Flink EventTime和Watermarks案例分析
https://blog.csdn.net/xu470438000/article/details/83271123
最近找到这个对事件时间处理和水印说的比较好的文章,所以转载一下,供大家分享,原文连接:http://vishnuviswanath.com/flink_eventtime.html
本文用途纯粹是为了分享,如若有侵权,请与我联系~
下面是原文:
如果您正在构建实时流媒体应用程序,则事件时间处理是您必须迟早使用的功能之一。由于在大多数现实世界的用例中,消息到达无序,应该有一些方法,您建立的系统了解消息可能迟到并且相应地处理的事实。在这篇博文中,我们将看到为什么我们需要事件时间处理,以及我们如何在ApacheFlink中启用它。
EventTime是事件在现实世界中发生的时间,ProcessingTime是Flink系统处理该事件的时间。要了解事件时间处理的重要性,我们首先要建立一个基于处理时间的系统,看看它的缺点。
我们将创建一个大小为10秒的SlidingWindow,每5秒滑动一次,在窗口结束时,系统将发出在此期间收到的消息数。一旦了解EventTime处理如何与SlidingWindow相关的工作,那么了解如何在TumblingWindow中工作也不难。所以让我们开始吧。
#基于处理时间的系统
对于这个例子,我们期望消息具有格式值,timestamp,其中value是消息,timestamp是在源生成此消息的时间。由于我们正在构建基于处理时间的系统,因此以下代码忽略了时间戳部分。
了解消息应包含生成时间的信息是一个重要的方面。Flink或任何其他系统不是一个魔术盒,可以以某种方式自己形成这个。稍后我们将看到,事件时间处理提取此时间戳信息以处理较晚的消息。
