一. 自定义过滤器配置:
dubbo filter可能是我们使用dubbo时最经常自定义的。通常用作一些公共处理,比如公共的日志打印让代码更简洁,和如上示例的通用异常结果处理等,配置过程如下:
1. 定义过滤器实现org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Filter接口,并在类上增加@Activate注解激活。
注解常用参数:
group:URL(org.apache.dubbo.common.URL)中的分组如果匹配则激活,如provider、consumer
value:URL中如果包含该key值则激活
before:填写扩展点列表,表示哪些扩展点要在本扩展点之前激活
after:表示哪些扩展点要在本扩展点之前激活
order:优先级(执行顺序)
过滤器类示例:
@Activate(
group = {CommonConstants.PROVIDER},
order = 1
)
public class DubboExceptionFilter implements Filter, Filter.Listener {
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Result appResponse, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable t, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
}
}2. 在配置文件 META-INF/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Filter 中增加:
xxFilter = 自定义Filter
例:
dubboExceptionFilter=com.wenzq.filter.DubboExceptionFilter使用dubbo提供的SPI扩展机制,扩展很便捷。
3. 如果需要排除指定过滤器,使其不生效,可在xml中配置filter名称前加"-"
例:
<dubbo:provider filter="-dubboLogFilter" ... ... />
<dubbo:consumer filter="-dubboLogFilter" ... ... />
<dubbo:service id="xxxProvider" interface="com.xxx.xxx" filter="-dubboLogFilter" ... ... />
<dubbo:reference id="xxxConsumer" interface="com.xxx.xxx" filter="-dubboLogFilter" ... ... />二. Dubbo过滤器原理:
使用起来这么便捷,那么过滤器是如何加载配置和执行的呢,接下来根据提供者、消费者过滤器一一分析。
Provider:
dubbo暴露服务时序大致如下:
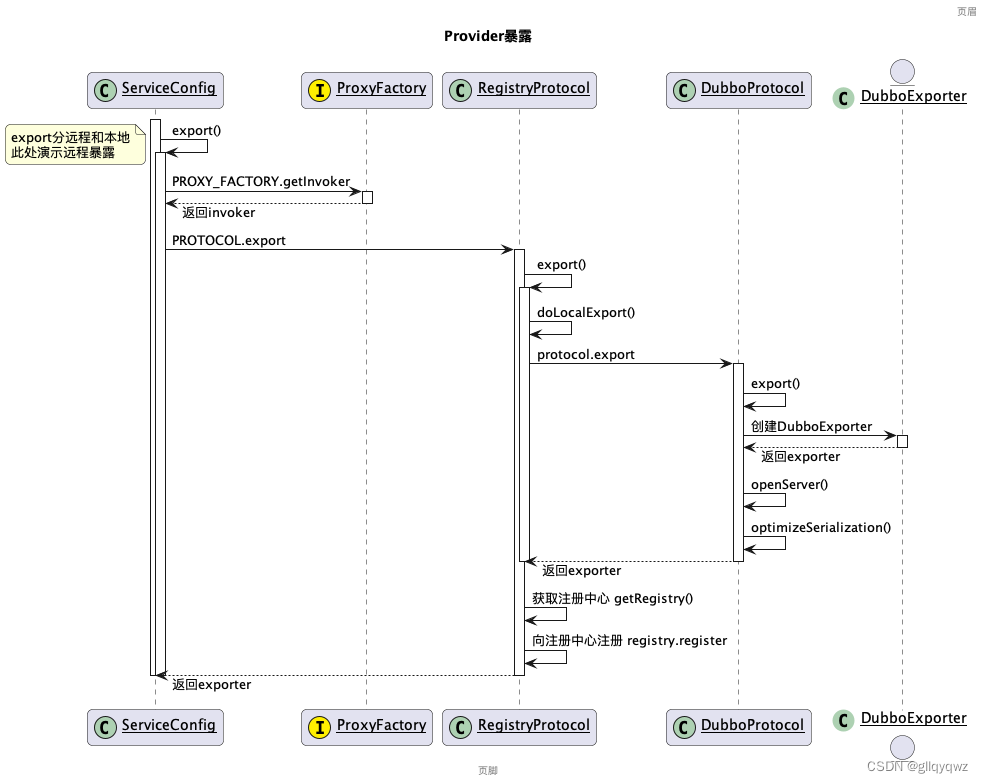
从上图可看出服务暴露调用顺序:
ServiceConfig.export -> RegistryProtocol.export -> DubboProtocol.export
此处我们重点关注DubboProtocol,注意DubboProtocol为包装后的增强实现(dubbo的SPI扩展点自适应机制,此处简单类比成spring的AOP,详细了解SPI机制可参考 官方文档),调用DubboProtocol时实际调用为:
ProtocolListenerWrapper -> ProtocolFilterWrapper -> QosProtocolWrapper -> DubboProtocol
构建过滤器链就在ProtocolListenerWrapper.export方法中完成,相关源码如下:
@Override
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
if (UrlUtils.isRegistry(invoker.getUrl())) {
return protocol.export(invoker);
}
// 构建过滤器链并暴露
return protocol.export(buildInvokerChain(invoker, SERVICE_FILTER_KEY, CommonConstants.PROVIDER));
}
/**
* 构建过滤器链
*/
private static <T> Invoker<T> buildInvokerChain(final Invoker<T> invoker, String key, String group) {
Invoker<T> last = invoker;
// 基于dubbo SPI active机制加载filter列表
