用链表实现线性表
正如上一篇看到,使用数组实现ADT线性表既有优点也有优点。数组的长度可以是固定的,也可以动态扩展数组,但每次动态扩展数组时,都需要移动数据。不管是定长的数组还是可扩展的动态数组,在需要为新元素腾出空间或者弥合删除后留下的间隙时,都要求移动数据。而基于链表实现的线性表可以避免移动数据,并且在插入和删除操作上需要更少的开销,反而查找速率降低了。通过这篇文章,你可以知道LinkedList的基本工作方式。
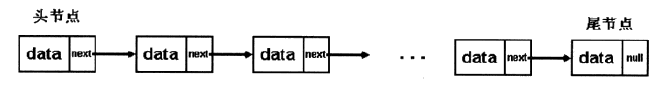
下图就是最简单的单向链表。
链表接口
public interface ListInterface<T> {
public boolean add(T newEntry);
public boolean add(int newPosition,T newEntry);
public T remove(int givenPosition);
public void clear();
public boolean replace(int givenPosition,T newEntry);
public T getEntry(int givenPosition);
public boolean contains(T anEntry);
public int getLength();
public boolean isEmpty();
public boolean isFull();
public void display();
}
链表实现类
链表是由一个个结点(Node)组成的,而结点应该是实现类所私有的,应该定义成内部类。单向链表的结点有两个数据域,一个引用线性表中的元素,一个引用另一个结点。
public class Linked_list<T> implements ListInterface<T>{
private Node firstNode;
private int length;
public Linked_list() {
firstNode=null;
length=0;
}
private Node getNodeAt(int givenPosition){
assert !isEmpty() && givenPosition>=1 && givenPosition<=length;
Node currentNote=firstNode;
for(int i=1;i<givenPosition;i++){
currentNote=currentNote.next;
}
assert currentNote!=null;
return currentNote;
}
@Override
public boolean add(T newEntry) {
Node newNode=new Node(newEntry);
if(isEmpty())
firstNode=newNode;
else{
Node lastNode=getNodeAt(length);
lastNode.next=newNode;
}
length++;
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean add(int newPosition, T newEntry) {
boolean isSuccessful=true;
if(newPosition>=1 && newPosition<=length+1){
Node newNode=new Node(newEntry);
if(isEmpty() || newPosition==1){
newNode.next=firstNode;
firstNode=newNode;
}else{
Node beforeNode=getNodeAt(newPosition-1);
Node afterNode=beforeNode.next;
beforeNode.next=newNode;
newNode.next=afterNode;
}
length++;
}else
isSuccessful=false;
return isSuccessful;
}
@Override
public T remove(int givenPosition) {
T result=null;
if(!isEmpty() && givenPosition>=1 && givenPosition<=length){
if(givenPosition==1){
result=firstNode.element;
firstNode=firstNode.next;
}else{
Node beforeNode=getNodeAt(givenPosition-1);
Node ToremoveNode=beforeNode.next;
Node afterNode=ToremoveNode.next;
result=ToremoveNode.element;
beforeNode.next=afterNode;
}
length--;
}
return result;
}
@Override
public final void clear() {
firstNode=null;
length=0;
}
@Override
public boolean replace(int givenPosition, T newEntry) {
boolean isSuccessful=true;
if(!isEmpty() && givenPosition>=1 && givenPosition<=length){
Node desiredNode=getNodeAt(givenPosition);
desiredNode.element=newEntry;
}else
isSuccessful=false;
return isSuccessful;
}
@Override
public T getEntry(int givenPosition) {
T result=null;
if(!isEmpty() && givenPosition>=1 && givenPosition<=length){
Node desiredNode=getNodeAt(givenPosition);
result=desiredNode.element;
}
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(T anEntry) {
boolean isSuccessful=false;
Node currentNode=firstNode;
while (currentNode!=null) {
if(currentNode.element.equals(anEntry)){
isSuccessful=true;
break;
}
currentNode=currentNode.next;
}
return isSuccessful;
}
@Override
public int getLength() {
return length;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return length==0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return false;
}
@Override
public void display() {
Node currentNode=firstNode;
while (currentNode!=null) {
System.out.print(currentNode.element+" ");
currentNode=currentNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
private class Node {
private T element;
private Node next;
private Node(T element) {
this(element,null);
}
private Node(T element,Node next){
this.element=element;
this.next=next;
}
}
}测试代码
public class main_Link {
private static Linked_list<Integer> list;
public static void main(String[] args) {
list=new Linked_list<Integer>();
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++)
list.add(i);
list.add(11, 24);
list.display();
list.remove(13);
list.display();
list.replace(19, 56);
list.display();
System.out.println(list.getEntry(19));
if(list.contains(56))
System.out.println("包含了");
System.out.println("链表长度:"+list.getLength());
}
}1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 24 11 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 24 11 13 14 15 16 17 18 56 20
56
包含了
链表长度:20
......................................................................................................华丽分割线........................................................................................................