val text = senv.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
val counts = text.map {(m: String) => (m.split(",")(0), 1) }
.keyBy(0)
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(10), Time.seconds(5))
.sum(1)
counts.print
senv.execute("ProcessingTime processing example")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
##情况1:消息到达不间断
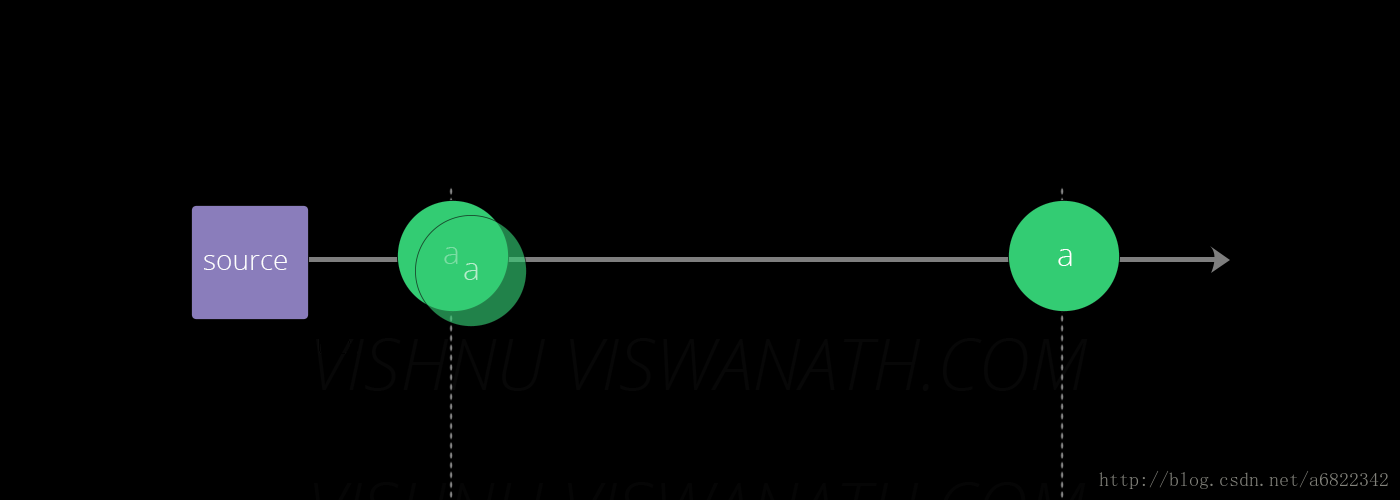
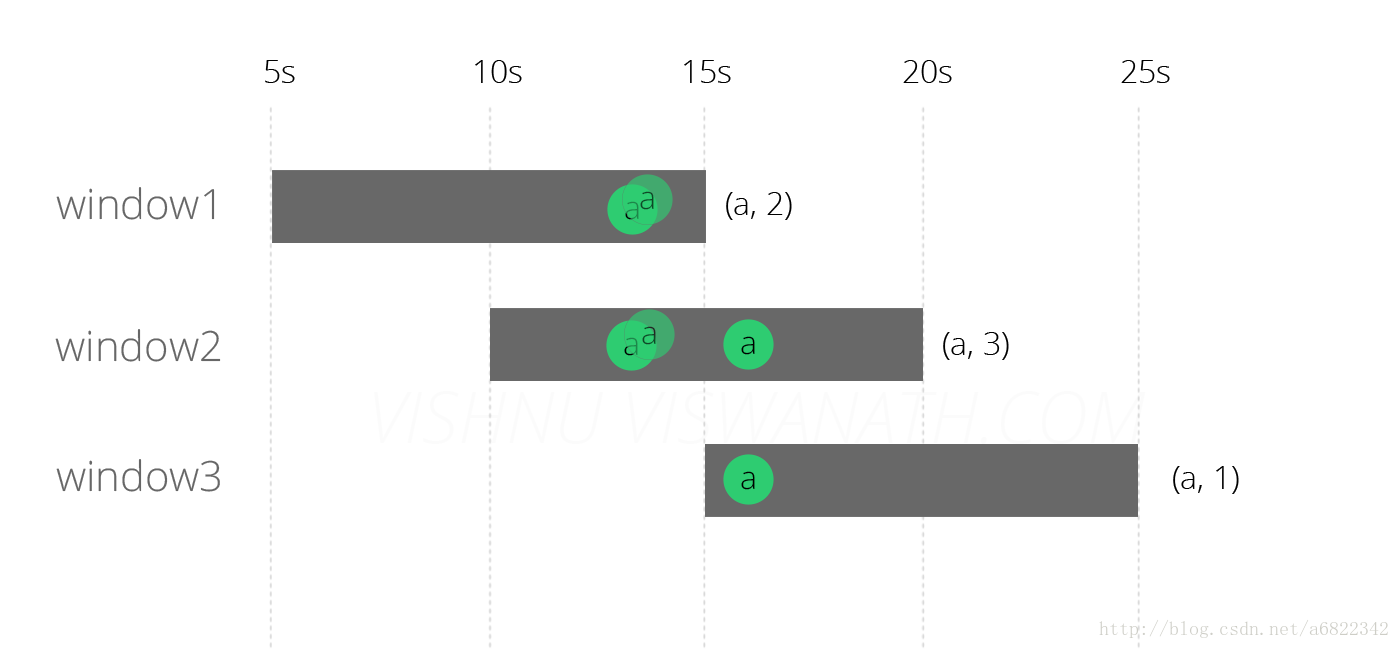
假设源分别在时间13秒,第13秒和第16秒产生类型a的三个消息。(小时和分钟不重要,因为窗口大小只有10秒)。
这些消息将落入Windows中,如下所示。在第13秒产生的前两个消息将落入窗口1 [5s-15s]和window2 [10s-20s],第16个时间生成的第三个消息将落入window2 [ 10s-20s]和window3 [15s-25s] ]。每个窗口发出的最终计数分别为(a,2),(a,3)和(a,1)。
该输出可以被认为是预期的行为。现在我们将看看当一个消息到达系统的时候会发生什么。
##情况2:消息到达延迟
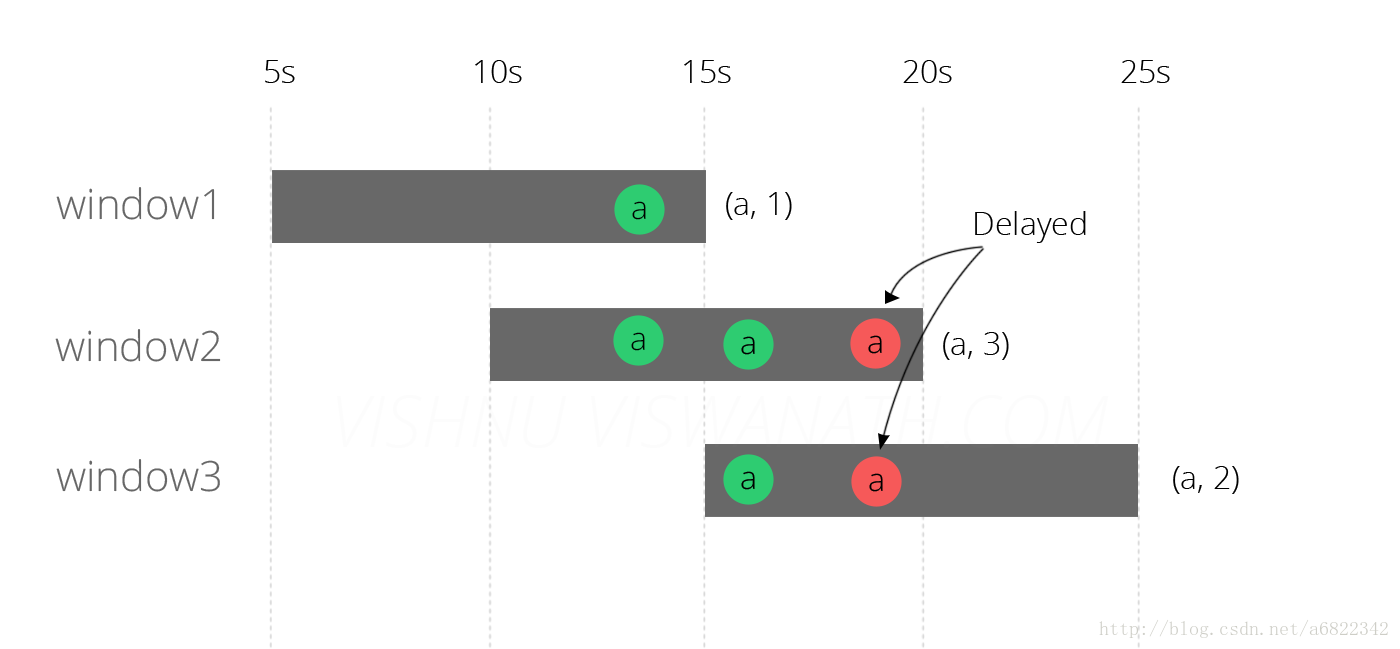
现在假设其中一条消息(在第13秒生成)到达延迟6秒(第19秒),可能是由于某些网络拥塞。你能猜测这个消息会落入哪个窗口?
