TCP网络通信时候会发生粘包/拆包的问题,接下来探讨其解决之道。
什么是粘包/拆包
一般所谓的TCP粘包是在一次接收数据不能完全地体现一个完整的消息数据。TCP通讯为何存在粘包呢?主要原因是TCP是以流的方式来处理数据,再加上网络上MTU(最大传输单元)的往往小于在应用处理的消息数据,所以就会引发一次接收的数据无法满足消息的需要,导致粘包的存在。处理粘包的唯一方法就是制定应用层的数据通讯协议,通过协议来规范现有接收的数据是否满足消息数据的需要。
情况分析
TCP粘包通常在流传输中出现,UDP则不会出现粘包,因为UDP有消息边界,发送数据段需要等待缓冲区满了才将数据发送出去,当满的时候有可能不是一条消息而是几条消息合并在换中去内,在成粘包;另外接收数据端没能及时接收缓冲区的包,造成了缓冲区多包合并接收,也是粘包。
解决办法
1、消息定长,报文大小固定长度,不够空格补全,发送和接收方遵循相同的约定,这样即使粘包了通过接收方编程实现获取定长报文也能区分。
2、包尾添加特殊分隔符,例如每条报文结束都添加回车换行符(例如FTP协议)或者指定特殊字符作为报文分隔符,接收方通过特殊分隔符切分报文区分。
3、将消息分为消息头和消息体,消息头中包含表示信息的总长度(或者消息体长度)的字段
4、更复杂的自定义应用层协议
代码例子
1、Netty中提供了FixedLengthFrameDecoder定长解码器可以帮助我们轻松实现第一种解决方案,定长解码报文。
服务器端:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
package
im;
import
io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import
io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import
io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import
io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import
io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
import
io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import
io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import
io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
/**
* 定长解码 服务器端
* @author xwalker
*/
public
class
Server {
public
void
bind(
int
port)
throws
Exception{
//接收客户端连接用
EventLoopGroup bossGroup=
new
NioEventLoopGroup();
//处理网络读写事件
EventLoopGroup workerGroup=
new
NioEventLoopGroup();
try
{
//配置服务器启动类
ServerBootstrap b=
new
ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.
class
).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,
100
)
.handler(
new
LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
//配置日志输出
.childHandler(
new
ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected
void
initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws
Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new
FixedLengthFrameDecoder(
30
));
//设置定长解码器 长度设置为30
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new
StringDecoder());
//设置字符串解码器 自动将报文转为字符串
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new
Serverhandler());
//处理网络IO 处理器
}
});
//绑定端口 等待绑定成功
ChannelFuture f=b.bind(port).sync();
//等待服务器退出
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
finally
{
//释放线程资源
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception {
int
port=
8000
;
new
Server().bind(port);
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
package
im;
import
io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import
io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* 服务器handler
* @author xwalker
*/
public
class
Serverhandler
extends
ChannelHandlerAdapter {
int
counter=
0
;
private
static
final
String MESSAGE=
"It greatly simplifies and streamlines network programming such as TCP and UDP socket server."
;
@Override
public
void
channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws
Exception {
System.out.println(
"接收客户端msg:["
+msg+
"]"
);
ByteBuf echo=Unpooled.copiedBuffer(MESSAGE.getBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(echo);
}
@Override
public
void
exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws
Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
|
客户端:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
package
im;
import
io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import
io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import
io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import
io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import
io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import
io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder;
import
io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
/**
* 客户端
* @author xwalker
*
*/
public
class
Client {
/**
* 链接服务器
* @param port
* @param host
* @throws Exception
*/
public
void
connect(
int
port,String host)
throws
Exception{
//网络事件处理线程组
EventLoopGroup group=
new
NioEventLoopGroup();
try
{
//配置客户端启动类
Bootstrap b=
new
Bootstrap();
b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.
class
)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY,
true
)
//设置封包 使用一次大数据的写操作,而不是多次小数据的写操作
.handler(
new
ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected
void
initChannel(SocketChannel ch)
throws
Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new
FixedLengthFrameDecoder(
30
));
//设置定长解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new
StringDecoder());
//设置字符串解码器
ch.pipeline().addLast(
new
ClientHandler());
//设置客户端网络IO处理器
}
});
//连接服务器 同步等待成功
ChannelFuture f=b.connect(host,port).sync();
//同步等待客户端通道关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
finally
{
//释放线程组资源
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public
static
void
main(String[] args)
throws
Exception {
int
port=
8000
;
new
Client().connect(port,
"127.0.0.1"
);
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
package
im;
import
io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import
io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* 客户端处理器
* @author xwalker
*
*/
public
class
ClientHandler
extends
ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private
static
final
String MESSAGE=
"Netty is a NIO client server framework which enables quick and easy development of network applications such as protocol servers and clients."
;
public
ClientHandler(){}
@Override
public
void
channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx)
throws
Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(MESSAGE.getBytes()));
}
@Override
public
void
channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
throws
Exception {
System.out.println(
"接收服务器响应msg:["
+msg+
"]"
);
}
@Override
public
void
channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx)
throws
Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public
void
exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws
Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
|
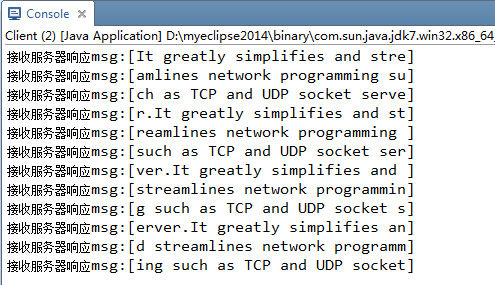
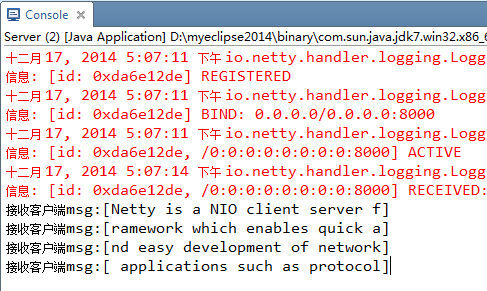
服务器和客户端分别设置了定长解码器 长度为30字节,也就是规定发送和接收一次报文定长为30字节。
运行结果:
客户端接收到服务器的响应报文 一段文字被定长分成若干段接收。
服务器端接收客户端发送的报文 一段话也是分成了等长的若干段。
上述是一个简单长字符串传输例子,将一个长字符串分割成若干段。我们也可以自定义一系列定长的指令发送出去
例如指令长度都是30个字节,批量发出N条指令,这样客户端粘包后发出一个比较大的数据指令集,服务器接收到的数据在缓冲区内,只需要按照定长一个个指令取出来执行即可。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