List<Filter> filters = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Filter.class).getActivateExtension(invoker.getUrl(), key, group);
if (!filters.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = filters.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final Filter filter = filters.get(i);
// 新建过滤器节点,并放入当前节点
last = new FilterNode<T>(invoker, last, filter);
}
}
return last;
}其中入参invoker为实际调用,通过ExtensionLoader获取过滤器列表(已根据order排序),并以invoker作为最后一个节点倒序构建过滤器链。
接下来看过滤器链节点执行过程:每个节点执行invoke方法时,内部实际调用节点持有filter的invoke方法,执行时传入下一个节点。当前filter逻辑执行完毕后,内部会手动调用下一个节点的invoke方法,依次向下调用直到最终invoker,最终invoker执行完毕返回结果至顶层节点,调用完成,所以过滤器链最终调用顺序为:Filter1 -> Filter2 -> Filter3 ... ... -> Invoker。
可以看出调用链的每个节点都为invoker增加了功能,属装饰器模式的一种实现。
class FilterNode<T> implements Invoker<T>{
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result asyncResult;
try {
// 执行invoke传入下一个节点
asyncResult = filter.invoke(next, invocation);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (filter instanceof ListenableFilter) {
ListenableFilter listenableFilter = ((ListenableFilter) filter);
try {
Filter.Listener listener = listenableFilter.listener(invocation);
if (listener != null) {
listener.onError(e, invoker, invocation);
}
} finally {
listenableFilter.removeListener(invocation);
}
} else if (filter instanceof Filter.Listener) {
Filter.Listener listener = (Filter.Listener) filter;
listener.onError(e, invoker, invocation);
}
throw e;
} finally {
}
return asyncResult.whenCompleteWithContext((r, t) -> {
if (filter instanceof ListenableFilter) {
ListenableFilter listenableFilter = ((ListenableFilter) filter);
Filter.Listener listener = listenableFilter.listener(invocation);
try {
if (listener != null) {
if (t == null) {
listener.onResponse(r, invoker, invocation);
} else {
listener.onError(t, invoker, invocation);
}
}
} finally {
listenableFilter.removeListener(invocation);
}
} else if (filter instanceof Filter.Listener) {
Filter.Listener listener = (Filter.Listener) filter;
if (t == null) {
listener.onResponse(r, invoker, invocation);
} else {
listener.onError(t, invoker, invocation);
}
}
});
}
/**
* 省略部分代码 ... ...
