正则表达式:符合一定规则的表达式。
作用:用于专门操作字符串。
特点:用于一些特定的符号来表示一些代码操作。这样就简化书写。
所以学习正则表达式,就是在学习一些特殊符号的使用。
好处:可以简化对字符串的复杂操作。
弊端:符号定义越多,正则越长,阅读性越差。
具体操作功能:
1,匹配:String matches方法。用规则匹配整个字符串,只要有一处不符合规则,就匹配结束,返回false。
2,切割:String split();
3,替换:String replaceAll(regex,str);如果regex中有定义组,可以在第二参数中通过$符号获取正则表达式中的已有的组。
class RegexDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//demo();
//System.out.println((char)11);
// checkTel();
//splitDemo("zhangsan.lisi.wangwu","\\.");
//splitDemo("c:\\abc\\a.txt","\\\\");
//splitDemo("erkktyqqquizzzzzo","(.)\\1+");//按照叠词完成切割。为了可以让规则的结果被重用
//可以将规则封装成一个组。用()完成。组的出现都有编号。
//从1开始。 想要使用已有的组可以通过 \n(n就是组的编号)的形式来获取。
String str = "wer1389980000ty1234564uiod234345675f";//将字符串中的数组替换成#。
//replaceAllDemo(str,"\\d{5,}","#");
String str1 = "erkktyqqquizzzzzo";//将叠词替换成$. //将重叠的字符替换成单个字母。zzzz->z
replaceAllDemo(str1,"(.)\\1+","$1");
}
public static void replaceAllDemo(String str,String reg,String newStr)
{
str = str.replaceAll(reg,newStr);
System.out.println(str);
}
public static void splitDemo(String str,String reg)
{
//String reg = " +";//按照多个空格来进行切割
String[] arr = str.split(reg);
System.out.println(arr.length);
for(String s : arr)
{
System.out.println(s);
}
}
/*
匹配
手机号段只有 13xxx 15xxx 18xxxx
*/
public static void checkTel()
{
String tel = "16900001111";
String telReg = "1[358]\\d{9}";
System.out.println(tel.matches(telReg));
}
public static void demo()
{
String str = "b23a23456789";
String reg = "[a-zA-Z]\\d*";
boolean b= str.matches(reg);
System.out.println(b);
}
public static void checkQQ()
{
String qq = "123a454";
String regex = "[1-9]\\d{4,14}";
boolean flag = qq.matches(regex);
if(flag)
System.out.println(qq+"...is ok");
else
System.out.println(qq+"... 不合法");
}
/*
对QQ号码进行校验
要求:5~15 0不能开头,只能是数字
这种方式,使用了String类中的方法,进行组合完成了需求。但是代码过于复杂。
*/
public static void checkQQ_1()
{
String qq = "1882345a0";
int len = qq.length();
if(len>=5 && len<=15)
{
if(!qq.startsWith("0"))//Integer.parseInt("12a");NumberFormatException
{
try
{
long l = Long.parseLong(qq);
System.out.println("qq:"+l);
}
catch (NumberFormatException e)
{
System.out.println("出现非法字符.......");
}
/*
char[] arr = qq.toCharArray();//123a4
boolean flag = true;
for(int x=0;x<arr.length; x++)
{
if(!(arr[x]>='0' && arr[x]<='9'))
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
{
System.out.println("qq:"+qq);
}
else
{
System.out.println("出现非法字符");
}
*/
}
else
{
System.out.println("不可以0开头");
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("长度错误");
}
}
}
/*
正则表达式的第四个功能。
4,获取:将字符串中的符合规则的子串取出。
操作步骤:
1,将正则表达式封装成对象。
2,让正则对象和要操作的字符串相关联。
3,关联后,获取正则匹配引擎。
4,通过引擎对符合规则的子串进行操作,比如取出。
*/
import java.util.regex.*;
class RegexDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
getDemo();
}
public static void getDemo()
{
String str = "ming tian jiu yao fang jia le ,da jia。";
System.out.println(str);
String reg = "\\b[a-z]{4}\\b";
//将规则封装成对象。
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(reg);
//让正则对象和要作用的字符串相关联。获取匹配器对象。
Matcher m = p.matcher(str);
//System.out.println(m.matches());//其实String类中的matches方法。用的就是Pattern和Matcher对象来完成的。
//只不过被String的方法封装后,用起来较为简单。但是功能却单一。
// boolean b = m.find();//将规则作用到字符串上,并进行符合规则的子串查找。
// System.out.println(b);
// System.out.println(m.group());//用于获取匹配后结果。
//System.out.println("matches:"+m.matches());
while(m.find())
{
System.out.println(m.group());
System.out.println(m.start()+"...."+m.end());
}
}
}
import java.util.*;
class RegexTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// test_1();
// ipSort();
checkMail();
}
/*
需求:对邮件地址进行校验。
*/
public static void checkMail()
{
String mail = "abc12@sina.com";
mail = "1@1.1";
String reg = "[a-zA-Z0-9_]+@[a-zA-Z0-9]+(\\.[a-zA-Z]+)+";//较为精确的匹配。
reg = "\\w+@\\w+(\\.\\w+)+";//相对不太精确的匹配。
//mail.indexOf("@")!=-1
System.out.println(mail.matches(reg));
}
/*
需求:
将下列字符串转成:我要学编程.