延迟的消息落入窗口2和3,因为19在10-20和15-25之间。在window2中计算没有任何问题(因为消息应该落入该窗口),但是它影响了window1和window3的结果。我们现在将尝试使用EventTime处理来解决这个问题。
##基于EventTime的系统
要启用EventTime处理,我们需要一个时间戳提取器,从消息中提取事件时间信息。请记住,消息是格式值,时间戳。该extractTimestamp方法获取时间戳部分并将其作为一个长期。现在忽略getCurrentWatermark方法,我们稍后再回来。
class TimestampExtractor extends AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks[String] with Serializable {
override def extractTimestamp(e: String, prevElementTimestamp: Long) = {
e.split(",")(1).toLong
}
override def getCurrentWatermark(): Watermark = {
new Watermark(System.currentTimeMillis)
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
我们现在需要设置这个时间戳提取器,并将TimeCharactersistic设置为EventTime。其余的代码与ProcessingTime的情况保持一致。
senv.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
val text = senv.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new TimestampExtractor)
val counts = text.map {(m: String) => (m.split(",")(0), 1) }
.keyBy(0)
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(10), Time.seconds(5))
.sum(1)
counts.print
senv.execute("EventTime processing example")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
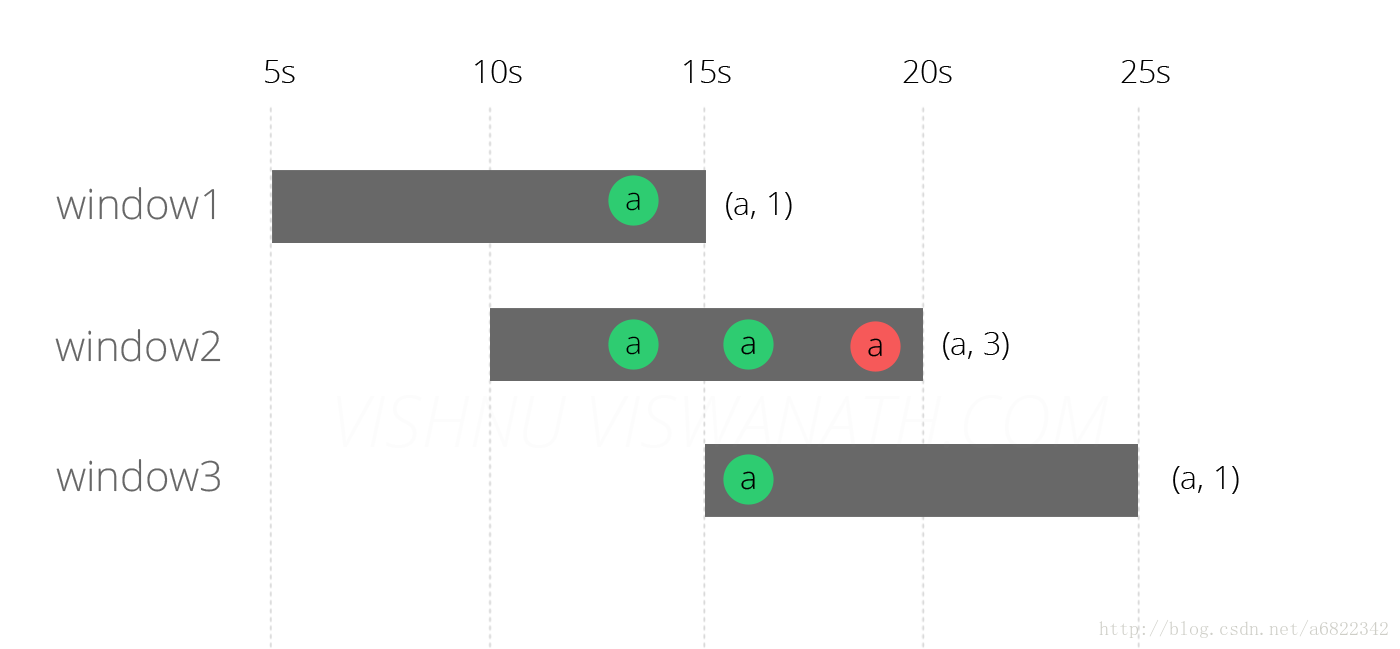
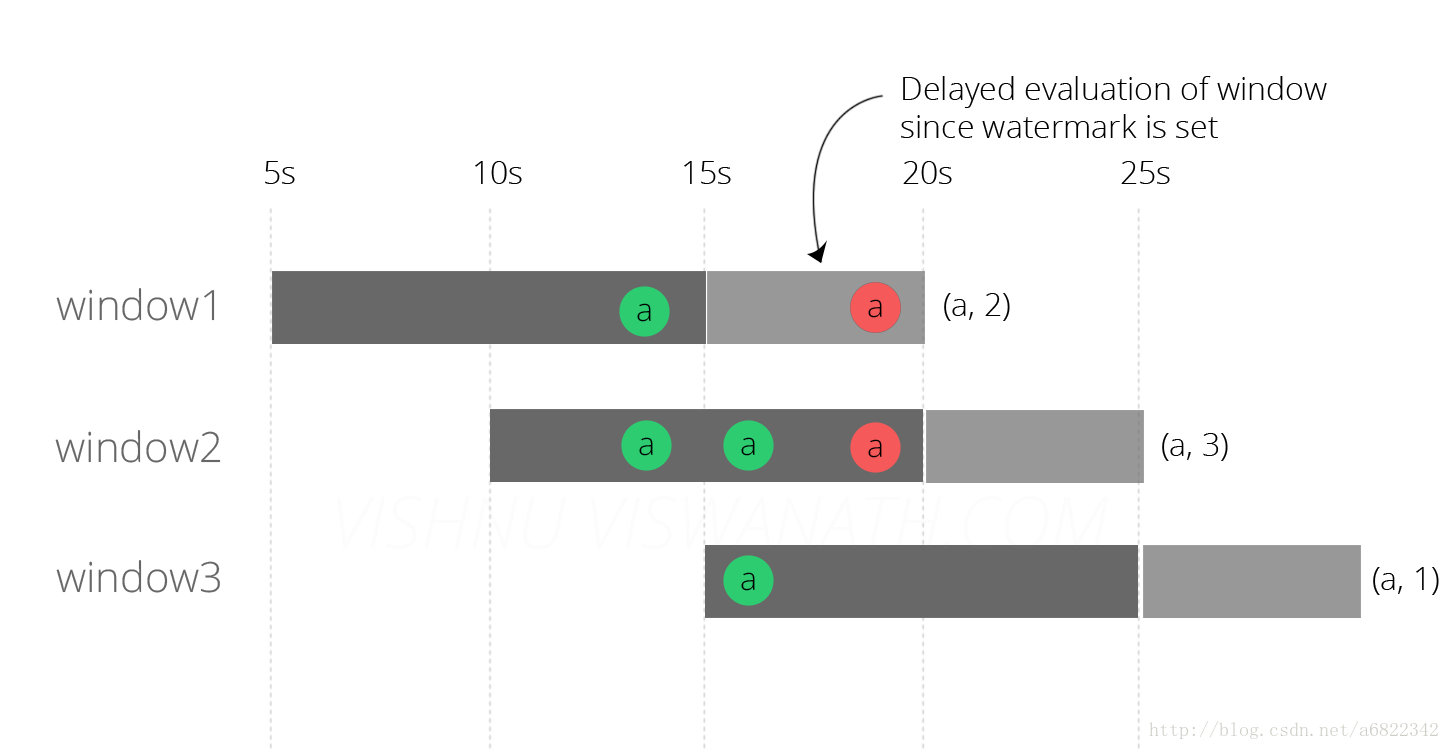
运行上述代码的结果如下图所示。