*/
}Consumer:
dubbo服务引用时序大致如下:
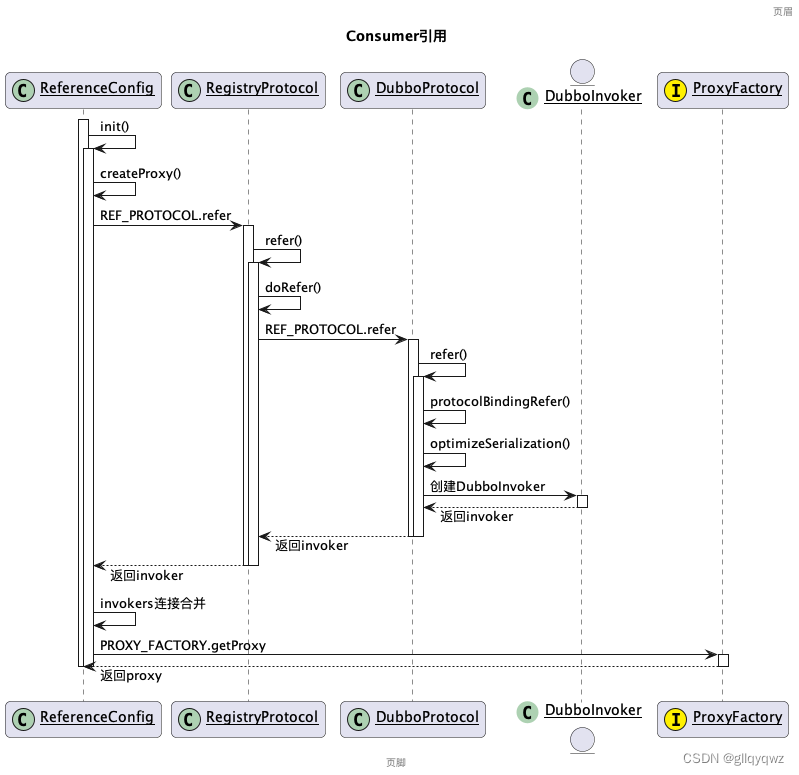
可以看出调用顺序:
RefrenceConfig.refer -> RegistryProtocol.refer -> DubboProtocol.refer
DubboProtocol与提供者同理,构建过滤器链在ProtocolListenerWrapper.refer方法中完成。
buildInvokerChain方法与服务提供者相同,过滤器调用也是类似的。
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
if (UrlUtils.isRegistry(url)) {
return protocol.refer(type, url);
}
return buildInvokerChain(protocol.refer(type, url), REFERENCE_FILTER_KEY, CommonConstants.CONSUMER);
}三. 原生过滤器:
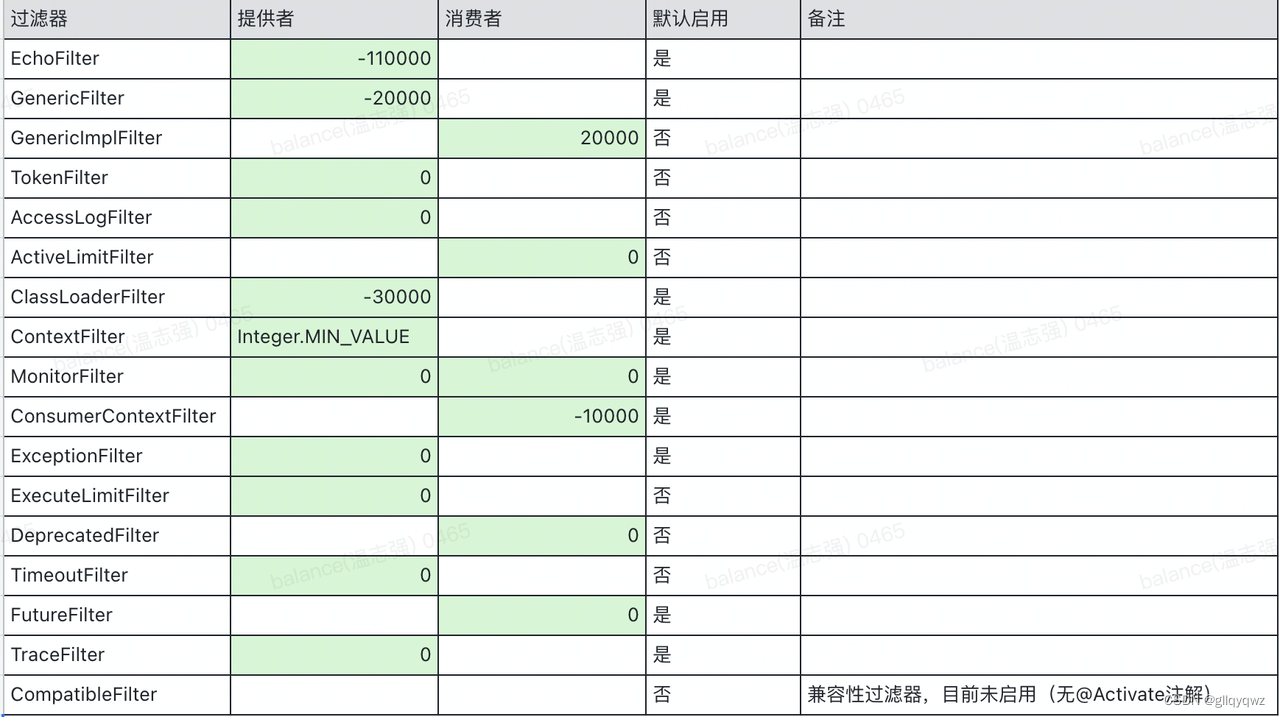
dubbo原生提供多个过滤器,配置在META-INF/dubbo/internal/org.apache.dubbo.rpc.filter文件中(详情见表格,绿色代表提供者/消费者生效,值为order)。接下来简要讲解过滤器用途和主要源码,篇幅原因挑选部分过滤器讲解。
说明:本文源码基于dubbo 2.7.16-release
提供者:
过滤器调用顺序:EchoFilter -> ClassLoaderFilter -> GenericFilter -> ContextFilter -> TraceFilter -> TimeoutFilter -> MonitorFilter -> ExceptionFilter
EchoFilter
用于回音测试,所谓回音测试就是Provider返回Consumer请求数据。
@Activate(group = CommonConstants.PROVIDER, order = -110000)
public class EchoFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
// 判断方法名是否$echo && 参数长度是否等于1
if (inv.getMethodName().equals($ECHO) && inv.getArguments() != null && inv.getArguments().length == 1) {
// 将传入参数返回(回声)
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(inv.getArguments()[0], inv);
}
return invoker.invoke(inv);
}
}ClassLoaderFilter
类加载过滤器,诈一看代码有点懵,切换线程的类加载器干啥?因为当前线程类加载器可能与Invoker接口类加载器不一致,但是当前线程中需要获取 Invoker 的类加载器中的一些 Class,以防出现 ClassNotFoundException异常。
@Activate(group = CommonConstants.PROVIDER, order = -30000)
public class ClassLoaderFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// 获取当前线程原类加载器
