awk 是一种优秀的文本处理工具,用它来处理文本中的数据非常方便。我们现在用的绝大部分是gawk,也就是gnu awk,gnu的软件一贯表现不错,跟其他AWK的实现版本比起来,gawk添加了对网络的支持,比如我可以用awk模拟发送http请求给浏览器,然后用正则表达式过滤网页内容,例如这里 是一个awk和sed搭配获取五大联赛计分表的shell程序。
gawk编程最权威的资料在其info帮助文件 里,这份帮助资料值得称道的并不是它全面的reference,而是里面包含了大量akw应用的实例。虽然用gawk进行网络编程有点类似所谓的奇技淫巧,但是相比用c来完成同样的工作,awk还是颇具生产力的。
下面这个程序是用来获取youku视频的,程序运行起来是这个样子:
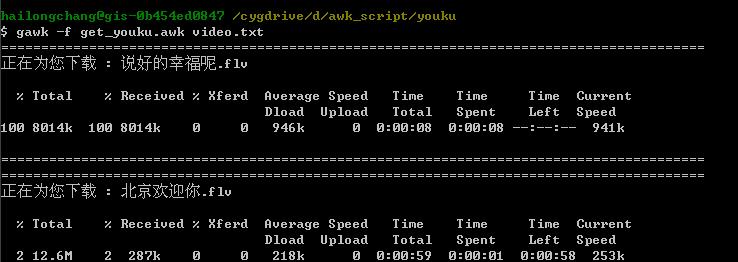
程序的基本原理是用gawk发送http请求,获取服务器返回的信息,然后根据这些信息进行一些处理后重新发送,经过三次请求,youku会发送真正的flv地址,根据这个真实地址就可以下载了,由于gawk在I/O这方面功能很弱,所以我在gawk中通过system()调用curl 来完成这最后一步的下载。
这个程序可以在命令行下如此调用:
gawk -f get_youku.awk youku.txt
其中youku是视频所在的网页地址和下载回来后要保存的名称,其格式可以这样:
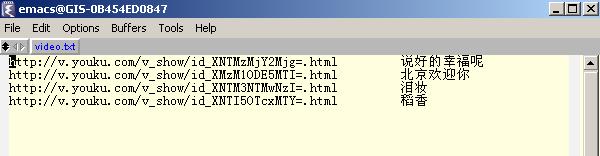
csdn blog的代码模板没有awk,代码有300多行,下面是代码,可能有点乱,有兴趣仔细研究的可以留下邮箱索取源代码。
- #! /usr/bin/gawk -f
- ################################################################################
- #
- #优酷视频下载器
- #
- #Author: hailongchang@163.com
- #
- #Date: 11/15/2008
- #
- ################################################################################
- {
- adr = $1;
- fn = $2;
- download_video(adr,fn);
- }
- ################################################################################
- #实际的下载函数,参数url是flv的网络地址,filename是下载后保存的名称
- ################################################################################
- function download_video(url,filename)
- {
- Get_Info(Get_Vid(url));
- system( "echo ========================================================================================" );
- for (i=1;i<=video_info[ "clipcn" ];i++)
- {
- if (video_info[ "clipcn" ] > 1)
- {
- filename = filename "_" i;
- }
- tlink = "url_" i;
- filename = filename ".flv" ;
- echo_hint = "正在为您下载 : " filename;
- echo_command = "echo " echo_hint;
- system(echo_command);
- system( "echo" );
- command = "curl " Identify_video(video_info[tlink]) " >" filename;
- system(command);
- system( "echo" );
- system( "echo ========================================================================================" );
- }
- }
- ################################################################################
- #提取网页地址,参数web_url来自于youtube.txt,是视频所在的网页地址
- ################################################################################
- function Get_url(web_url)
- {
- gsub(/http:/// //,"",web_url)
- gsub(/v/.youku/.com/, "" ,web_url)
- return web_url;
- }
- ################################################################################
- #提取视频id的函数
- ################################################################################
- function Get_Vid(web_url)
- {
- RS= "/r/n"
- url = Get_url(web_url)
- InetFile = "/inet/tcp/0/v.youku.com/80"
- Request = "GET " url " HTTP/1.1/r/n"
- Request = Request "Accept: image/gif, image/x-xbitmap, image/jpeg, image/pjpeg, application/vnd.ms-excel, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint, application/msword, application/x-shockwave-flash, */*"
- Request = Request "Accept-Language: zh-cn/r/n"
- Request = Request "UA-CPU: x86/r/n"
- Request = Request "Accept-Encoding: unzip, deflate/r/n"
- Request = Request "User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT5.1; .NET CLR 1.1.4322)/r/n"
- Request = Request "Host: v.youku.com/r/n/r/n"
- print Request |& InetFile;
- while ((InetFile |& getline) >0)
- {
- if (match($0,/videoId = '[0-9]*' /,matchtext))
- {
- if (match(matchtext[0],/ '[0-9]*' /,array_vid))
- {
- vid = array_vid[0];
- gsub(/'/, "" ,vid);
- }
- }
- }
- close(InetFile);
- return vid;
- }
- ################################################################################
- #获取服务器发送的key
