普通的长列表就是直接生成对应的dom元素节点,但10万加的数据需要生成10万加个元素。我们先来看看浏览器渲染一万条数据的性能:
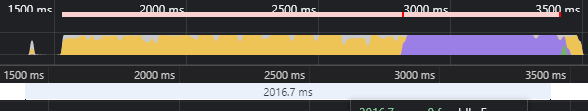
从上图可以看到 React 渲染 10000 个节点数据使用了 2 秒时间。
黄色段 生成数据节点使用了 1.3秒
蓝色段 Layout计算 使用了0.7秒
初始化加载表单就需要两秒 显然不可接受。
在看一下优化后的长列表方案性能:
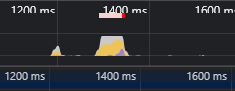
黄色段 生成节点 使用57毫秒
蓝色段 Layout计算 1.26毫秒
为什么差异如此之大。实际上是因为节点过多对于浏览器而言是有额外的计算开销的。
那么如何实现一个有效的长列表呢?
别急,我们接着讲。
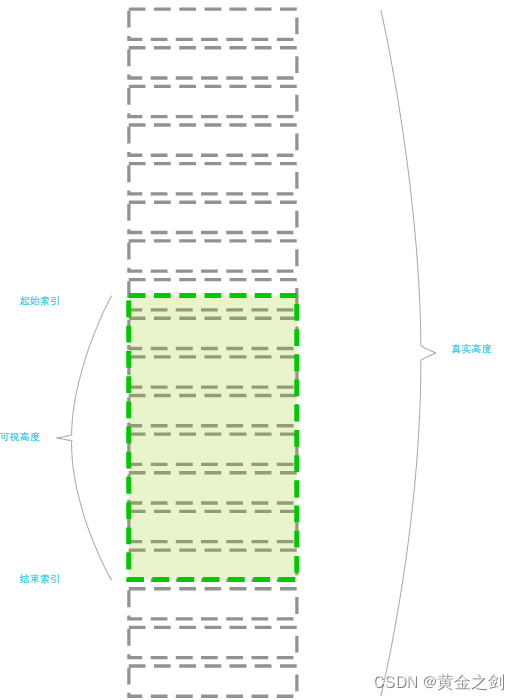
为了节省节点数量,我们仅渲染可视区内部的节点。即开始索引和结束索引之间的内容。通过控制开始索引和结束索引来控制和切换显示的数据消息。
通过 onScroll 事件来更新起始索引和结束索引。
具体代码如下:
render(): React.ReactNode {
const { start, end, itemHeight, dataSource, cellRender } = this.props;
return (
<>
<div className="virtual-list-grid-base" style={{ height: dataSource.length * itemHeight }}>
{dataSource.map((item, index) => {
return (
index >= start &&
index <= end && (
<Cell key={index} index={index} itemHeight={itemHeight}>
{cellRender(item, { index })}
</Cell>
)
);
})}
</div>
</>
);
}
handleScroll = (): void => {
const {
total,
limit,
originStartIdx,
props: { overScan },
} = this;
const scrollTop = this.domRef.current.scrollTop;
const currIndex = this.getStartIndex(scrollTop);
if (originStartIdx !== currIndex) {
this.originStartIdx = currIndex;
this.startIndex = Math.max(currIndex - overScan, 0);
this.endIndex = Math.min(currIndex + limit + overScan, total - 1);
this.setState({
scrollTop: scrollTop,
});
}
}
如此便实现了一个简版的长列表渲染
代码
滚动区
import * as React from 'react';
import { binarySearch } from '../../helper';
import { CompareResult, IListCachedPosition, IListOption } from '../../type';
import Grid from './Grid';
import './ScrollBar.css';
interface IProps<T> {
overScan?: number; // 超出的预加载数量
style?: React.CSSProperties | { width: number; height: number }; // 滚动的样式
className?: string;
itemHeight?: number;
dataSource: T[]; // 数据
extra?: { [key: string]: any };
cellRender: (node: T, option: IListOption) => React.ReactNode; // 自定义节点渲染
}
interface IStates<T> {
scrollTop: number;
cachedPositions: IListCachedPosition[];
}
/**
* 虚拟滚动列表
*
* 仅显示可见区域的节点
* TODO: 实现行高自适配
*/
class ScrollBar<T> extends React.Component<React.PropsWithChildren<IProps<T>>, IStates<T>> {
private domRef: React.RefObject<HTMLDivElement> = React.createRef();
private cachedPositions: IListCachedPosition[] = []; // 缓存的节点位置列表
private startIndex = 0;
private endIndex = 0;
private originStartIdx = 0;
private limit = 0;
private total = 0;
private estimateMinHeight = 25; // 预估节点高度
static defaultProps = {
overScan: 2,
};
constructor(props: IProps<T>) {
super(props);
this.total = props.dataSource.length;
this.estimateMinHeight = props.itemHeight ?? this.estimateMinHeight;
this.initCachedPositions();
this.state = {
cachedPositions: this.cachedPositions,
scrollTop: 0,
};
this.originStartIdx = 0;
}
componentDidMount(): void {
const contentHeight = this.domRef.current?.getBoundingClientRect().height;
this.limit = Math.ceil(contentHeight / this.estimateMinHeight);
this.startIndex = Math.max(this.originStartIdx - this.props.overScan, 0);
this.endIndex = Math.min(this.originStartIdx + this.limit + this.props.overScan, this.total - 1);
this.setState({ scrollTop: this.domRef.current.scrollTop });
}
// 初始化cachedPositions
initCachedPositions = (): void => {
const { estimateMinHeight } = this;
this.cachedPositions = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.total; ++i) {