到底用四种功能中的哪一个呢?或者哪几个呢?
思路方式:
1,如果只想知道该字符是否对是错,使用匹配。
2,想要将已有的字符串变成另一个字符串,替换。
3,想要按照自定的方式将字符串变成多个字符串。切割。获取规则以外的子串。
4,想要拿到符合需求的字符串子串,获取。获取符合规则的子串。
*/
public static void test_1()
{
String str = "我我...我我...我要..要要...要要...学学学....学学...编编编...编程..程.程程...程...程";
/*
将已有字符串变成另一个字符串。使用 替换功能。
1,可以先将 . 去掉。
2,在将多个重复的内容变成单个内容。
*/
str = str.replaceAll("\\.+","");
System.out.println(str);
str = str.replaceAll("(.)\\1+","$1");
System.out.println(str);
}
/*
192.68.1.254 102.49.23.013 10.10.10.10 2.2.2.2 8.109.90.30
将ip地址进行地址段顺序的排序。
还按照字符串自然顺序,只要让它们每一段都是3位即可。
1,按照每一段需要的最多的0进行补齐,那么每一段就会至少保证有3位。
2,将每一段只保留3位。这样,所有的ip地址都是每一段3位。
*/
public static void ipSort()
{
String ip = "192.68.1.254 102.49.23.013 10.10.10.10 2.2.2.2 8.109.90.30";
ip = ip.replaceAll("(\\d+)","00$1");
System.out.println(ip);
ip = ip.replaceAll("0*(\\d{3})","$1");
System.out.println(ip);
String[] arr = ip.split(" ");
TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<String>();
for(String s : arr)
{
ts.add(s);
}
for(String s : ts)
{
System.out.println(s.replaceAll("0*(\\d+)","$1"));
}
}
}
/*
网页爬虫(蜘蛛)
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
class RegexTest2
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
getMails_1();
}
public static void getMails_1()throws Exception
{
URL url = new URL("http://192.168.1.254:8080/myweb/mail.html");
URLConnection conn = url.openConnection();
BufferedReader bufIn = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
String mailreg = "\\w+@\\w+(\\.\\w+)+";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(mailreg);
while((line=bufIn.readLine())!=null)
{
Matcher m = p.matcher(line);
while(m.find())
{
System.out.println(m.group());
}
}
}
/*
获取指定文档中的邮件地址。
使用获取功能。Pattern Matcher
*/
public static void getMails()throws Exception
{
BufferedReader bufr =
new BufferedReader(new FileReader("mail.txt"));
String line = null;
String mailreg = "\\w+@\\w+(\\.\\w+)+";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(mailreg);
while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null)
{
Matcher m = p.matcher(line);
while(m.find())
{
System.out.println(m.group());
}
}
}
}
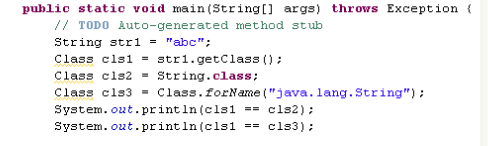
反射
Class类
反射概念
Constructor
Field类
Field类代表某个类中的一个成员变量。
public class ReflectPoint {
private int x;
public int y;
public ReflectPoint(int x, int y) {
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class ReflectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ReflectPoint pt1=new ReflectPoint(3,5);
Field fieldY = pt1.getClass().getField("y");
//fieldY的值是多少? 是5?错!