因为Node是内部类,则Linked_list类可以按名称直接访问Node的私有数据域。然而一些计算机科学家认为,应该使用getter和setter方法访问类的数据域。并且可以实现迭代器来历遍链表的数据,从而代替上述display()函数。
链表接口扩展
public interface ListWithIteratorInterface<T> extends ListInterface<T>{
public Iterator<T> getIterator();
}链表实现类
public class LinkedListWithIterator<T> implements ListWithIteratorInterface<T>{
private Node firstNode;
private int length;
public LinkedListWithIterator() {
firstNode=null;
length=0;
}
private Node getNodeAt(int givenPosition){
assert !isEmpty() && givenPosition>=1 && givenPosition<=length;
Node currentNote=firstNode;
for(int i=1;i<givenPosition;i++){
currentNote=currentNote.getNextNode();
}
assert currentNote!=null;
return currentNote;
}
@Override
public boolean add(T newEntry) {
Node newNode=new Node(newEntry);
if(isEmpty())
firstNode=newNode;
else{
Node lastNode=getNodeAt(length);
lastNode.setNextNode(newNode);;
}
length++;
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean add(int newPosition, T newEntry){
boolean isSuccessful=true;
if(newPosition>=1 && newPosition<=length+1){
Node newNode=new Node(newEntry);
if(isEmpty() || newPosition==1){
newNode.setNextNode(firstNode);;
firstNode=newNode;
}else{
Node beforeNode=getNodeAt(newPosition-1);
Node afterNode=beforeNode.getNextNode();
beforeNode.setNextNode(newNode);
newNode.setNextNode(afterNode);
}
length++;
}else
isSuccessful=false;
return isSuccessful;
}
@Override
public T remove(int givenPosition) {
T result=null;
if(!isEmpty() && givenPosition>=1 && givenPosition<=length){
if(givenPosition==1){
result=firstNode.getData();
firstNode=firstNode.getNextNode();
}else{
Node beforeNode=getNodeAt(givenPosition-1);
Node ToremoveNode=beforeNode.getNextNode();
Node afterNode=ToremoveNode.getNextNode();
result=ToremoveNode.getData();
beforeNode.setNextNode(afterNode);;
}
length--;
}
return result;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
firstNode=null;
length=0;
}
@Override
public boolean replace(int givenPosition, T newEntry) {
boolean isSuccessful=true;
if(!isEmpty() && givenPosition>=1 && givenPosition<=length){
Node desiredNode=getNodeAt(givenPosition);
desiredNode.setData(newEntry);;
}else
isSuccessful=false;
return isSuccessful;
}
@Override
public T getEntry(int givenPosition) {
T result=null;
if(!isEmpty() && givenPosition>=1 && givenPosition<=length){
Node desiredNode=getNodeAt(givenPosition);
result=desiredNode.getData();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(T anEntry) {
boolean isSuccessful=false;
Node currentNode=firstNode;
while (currentNode!=null) {
if(currentNode.element.equals(anEntry)){
isSuccessful=true;
break;
}
currentNode=currentNode.getNextNode();
}
return isSuccessful;
}
@Override
public int getLength() {
return length;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return length==0;
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return false;
}
@Override
public void display() {
Iterator iterator=getIterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.print(iterator.next()+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> getIterator() {
return new IteratorForLinkedList();
}
/**
* 内部类迭代器
* @author Administrator
*
*/
private class IteratorForLinkedList implements Iterator<T>{
private Node nextNode;
private IteratorForLinkedList() {
this.nextNode=firstNode;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextNode!=null;
}
@Override
public T next() {
if(hasNext()){
Node returnNode=nextNode;
nextNode=nextNode.getNextNode();
return returnNode.element;
}else
throw new NoSuchElementException("Illegal call to next();"+"iteration is after end of list.");
}
public void remove(){//不允许在历遍过程中删除
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove() is not suported.");
}
}
private class Node {
private T element;
private Node next;
private Node(T element) {
this(element,null);
}
private Node(T element,Node next){
this.element=element;
this.next=next;
}
private T getData(){
return element;
}
private void setData(T newData){
element=newData;
}
private Node getNextNode(){
return next;
}
private void setNextNode(Node nextNode){
next=nextNode;
}
}
}























 1197
1197

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