this.cachedPositions[i] = {
index: i,
height: estimateMinHeight, // 先使用estimateHeight估计
top: i * estimateMinHeight, // 同上
bottom: (i + 1) * estimateMinHeight,
};
}
};
getStartIndex = (scrollTop = 0): number => {
let idx = binarySearch<IListCachedPosition, number>(
this.cachedPositions,
scrollTop,
(currentValue: IListCachedPosition, targetValue: number) => {
const currentCompareValue = currentValue.bottom;
if (currentCompareValue === targetValue) {
return CompareResult.eq;
}
if (currentCompareValue < targetValue) {
return CompareResult.lt;
}
return CompareResult.gt;
},
);
const targetItem = this.cachedPositions[idx];
// Incase of binarySearch give us a not visible data(an idx of current visible - 1)...
if (targetItem.bottom < scrollTop) {
idx += 1;
}
return idx;
};
handleScroll = (): void => {
const {
total,
limit,
originStartIdx,
props: { overScan },
} = this;
const scrollTop = this.domRef.current.scrollTop;
const currIndex = this.getStartIndex(scrollTop);
if (originStartIdx !== currIndex) {
this.originStartIdx = currIndex;
this.startIndex = Math.max(currIndex - overScan, 0);
this.endIndex = Math.min(currIndex + limit + overScan, total - 1);
this.setState({
scrollTop: scrollTop,
});
}
};
scrollToRow(index: number): void {
this.domRef.current.scrollTo({ top: this.cachedPositions[index].top });
}
render(): React.ReactNode {
const {
startIndex,
endIndex,
props: { className, extra, style, dataSource, cellRender },
} = this;
return (
<div
ref={this.domRef}
className={`virtual-list-scroll-base ${className}`}
style={style}
onScroll={this.handleScroll}
>
<Grid
start={startIndex}
end={endIndex}
itemHeight={this.estimateMinHeight}
dataSource={dataSource}
extra={extra}
cellRender={cellRender}
/>
</div>
);
}
}
export default ScrollBar;
加载器
import * as React from 'react';
import { IListOption } from '../../type';
import Cell from './Cell';
interface IProps<T> {
dataSource: T[];
start: number; // 起始索引
end: number; //结束索引
itemHeight: number; // 节点高度
extra?: { [key: string]: any };
cellRender: (node: T, option: IListOption) => React.ReactNode;
}
/**
* 网格类
* TODO: 实现多行多列布局
*/
class Grid<T> extends React.PureComponent<IProps<T>> {
render(): React.ReactNode {
const { start, end, itemHeight, dataSource, cellRender } = this.props;
return (
<>
<div className="virtual-list-grid-base" style={{ height: dataSource.length * itemHeight }}>
{dataSource.map((item, index) => {
return (
index >= start &&
index <= end && (
<Cell key={index} index={index} itemHeight={itemHeight}>
{cellRender(item, { index })}
</Cell>
)
);
})}
</div>
</>
);
}
}
export default Grid;
节点
import * as React from 'react';
import './Cell.css';
interface IProps {
index: number;
itemHeight: number;
onMount?: (dom: Element, index: number) => void;
}
/**
* 当行类
* 自定义的渲染
*/
class Cell extends React.PureComponent<React.PropsWithChildren<IProps>> {
render(): React.ReactNode {
const { children, index, itemHeight } = this.props;
return (
<div
className="virtual-list-cell-base"
id={`virtual-list-cell-base-${index}`}
style={{ height: itemHeight, top: index * itemHeight }}
>
{children}
</div>
);
}
}
export default Cell;
如上,我们就已经实现了一个固定节点高度的长列表了。
但很多情况节点并不是固定高度怎么办?
这个问题后面继续讲解。





















 4449
4449











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