结果看起来更好,窗口2和3现在发出正确的结果,但是window1仍然是错误的。Flink没有将延迟的消息分配给窗口3,因为它现在检查了消息的事件时间,并且理解它不在该窗口中。但是为什么没有将消息分配给窗口1?原因是在延迟的信息到达系统时(第19秒),窗口1的评估已经完成了(第15秒)。现在让我们尝试通过使用水印来解决这个问题。
ps:请注意,在窗口2中,延迟的消息仍然位于第19秒,而不是第13秒(事件时间)。该图中的描述是故意表示窗口中的消息不会根据事件时间进行排序。(这可能会在将来改变)
#水印
水印是一个非常重要和有趣的想法,我将尽力给您一个简短的概述。如果您有兴趣了解更多信息,您可以从Google 观看这个令人敬畏的演讲,还可以从dataArtisans那里阅读此博客。水印本质上是一个时间戳。当Flink中的运算符接收到水印时,它明白(假设)它不会看到比该时间戳更早的消息。
( 原文:A Watermark is essentially a timestamp. When an Operator in Flink receives a watermark, it understands(assumes) that it is not going to see any message older than that timestamp.我这里理解是翻译为更早的信息或者更晚的信息都可以,因为从时间上来说,1990年比1994年要老,但是1990年比1994年也是可以说是早的,那么就是它看不到更早/老的信息)
因此,在“EventTime”中,水印也可以被认为是一种告诉Flink它有多远的一种方式。
为了这个例子的目的,把它看作是一种告诉Flink一个消息延迟多少的方式。在最后一次尝试中,我们将水印设置为当前系统时间。因此,不要指望任何延迟的消息。我们现在将水印设置为当前时间-5秒,这告诉Flink希望消息最多有5s的延迟,这是因为每个窗口仅在水印通过时被评估。由于我们的水印是当前时间-5秒,所以第一个窗口[5s-15s]将仅在第20秒被评估。类似地,窗口[10s-20s]将在第25秒进行评估,依此类推。
override def getCurrentWatermark(): Watermark = {
new Watermark(System.currentTimeMillis - 5000)
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
通常最好保持接收到的最大时间戳,并创建具有最大预期延迟的水印,而不是从当前系统时间减去。
进行上述更改后运行代码的结果是:
最后我们得到了正确的结果,所有这三个窗口现在都按照预期的方式发射计数,这是(a,2),(a,3)和(a,1)。
更新:我们也可以使用AllowedLateness功能设置消息的最大允许时间来解决这个问题。
结论:
实时流处理系统的重要性日益增长,必须处理延迟的消息是您构建的任何此类系统的一部分。在这篇博文中,我们看到到达的消息迟到会影响系统的结果,以及如何使用ApacheFlink的事件时间处理功能来解决它们。谢谢你的阅读!
