Socket编程
socket不是新兴的技术,也不是时的技术,但是是最基本的技术,如果我们做系统架构或者开发组件的时候,就看这方面的知识功底是否扎实,这个知识对大家的长远发展是有好处的。
socket和做项目不同,socket虽然可能没有项目对 找工作更有用。做项目用到的技术一般都是基本的增删改查,有些项目的技术含量可能没有那么高,但是确实对找工作很有帮助。但是如果大家想要在技术行业长远发展,socket通信和多线程等基本知识是必须要掌握的。
所以,为什么要学习socket?可以说,socket是大家后面要学习的iavaweb的基石。整个的iavaweb开发都是建立在socket通信的基础之上的。而ssm或者springboot,或者分布式微服务,都是基于socket的上层建筑。学习socket对于我们理解tomcat底层原理,框架、rpc框架原理以及其他中间件的底层等都是有好处的。
软件架构
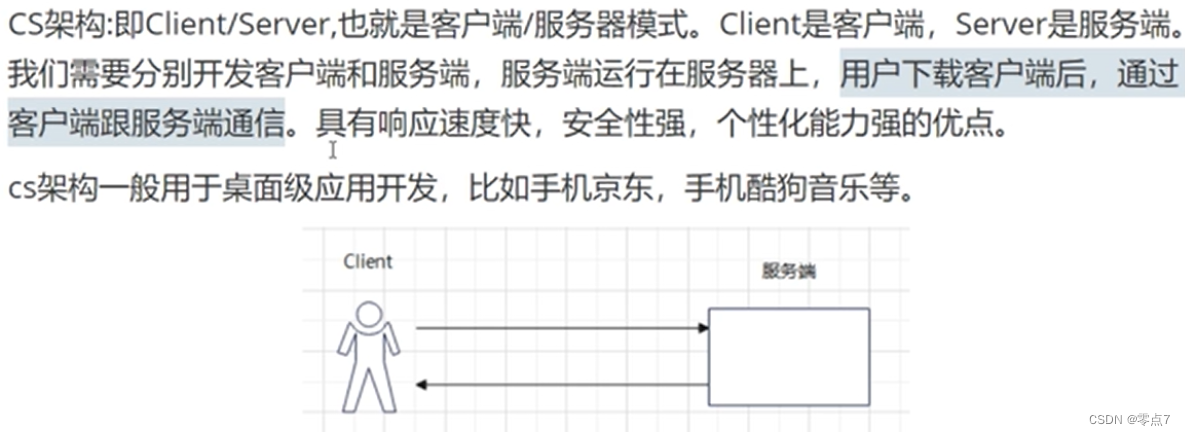
C/S(Client/Server)
客户端和服务器结构 QQ 360 美团app 需不断更新升级 重新下载等
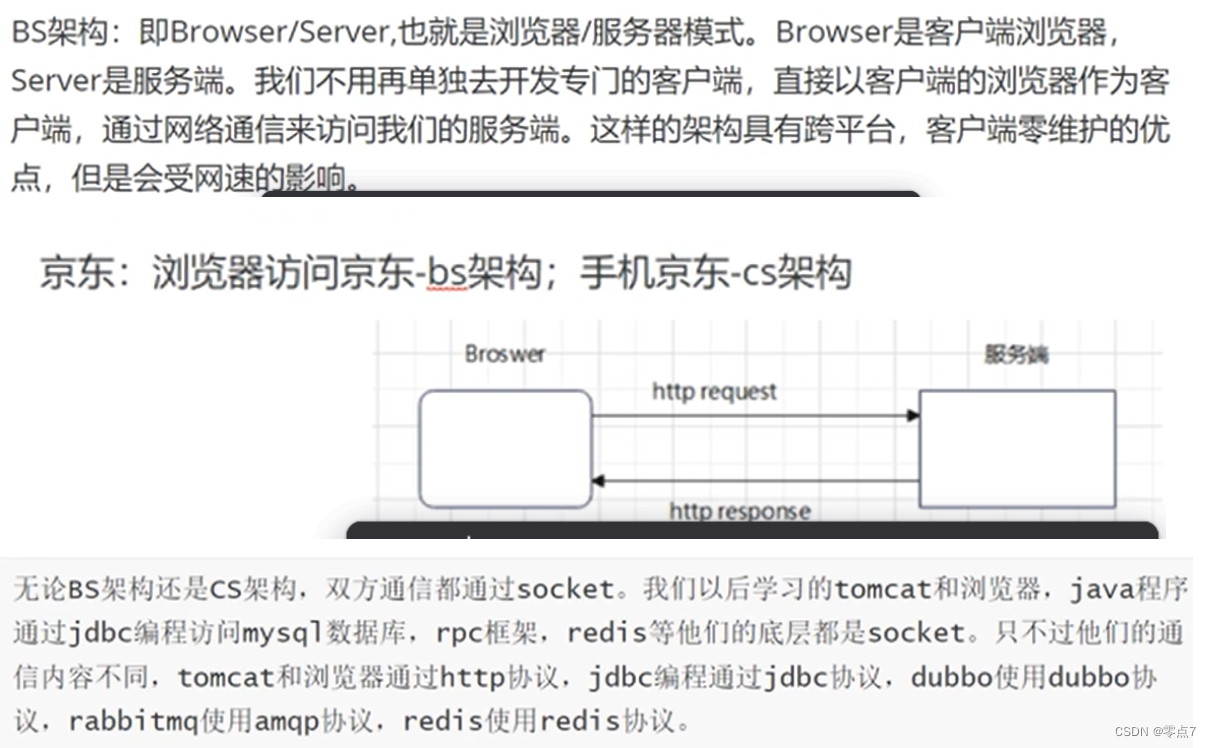
B/S架构 Browser/Server
网络协议
-
TCP:TCP(英语:Transmission Control Protocol,传输控制协议) 是一种面向连接的、可靠的、基于字节流的传输层通信协议,TCP 层是位于 IP 层之上,应用层之下的中间层。TCP 保障了两个应用程序之间的可靠通信。通常用于互联网协议,被称 TCP / IP。
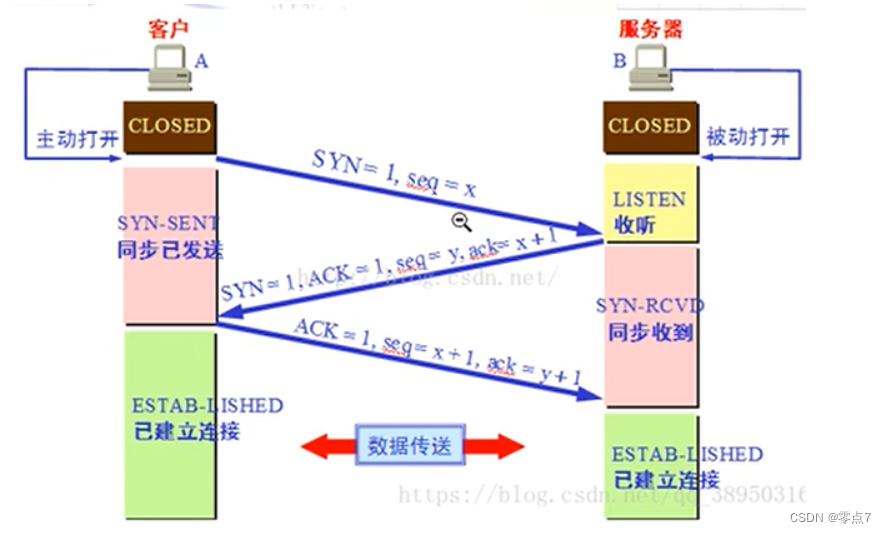
三次握手 四次挥手
1.A请求建立连接
2.B收到请求,确认连接
3.A接收连接,建立连接
1.A请求断开
2.B接收断开信息
3.B询问A是否已经断 开
4.A通知B已经断开
-
UDP:UDP (英语:User Datagram Protocol,用户数据报协议),位于 OSI 模型的传输层。一个无连接的协议。提供了应用程序之间要发送数据的数据报。由于UDP缺乏可靠性且属于无连接协议,所以应用程序通常必须容许一些丢失、错误或重复的数据包。
Socket编程
套接字使用TCP提供了两台计算机之间的通信机制。 客户端程序创建一个套接字,并尝试连接服务器的套接字。当连接建立时,服务器会创建一个 Socket 对象。客户端和服务器现在可以通过对 Socket 对象的写入和读取来进行通信。
以下步骤在两台计算机之间使用套接字建立TCP连接时会出现:
- 服务器示例化一个 ServerSocket 对象,表示通过服务器上的端口通信。
- 服务器调用 ServerSocket 类的 accept() 方法,该方法将一直等待,直到客户端连接到服务器上给定的端口。
- 服务器正在等待时,一个客户端示例化一个 Socket 对象,指定服务器名称和端口号来请求连接。
- Socket 类的构造函数试图将客户端连接到指定的服务器和端口号。如果通信被建立,则在客户端创建一个 Socket 对象能够与服务器进行通信。
- 在服务器端,accept() 方法返回服务器上一个新的 socket 引用,该 socket 连接到客户端的 socket。
连接建立后,通过使用 I/O 流在进行通信,每一个socket都有一个输出流和一个输入流,客户端的输出流连接到服务器端的输入流,而客户端的输入流连接到服务器端的输出流。
TCP 是一个双向的通信协议,因此数据可以通过两个数据流在同一时间发送.以下是一些类提供的一套完整的有用的方法来实现 socket。
ServerSocket 类的方法
服务器应用程序通过使用 java.net.ServerSocket 类以获取一个端口,并且侦听客户端请求。
ServerSocket 类有四个构造方法:
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public ServerSocket(int port) throws IOException 创建绑定到特定端口的服务器套接字。 |
| 2 | public ServerSocket(int port, int backlog) throws IOException 利用指定的 backlog 创建服务器套接字并将其绑定到指定的本地端口号。 |
| 3 | public ServerSocket(int port, int backlog, InetAddress address) throws IOException 使用指定的端口、侦听 backlog 和要绑定到的本地 IP 地址创建服务器。 |
| 4 | public ServerSocket() throws IOException 创建非绑定服务器套接字。 |
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public int getLocalPort() 返回此套接字在其上侦听的端口。 |
| 2 | public Socket accept() throws IOException 侦听并接受到此套接字的连接。 |
| 3 | public void setSoTimeout(int timeout) 通过指定超时值启用/禁用 SO_TIMEOUT,以毫秒为单位。 |
| 4 | public void bind(SocketAddress host, int backlog) 将 ServerSocket 绑定到特定地址(IP 地址和端口号)。 |
Socket 类的方法
java.net.Socket 类代表客户端和服务器都用来互相沟通的套接字。客户端要获取一个 Socket 对象通过示例化 ,而 服务器获得一个 Socket 对象则通过 accept() 方法的返回值。
Socket 类有五个构造方法.
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public Socket(String host, int port) throws UnknownHostException, IOException. 创建一个流套接字并将其连接到指定主机上的指定端口号。 |
