Proxies Valve是代理Valve,其作用是可以对负载均衡代理服务器的IP地址与原request的IP地址做请求转换,让服务器端真正识别原IP地址(如果服务器端有需要的话);
本文主要讨论这种地址转换是如何做的;
1.X-Forwarded-For等http头字段
在我们现实的真正的场景中,通常Tomcat直接和用户接触的场景不多,主要是通过代理转发机制进行,如下:

真正的用户客户端是Client1,代理转发服务器采用的是Nginx,Proxy1,那么在此场景下,如果在Tomcat中进行获取客户端的地址:
request.getRemoteAddr,获得的IP地址绝对是Proxy1的,也就是负载均衡的地址;
而如果你想要获取Client1的地址,也是可以获取到的,就是通过X-Forwarded-For字段;
X-Forwarded-For:简称XFF头,它代表客户端,也就是HTTP的请求端真实的IP,只有在通过了HTTP 代理或者负载均衡服务器时才会添加该项。
X-Forwarded-For内置在Http协议头中,一般格式如下:
X-Forwarded-For: client1, proxy1, proxy2, proxy3
其中的值通过一个 逗号+空格 把多个IP地址区分开,;
最左边(client1)是最原始客户端的IP地址, 代理服务器每成功收到一个请求,就把请求来源IP地址添加到右边。
在上面这个例子中,这个请求成功通过了三台代理服务器:proxy1, proxy2 及 proxy3。请求由client1发出,到达了proxy3(proxy3可能是请求的终点)。请求刚从client1中发出时,XFF是空的,请求被发往proxy1;通过proxy1的时候,client1被添加到XFF中,之后请求被发往proxy2;通过proxy2的时候,proxy1被添加到XFF中,之后请求被发往proxy3;通过proxy3时,proxy2被添加到XFF中,之后请求的的去向不明,如果proxy3不是请求终点,请求会被继续转发。
鉴于伪造这一字段非常容易,应该谨慎使用X-Forwarded-For字段。正常情况下XFF中最后一个IP地址是最后一个代理服务器的IP地址, 这通常是一个比较可靠的信息来源。[1]
其次,还有一个是X-Forwarded-by字段,该字段是标识为负载均衡proxy的可信代理的IP地址;
例如上面的这个例子,X-Forwarded-For: client1, proxy1, proxy2, proxy3,可以配置当前的应用服务器的X-Forwarded-by字段可信IP为 proxy1, proxy2, proxy3;
这样通过X-Forwarded-For,X-Forwarded-by两个字段进行减法,直接就得到client1了;
还有一个是X-Forwarded-Proto,该字段记录最初从浏览器发出时候,是使用什么协议。因为有可能当一个请求最初和反向代理通信时,是使用https,但反向代理和服务器通信时改变成http协议,这个时候,X-Forwarded-Proto的值应该是https;
X-Forwarded-For和X-Forwarded-Proto的信息是很有价值的,在Tomcat中可以通过获取这两个字段的信息,拿到真实的客户端的请求IP和协议;
2.Remote IP Valve
Remote IP Valve就是利用X-Forwarded-For和X-Forwarded-Proto等字段,反转得到最原始的客户端的IP和请求信息的;
Attributes
The Remote IP Valve supports the following configuration attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
className | Java class name of the implementation to use. This MUST be set to org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteIpValve. 可以自定义RemoteIPValve; |
remoteIpHeader | Name of the HTTP Header read by this valve that holds the list of traversed IP addresses starting from the requesting client. If not specified, the default of X-Forwarded-For属性(可以更改为其它的属性) |
