http://godorz.info/2011/03/the-annotated-libevent-sources-about-http/
libevent自带了一个http库,用它可以很简单的实现一个http服务器,本文非常简单地分析之.
evhttp
evhttp库有几个主要的结构体,它们之间的联系非常龌龊:

其中,结构体event, min_heap, evsignal_info, eventop, event_base在前面几篇文章中已经介绍过了,这里不再啰嗦.
evbuffer
evbuffer用于读或写缓冲,图示为:
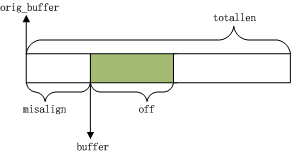
和evbuffer有关的外露接口主要是:
1.
//从文件读数据到缓冲,读取量为max(howmuch, 4096)
2.
int evbuffer_read(struct evbuffer *buf, int fd, int howmuch);
3.
4.
//把缓冲写出文件
5.
int evbuffer_write(struct evbuffer *buffer, int fd)
evbuffer比较简单,不多介绍.
evhttp, evhttp_connection, evhttp_request
libevent对成员的命名不太在意,其实evhttp可以看做是echttpsever,它绑定到某个特定端口和地址(socket(), bind()),保存访问该server的连接(通过成员connections,).evhttp_connection是保存连接信息的结构体, evhttp_request表示请求.
看看http库的使用流程:
01.
void http_handler(struct evhttp_request *req, void *arg)
02.
{
03.
struct evbuffer *buf;
04.
buf = evbuffer_new();
05.
06.
// 分析请求
07.
char *decode_uri = strdup((char*) evhttp_request_uri(req));
08.
struct evkeyvalq http_query;
09.
evhttp_parse_query(decode_uri, &http_query);
10.
free(decode_uri);
11.
12.
// 从http头中获取参数
13.
const char *request_value = evhttp_find_header(&http_query, "data");
14.
15.
// 返回HTTP头部
16.
evhttp_add_header(req->output_headers, "Content-Type", "text/html; charset=UTF-8");
17.
evhttp_add_header(req->output_headers, "Server", "my_httpd");
18.
//evhttp_add_header(req->output_headers, "Connection", "keep-alive");
19.
20.
evhttp_add_header(req->output_headers, "Connection", "close");
21.
22.
// 将要输出的值写入输出缓存
23.
if(request_value != NULL) {
24.
evbuffer_add_printf(buf, "%s", request_value);
25.
} else {
26.
evbuffer_add_printf(buf, "%s", "no error.");
27.
}
28.
29.
// 输出
30.
evhttp_send_reply(req, HTTP_OK, "OK", buf);
31.
32.
// 内存释放
33.
evhttp_clear_headers(&http_query);
34.
evbuffer_free(buf);
35.
}
36.
37.
int main(int argc, char **argv)
38.
{
39.
char *host_ip = "0.0.0.0";
40.
int host_port = 8080;
41.
int timeout = 3;
42.
43.
struct evhttp *httpd;
44.
45.
event_init();
46.
47.
//根据host_ip和host_port创建一个addrinfo结构体,然后创建一个socket,绑定到这个socket后,
48.
//根据这些信息得到得到一个event(回调函数设置为accept_socket),然后将这个event关联到对应的event_base,
49.
//之后插入到&http->sockets队列中,然后返回&http
50.
httpd = evhttp_start(host_ip, host_port);
51.
52.
if (httpd == NULL) {
53.
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Unable to listen on %s:%d\n\n", host_ip, host_port);
54.
exit(1);
55.
}
56.
57.
// 设置请求超时时间
58.
evhttp_set_timeout(httpd, timeout);
59.
60.
// 设置请求的处理函数
61.
evhttp_set_gencb(httpd, http_handler, NULL);
62.
63.
event_dispatch();
64.
65.
evhttp_free(httpd);
66.
67.
return 0;
68.
}
[1] 首先看看evhttp_start():
1.
//创建一个evhttp,绑定到端口和地址
2.
struct evhttp * evhttp_start(const char *address, u_short port)
3.
{
4.
struct evhttp *http = evhttp_new_object();
5.
evhttp_bind_socket(http, address, port);
6.
return (http);
7.
}
函数evhttp_bind_socket()代码如下:
01.
//根据address和port创建一个非阻塞的socket,
02.
//将其bind后的fd创建一个event(在这里设置好回调函数)后添加到&http->sockets
03.
int evhttp_bind_socket(struct evhttp *http, const char *address, u_short port)
04.
{
05.
int fd;
06.
int res;
07.
08.
//绑定一个socket
09.
fd = bind_socket(address, port, 1 /*reuse*/);
10.
11.
//根据fd创建一个event,设置好回调函数,
12.
//然后将这个event关联到对应的event_base,并将它插入到&http->sockets中.
13.
res = evhttp_accept_socket(http, fd);
14.
15.
return (res);
16.
