以声卡驱动的数据结构为切入点分析:
/* SoC card */ struct snd_soc_card { const char *name; struct device *dev; struct snd_card *snd_card; //在snd_soc_instantiate_card中利用snd_card_create创建声卡 struct module *owner; struct list_head list; struct mutex mutex; bool instantiated; int (*probe)(struct snd_soc_card *card); int (*late_probe)(struct snd_soc_card *card); int (*remove)(struct snd_soc_card *card); /* the pre and post PM functions are used to do any PM work before and * after the codec and DAI's do any PM work. */ int (*suspend_pre)(struct snd_soc_card *card); int (*suspend_post)(struct snd_soc_card *card); int (*resume_pre)(struct snd_soc_card *card); int (*resume_post)(struct snd_soc_card *card); /* callbacks */ int (*set_bias_level)(struct snd_soc_card *, enum snd_soc_bias_level level); int (*set_bias_level_post)(struct snd_soc_card *, enum snd_soc_bias_level level); long pmdown_time; /* CPU <--> Codec DAI links */ struct snd_soc_dai_link *dai_link; int num_links; struct snd_soc_pcm_runtime *rtd; int num_rtd; /* optional codec specific configuration */ struct snd_soc_codec_conf *codec_conf; int num_configs; /*optional auxiliary devices such as amplifiers or codecs with DAI link unused*/ struct snd_soc_aux_dev *aux_dev; int num_aux_devs; struct snd_soc_pcm_runtime *rtd_aux; int num_aux_rtd; /* Card-specific routes and widgets.*/ struct snd_soc_dapm_widget *dapm_widgets; int num_dapm_widgets; struct snd_soc_dapm_route *dapm_routes; int num_dapm_routes; struct work_struct deferred_resume_work; //属于这个card的已经探测到的设备列表 /* lists of probed devices belonging to this card */ struct list_head codec_dev_list; struct list_head platform_dev_list; struct list_head dai_dev_list; struct list_head widgets; struct list_head paths; struct list_head dapm_list; /* Generic DAPM context for the card */ struct snd_soc_dapm_context dapm; #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS struct dentry *debugfs_card_root; struct dentry *debugfs_pop_time; #endif u32 pop_time; void *drvdata; }; /* SoC machine DAI configuration, glues(胶水) a codec and cpu DAI together */ struct snd_soc_pcm_runtime { struct device dev; struct snd_soc_card *card; struct snd_soc_dai_link *dai_link; unsigned int complete:1; unsigned int dev_registered:1; /* Symmetry data - only valid if symmetry is being enforced */ unsigned int rate; long pmdown_time; /* runtime devices */ struct snd_pcm *pcm; struct snd_soc_codec *codec; struct snd_soc_platform *platform; struct snd_soc_dai *codec_dai; struct snd_soc_dai *cpu_dai; struct delayed_work delayed_work; }; 1) struct snd_soc_codec - 由与平台无关的codec驱动实现。 2) struct snd_soc_platform - 由与imx平台相关的DAI驱动实现,主要实现了音频数据的DMA传输功能。 3) struct snd_soc_dai_link - 将平台相关的DAI与平台无关的codec联系起来。与声音相关的逻辑设备都是在snd_card的管理之下,声卡驱动的第一个动作通常就是创建一个snd_card结构体。 