allowedLateness
allowedLateness也是Flink处理乱序事件的一个特别重要的特性,默认情况下,当wartermark通过window后,再进来的数据,也就是迟到或者晚到的数据就会别丢弃掉了,但是有的时候我们希望在一个可以接受的范围内,迟到的数据,也可以被处理或者计算,这就是allowedLateness产生的原因了,简而言之呢,allowedLateness就是对于watermark超过end-of-window之后,还允许有一段时间(也是以event time来衡量)来等待之前的数据到达,以便再次处理这些数据。
默认情况下,如果不指定allowedLateness,其值是0,即对于watermark超过end-of-window之后,还有此window的数据到达时,这些数据被删除掉了。
注意:对于trigger是默认的EventTimeTrigger的情况下,allowedLateness会再次触发窗口的计算,而之前触发的数据,会buffer起来,直到watermark超过end-of-window + allowedLateness()的时间,窗口的数据及元数据信息才会被删除。再次计算就是DataFlow模型中的Accumulating的情况。
同时,对于sessionWindow的情况,当late element在allowedLateness范围之内到达时,可能会引起窗口的merge,这样,之前窗口的数据会在新窗口中累加计算,这就是DataFlow模型中的AccumulatingAndRetracting的情况。
下面看一下完整的代码:
package flink
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat
import java.util.Properties
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.{CheckpointingMode, TimeCharacteristic}
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala.StreamExecutionEnvironment
import org.apache.flink.streaming.util.serialization.SimpleStringSchema
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.scala._
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.watermark.Watermark
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.triggers.CountTrigger
import org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.kafka.FlinkKafkaConsumer010
import org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.redis.RedisSink
import org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.redis.common.config.FlinkJedisPoolConfig
import org.apache.flink.streaming.connectors.redis.common.mapper.{RedisCommand, RedisCommandDescription, RedisMapper}
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory
/**
* flinkstreaming消费kafka的数据实现exactly-once的语义;
*/
object flinkStreamingJason {
private val zk = "192.168.17.142:2181,192.168.17.145:2181,192.168.17.147:2181"
private val broker = "192.168.17.142:9092,192.168.17.145:9092,192.168.17.147:9092"
private val group_id = "jason_"
private val topic = "jason_1027"
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
lazy val logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(classOf[Nothing])
val env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
//设置时间Time Notion;默认使用的是ProcessTime;
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
env.getConfig.enableObjectReuse()
env.enableCheckpointing(5000)
env.getCheckpointConfig.setCheckpointingMode(CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE)
val properties = new Properties()
properties.setProperty("zookeeper.connect", zk)
properties.setProperty("bootstrap.servers", broker)
properties.setProperty("group.id", group_id)
val consumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer010[String](topic,new SimpleStringSchema, properties)
val stream = env.addSource(consumer)
val wordcount = stream
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new TimestampExtractor)
.filter(_.nonEmpty)
.filter(_.contains(","))
.map(x=>{
val arr = x.split(",")
val code = arr(0)
val time = arr(1).toLong
(code,time)
}) // 指派时间戳,并生成WaterMark
.keyBy(0)
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(10),Time.seconds(5))
.trigger(CountTrigger.of(2)) //决定了一个窗口何时能被窗口函数计算或者清除,每个窗口都有自己的trigger;
.sum(1)
.map(x=> (x._1,x._2.toString))
val conf = new FlinkJedisPoolConfig.Builder().setHost("192.168.17.142").setPort(6379).build()
val sink = new RedisSink[(String,String)](conf, new RedisExampleMapperJason)
wordcount.addSink(sink)
env.execute("flink streaming Event Time And WaterMark Jason")
}
}
class RedisExampleMapperJason extends RedisMapper[(String, String)] {
override def getCommandDescription: RedisCommandDescription = {
new RedisCommandDescription(RedisCommand.SET, null)
}
override def getKeyFromData(data: (String, String)): String = data._1
override def getValueFromData(data: (String, String)): String = data._2
}
/**
* 时间戳提取器需要实现AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks;
*
*/
class TimestampExtractor extends AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks[String] with Serializable {
private val maxOutOfOrderness = 5000L //允许数据晚到的最大时间5s;
private var wm: Watermark = null
override def getCurrentWatermark: Watermark = {
wm = new Watermark(System.currentTimeMillis() - maxOutOfOrderness)
wm
}
override def extractTimestamp(t: String, l: Long): Long = {
l
}
}
提交后到web,ui上面可以看到watermark的如下图所示:

代码写的比较简单,有时间的话,在更新.
本文主要研究一下flink的EventTime
SourceFunction
flink-streaming-java_2.11-1.7.0-sources.jar!/org/apache/flink/streaming/api/functions/source/SourceFunction.java
/**
* Interface that source functions use to emit elements, and possibly watermarks.
*
* @param <T> The type of the elements produced by the source.
*/
@Public // Interface might be extended in the future with additional methods.
interface SourceContext<T> {
/**
* Emits one element from the source, without attaching a timestamp. In most cases,
* this is the default way of emitting elements.