}
在这里,函数bing_socket()的作用是根据地址和端口创建一个socket,返回bind()后的文件描述符.函数evhttp_accept_socket()的作用在注释中也说明了,其代码如下:
01.
int evhttp_accept_socket(struct evhttp *http, int fd)
02.
{
03.
struct evhttp_bound_socket *bound;
04.
struct event *ev;
05.
int res;
06.
07.
bound = malloc(sizeof(struct evhttp_bound_socket));
08.
ev = &bound->bind_ev;
09.
10.
/* Schedule the socket for accepting */
11.
//设置这个ev,回调函数为accept_socket,针对的文件描述符为fd
12.
event_set(ev, fd, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, accept_socket, http);
13.
14.
//将ev关联到&http->base
15.
EVHTTP_BASE_SET(http, ev);
16.
17.
//将ev添加进&http->base
18.
res = event_add(ev, NULL);
19.
20.
//将bound插入到&http->sockets
21.
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&http->sockets, bound, next);
22.
}
需要指出的是,在这个函数中,struct event *ev可以看成是服务器struct evhttp的代理,evhttp通过这个ev是否可读来注意到是否有新的连接.(后文会分析.)
[2] 函数evhttp_set_timeout()和evhttp_set_gencb()逻辑比较简单,分别设置超时时间和回调函数.
[3]重头戏来了,函数event_dispatch()负责分发,在前面的文章已经介绍过了,它最终会调用event_base_loop(),分别查看定时器最小堆,信号队列和I/O队列.在http库中,当有一个新的连接时,[1]中已加入到event_base已注册事件队列的事件ev->fd将变成可读,它被移入已就绪事件队列,然后由函数event_process_active()调用ev的回调函数accept_socket()(回调函数在evhttp_accept_socket()函数中设置).
需要说明的是,以下的内容都是在event_base_loop()死循环中被处理的.
现在看一下回调函数accept_socket()的代码:
01.
//作为回调函数,accept 一个 socket
02.
static void accept_socket(int fd, short what, void *arg)
03.
{
04.
struct evhttp *http = arg;
05.
struct sockaddr_storage ss;
06.
socklen_t addrlen = sizeof(ss);
07.
int nfd;
08.
09.
//获得accept()后的文件描述符
10.
nfd = accept(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&ss, &addrlen);
11.
12.
//设置为非阻塞
13.
evutil_make_socket_nonblocking(nfd);
14.
15.
//获得连接
16.
evhttp_get_request(http, nfd, (struct sockaddr *)&ss, addrlen);
17.
}
代码很好懂,看看evhttp_get_request()函数:
01.
//在回调函数accept_socket中被调用.
02.
//这里传入的参数fd是accept()后返回的描述符
03.
void evhttp_get_request(struct evhttp *http, int fd, struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t salen)
04.
{
05.
struct evhttp_connection *evcon;
06.
07.
//根据fd和sa创建一个evhttp_connection,并将它关联到http->base.
08.
evcon = evhttp_get_request_connection(http, fd, sa, salen);
09.
10.
if (http->timeout != -1)
11.
//watch out!!!在这里evcon会被设置超时时间.
12.
evhttp_connection_set_timeout(evcon, http->timeout);
13.
14.
//将evcon关联到http
15.
evcon->http_server = http;
16.
17.
//将evcon插入到&http->connections
18.
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&http->connections, evcon, next);
19.
20.
evhttp_associate_new_request_with_connection(evcon);
21.
}
跟踪下去看看evhttp_associate_new_request_with_connection()函数:
01.
//初始化一个绑定到evcon的evhttp_request
02.
static int evhttp_associate_new_request_with_connection(struct evhttp_connection *evcon)
03.
{
04.
struct evhttp *http = evcon->http_server;
05.
struct evhttp_request *req;
06.
07.
//在这里会设置该req的回调函数evhttp_handle_request(),此函数很重要..
08.
req = evhttp_request_new(evhttp_handle_request, http);
09.
10.
req->evcon = evcon;
11.
req->flags |= EVHTTP_REQ_OWN_CONNECTION;
12.
13.
TAILQ_INSERT_TAIL(&evcon->requests, req, next);
14.
15.
req->kind = EVHTTP_REQUEST;
16.
17.
req->remote_host = strdup(evcon->address);
18.
19.
req->remote_port = evcon->port;
20.
21.
evhttp_start_read(evcon);
22.
23.
return (0);
24.
}
经过这么多层次的函数调用,终于要读数据了,evhttp_start_read()代码:
01.
void evhttp_start_read(struct evhttp_connection *evcon)
02.
{
03.
/* Set up an event to read the headers */
04.
if (event_initialized(&evcon->ev))
05.
event_del(&evcon->ev);
06.
07.
//根据这些参数设置好evcon->ev.回调函数为evhttp_read()
08.
event_set(&evcon->ev, evcon->fd, EV_READ, evhttp_read, evcon);
09.
10.
//关联到event_base中
11.
EVHTTP_BASE_SET(evcon, &evcon->ev);
12.
13.
//将该ev插入到event_base中
14.
15.
//watch out!!!!