1. struct snd_card { 2. int number; /* number of soundcard (index to snd_cards) */ 3. char id[16]; /* id string of this card */ 4. char driver[16]; /* driver name */ 5. char shortname[32]; /* short name of this soundcard */ 6. char longname[80]; /* name of this soundcard */ 7. char mixername[80]; /* mixer name */ 8. char components[128]; /* card components delimited with space */ 9. struct module *module; /* top-level module */ 10. 11. void *private_data; /* private data for soundcard 声卡的私有数据,可以在创建声卡时通过参数指定数据的大小 */ 12. void (*private_free) (struct snd_card *card); /* callback for freeing of private data */ 13. struct list_head devices; /* devices 记录该声卡下所有逻辑设备的链表 */ 14. 15. unsigned int last_numid; /* last used numeric ID */ 16. struct rw_semaphore controls_rwsem; /* controls list lock */ 17. rwlock_t ctl_files_rwlock; /* ctl_files list lock */ 18. int controls_count; /* count of all controls */ 19. int user_ctl_count; /* count of all user controls */ 20. struct list_head controls; /* all controls for this card 记录该声卡下所有的控制单元的链表 */ 21. struct list_head ctl_files; /* active control files */ 22. 23. struct snd_info_entry *proc_root; /* root for soundcard specific files */ 24. struct snd_info_entry *proc_id; /* the card id */ 25. struct proc_dir_entry *proc_root_link; /* number link to real id */ 26. 27. struct list_head files_list; /* all files associated to this card */ 28. struct snd_shutdown_f_ops *s_f_ops; /* file operations in the shutdown state */ 29. spinlock_t files_lock; /* lock the files for this card */ 30. int shutdown; /* this card is going down */ 31. int free_on_last_close; /* free in context of file_release */ 32. wait_queue_head_t shutdown_sleep; 33. struct device *dev; /* device assigned to this card */ 34. #ifndef CONFIG_SYSFS_DEPRECATED 35. struct device *card_dev; /* cardX object for sysfs */ 36. #endif 37. 38. #ifdef CONFIG_PM 39. unsigned int power_state; /* power state */ 40. struct mutex power_lock; /* power lock */ 41. wait_queue_head_t power_sleep; 42. #endif 43. 44. #if defined(CONFIG_SND_MIXER_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_MIXER_OSS_MODULE) 45. struct snd_mixer_oss *mixer_oss; 46. int mixer_oss_change_count; 47. #endif 48. };
创建声卡的功能部件(逻辑设备),例如PCM,Mixer,MIDI等。每一种部件的创建最终会调用snd_device_new()来生成一个snd_device实例,并把该实例链接到snd_card的devices链表中。
通常,alsa-driver的已经提供了一些常用的部件的创建函数,而不必直接调用snd_device_new(),比如:
PCM ---- snd_pcm_new()
RAWMIDI -- snd_rawmidi_new()
CONTROL -- snd_ctl_create()
- controlC0 --> 用于声卡的控制,例如通道选择,混音,麦克风的控制等
- midiC0D0 --> 用于播放midi音频
- pcmC0D0c --〉 用于录音的pcm设备
- pcmC0D0p --〉 用于播放的pcm设备
- seq --〉 音序器
- timer --〉 定时器
每个声卡最多可以包含4个pcm的实例,每个pcm实例对应一个pcm设备文件。大多数情况下,在嵌入式设备中,一个pcm实例已经足够了。一个pcm实例由一个playback stream和一个capture stream组成,这两个stream又分别有一个或多个substreams组成。
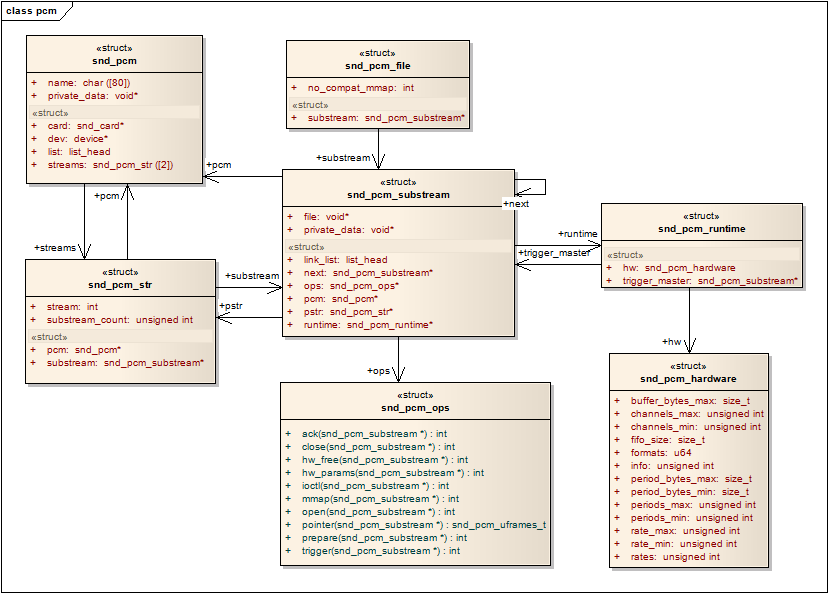
pcm中间层的几个重要的结构体的关系图
struct snd_pcm {
struct snd_card *card;
struct list_head list;
int device; /* device number */
unsigned int info_flags;
unsigned short dev_class;
unsigned short dev_subclass;
