避免使用GroupByKey
我们看一下两种计算word counts 的方法,一个使用reduceByKey,另一个使用 groupByKey:
val words = Array("one", "two", "two", "three", "three", "three")
val wordPairsRDD = sc.parallelize(words).map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCountsWithReduce = wordPairsRDD
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
.collect()
val wordCountsWithGroup = wordPairsRDD
.groupByKey()
.map(t => (t._1, t._2.sum))
.collect()以上两个函数都会产生正确的结果,reduceByKey的例子在大型数据集上工作的效率会更高。因为Spark知道:在shuffle data之前,它可以根据key, 在每个partition上,对输出数据在本地做combine。
下图描述了reduceByKey的执行过程。值得注意的是,在shuffle 数据之前,同一个机器上具有相同key的item会先在本地combine(使用的combine函数是传递给reduceByKey的lambda 函数)。然后这个lambda 函数会再次在执行shuffle后的每个分区上被调用,以产生最终的结果。
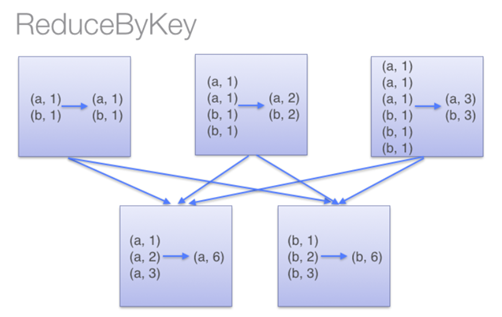
而在groupByKey中,所有的key-value对被先shuffle到下游RDD分区中。这会导致很多不必要的网络数据传输。
在决定将一个key-value对shuffle到哪个机器上时,spark会key-value对中的key调用一个partitioning 函数,以决定分到的目标机器。在shuffle时,若是shuffle的数据(由于内存大小限制)无法全部放入到一个executor中,则Spark会将数据spill到disk。但是,在flush数据到disk时,一次只flush一个key(对应的key-value pairs 数据):所以如果单个key对应的key-value pairs 数据超出了executor可用的memory,则会抛出OOM异常。在较新版的Spark中会处理此异常并让job可以继续执行,但是仍需要尽量避免此类现象:当spark需要spill到磁盘时,spark性能会受到显著影响。

