相信大家都对ArrayList相当熟悉了,今天笔者就对ArrayList的源码进行解读,讲解一下对ArrayList扩容的基本原理。
虽然大家都有用过,但还是简单介绍一下吧,ArrayList实现了List的接口,并且实现了序列化,同样具有collection的方法,add,remove等,时间复杂度都是O(1),对于n个数据则为O(n)。好了,接下来具体看下ArrayList的源码(笔者使用的是jdk1.8版本):
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}此处我们可以看到,我们的数据其实是放在ArrayList<E>引用的一个Object数组,也就是elementData数组,我们来看看它的add方法:
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
} private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}从add传进来的元素开始,在ensure方法中进行了size的判断,首先判断取最小容量,然后对最小容量和目前数据所需容量最比对,如果最小容量并不满足,则需要增加大小:
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}这里新的容量是将就旧的加上后移一位的,也就是二进制位右移,然后进行判断,如果新增的比最小容量要小,则赋值为最小容量,如果超过了最大值,则赋值int的最大值,也就是2^31-1,十六进制数为0x7fffffff,然后调用Arrays的copyof方法去将原来数组的值复制过去。
这里可以做一个测试demo,由于属性是非公有的,所以使用了反射的方法去获取(关于反射的使用可以参考笔者的另一篇文章):
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
TestIntValue value = new TestIntValue();
list.add("ss");
int actualLength = value.getActualLength(list);
int size = list.size();
System.out.println("list此时的容量为:" + actualLength);
System.out.println("list此时的大小为:" + size);
}
/**
* 反射获取elementData容量大小
* @param mList
* @return
*/
public int getActualLength(ArrayList<String> mList){
Class<?> mClass = mList.getClass();
Field f = null;
int length = 0;
try {
f = mClass.getDeclaredField("elementData");
f.setAccessible(true);
Object[] o = (Object[])f.get(mList);
length = o.length;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return length;
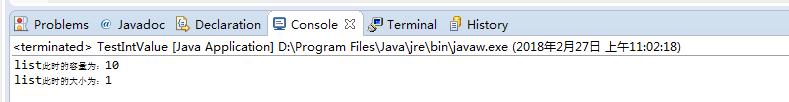
}此时只是增加了一个值,所以此时的大小为1,容量大小为10:
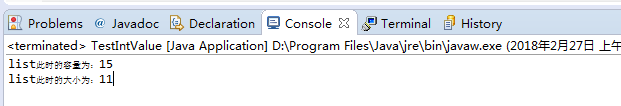
如果我们给他塞入超出10的值呢:
此时容量大小已经变成15了,可见,大小的确是10 + 5来的,所以,他的扩容是大概增加了1.5倍的大小。
以上就是扩容的过程了,谢谢大家~






















 1208
1208

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








