- 深度优先搜索
一条路走到黑,回溯 - 广度优先搜索
一石激起千层浪
一、走迷宫问题,只有一条路
1. 题目描述
题目链接
2. 题目分析 + 加解决方法
- 新建Pos(x,y)类,表示位置
- List< Pos >保存各个位置
- boolean[][] 标记数组,标记位置是否走过

import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Pos{
int x;
int y;
public Pos(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static int[][] nextP = {
{
1, 0}, {
0, 1}, {
-1, 0}, {
0, -1}};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int row = scanner.nextInt();
int col = scanner.nextInt();
int[][] map = new int[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
map[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
boolean[][] book = new boolean[row][col];
List<Pos> results = DFS(map, row, col, new ArrayList<>(), book, 0, 0);
for (Pos pos : results) {
System.out.println("(" + pos.x + "," + pos.y + ")");
}
}
public static List<Pos> DFS(int[][] map, int row, int col, List<Pos> results, boolean[][] book, int x, int y){
if(x < 0 || x >= row || y < 0 || y >= col || book[x][y]){
return results;
}
if(map[x][y] == 1){
return results;
}
results.add(new Pos(x, y));
book[x][y] = true;
if(x == row - 1 && y == col - 1){
return results;
}
for (int[] next : nextP) {
int newX = x + next[0];
int newY = y + next[1];
DFS(map, row, col, results, book, newX, newY);
if(book[row - 1][col - 1]){
return results;
}
}
results.remove(results.size() - 1);
return results;
}
}
二、走迷宫之最短路径(多条路找最短路径)
1. 题目描述
题目链接
2. 题目分析 + 解决方法
多条路径找最短路径
通过一条路径走到终点,可能并不是最短路径;因此到达终点后,需要回退到前面的位置,继续寻找其他路径,通过比较,找到最短路径
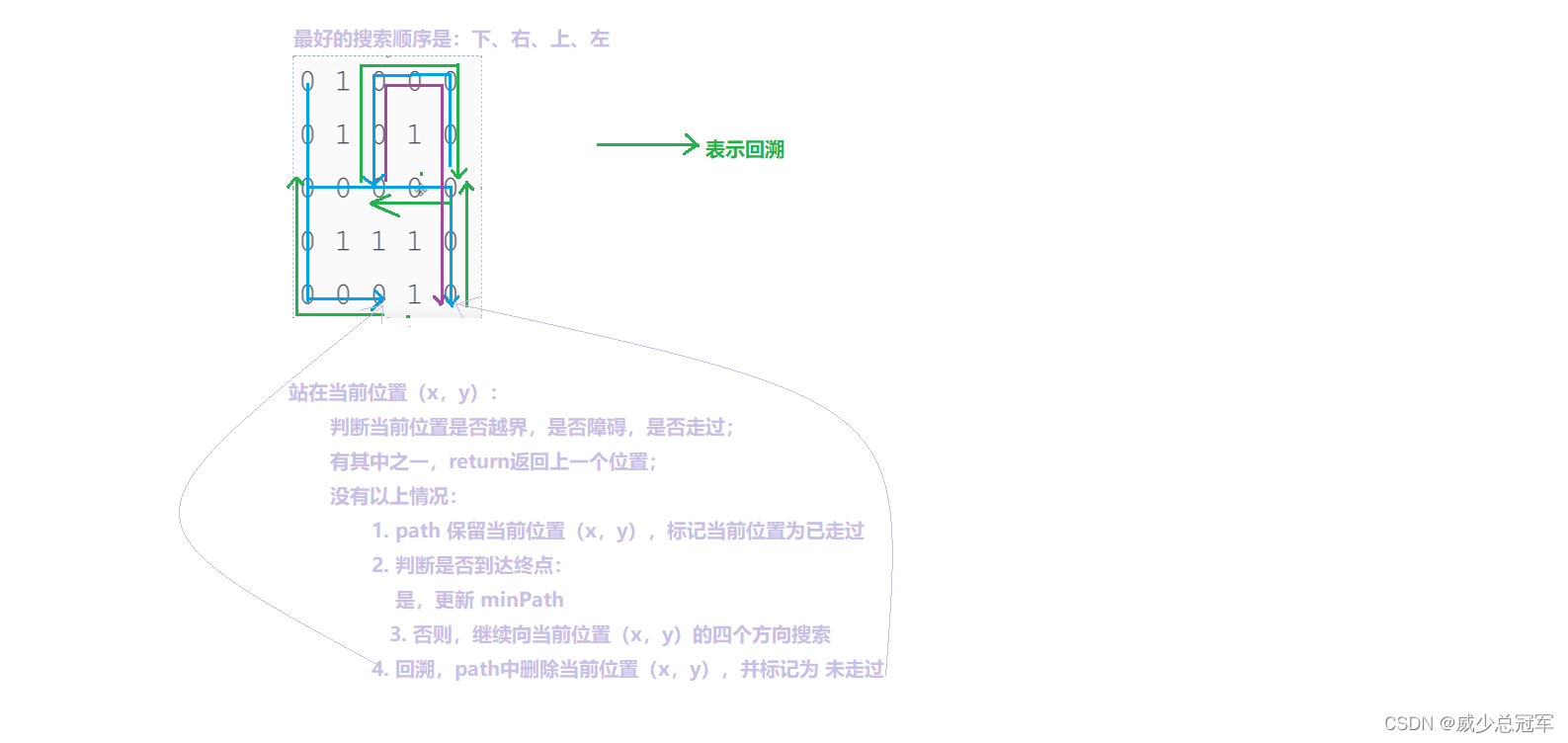
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Pos{
int x;
int y;
public Pos(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this 迷宫问题解析:深度优先搜索与广度优先搜索
迷宫问题解析:深度优先搜索与广度优先搜索





 本文详细介绍了三种不同的迷宫问题解决方案:1) 使用深度优先搜索(DFS)找到唯一路径;2) 通过DFS找到最短路径;3) 利用BFS找到最短步数。每种方法都配合代码实例,解释了如何标记位置、回溯及优化搜索策略。此外,还指出了错误示例及其纠正方法,强调了在回溯时正确重置已走过路径的重要性。
本文详细介绍了三种不同的迷宫问题解决方案:1) 使用深度优先搜索(DFS)找到唯一路径;2) 通过DFS找到最短路径;3) 利用BFS找到最短步数。每种方法都配合代码实例,解释了如何标记位置、回溯及优化搜索策略。此外,还指出了错误示例及其纠正方法,强调了在回溯时正确重置已走过路径的重要性。



 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 8791
8791

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