ClassLoader ocl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// 切换当前线程的类加载器为服务接口的类加载器
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(invoker.getInterface().getClassLoader());
try {
// 执行invoker
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} finally {
// 完成后,切换当前线程的类加载器为原类加载器
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(ocl);
}
}
}ContextFilter
服务提供者上下文过滤器,对应消费者上下文过滤器为ConsumerContextFilter。讲解ContextFilter就不得不谈谈RpcContext,dubbo提供了这个上下文用于给提供者/消费者隐式传递参数,并且只在当前调用链上生效。用途如:分布式链路追踪,traceId、spanId传递等。
消费端设置参数:
RpcContext.getContext().getObjectAttachments().put("consumerInfo","params");服务端读取参数:
Object providerInfo = RpcContext.getServerContext().getObjectAttachments().get("consumerInfo");反之服务端设置参数、消费端获取参数亦可。
@Activate(group = PROVIDER, order = Integer.MIN_VALUE)
public class ContextFilter implements Filter, Filter.Listener {
private static final String TAG_KEY = "dubbo.tag";
private static final Set<String> UNLOADING_KEYS;
static {
UNLOADING_KEYS = new HashSet<>(128);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(PATH_KEY);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(INTERFACE_KEY);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(GROUP_KEY);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(VERSION_KEY);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(DUBBO_VERSION_KEY);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(TOKEN_KEY);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(TIMEOUT_KEY);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(TIMEOUT_ATTACHMENT_KEY);
// Remove async property to avoid being passed to the following invoke chain.