*
* <p>The timestamp that the element will get assigned depends on the time characteristic of
* the streaming program:
* <ul>
* <li>On {@link TimeCharacteristic#ProcessingTime}, the element has no timestamp.</li>
* <li>On {@link TimeCharacteristic#IngestionTime}, the element gets the system's
* current time as the timestamp.</li>
* <li>On {@link TimeCharacteristic#EventTime}, the element will have no timestamp initially.
* It needs to get a timestamp (via a {@link TimestampAssigner}) before any time-dependent
* operation (like time windows).</li>
* </ul>
*
* @param element The element to emit
*/
void collect(T element);
/**
* Emits one element from the source, and attaches the given timestamp. This method
* is relevant for programs using {@link TimeCharacteristic#EventTime}, where the
* sources assign timestamps themselves, rather than relying on a {@link TimestampAssigner}
* on the stream.
*
* <p>On certain time characteristics, this timestamp may be ignored or overwritten.
* This allows programs to switch between the different time characteristics and behaviors
* without changing the code of the source functions.
* <ul>
* <li>On {@link TimeCharacteristic#ProcessingTime}, the timestamp will be ignored,
* because processing time never works with element timestamps.</li>
* <li>On {@link TimeCharacteristic#IngestionTime}, the timestamp is overwritten with the
* system's current time, to realize proper ingestion time semantics.</li>
* <li>On {@link TimeCharacteristic#EventTime}, the timestamp will be used.</li>
* </ul>
*
* @param element The element to emit
* @param timestamp The timestamp in milliseconds since the Epoch
*/
@PublicEvolving
void collectWithTimestamp(T element, long timestamp);
/**
* Emits the given {@link Watermark}. A Watermark of value {@code t} declares that no
* elements with a timestamp {@code t' <= t} will occur any more. If further such
* elements will be emitted, those elements are considered <i>late</i>.
*
* <p>This method is only relevant when running on {@link TimeCharacteristic#EventTime}.
* On {@link TimeCharacteristic#ProcessingTime},Watermarks will be ignored. On
* {@link TimeCharacteristic#IngestionTime}, the Watermarks will be replaced by the
* automatic ingestion time watermarks.
*
* @param mark The Watermark to emit
*/
@PublicEvolving
void emitWatermark(Watermark mark);
/**
* Marks the source to be temporarily idle. This tells the system that this source will
* temporarily stop emitting records and watermarks for an indefinite amount of time. This
* is only relevant when running on {@link TimeCharacteristic#IngestionTime} and
* {@link TimeCharacteristic#EventTime}, allowing downstream tasks to advance their
* watermarks without the need to wait for watermarks from this source while it is idle.
*
* <p>Source functions should make a best effort to call this method as soon as they
* acknowledge themselves to be idle. The system will consider the source to resume activity
* again once {@link SourceContext#collect(T)}, {@link SourceContext#collectWithTimestamp(T, long)},
* or {@link SourceContext#emitWatermark(Watermark)} is called to emit elements or watermarks from the source.
*/
@PublicEvolving
void markAsTemporarilyIdle();
/**
* Returns the checkpoint lock. Please refer to the class-level comment in
* {@link SourceFunction} for details about how to write a consistent checkpointed
* source.
*
* @return The object to use as the lock
*/
Object getCheckpointLock();
/**
* This method is called by the system to shut down the context.
*/
void close();
}- SourceFunction里头定义了SourceContext接口,它里头定义了collectWithTimestamp、emitWatermark方法,前者用来assign event timestamp,后者用来emit watermark
实例
public abstract class TestSource implements SourceFunction {
private volatile boolean running = true;
protected Object[] testStream;
@Override
public void run(SourceContext ctx) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; (i < testStream.length) && running; i++) {
if (testStream[i] instanceof TaxiRide) {
TaxiRide ride = (TaxiRide) testStream[i];
ctx.collectWithTimestamp(ride, ride.getEventTime());
} else if (testStream[i] instanceof TaxiFare) {
TaxiFare fare = (TaxiFare) testStream[i];
ctx.collectWithTimestamp(fare, fare.getEventTime());
} else if (testStream[i] instanceof String) {
String s = (String) testStream[i];
ctx.collectWithTimestamp(s, 0);
} else if (testStream[i] instanceof Long) {
Long ts = (Long) testStream[i];
ctx.emitWatermark(new Watermark(ts));
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(testStream[i].toString());
}
}
// test sources are finite, so they have a Long.MAX_VALUE watermark when they finishes
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
running = false;
}
}- 这里展示了如何在SourceFunction里头来assign timestamp(
collectWithTimestamp)以及emit watermark(emitWatermark)
DataStream.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks
flink-streaming-java_2.11-1.7.0-sources.jar!/org/apache/flink/streaming/api/datastream/DataStream.java
/**
* Assigns timestamps to the elements in the data stream and periodically creates
* watermarks to signal event time progress.
*
* <p>This method creates watermarks periodically (for example every second), based
* on the watermarks indicated by the given watermark generator. Even when no new elements
* in the stream arrive, the given watermark generator will be periodically checked for
* new watermarks. The interval in which watermarks are generated is defined in
* {@link ExecutionConfig#setAutoWatermarkInterval(long)}.