| 2 | public Socket(InetAddress host, int port) throws IOException 创建一个流套接字并将其连接到指定 IP 地址的指定端口号。 |
| 3 | public Socket(String host, int port, InetAddress localAddress, int localPort) throws IOException. 创建一个套接字并将其连接到指定远程主机上的指定远程端口。 |
| 4 | public Socket(InetAddress host, int port, InetAddress localAddress, int localPort) throws IOException. 创建一个套接字并将其连接到指定远程地址上的指定远程端口。 |
| 5 | public Socket() 通过系统默认类型的 SocketImpl 创建未连接套接字 |
当 Socket 构造方法返回,并没有简单的示例化了一个 Socket 对象,它实际上会尝试连接到指定的服务器和端口。
下面列出了一些感兴趣的方法,注意客户端和服务器端都有一个 Socket 对象,所以无论客户端还是服务端都能够调用这些方法。
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public void connect(SocketAddress host, int timeout) throws IOException 将此套接字连接到服务器,并指定一个超时值。 |
| 2 | public InetAddress getInetAddress() 返回套接字连接的地址。 |
| 3 | public int getPort() 返回此套接字连接到的远程端口。 |
| 4 | public int getLocalPort() 返回此套接字绑定到的本地端口。 |
| 5 | public SocketAddress getRemoteSocketAddress() 返回此套接字连接的端点的地址,如果未连接则返回 null。 |
| 6 | public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException 返回此套接字的输入流。 |
| 7 | public OutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException 返回此套接字的输出流。 |
| 8 | public void close() throws IOException 关闭此套接字。 |
InetAddress 类的方法
这个类表示互联网协议(IP)地址。下面列出了 Socket 编程时比较有用的方法:
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | static InetAddress getByAddress(byte[] addr) 在给定原始 IP 地址的情况下,返回 InetAddress 对象。 |
| 2 | static InetAddress getByAddress(String host, byte[] addr) 根据提供的主机名和 IP 地址创建 InetAddress。 |
| 3 | static InetAddress getByName(String host) 在给定主机名的情况下确定主机的 IP 地址。 |
| 4 | String getHostAddress() 返回 IP 地址字符串(以文本表现形式)。 |
| 5 | String getHostName() 获取此 IP 地址的主机名。 |
| 6 | static InetAddress getLocalHost() 返回本地主机。 |
| 7 | String toString() 将此 IP 地址转换为 String。 |
案例 1
此案例中客户端向服务端发送数据,服务端将其打印到控制台。
客户端
//客户端 发送消息
@Test
public void client() {
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
//创建一个socket
InetAddress inetAddress = Inet4Address.getByName("localhost");//声明对方的IP地址
int port = 8989; //声明对方的端口号
socket = new Socket(inetAddress, port);
//发送数据
outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("你好,我是客户端".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//关闭socket
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
// 关闭流
if (outputStream != null) {
outputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
服务器端
//服务器 接收消息并打印
@Test
public void server(){
int port = 8989;
//创建一个serverSocket
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
Socket accept = null;
try {
serverSocket= new ServerSocket(port);
//调用accept方法,接收客户端socket
accept = serverSocket.accept(); //阻塞式
System.out.println("服务器端开启");
System.out.println("收到了来自"+accept.getInetAddress().getHostAddress()+"的连接");
//接收数据