- ################################################################################
- function Get_key(item)
- {
- split(item,item_info, ":" )
- gsub(/ "/," ",item_info[2])
- return item_info[2]
- }
- ################################################################################
- #获取视频的大小
- ################################################################################
- function Get_size(item)
- {
- split(item,item_info, ":" )
- gsub(/ "/," ",item_info[3])
- gsub(/}/, "" ,item_info[3])
- return item_info[3]
- }
- ################################################################################
- #获取视频的seed
- ################################################################################
- function Get_seed(item)
- {
- split(item,item_info, ":" )
- return item_info[2]
- }
- ################################################################################
- #一个随机数发生器
- ################################################################################
- function Genrate_rand()
- {
- seed = (seed * 211 + 30031) % 65536;
- num = seed / 65536;
- return num;
- }
- function convert_fileid(fileid)
- {
- split(fileid,fid, "*" );
- i = 1;
- while (fid[i] != "" )
- {
- i++;
- }
- fid_length = i-1;
- cg_str = "" ;
- str = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ///:._-1234567890" ;
- seed = video_info[ "seed" ];
- str_length = length(str);
- for (i = 1; i <= str_length; ++i)
- {
- seed = (seed * 211 + 30031) % 65536;
- num = seed / 65536;
- pos = int (length(str) * num);
- pos += 1;
- ch = substr(str,pos,1);
- cg_str = cg_str ch;
- split(str,str_array,ch);
- str = str_array[1] str_array[2];
- }
- id = "" ;
- for (i = 1; i <= fid_length; ++i)
- {
- id = id substr(cg_str,fid[i]+1,1);
- }
- return (id);
- }
- ################################################################################
- #提取fileid
- ################################################################################
- function Get_fileid(item)
- {
- split(item,item_info, ":" )
- gsub(/ "/," ",item_info[2])
- split(item_info[2],fileid, "*" )
- return item_info[2]
- }
- ################################################################################
- #将16进制字符转换为数字
- ################################################################################
- function hex_convention(ch)
- {
- if (ch == "a" )
- num = 10;
- else if (ch == "b" )
- num = 11;
- else if (ch == "c" )
- num = 12;
- else if (ch == "d" )
- num = 13;
- else if (ch == "e" )
- num = 14;
- else if (ch == "f" )
- num = 15;
- else
- num = ch;
- return num;
- }
- ################################################################################
- #将16进制字符串转换为十进制数字
- ################################################################################
- function HexStr_int(str)
- {
- sum = 0;
- for (i=length(str);i>=1;i--)
- {
- n = substr(str,i,1);
- tmp = 16**(length(str)-i);
- sum += (hex_convention(n)) * tmp;
- }
- return sum;
- }
- ################################################################################
- #获取视频的相关信息
- ################################################################################
- function Get_Info(video_id)
- {
- url = "/player/getPlayList/VideoIDS/" video_id "/version/v1.0.0312/source/video/password//Type/flv" ;
- flvHttpFile = "/inet/tcp/0/v.youku.com/80"
- Request = "GET " url " HTTP/1.1/r/n"
- Request = Request "Accept: image/gif, image/x-xbitmap, image/jpeg, image/pjpeg, application/vnd.ms-excel, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint, application/msword, application/x-shockwave-flash, */*"
