其余编码如gbk,需在jna函数调用时手动设置系统编码
jna function(){
System.setProperty("jna.encoding", "gbk");
xxx_c_function();
}
4,maven打包部署时(springboot项目),需要将动态库也打包到jar包中,所以需在pom文件中进行设置。
有两种方式:
<1> 在pom文件中用标签指明放置动态库的目录,则该目录会被作为resources资源目录。因为resources目录拷贝时会进行统一编码,所以还需用标签将dll、so后缀文件进行过滤,否则会破坏原有动态库文件,导致不可用。

<2>不使用项目的resources目录属性,自己使用标签执行目标配置,将动态库打包到jar包中指定路径。此操作可免去设置编码过滤。

<3>在Pom文件中指定主类mainClass
<4>使用maven进行编译打包,如下红框处,先执行clean,再compile,在package;
获得的包在target目录下,如下黄框。 
打包后,即可在linux环境执行:java -jar jna_commonxxxx.jar 执行,会执行pom文件中的的内容

5,调用jna报如下的错时,可能是找不到对应的库引起的。
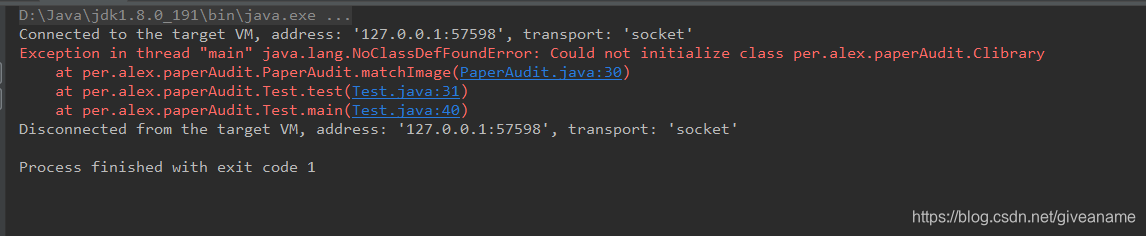
首先检查下是否将库放在系统路径或设置的resource目录了,即tip第一步;
若已经设置好了仍报错,就需要检查放置在目录中的库是否依赖了其他库(windows可以通过vs的dumpbin.exe来判断,linux可以通过ldd指令),而这些其他库也需要全部放进来。
五、结语
写了这么多,都是硬调试出来的结果… 没有从源码和理论研究,感觉还是不踏实 =_=!





 本文详述使用JNA在Java中调用C/C++动态库的方法,包括基本数据类型、指针、数组、结构体的处理,以及调试和部署技巧。
本文详述使用JNA在Java中调用C/C++动态库的方法,包括基本数据类型、指针、数组、结构体的处理,以及调试和部署技巧。
















 3145
3145

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