inputStream = accept.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
int len = 0;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
// String s = new String(bytes, 0, len);
// System.out.print(s);
baos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
System.out.println("数据接收完毕");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (accept != null) {
accept.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (serverSocket != null) {
serverSocket.close();//实际引用不关闭
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
案例2
此案例客户端先服务端发送文件,服务端接收并保存到本地后返回保存成功信息。
服务端
// 服务器将文件保存至本地 返回上传成功给客户端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket clientSocket = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
//创建ServerSocket
int port = 8989;
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
//accept接收
clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
//通过socket获取输入流
inputStream = clientSocket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
//创建File FileOutPutStream
File file = new File("F:\\Java\\徐Java\\src\\com\\baseStage\\socket\\鬼灭_copy.jpg");
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
//读写
while ((len =inputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
System.out.println("文件成功保存到本地");
//发送 上传成功给客户端
OutputStream outputStream = clientSocket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("图片保存本地成功".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
// clientSocket.shutdownOutput();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {//关闭socket 和流
try {
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (clientSocket != null) {
clientSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (serverSocket != null) {
serverSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户端
//客户端发送文件给服务器。
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
Socket socket = null;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
OutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
//创建socket
InetAddress inetAddress = Inet4Address.getByName("localhost");
int port =8989;
socket = new Socket(inetAddress,port);
//创建File 和FileInputStream
File file = new File("F:\\Java\\徐Java\\src\\com\\baseStage\\socket\\鬼灭.jpg");
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
// 读取文件
//通过socket获取输出流
outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
while ((len = fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
outputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
// 读写数据
System.out.println("图片上传成功");
socket.shutdownOutput();
//接收服务器发送的数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
baos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
System.out.println("接收服务器返回数据成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {//关闭socket 和流