char id[64];
char name[80];
struct snd_pcm_str streams[2];
struct mutex open_mutex;
wait_queue_head_t open_wait;
void *private_data;
void (*private_free) (struct snd_pcm *pcm);
struct device *dev; /* actual hw device this belongs to */
#if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE)
struct snd_pcm_oss oss;
#endif
};
1 snd_pcm是挂在snd_card下面的一个snd_device
2 snd_pcm中的字段:streams[2],该数组中的两个元素指向两个snd_pcm_str结构,分别代表playback stream和capture stream。
3 snd_pcm_str中的substream字段,指向snd_pcm_substream结构
4 snd_pcm_substream是pcm中间层的核心,绝大部分任务都是在substream中处理,尤其是他的ops(snd_pcm_ops)字段,
许多user空间的应用程序通过alsa-lib对驱动程序的请求都是由该结构中的函数处理。它的runtime字段则指向snd_pcm_runtime结构,
snd_pcm_runtime记录这substream的一些重要的软件和硬件运行环境和参数。
struct snd_pcm_str {
int stream; /* stream (direction) */
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
/* -- substreams -- */
unsigned int substream_count;
unsigned int substream_opened;
struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;
#if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE)
/* -- OSS things -- */
struct snd_pcm_oss_stream oss;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_VERBOSE_PROCFS
struct snd_info_entry *proc_root;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_info_entry;
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_PCM_XRUN_DEBUG
unsigned int xrun_debug; /* 0 = disabled, 1 = verbose, 2 = stacktrace */
struct snd_info_entry *proc_xrun_debug_entry;
#endif
#endif
};
struct snd_pcm_substream {
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
struct snd_pcm_str *pstr;
void *private_data; /* copied from pcm->private_data */
int number;
char name[32]; /* substream name */
int stream; /* stream (direction) */
struct pm_qos_request_list latency_pm_qos_req; /* pm_qos request */
size_t buffer_bytes_max; /* limit ring buffer size */
struct snd_dma_buffer dma_buffer;
unsigned int dma_buf_id;
size_t dma_max;
/* -- hardware operations -- */
struct snd_pcm_ops *ops;
/* -- runtime information -- */
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime;
/* -- timer section -- */
struct snd_timer *timer; /* timer */
unsigned timer_running: 1; /* time is running */
/* -- next substream -- */
struct snd_pcm_substream *next;
/* -- linked substreams -- */
struct list_head link_list; /* linked list member */
struct snd_pcm_group self_group; /* fake group for non linked substream (with substream lock inside) */
struct snd_pcm_group *group; /* pointer to current group */
/* -- assigned files -- */
void *file;
int ref_count;
atomic_t mmap_count;
unsigned int f_flags;
void (*pcm_release)(struct snd_pcm_substream *);
struct pid *pid;
#if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE)
/* -- OSS things -- */
struct snd_pcm_oss_substream oss;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_VERBOSE_PROCFS