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(ASYNC_KEY);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(TAG_KEY);
UNLOADING_KEYS.add(FORCE_USE_TAG);
}
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Map<String, Object> attachments = invocation.getObjectAttachments();
// 新建attachments
if (attachments != null) {
Map<String, Object> newAttach = new HashMap<>(attachments.size());
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : attachments.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
if (!UNLOADING_KEYS.contains(key)) {
newAttach.put(key, entry.getValue());
}
}
attachments = newAttach;
}
// 获取并设置RpcContext
RpcContext context = RpcContext.getContext();
context.setInvoker(invoker)
.setInvocation(invocation)
.setLocalAddress(invoker.getUrl().getHost(), invoker.getUrl().getPort());
String remoteApplication = (String) invocation.getAttachment(REMOTE_APPLICATION_KEY);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(remoteApplication)) {
context.setRemoteApplicationName(remoteApplication);
} else {
context.setRemoteApplicationName((String) context.getAttachment(REMOTE_APPLICATION_KEY));
}
long timeout = RpcUtils.getTimeout(invocation, -1);
if (timeout != -1) {
context.set(TIME_COUNTDOWN_KEY, TimeoutCountDown.newCountDown(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
// 设置RpcContext设置/添加attachments
if (attachments != null) {
if (context.getObjectAttachments() != null) {
context.getObjectAttachments().putAll(attachments);
} else {
context.setObjectAttachments(attachments);
}
}
// 设置RpcInvocation的invoker
if (invocation instanceof RpcInvocation) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).setInvoker(invoker);
}
try {
// 设置执行后不清除上下文
context.clearAfterEachInvoke(false);
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} finally {
// 设置执行后清除上下文
context.clearAfterEachInvoke(true);
// 并发场景下必须从当前线程移除RPCContext,所以同一线程每次调用都重新创建上下文
RpcContext.removeContext(true);
RpcContext.removeServerContext();
}
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Result appResponse, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
// 传递attachments到结果
appResponse.addObjectAttachments(RpcContext.getServerContext().getObjectAttachments());
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable t, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
}
}TimeOutFilter
超时过滤器
@Activate(group = CommonConstants.PROVIDER)
public class TimeoutFilter implements Filter, Filter.Listener {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TimeoutFilter.class);
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Result appResponse, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
// 从上下文中获取超时计时器
Object obj = RpcContext.getContext().get(TIME_COUNTDOWN_KEY);
if (obj != null) {
TimeoutCountDown countDown = (TimeoutCountDown) obj;
// 判断是否超时过期
if (countDown.isExpired()) {
// 超时情况,清空response
((AppResponse) appResponse).clear();
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
// 输出警告日志
logger.warn("invoke timed out. method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " arguments: " +
Arrays.toString(invocation.getArguments()) + " , url is " + invoker.getUrl() +
", invoke elapsed " + countDown.elapsedMillis() + " ms.");
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable t, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
}
}MonitorFilter
监控过滤器,用于采集请求成功数、失败数、吞吐量、当前并发数、接口响应时长等。配置monitor后,MonitorFilter将采集监控信息并完成上报。
配置示例:
<dubbo:monitor address="dubbo://127.0.0.1:10880" />@Activate(group = {PROVIDER, CONSUMER})
public class MonitorFilter implements Filter, Filter.Listener {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MonitorFilter.class);
private static final String MONITOR_FILTER_START_TIME = "monitor_filter_start_time";
private static final String MONITOR_REMOTE_HOST_STORE = "monitor_remote_host_store";
/**
* The Concurrent counter
*/
private final ConcurrentMap<String, AtomicInteger> concurrents = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, AtomicInteger>();
/**
* The MonitorFactory
*/
private MonitorFactory monitorFactory;
public void setMonitorFactory(MonitorFactory monitorFactory) {
this.monitorFactory = monitorFactory;
}
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (invoker.getUrl().hasParameter(MONITOR_KEY)) {
invocation.put(MONITOR_FILTER_START_TIME, System.currentTimeMillis());
invocation.put(MONITOR_REMOTE_HOST_STORE, RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost());
// 获取计数器+1
getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).incrementAndGet(); // count up
}
// 执行invoker
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