try {
if (outputStream != null) {
outputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fileInputStream != null) {
fileInputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
案例3
此案例,采用多线程,实现一个服务端可以同时被多个客户端访问,每个客户端访问都会创建一个线程来为客户端处理请求。
服务端
public class ServerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("服务端: " + "服务器启动");
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
Worker worker = new Worker(socket);
Thread thread = new Thread(worker);
thread.start();
}
}
线程类
public class Worker implements Runnable{
Socket socket;
public Worker(Socket socket){
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
InputStream inputStream =null;
OutputStream outputStream = null;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("服务端: " + "客户端可以发送消息了");
while (true){
try {
inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
//读取客户端发送的信息
byte[] bytes = new byte[2048];
int len = inputStream.read(bytes);
String s = new String(bytes, 0, len);
if (s.equals("bye")) {
break;
}else {System.out.println(s);}
//发送给客户端消息
outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
String str = scanner.nextLine();
outputStream.write(("服务端: " + str).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (outputStream != null) {
outputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
客户端1
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 9999);
System.out.println("客户端1: " + "连接到服务器端口");
OutputStream socketOutputStream = null;
InputStream socketInputStream = null;
while (true){
//获取控制台输入,发送给服务端
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.nextLine();
socketOutputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
socketOutputStream.write(("客户端1: " + str).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
socketOutputStream.close();
//获取服务端传递的信息
socketInputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[2048];
int read = socketInputStream.read(bytes1);
System.out.println(new String(bytes1, 0, read));
}
}
}
客户端2
public class ClientTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 9999);
System.out.println("客户端2: " + "连接到服务器端口");
OutputStream socketOutputStream = null;
InputStream socketInputStream = null;
while (true){
//获取控制台输入,发送给服务端
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.nextLine();
socketOutputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
socketOutputStream.write(("客户端2: " + str).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//获取服务端传递的信息
socketInputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[2048];
int read = socketInputStream.read(bytes1);
System.out.println(new String(bytes1, 0, read));
}
}
}





















 7962
7962











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