16.
//在这里会设置这个event的超时时间,它将被加入到定时器最小堆中
17.
//超时之后,该事件会被event_active(),插入到就绪队列中,然后执行其回调函数.
18.
19.
//evcon->timeout是在evhttp_get_request()被设置的
20.
evhttp_add_event(&evcon->ev, evcon->timeout, HTTP_READ_TIMEOUT);
21.
evcon->state = EVCON_READING_FIRSTLINE;
22.
}
可以看到,对于这个连接,evhttp_connection结构体evcon是通过内部成员event *ev来处理的.函数evhttp_start_read()对&evcon->ev设置好超时时间和回调函数后将它插入到event_base中.
直到这里,回调函数accept_socket()的功能终于完成了.
(3.2) 上一段提到accept_socket()函数最终会调用evhttp_start_read()来设置连接对应的event(&evcon->ev)的超时时间和回调函数,并将它插入已激活事件队列进行schedule.
在&evcon->ev超时之后,它会被函数timeout_process()从已激活事件队列移入已就绪事件队列,然后由函数event_process_active()调用它的回调函数,也即是evhttp_read()(此回调函数在函数evhttp_start_read()中设置).代码如下:
01.
//读数据
02.
void evhttp_read(int fd, short what, void *arg)
03.
{
04.
struct evhttp_connection *evcon = arg;
05.
//拿到第一个req
06.
struct evhttp_request *req = TAILQ_FIRST(&evcon->requests);
07.
struct evbuffer *buf = evcon->input_buffer;
08.
int n, len;
09.
10.
if (what == EV_TIMEOUT) {
11.
evhttp_connection_fail(evcon, EVCON_HTTP_TIMEOUT);
12.
return;
13.
}
14.
15.
//从fd读数据到buf
16.
n = evbuffer_read(buf, fd, -1);
17.
len = EVBUFFER_LENGTH(buf);
18.
19.
if (n == -1) {
20.
if (errno != EINTR && errno != EAGAIN) {
21.
event_debug(("%s: evbuffer_read", __func__));
22.
evhttp_connection_fail(evcon, EVCON_HTTP_EOF);
23.
} else {
24.
evhttp_add_event(&evcon->ev, evcon->timeout,
25.
HTTP_READ_TIMEOUT);
26.
}
27.
return;
28.
} else if (n == 0) {
29.
/* Connection closed */
30.
evhttp_connection_done(evcon);
31.
return;
32.
}
33.
34.
switch (evcon->state) {
35.
case EVCON_READING_FIRSTLINE:
36.
evhttp_read_firstline(evcon, req);
37.
break;
38.
case EVCON_READING_HEADERS:
39.
evhttp_read_header(evcon, req);
40.
break;
41.
case EVCON_READING_BODY:
42.
evhttp_read_body(evcon, req);
43.
break;
44.
case EVCON_READING_TRAILER:
45.
evhttp_read_trailer(evcon, req);
46.
break;
47.
case EVCON_DISCONNECTED:
48.
case EVCON_CONNECTING:
49.
case EVCON_IDLE:
50.
case EVCON_WRITING:
51.
default:
52.
event_errx(1, "%s: illegal connection state %d",
53.
__func__, evcon->state);
54.
}
55.
}
代码中的fd其实是evcon->fd,也就是accept()后返回的文件描述符..
函数evhttp_read()就这么一直读数据下去(可能经过了多次循环,因为在evhttp_accept_socket()函数中被设置了EV_PERSIST标志,所以它不会从已注册时间队列中被移除,而是不断的超时,不断地被调用其回调函数),直到数据读完了(这里经过了好多状态,非常让人不爽的是,libevent官网上连个FSM图都没有,这种体力活我也不会干的,哈哈~),就调用evhttp_connection_done(),代码如下:
01.
//累个半死终于读完啦
02.
static void evhttp_connection_done(struct evhttp_connection *evcon)
03.
{
04.
...//省略
05.
06.
//调用req的回调函数
07.
(*req->cb)(req, req->cb_arg);
08.
09.
}
在这里,会调用req的回调函数,也就是在函数evhttp_associate_new_request_with_connection()中设置的evhttp_handle_request(),此回调函数代码为:
01.
//处理请求,在这里会调用http的回调函数http->gencb
02.
static void evhttp_handle_request(struct evhttp_request *req, void *arg)
03.
{
04.
...//一堆无用的噪音
05.
06.
//由用户指定的回调函数终于显灵了.
07.
if (http->gencb) {
08.
(*http->gencb)(req, http->gencbarg);
09.
return;
10.
}
11.
12.
}
在数据全都读入后,libevent终于终于终于调用了用户指定的回调函数(*http->gencb).在本文一开始的小例子中,也就是函数http_handler(),要达到这一步可真不容易啊,撒花..
由上文提到的种种的繁琐的过程可以看出,libevent对于user来说是很友善的,几句代码就可以实现一个httpd,可以对于developer来说就太恶心了..





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