internalProxies | Regular expression (using 对x-forwarded-for 中出现的IP进行过滤,过滤的方式采用的是正则表达式; |
proxiesHeader | Name of the HTTP header created by this valve to hold the list of proxies that have been processed in the incoming remoteIpHeader. If not specified, the default of x-forwarded-by 属性(可以更改为其它的属性) |
requestAttributesEnabled | Set to 当上述的几个属性开启后,通过request.getAttribute(xxx)就可以拿到原始客户端的一些信息,而不是代理服务器的; 而AccessLog和Manager应用的状态监控页面中,就是通过request.getAttribute(xxx) 拿信息的,这个设置也就是可以影响这两个功能; |
trustedProxies | Regular expression (using 与internalProxies 需要区分开来; internalProxies 是对x-forwarded-for 中出现的IP进行过滤,并不会加入到http头的x-forwarded-by 中; 而这个trustedProxies 也是对x-forwarded-for 中出现的IP进行过滤,但会加入httphttp头的x-forwarded-by 中; 从字面意思理解,internalProxies 可以理解为内部的代理地址(貌似是一个内部的过滤匹配或者是内部的proxy协议转换,没什么价值), 而trustedProxies是可信的代理服务器的IP地址,是需要进行记录的 |
protocolHeader | Name of the HTTP Header read by this valve that holds the protocol used by the client to connect to the proxy. If not specified, the default of http头的协议设置,如果你要检测代理是否把协议给转换了,可以设置前面讲过的X-Forwarded-Proto |
portHeader | Name of the HTTP Header read by this valve that holds the port used by the client to connect to the proxy. If not specified, the default of http的端口转换设置,能从http的header中拿到客户端的最原始端口 |
protocolHeaderHttpsValue | Value of the protocolHeader to indicate that it is an HTTPS request. If not specified, the default of |
httpServerPort | Value returned by 如果设置了protocolHeader ,但没设置portHeader属性,并且是http协议的; 该属性就是设置 ServletRequest.getServerPort() 的,默认如果不设置是80端口; |
httpsServerPort | Value returned by 该属性就是设置 ServletRequest.getServerPort() 的,默认如果不设置是443端口; |
changeLocalPort | If 端口
|
我们可以从属性推断,Tomcat实际是通过http头的属性,来找到原始IP地址,proxy地址的;
上述属性中需要区分的是internalProxies,trustProxies两个属性,这两个属性都是过滤的:
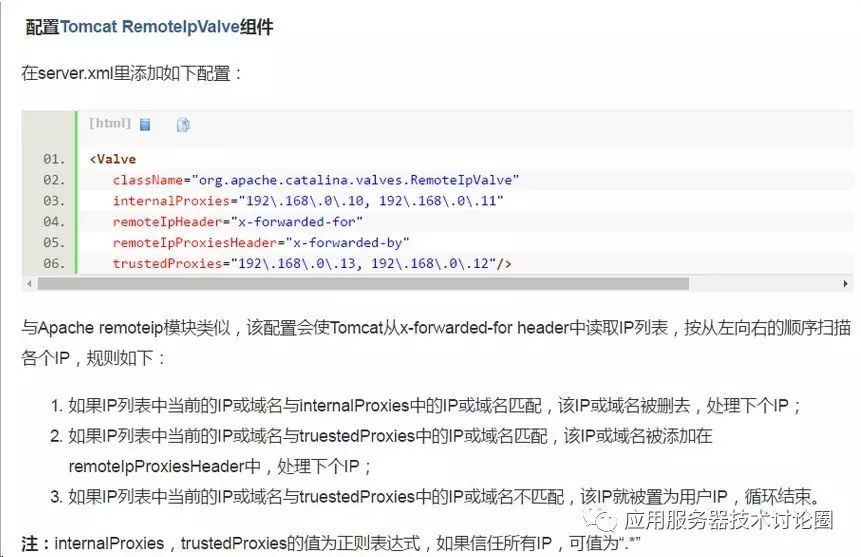
3.invoke方法源码解析

从invoke方法来看,最开始是保存了原有的request的这些属性,然后再进行原始IP,协议,端口等属性的改变,最后当执行完容器组件的pipeline之后,还原回来,保证整个web交易和原来一样,就像没有改过一样;





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