struct snd_info_entry *proc_root;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_info_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_hw_params_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_sw_params_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_status_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_prealloc_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_prealloc_max_entry;
#endif
/* misc flags */
unsigned int hw_opened: 1;
};
新建一个pcm可以用下面一张新建pcm的调用的序列图进行描述:
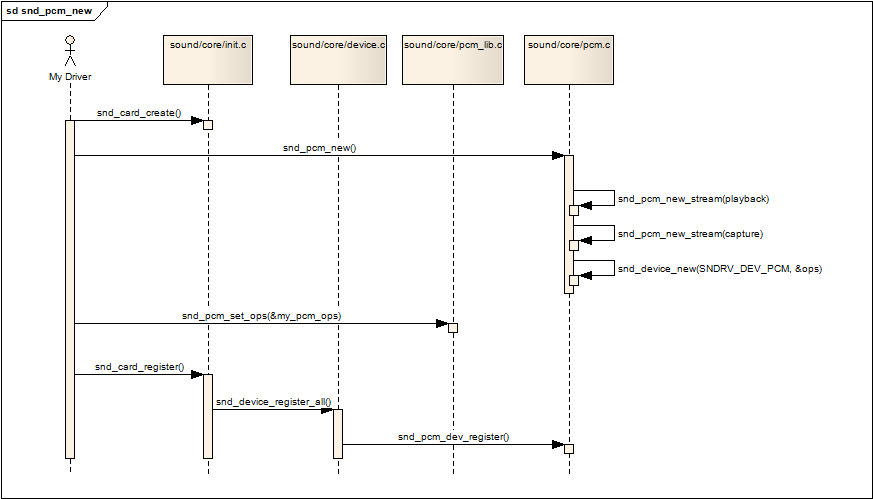
新建pcm的序列图
snd_pcm_set_ops 设置操作该pcm的控制/操作接口函数,参数中的snd_pcm_ops结构中的函数通常就是我们驱动要实现的函数snd_card_register 注册声卡,在这个阶段会遍历声卡下的所有逻辑设备,并且调用各设备的注册回调函数,
对于pcm,就是第二步提到的snd_pcm_dev_register函数,该回调函数建立了和用户空间应用程序(alsa-lib)通信所用的设备文件节点:/dev/snd/pcmCxxDxxp
和/dev/snd/pcmCxxDxxc (这些设备节点由alsa-lib使用,用户不直接使用)。
snd_pcm_dev_register调用snd_register_device_for_dev,snd_register_device_for_dev调用device_create创建设备节点。snd_register_device_for_dev有个参数
snd_pcm_f_ops,它是一个标准的文件系统file_operations结构数组,它的定义在sound/core/pcm_native.c中:并被记录在snd_minors[minor]中的字段f_ops中。
/*
* Register section
*/
//used in pcm.c
const struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = {
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.write = snd_pcm_write,
.aio_write = snd_pcm_aio_write,
.open = snd_pcm_playback_open,
.release = snd_pcm_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_pcm_playback_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_playback_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,
.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,
.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,
.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,
},
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = snd_pcm_read,
.aio_read = snd_pcm_aio_read,
.open = snd_pcm_capture_open,
.release = snd_pcm_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_pcm_capture_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_capture_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,
.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,
.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,
.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,
}
};
在sound/core/sound.c中有alsa_sound_init()函数,其中有:
register_chrdev(major, "alsa", &snd_fops),参数major与之前创建pcm设备是device_create时的major是同一个,这样的结果是,
当应用程序open设备文件/dev/snd/pcmCxDxp时,会进入snd_fops的open回调函数。
static const struct file_operations snd_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = snd_open,
.llseek = noop_llseek,
};
snd_open函数,它首先从inode中取出此设备号,然后以次设备号为索引,从snd_minors全局数组中取出当初注册pcm设备时填充的snd_minor结构
,然后从snd_minor结构中取出pcm设备的f_ops,并且把file->f_op替换为pcm设备的f_ops,紧接着直接调用pcm设备的f_ops->open(),然后返回。
因为file->f_op已经被替换,以后,应用程序的所有read/write/ioctl调用都会进入pcm设备自己的回调函数中,也就是snd_pcm_f_ops结构中定义的回调。
本博内容均由http://blog.csdn.net/droidphone原创






















 1008
1008











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