private AtomicInteger getConcurrent(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
String key = invoker.getInterface().getName() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
return concurrents.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new AtomicInteger());
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Result result, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
if (invoker.getUrl().hasParameter(MONITOR_KEY)) {
collect(invoker, invocation, result, (String) invocation.get(MONITOR_REMOTE_HOST_STORE), (long) invocation.get(MONITOR_FILTER_START_TIME), false);
// 获取计数器-1
getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).decrementAndGet(); // count down
}
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable t, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
if (invoker.getUrl().hasParameter(MONITOR_KEY)) {
collect(invoker, invocation, null, (String) invocation.get(MONITOR_REMOTE_HOST_STORE), (long) invocation.get(MONITOR_FILTER_START_TIME), true);
// 获取计数器-1
getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).decrementAndGet(); // count down
}
}
private void collect(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation, Result result, String remoteHost, long start, boolean error) {
try {
URL monitorUrl = invoker.getUrl().getUrlParameter(MONITOR_KEY);
// 通过监控工厂获取监控对象
Monitor monitor = monitorFactory.getMonitor(monitorUrl);
if (monitor == null) {
return;
}
URL statisticsURL = createStatisticsUrl(invoker, invocation, result, remoteHost, start, error);
monitor.collect(statisticsURL);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to monitor count service " + invoker.getUrl() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
}
private URL createStatisticsUrl(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation, Result result, String remoteHost, long start, boolean error) {
// ---- service statistics ----
// 计算调用耗时
long elapsed = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
// 当前并发数量
int concurrent = getConcurrent(invoker, invocation).get();
String application = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(APPLICATION_KEY);
// 接口名称
String service = invoker.getInterface().getName();
// 方法名称
String method = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
// 分组信息
String group = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(GROUP_KEY);
// 版本信息
String version = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(VERSION_KEY);
int localPort;
String remoteKey, remoteValue;
if (CONSUMER_SIDE.equals(invoker.getUrl().getParameter(SIDE_KEY))) {
// 消费者时
localPort = 0;
remoteKey = MonitorService.PROVIDER;
remoteValue = invoker.getUrl().getAddress();
} else {
// 提供者时
localPort = invoker.getUrl().getPort();
remoteKey = MonitorService.CONSUMER;
remoteValue = remoteHost;
}
String input = "", output = "";
if (invocation.getAttachment(INPUT_KEY) != null) {
input = invocation.getAttachment(INPUT_KEY);
}
if (result != null && result.getAttachment(OUTPUT_KEY) != null) {
output = result.getAttachment(OUTPUT_KEY);
}
// 返回统计URL
return new URL(COUNT_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.getLocalHost(), localPort, service + PATH_SEPARATOR + method, MonitorService.APPLICATION, application, MonitorService.INTERFACE, service, MonitorService.METHOD, method, remoteKey, remoteValue, error ? MonitorService.FAILURE : MonitorService.SUCCESS, "1", MonitorService.ELAPSED, String.valueOf(elapsed), MonitorService.CONCURRENT, String.valueOf(concurrent), INPUT_KEY, input, OUTPUT_KEY, output, GROUP_KEY, group, VERSION_KEY, version);
}
}ExceptionFilter
异常处理过滤器
@Activate(group = CommonConstants.PROVIDER)
public class ExceptionFilter implements Filter, Filter.Listener {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExceptionFilter.class);
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Result appResponse, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
// 判断是否包含异常
if (appResponse.hasException() && GenericService.class != invoker.getInterface()) {
try {
Throwable exception = appResponse.getException();
// 1. 非运行时异常且是检查型异常时,直接抛出
if (!(exception instanceof RuntimeException) && (exception instanceof Exception)) {
return;
}
// 2. 判断接口声明中是否抛出目标异常,是则直接抛出
try {
Method method = invoker.getInterface().getMethod(invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes());
Class<?>[] exceptionClasses = method.getExceptionTypes();
for (Class<?> exceptionClass : exceptionClasses) {
if (exception.getClass().equals(exceptionClass)) {
return;
}
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
return;
}
// 接口声明中没有包含目标异常,打印ERROR日志
logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost() + ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", exception: " + exception.getClass().getName() + ": " + exception.getMessage(), exception);
// 3. 如果异常类和接口类型在同一jar中,直接抛出
String serviceFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(invoker.getInterface());
String exceptionFile = ReflectUtils.getCodeBase(exception.getClass());
if (serviceFile == null || exceptionFile == null || serviceFile.equals(exceptionFile)) {
return;
}
// 4. 根据异常类包名前缀判断是否jdk异常,是则抛出
String className = exception.getClass().getName();
if (className.startsWith("java.") || className.startsWith("javax.")) {
return;
}
// 5. 判断是否dubbo异常,是则抛出
if (exception instanceof RpcException) {
return;
}
// 6. 包装成RuntimeException抛出(填充异常内容)
appResponse.setException(new RuntimeException(StringUtils.toString(exception)));
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.warn("Fail to ExceptionFilter when called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost() + ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", exception: " + e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
logger.error("Got unchecked and undeclared exception which called by " + RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteHost() + ". service: " + invoker.getInterface().getName() + ", method: " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", exception: " + e.getClass().getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
public void setLogger(Logger logger) {
this.logger = logger;
}
}消费者:
消费者过滤器调用顺序:ConsumerContextFilter->FutureFilter->MonitorFilter->GenericImplFilter(仅限泛化调用)
ConsumerContextFilter
服务消费者上下文过滤器
@Activate(group = CONSUMER, order = -10000)
public class ConsumerContextFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// 获取并设置context
RpcContext context = RpcContext.getContext();
context.setInvoker(invoker)
.setInvocation(invocation)
.setLocalAddress(NetUtils.getLocalHost(), 0)
.setRemoteAddress(invoker.getUrl().getHost(), invoker.getUrl().getPort())
.setRemoteApplicationName(invoker.getUrl().getParameter(REMOTE_APPLICATION_KEY))
.setAttachment(REMOTE_APPLICATION_KEY, invoker.getUrl().getParameter(APPLICATION_KEY));
// 设置RpcInvocation的invoker
if (invocation instanceof RpcInvocation) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).setInvoker(invoker);
}
// 获取超时计时器(此处为用户最终配置超时时间)
Object countDown = context.get(TIME_COUNTDOWN_KEY);
if (countDown != null) {
TimeoutCountDown timeoutCountDown = (TimeoutCountDown) countDown;
// 如果超时返回超时异常结果
if (timeoutCountDown.isExpired()) {
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(new RpcException(RpcException.TIMEOUT_TERMINATE,
"No time left for making the following call: " + invocation.getServiceName() + "."
+ invocation.getMethodName() + ", terminate directly."), invocation);
}
}
// 调用invoker并返回
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
}MonitorFilter
同提供者
FutureFilter
FutureFilter调用之前、调用之后、出现异常时,会触发 oninvoke、onreturn、onthrow 三个事件,可以配置当事件发生时,通知对应类的对应方法。
详细可参考:官方示例
@Activate(group = CommonConstants.CONSUMER)
public class FutureFilter implements Filter, Filter.Listener {
protected static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FutureFilter.class);
@Override
public Result invoke(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
fireInvokeCallback(invoker, invocation);
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Result result, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
if (result.hasException()) {
fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, result.getException());
} else {
fireReturnCallback(invoker, invocation, result.getValue());
}
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable t, Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, t);
}
private void fireInvokeCallback(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation) {
// 获取异步方法MethodInfo
final AsyncMethodInfo asyncMethodInfo = getAsyncMethodInfo(invoker, invocation);
if (asyncMethodInfo == null) {
return;
}
// 获取回调方法、回调实例
final Method onInvokeMethod = asyncMethodInfo.getOninvokeMethod();
final Object onInvokeInst = asyncMethodInfo.getOninvokeInstance();
if (onInvokeMethod == null && onInvokeInst == null) {
return;
}
if (onInvokeMethod == null || onInvokeInst == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("service:" + invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey() + " has a oninvoke callback config , but no such " + (onInvokeMethod == null ? "method" : "instance") + " found. url:" + invoker.getUrl());
}
// 修改方法访问权限
ReflectUtils.makeAccessible(onInvokeMethod);