所以在非常大的数据集上计算时,对于reduceByKey与groupByKey来说,它们所需要传输的shuffle数据是有显著不同的。
而在小型数据集上进行测试时(仍使用word count的例子),从测试结果来看,groupByKey的表现要优于reduceByKey。抛开shuffle阶段来看,reduceByKey对内存率会更高于groupByKey,所以相对会报出更多内存不足的情况。若是需要使用reduceByKey,则需要给executor 更多内存在本地做计算。
相对于groupByKey,除了reduceByKey,下面的函数也会是更好的选择:
- combineByKey:可以用于combine元素,用于返回与输入类型不同类型的值
- foldByKey:初始化一个“zero value”,然后对每个Key的值做聚合操作
接下来详细介绍一下这两个函数。
combineByKey
我们先看一下combineByKey的定义:
def combineByKey[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C): RDD[(K, C)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag(createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners)(null)
}可以看到此方法调用的是 combineByKeyWithClassTag:
def combineByKeyWithClassTag[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C)(implicit ct: ClassTag[C]): RDD[(K, C)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag(createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, defaultPartitioner(self))
}继续查看下一层调用:
def combineByKeyWithClassTag[C](
createCombiner: V => C,
mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C,
partitioner: Partitioner,
mapSideCombine: Boolean = true,
serializer: Serializer = null)(implicit ct: ClassTag[C]): RDD[(K, C)]查看reduceByKey代码,可以发现它最终调用的也是combineByKeyWithClassTag 方法:
def reduceByKey(partitioner: Partitioner, func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {
combineByKeyWithClassTag[V]((v: V) => v, func, func, partitioner)
}从combineByKeyWithClassTag方法定义来看,第一个参数是提供用户自定义的类型,用于将输入的<K,V> 中的 V 转化为用户指定类型,第二个参数用于merge V 的值到 C(用户定义类型),第三个参数用于将 C 的值 combine 为一个单值。这里可以看到默认是会在map端做combine,所以默认combineByKey与reduceByKey都是会在map端先做combine操作。
但是对于 groupByKey来说:
def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope {
// groupByKey shouldn't use map side combine because map side combine does not
// reduce the amount of data shuffled and requires all map side data be inserted
// into a hash table, leading to more objects in the old gen.
val createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v)
val mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += v
val mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2
val bufs = combineByKeyWithClassTag[CompactBuffer[V]](
createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, partitioner, mapSideCombine = false)
bufs.asInstanceOf[RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]]
}可以看到,groupByKey虽然最终调用的也是combineByKeyWithClassTag 方法,但是并不会在map端执行Combine操作(mapSideCombine为false)。
下面我们写一个combineByKey求解平均数的例子:
type ScoreCollector = (Int, Double)
type PersonScores = (String, (Int, Double))<br>
val initialScores = Array(("Alice", 90.0), ("Bob", 100.0), ("Tom", 93.0), ("Alice", 95.0), ("Bob", 70.0), ("Jack", 98.0))
val scoreData = sc.parallelize(initialScores).cache()
val createScoreCombiner = (score: Double) => (1, score)<br>
val scoreMerge = (scorecollector: ScoreCollector, score: Double) =>
(scorecollector._1 +1, scorecollector._2 + score)
val scoreCombine = (scorecollector1: ScoreCollector, scorecollector2: ScoreCollector) =>
(scorecollector1._1 + scorecollector2._1, scorecollector1._2 + scorecollector2._2)
scoreData.combineByKey(
createScoreCombiner,
scoreMerge,
scoreCombine
).map( {pscore: PersonScores => (pscore._1, pscore._2._2 / pscore._2._1)}).collect输出为: Array[(String, Double)] = Array((Tom,93.0), (Alice,92.5), (Bob,85.0), (Jack,98.0))
可以看到,首先原类型为(String, Double),然后我们通过combineByKey的第一个参数,将其转化为(Int, Double) 形式,用于统计次数与分数。接下来第二个参数用于merge,将同样key条目出现的次数、以及分数相加。最后第三个参数用于做combine,对每个key,求得的分数求总和,然后除以次数,求得平均值。
这里可以看出 combineByKey与reduceByKey的区别是:combineByKey的可以返回与输入数据类型不一样的输出。
foldByKey
foldByKey 是初始化一个“zero value“,然后对key的value值做聚合操作。例如:
val initialScores = Array(("Alice", 90.0), ("Bob", 100.0), ("Tom", 93.0), ("Alice", 95.0), ("Bob", 70.0), ("Jack", 98.0))
val scoreData = sc.parallelize(initialScores).cache()
scoreData.foldByKey(0)(_+_).collect输出为: Array[(String, Double)] = Array((Tom,93.0), (Alice,185.0), (Bob,170.0), (Jack,98.0))
可以看到,这里给出的“zero value“为0,在执行计算时,会先将所有key的value值与”zero value“做一次加法操作(由_+_定义),然后再对所有key-pair做加法操作。所以若是此时使用:
scoreData.foldByKey(1)(_+_).collect则输出为:Array[(String, Double)] = Array((Tom,94.0), (Alice,187.0), (Bob,172.0), (Jack,99.0))
下面是 foldByKey的源码:
def foldByKey(
zeroValue: V,
partitioner: Partitioner)(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {<br>
// Serialize the zero value to a byte array so that we can get a new clone of it on each key
val zeroBuffer = SparkEnv.get.serializer.newInstance().serialize(zeroValue)
val zeroArray = new Array[Byte](zeroBuffer.limit)
zeroBuffer.get(zeroArray)
// When deserializing, use a lazy val to create just one instance of the serializer per task
lazy val cachedSerializer = SparkEnv.get.serializer.newInstance()
val createZero = () => cachedSerializer.deserialize[V](ByteBuffer.wrap(zeroArray))
val cleanedFunc = self.context.clean(func)
combineByKeyWithClassTag[V]((v: V) => cleanedFunc(createZero(), v),
cleanedFunc, cleanedFunc, partitioner)
}可以看到它与reduceByKey和combineByKye类似,最终调用的也是combineByKeyWithClassTag 方法,且未覆盖mapSideCombine 的值,所以默认也会在map端进行combine操作。
所以在大型数据集中,为了减少shuffle的数据量,相对于groupByKey来说,使用reduceByKey、combineByKey以及foldByKey 会是更好的选择。
References:
[2] http://codingjunkie.net/spark-combine-by-key/
原文链接:cnblogs.com/zackstang/p/10990750.html
Spark中groupBy groupByKey reduceByKey的区别
groupBy
和SQL中groupby一样,只是后面必须结合聚合函数使用才可以。
例如:
hour.filter($"version".isin(version: _*)).groupBy($"version").agg(countDistinct($"id"), count($"id")).show()
groupByKey
对Key-Value形式的RDD的操作。
例如(取自link):
val a = sc.parallelize(List("dog", "tiger", "lion", "cat", "spider", "eagle"), 2)
val b = a.keyBy(_.length)//给value加上key,key为对应string的长度
b.groupByKey.collect
//结果 Array((4,ArrayBuffer(lion)), (6,ArrayBuffer(spider)), (3,ArrayBuffer(dog, cat)), (5,ArrayBuffer(tiger, eagle)))
reduceByKey
与groupByKey功能一样,只是实现不一样。本函数会先在每个分区聚合然后再进行总的统计,如图:

而groupByKey则是

因此,本函数比groupByKey节省了传播的开销,尽量少用groupByKey
参考
- https://www.iteblog.com/archives/1357.html
- http://blog.csdn.net/guotong1988/article/details/50556871
- http://blog.cheyo.net/178.html
原文:cnblogs.com/wswang/p/8360755.html
Spark中reduceByKey()和groupByKey()的区别
在Spark当中,分组操作时,提供了这么两个函数,用WordCount程序来举例。
val words = Array("one", "two", "two", "three", "three", "three")
val wordPairsRDD = sc.parallelize(words).map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCountsWithReduce = wordPairsRDD
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
.collect()
val wordCountsWithGroup = wordPairsRDD
.groupByKey()
.map(t => (t._1, t._2.sum))
.collect()
这两种做法的结果都是正确的。
在大的数据集上,reduceByKey()的效果比groupByKey()的效果更好一些。因为reduceByKey()会在shuffle之前对数据进行合并。
如图所示:
下面一张图就能表示reduceByKey()都做了什么。

reduceByKey
而当我们调用groupByKey()的时候,所有的键值对都会被shuffle到下一个stage,传输的数据比较多,自然效率低一些。
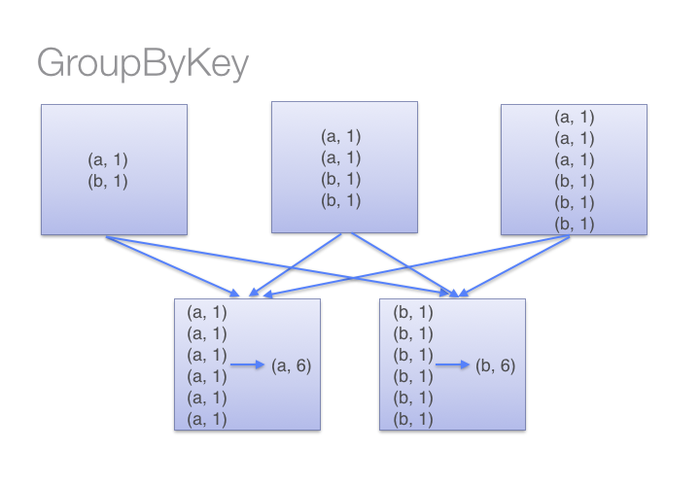
groupByKey
原文:Spark中reduceByKey()和groupByKey()的区别(译)
原文:jianshu.com/p/7f8d4484bfbd
Spark优化操作_自定义groupby
groupby或者groupbyKey算子效率太低,自己重写了一下。
//用combineByKey替代groupBy
val home_data_combine: RDD[(String, List[home_info])] = phone_date_key_data.
map(home => (home.phone_date, home)).
partitionBy(new org.apache.spark.HashPartitioner(1000)).
combineByKey((x: home_info) => List(x),
(curlist: List[home_info], x: home_info) => x :: curlist,
(curlist1: List[home_info], curlist2: List[home_info]) => curlist1 ::: curlist2)
大家都应该了解,reduceByKey的效率会比groupbyKey高很多,但你就是要实现一个聚合的过程,并不需要reduce,就需要用groupby或者groupbyKey,但他们的效率太低了。需要自己实现一个。此处combineByKey来实现聚合的过程。 实现说明: 1.先做partitionBy 2.调用combineByKey,在每个partition内用list实现聚合 要充分理解的combineByKey实现过程,如上过程就会比较了解了。
原文:blog.csdn.net/willyan2007/article/details/78875461
























 1290
1290

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