*
* <p>Use this method for the common cases, where some characteristic over all elements
* should generate the watermarks, or where watermarks are simply trailing behind the
* wall clock time by a certain amount.
*
* <p>For the second case and when the watermarks are required to lag behind the maximum
* timestamp seen so far in the elements of the stream by a fixed amount of time, and this
* amount is known in advance, use the
* {@link BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor}.
*
* <p>For cases where watermarks should be created in an irregular fashion, for example
* based on certain markers that some element carry, use the
* {@link AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks}.
*
* @param timestampAndWatermarkAssigner The implementation of the timestamp assigner and
* watermark generator.
* @return The stream after the transformation, with assigned timestamps and watermarks.
*
* @see AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks
* @see AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks
* @see #assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks)
*/
public SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks<T> timestampAndWatermarkAssigner) {
// match parallelism to input, otherwise dop=1 sources could lead to some strange
// behaviour: the watermark will creep along very slowly because the elements
// from the source go to each extraction operator round robin.
final int inputParallelism = getTransformation().getParallelism();
final AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks<T> cleanedAssigner = clean(timestampAndWatermarkAssigner);
TimestampsAndPeriodicWatermarksOperator<T> operator =
new TimestampsAndPeriodicWatermarksOperator<>(cleanedAssigner);
return transform("Timestamps/Watermarks", getTransformation().getOutputType(), operator)
.setParallelism(inputParallelism);
}
/**
* Assigns timestamps to the elements in the data stream and creates watermarks to
* signal event time progress based on the elements themselves.
*
* <p>This method creates watermarks based purely on stream elements. For each element
* that is handled via {@link AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks#extractTimestamp(Object, long)},
* the {@link AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks#checkAndGetNextWatermark(Object, long)}
* method is called, and a new watermark is emitted, if the returned watermark value is
* non-negative and greater than the previous watermark.
*
* <p>This method is useful when the data stream embeds watermark elements, or certain elements
* carry a marker that can be used to determine the current event time watermark.
* This operation gives the programmer full control over the watermark generation. Users
* should be aware that too aggressive watermark generation (i.e., generating hundreds of
* watermarks every second) can cost some performance.
*
* <p>For cases where watermarks should be created in a regular fashion, for example
* every x milliseconds, use the {@link AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks}.
*
* @param timestampAndWatermarkAssigner The implementation of the timestamp assigner and
* watermark generator.
* @return The stream after the transformation, with assigned timestamps and watermarks.
*
* @see AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks
* @see AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks
* @see #assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks)
*/
public SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks<T> timestampAndWatermarkAssigner) {
// match parallelism to input, otherwise dop=1 sources could lead to some strange
// behaviour: the watermark will creep along very slowly because the elements
// from the source go to each extraction operator round robin.
final int inputParallelism = getTransformation().getParallelism();
final AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks<T> cleanedAssigner = clean(timestampAndWatermarkAssigner);
TimestampsAndPunctuatedWatermarksOperator<T> operator =
new TimestampsAndPunctuatedWatermarksOperator<>(cleanedAssigner);
return transform("Timestamps/Watermarks", getTransformation().getOutputType(), operator)
.setParallelism(inputParallelism);
}- DataStream定义了assignTimestampsAndWatermarks方法,用来在source外头设置timestampAndWatermarkAssigner(
AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks或者AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks类型),告知flink如何提取eventTime
AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks
flink-streaming-java_2.11-1.7.0-sources.jar!/org/apache/flink/streaming/api/functions/AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks.java
public interface AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks<T> extends TimestampAssigner<T> {
/**
* Returns the current watermark. This method is periodically called by the
* system to retrieve the current watermark. The method may return {@code null} to
* indicate that no new Watermark is available.
*
* <p>The returned watermark will be emitted only if it is non-null and its timestamp
* is larger than that of the previously emitted watermark (to preserve the contract of
* ascending watermarks). If the current watermark is still
* identical to the previous one, no progress in event time has happened since
* the previous call to this method. If a null value is returned, or the timestamp
* of the returned watermark is smaller than that of the last emitted one, then no
* new watermark will be generated.
*
* <p>The interval in which this method is called and Watermarks are generated
* depends on {@link ExecutionConfig#getAutoWatermarkInterval()}.
*
* @see org.apache.flink.streaming.api.watermark.Watermark
* @see ExecutionConfig#getAutoWatermarkInterval()
*
* @return {@code Null}, if no watermark should be emitted, or the next watermark to emit.