// 获取调用入参
Object[] params = invocation.getArguments();
try {
// 调用回调方法(反射)
onInvokeMethod.invoke(onInvokeInst, params);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// 捕获异常调用异常处理方法fireThrowCallback
fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, e.getTargetException());
} catch (Throwable e) {
fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, e);
}
}
private void fireReturnCallback(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation, final Object result) {
// 获取异步方法MethodInfo
final AsyncMethodInfo asyncMethodInfo = getAsyncMethodInfo(invoker, invocation);
if (asyncMethodInfo == null) {
return;
}
// 获取回调方法、回调实例
final Method onReturnMethod = asyncMethodInfo.getOnreturnMethod();
final Object onReturnInst = asyncMethodInfo.getOnreturnInstance();
if (onReturnMethod == null && onReturnInst == null) {
return;
}
if (onReturnMethod == null || onReturnInst == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("service:" + invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey() + " has a onreturn callback config , but no such " + (onReturnMethod == null ? "method" : "instance") + " found. url:" + invoker.getUrl());
}
// 修改方法访问权限
ReflectUtils.makeAccessible(onReturnMethod);
// 获取调用入参
Object[] args = invocation.getArguments();
Object[] params;
Class<?>[] rParaTypes = onReturnMethod.getParameterTypes();
// 判断回调方法入参是否大于1
if (rParaTypes.length > 1) {
// 如果参数数量为2且第二个参数为Object数组,则1设置调用结果,2设置调用入参
if (rParaTypes.length == 2 && rParaTypes[1].isAssignableFrom(Object[].class)) {
params = new Object[2];
params[0] = result;
params[1] = args;
} else {
// 否则1设置调用结果,后续顺序设置入参
params = new Object[args.length + 1];
params[0] = result;
System.arraycopy(args, 0, params, 1, args.length);
}
} else {
// 参数数量为1,直接赋值调用结果
params = new Object[]{result};
}
try {
// 调用回调方法(反射)
onReturnMethod.invoke(onReturnInst, params);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// 捕获异常调用异常处理方法fireThrowCallback
fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, e.getTargetException());
} catch (Throwable e) {
fireThrowCallback(invoker, invocation, e);
}
}
// 核心代码与fireReturnCallback一致,不赘述
private void fireThrowCallback(final Invoker<?> invoker, final Invocation invocation, final Throwable exception) {
final AsyncMethodInfo asyncMethodInfo = getAsyncMethodInfo(invoker, invocation);
if (asyncMethodInfo == null) {
return;
}
final Method onthrowMethod = asyncMethodInfo.getOnthrowMethod();
final Object onthrowInst = asyncMethodInfo.getOnthrowInstance();
if (onthrowMethod == null && onthrowInst == null) {
return;
}
if (onthrowMethod == null || onthrowInst == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("service:" + invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey() + " has a onthrow callback config , but no such " + (onthrowMethod == null ? "method" : "instance") + " found. url:" + invoker.getUrl());
}
ReflectUtils.makeAccessible(onthrowMethod);
Class<?>[] rParaTypes = onthrowMethod.getParameterTypes();
if (rParaTypes[0].isAssignableFrom(exception.getClass())) {
try {
Object[] args = invocation.getArguments();
Object[] params;
if (rParaTypes.length > 1) {
if (rParaTypes.length == 2 && rParaTypes[1].isAssignableFrom(Object[].class)) {
params = new Object[2];
params[0] = exception;
params[1] = args;
} else {
params = new Object[args.length + 1];
params[0] = exception;
System.arraycopy(args, 0, params, 1, args.length);
}
} else {
params = new Object[]{exception};
}
onthrowMethod.invoke(onthrowInst, params);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(invocation.getMethodName() + ".call back method invoke error . callback method :" + onthrowMethod + ", url:" + invoker.getUrl(), e);
}
} else {
logger.error(invocation.getMethodName() + ".call back method invoke error . callback method :" + onthrowMethod + ", url:" + invoker.getUrl(), exception);
}
}
private AsyncMethodInfo getAsyncMethodInfo(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
AsyncMethodInfo asyncMethodInfo = (AsyncMethodInfo) invocation.get(ASYNC_METHOD_INFO);
if (asyncMethodInfo != null) {
return asyncMethodInfo;
}
ConsumerModel consumerModel = ApplicationModel.getConsumerModel(invoker.getUrl().getServiceKey());
if (consumerModel == null) {
return null;
}
String methodName = invocation.getMethodName();
if (methodName.equals($INVOKE)) {
methodName = (String) invocation.getArguments()[0];
}
// 返回AsyncMethodInfo(初始化:ReferenceConfig.init -> AbstractConfig.convertMethodConfig2AsyncInfo)
return consumerModel.getAsyncInfo(methodName);
}
}




















 3398
3398











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