System.out.println(fieldY.get(pt1));
Field fieldX = pt1.getClass().getDeclaredField("x");
fieldX.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(fieldX.get(pt1));
}
}
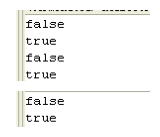
结果是
public class ReflectPoint {
private int x;
public int y;
public String str1="ball";
public String str2="basketball";
public String str3="itcast";
public ReflectPoint(int x, int y) {
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return str1+":"+str2+":"+str3;
}
}import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class ReflectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ReflectPoint pt1=new ReflectPoint(3,5);
Field fieldY = pt1.getClass().getField("y");
//fieldY的值是多少? 是5?错!
System.out.println(fieldY.get(pt1));
Field fieldX = pt1.getClass().getDeclaredField("x");
fieldX.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(fieldX.get(pt1));
changStringValue(pt1);
System.out.println(pt1);
}
private static void changStringValue(Object obj) throws Exception {
Field[] fields = obj.getClass().getFields();
for(Field field:fields){
if((field.getType())==String.class){
String oldValue=(String)field.get(obj);
String newValue =oldValue.replace('b','a');
field.set(obj, newValue);
}
}
}
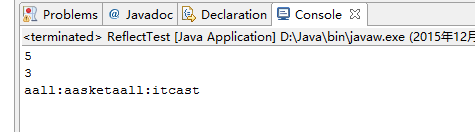
}结果是:
Method类
String str1="abc";
//str1.charAt(1);
Method methodCharAt=String.class.getMethod("charAt", int.class);
System.out.println(methodCharAt.invoke(str1, 1));运行主函数中
//TestArguments.main(new String[] {"1111","22222","3333333"};
String startingClassName=args[0];
Method mainMethod =Class.forName(startingClassName).getMethod("main", String[].class);
mainMethod.invoke(null, new Object[]{new String[]{"111","2222","333"}});
class TestArguments {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for (String arg:args){
System.out.println(arg);
}
}
}数组的反射
示例:
//主函数内:
int[] a1=new int[]{1,2,3};
int[] a2=new int[4];
int [] [] a3=new int[2][3];
String [] a4=new String[]{"a","b","c"};
System.out.println(a1.getClass()==a2.getClass());
//System.out.println(a1.getClass()==a3.getClass());
//System.out.println(a1.getClass()==a4.getClass());
System.out.println(a3.getClass().getName());
System.out.println(a1.getClass().getSuperclass().getName());
System.out.println(a4.getClass().getSuperclass().getName());
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(a1));
System.out.println(Arrays.asList(a4));
结果
示例2“
//主函数内
Object obj=null;
printObject(a4);
printObject("xyz");
private static void printObject(Object obj) {
Class clazz =obj.getClass();
if(clazz.isArray()){
int len=Array.getLength(obj);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println(Array.get(obj, i));
}
}else {
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
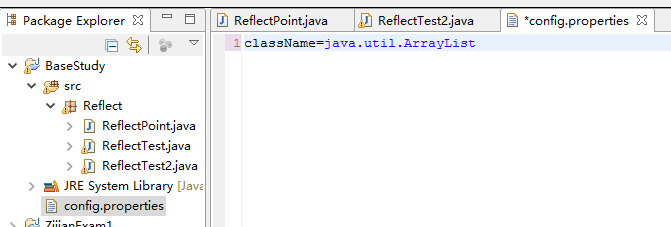
实现框架功能
创建一个文件
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.print.DocFlavor.INPUT_STREAM;
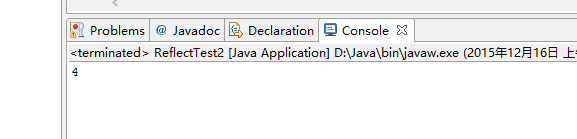
public class ReflectTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
InputStream ips =new FileInputStream("config.properties");
Properties props=new Properties();
props.load(ips);
ips.close();
String className=props.getProperty("className");
Collection collections=(Collection)Class.forName(className).newInstance();
//Collection collections=new ArrayList();
//Collection collections=new HashSet();
ReflectPoint pt1=new ReflectPoint(3, 3);
ReflectPoint pt2=new ReflectPoint(5, 5);
ReflectPoint pt3=new ReflectPoint(3, 3);
collections.add(pt1);
collections.add(pt2);
collections.add(pt3);
collections.add(pt1);
System.out.println(collections.size());
}
}
结果是
ps:
只要更改config.properties中 className 对应的键值对就可以对程序进行更改,方便使用和修改。



































 1122
1122

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