*/
@Nullable
Watermark getCurrentWatermark();
}- AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks继承了TimestampAssigner接口(
定义了extractTimestamp方法),这里定义了getCurrentWatermark方法,该方法会被周期性调用返回current watermark,如果没有的话返回null
AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks实例
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final int popThreshold = 20; // threshold for popular places
// set up streaming execution environment
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime);
env.getConfig().setAutoWatermarkInterval(1000);
// configure the Kafka consumer
Properties kafkaProps = new Properties();
kafkaProps.setProperty("zookeeper.connect", LOCAL_ZOOKEEPER_HOST);
kafkaProps.setProperty("bootstrap.servers", LOCAL_KAFKA_BROKER);
kafkaProps.setProperty("group.id", RIDE_SPEED_GROUP);
// always read the Kafka topic from the start
kafkaProps.setProperty("auto.offset.reset", "earliest");
// create a Kafka consumer
FlinkKafkaConsumer011<TaxiRide> consumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer011<>(
"cleansedRides",
new TaxiRideSchema(),
kafkaProps);
// assign a timestamp extractor to the consumer
consumer.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new TaxiRideTSExtractor());
// create a TaxiRide data stream
DataStream<TaxiRide> rides = env.addSource(consumer);
// find popular places
DataStream<Tuple5<Float, Float, Long, Boolean, Integer>> popularPlaces = rides
// match ride to grid cell and event type (start or end)
.map(new GridCellMatcher())
// partition by cell id and event type
.keyBy(0, 1)
// build sliding window
.timeWindow(Time.minutes(15), Time.minutes(5))
// count ride events in window
.apply(new RideCounter())
// filter by popularity threshold
.filter((Tuple4<Integer, Long, Boolean, Integer> count) -> (count.f3 >= popThreshold))
// map grid cell to coordinates
.map(new GridToCoordinates());
popularPlaces.print();
// execute the transformation pipeline
env.execute("Popular Places from Kafka");
}
/**
* Assigns timestamps to TaxiRide records.
* Watermarks are a fixed time interval behind the max timestamp and are periodically emitted.
*/
public static class TaxiRideTSExtractor extends BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor<TaxiRide> {
public TaxiRideTSExtractor() {
super(Time.seconds(MAX_EVENT_DELAY));
}
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(TaxiRide ride) {
if (ride.isStart) {
return ride.startTime.getMillis();
}
else {
return ride.endTime.getMillis();
}
}
}- 这里使用了DataStream的assignTimestampsAndWatermarks方法,设置的timestampAndWatermarkAssigner实现了AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks接口(
BoundedOutOfOrdernessTimestampExtractor实现了AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks接口);这里通过env.getConfig().setAutoWatermarkInterval(1000)来设置AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks的间隔
AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks
flink-streaming-java_2.11-1.7.0-sources.jar!/org/apache/flink/streaming/api/functions/AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks.java
public interface AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks<T> extends TimestampAssigner<T> {
/**
* Asks this implementation if it wants to emit a watermark. This method is called right after
* the {@link #extractTimestamp(Object, long)} method.
*
* <p>The returned watermark will be emitted only if it is non-null and its timestamp
* is larger than that of the previously emitted watermark (to preserve the contract of
* ascending watermarks). If a null value is returned, or the timestamp of the returned
* watermark is smaller than that of the last emitted one, then no new watermark will
* be generated.
*
* <p>For an example how to use this method, see the documentation of
* {@link AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks this class}.
*
* @return {@code Null}, if no watermark should be emitted, or the next watermark to emit.
*/
@Nullable
Watermark checkAndGetNextWatermark(T lastElement, long extractedTimestamp);
}- AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks接口继承了TimestampAssigner接口(
定义了extractTimestamp方法),这里定义了checkAndGetNextWatermark方法,该方法会在extractTimestamp方法执行之后被调用(调用时通过方法参数传递刚获取的extractedTimestamp)
AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks实例
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// read parameters
ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args);
String input = params.getRequired("input");
// set up streaming execution environment
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime);
env.setParallelism(1);
// connect to the data file
DataStream<String> carData = env.readTextFile(input);
// map to events
DataStream<ConnectedCarEvent> events = carData
.map((String line) -> ConnectedCarEvent.fromString(line))
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new ConnectedCarAssigner());
// sort events
events.keyBy((ConnectedCarEvent event) -> event.carId)
.process(new SortFunction())
.print();
env.execute("Sort Connected Car Events");
}
public class ConnectedCarAssigner implements AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks<ConnectedCarEvent> {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(ConnectedCarEvent event, long previousElementTimestamp) {
return event.timestamp;
}
@Override
public Watermark checkAndGetNextWatermark(ConnectedCarEvent event, long extractedTimestamp) {
// simply emit a watermark with every event
return new Watermark(extractedTimestamp - 30000);
}
}- 这里使用了DataStream的assignTimestampsAndWatermarks方法,设置的timestampAndWatermarkAssigner实现了AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks接口
小结
- 使用EventTime的话就需要告知flink每个数据的eventTime从哪里取,这个通常跟generate watermarks操作一起告知flink eventTime;有两种方式,一种是data stream source内部处理,一种是通过timestam assigner/watermark generator(
在flink中,timestamp assigners也定义了如何emit watermark,它们使用的是距离1970-01-01T00:00:00Z以来的毫秒数) - 在source里头定义的话,即使用SourceFunction里头定义的SourceContext接口的collectWithTimestamp、emitWatermark方法,前者用来assign event timestamp,后者用来emit watermark
- 在source外头定义的话,就是通过DataStream的assignTimestampsAndWatermarks方法,设置timestampAndWatermarkAssigner;它有两种类型:AssignerWithPeriodicWatermarks(
定义了getCurrentWatermark方法,用于返回当前的watermark;periodic间隔参数通过env.getConfig().setAutoWatermarkInterval(1000)来设置);AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks(定义了checkAndGetNextWatermark方法,该方法会在extractTimestamp方法执行之后被调用(调用时通过方法参数传递刚获取的extractedTimestamp`)






















 196
196











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








