在很多情况下,我们都会用到许多相同或者相似的对象,如果我们为每个对象都创建一个实例就显得比较浪费。享元模式便可以用来解决这个问题。享元模式说的文雅,简单地解释就是“共享”的意思。打个比方说--------->在Word中输入一段文字,如abaaccad,对于这段文字a,c都是重复出现的字母,那么只需创建一个a与一个b对象然后记录对象的位置就可以,而不需要创建多个a或b!!
享元模式的英文名是Flyweight,是”轻量级“的意思,这样命名的原因是:享元模式通过重复使用已经创建好的对象来达到减小系统开销的目的,显得十分”轻巧“。
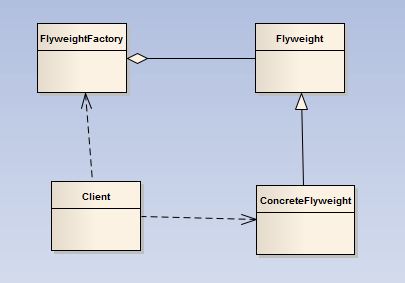
一图胜千言,上类图:
FlyweightFactory是享元工厂
Flyweight是抽象的享元类
ConcreteFlyweight是具体的享元类
Client是用户,它通过FlyweightFactory获得享元类的对象
享元类的主要目的就是重复使用已存在的类,而这一功能的实现,最大的奥秘就在FlyweightFactory中。
下面上一段代码,一探究竟:
这段代码描述的是一个下围棋的情景。有黑色和白色两种棋子。每个棋子有他在棋盘上的坐标。
coordinate类------------------------------------------------------>坐标类,外部状态类
IgoChessman类------------------------------------------------->抽象享元类
BlackIgoChessman类和WhiteIgoChessman类-------->具体享元类
IgoCHessmanFactory------------------------------------------>工厂类
import java.util.*;
//外部状态类
class Coordinates//坐标类
{
private int x;
private int y;
public Coordinates(int x, int y)//构造方法
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
}
//抽象享元类
public abstract class IgoChessman
{
public abstract String getColor();
//通过该方法设置外部状态(坐标)
public void locate(Coordinates coord)
{
System.out.println("棋子颜色:"+this.getColor()+"棋子位置"+coord.getX()+","+coord.getY());
}
}
//具体享元类
class BlackIgoChessman extends IgoChessman
{
public String getColor()
{
return "黑色";
}
}
class WhiteIgoChessman extends IgoChessman
{
public String getColor()
{
return "白色";
}
}
//享元工厂类(单例类)
class IgoChessmanFactory
{
private static IgoChessmanFactory instance=new IgoChessmanFactory();//饿汉式的单例类。
private static Hashtable ht;//创建的对象保存在hashtable中
private IgoChessmanFactory()//私有的构造函数
{
ht=new Hashtable();
IgoChessman black,white;
black=new BlackIgoChessman();
ht.put("b",black);
white=new WhiteIgoChessman();
ht.put("w",white);
}
public static IgoChessmanFactory getInstance()
{
return instance;
}
public static IgoChessman getIgoChessman(String color)
{
return (IgoChessman)ht.get(color);
}
}
class Client
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
IgoChessman black1,black2,black3,white1,white2;
IgoChessmanFactory factory;
factory=IgoChessmanFactory.getInstance();
black1=factory.getIgoChessman("b");
black2=factory.getIgoChessman("b");
black3=factory.getIgoChessman("b");
System.out.println("判断黑棋是否相同:"+(black1==black2));//true
white1=factory.getIgoChessman("w");
white2=factory.getIgoChessman("w");
System.out.println("判断白棋是否相同:"+(white1==white2));//true
black1.locate(new Coordinates(1,2)/*匿名类*/);
black2.locate(new Coordinates(3,2)/*匿名类*/);
black3.locate(new Coordinates(1,3)/*匿名类*/);
white1.locate(new Coordinates(2,2)/*匿名类*/);
white2.locate(new Coordinates(5,2)/*匿名类*/);
}
}可以看到,FlyweightFactory的实现有点像一个线程池,当Client发出对一类对象的使用请求时,首先判断是否已经创建了该类的对象,若有则使用该对象,否则创建该对象。






















 157
157











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