- Request = Request "Accept-Language: zh-cn/r/n"
- Request = Request "UA-CPU: x86/r/n"
- Request = Request "Accept-Encoding: unzip, deflate/r/n"
- Request = Request "User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 7.0; Windows NT5.1; .NET CLR 1.1.4322)/r/n"
- Request = Request "Host: v.youku.com/r/n"
- print Request |& flvHttpFile
- while ((flvHttpFile |& getline) > 0)
- {
- split($0,match_info, "," );
- }
- close(flvHttpFile);
- i = 1;
- while (match_info[i]!= "" )
- {
- if (0 != match(match_info[i],/ "seed" .*/))
- {
- video_info[ "seed" ] = Get_seed(match_info[i]);
- }
- if (0 != match(match_info[i],/ "streamsizes" .*/))
- {
- video_info[ "size" ] = Get_size(match_info[i]);
- }
- if ( 0 != match(match_info[i],/ "fileid" /))
- {
- video_info[ "fileid" ] = Get_fileid(match_info[i]);
- }
- if (0 != match(match_info[i],/ "key1" .*/))
- {
- video_info[ "key1" ] = Get_key(match_info[i]);
- }
- if ( 0 != match(match_info[i],/ "key2" .*/,match_key2))
- {
- video_info[ "key2" ] = Get_key(match_info[i]);
- }
- i++;
- }
- # printf("/n/n");
- # printf("seed = %s/n",video_info["seed"]);
- # printf("size = %s/n",video_info["size"]);
- # printf("fileid = %s/n",video_info["fileid"]);
- # printf("key1 = %s/n",video_info["key1"]);
- # printf("key2 = %s/n/n",video_info["key2"]);
- # printf("/n/n")
- file_id = convert_fileid(video_info[ "fileid" ]);
- key_stand = sprintf( "%d" ,0xA55AA5A5);
- key1 = HexStr_int(video_info[ "key1" ]);
- video_info[ "key1" ] = sprintf( "%x" ,xor(key1,key_stand));
- video_info[ "clipcn" ] = int (substr(file_id,7,2));
- if (video_info[ "clipcn" ] == 1)
- {
- last_url = "http://f.youku.com/player/getFlvPath/sid/00_00/st/flv/fileid/"
- last_url = last_url file_id "?K=" video_info[ "key2" ];
- last_url = last_url video_info[ "key1" ];
- video_info[ "url_1" ] = last_url;
- }
- else
- {
- for (i = 1; i<= video_info[ "clipcn" ];i++ )
- {
- if (video_info[ "clipcn" ] <= 10)
- {
- lev = "0" (i-1);
- }
- last_url = "http://f.youku.com/player/getFlvPath/sid/00_00/st/flv/fileid/"
- last_url = last_url substr(file_id,1,8);
- last_url = last_url lev;
- last_url = last_url substr(file_id,11,length(file_id)-10);
- last_url = last_url "?K=" ;
- last_url = last_url video_info[ "key2" ];
- last_url = last_url video_info[ "key1" ];
- tlink = "url_" i;
- video_info[tlink] = last_url;
- }
- }
- return ;
- }
- ################################################################################
- #最后一次放松http请求,服务器将返回真实的视频地址
- ################################################################################
- function Identify_video(req)
- {
- InetDown = "/inet/tcp/0/f.youku.com/80"
- gsub(/http:f.youku.com/, "" ,req);
- Request = "GET " req " HTTP/1.1/r/n" ;
- Request = Request "Accept: */*/r/n" ;
- Request = Request "Cache-Control: no-cache/r/n" ;
- Request = Request "Connection: close/r/n" ;
- Request = Request "Host: f.youku.com/r/n" ;
- Request = Request "Pragma: no-cache/r/n" ;
- Request = Request "Referer: http://f.youku.com/player/getFlvPath/sid/00_00/st/flv/fileid//r/n" ;
- Request = Request "User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; )/r/n"
- Request = Request "/r/n" ;
- print Request |& InetDown;
- while ((InetDown |& getline) >0)
- {
- pos = match($0,/http:/// //);
- if (0 != pos)
- {
- flvAddr = substr($0,pos,length($0) - 10);
- }
- }
- close(InetDown);
- return flvAddr;
- }






















 1250
1250

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








