目录
布局特点
帧式布局是一种层叠式的布局,后添加的控件会层叠在先添加的控件上。
常用属性
| 属性 | 含义 |
| scrollbars | 滚动条(none、horizontal、vertical) |
| layout_marginTop | 上边距 |
| layout_marginBottom | 下边距 |
| layout_marginLeft | 左边距 |
| layout_marginRight | 右内边距 |
| paddingLeft | 左内边距 |
| paddingRighe | 右内边距 |
| paddingTop | 上内边距 |
| paddingBottom | 下内边距 |
| background | 背景 |
案例演示
新建一个文件,打开主布局资源文件activity_main改为线性布局并在里面添加各种控件
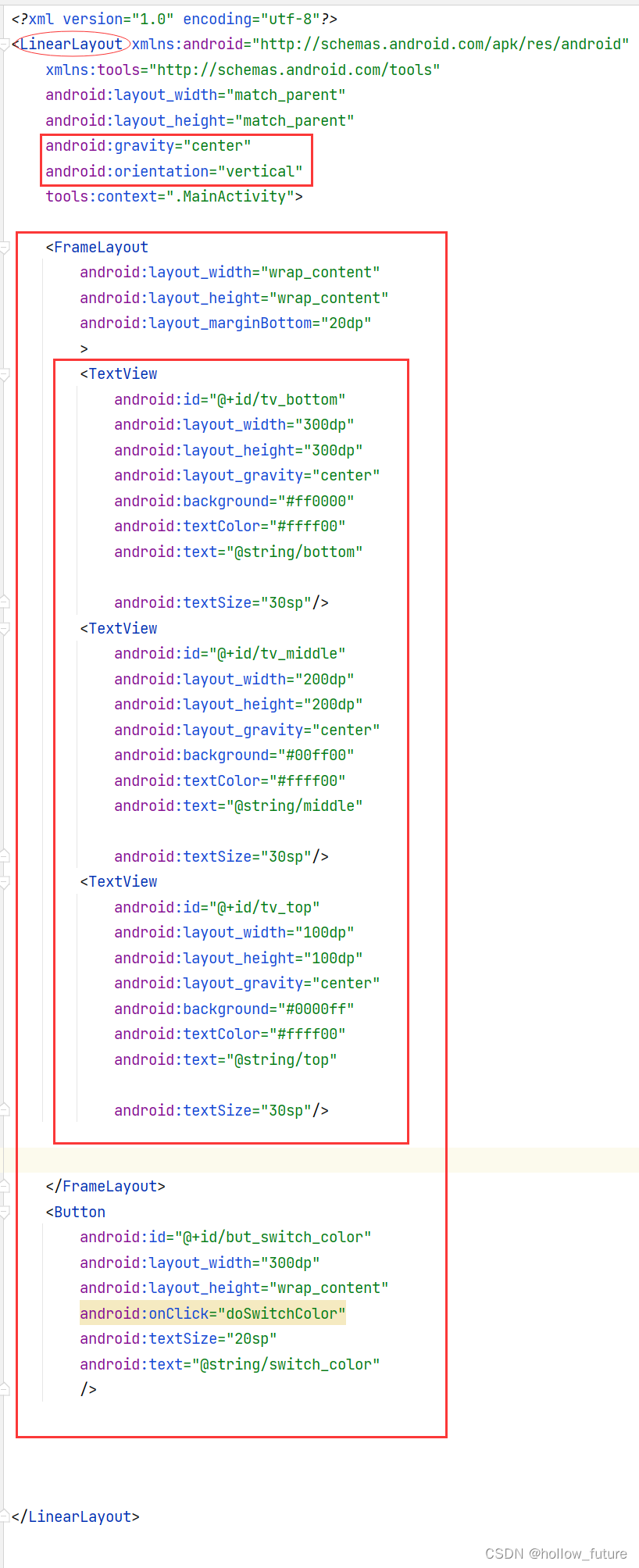
具体代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_bottom"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:textColor="#ffff00"
android:text="@string/bottom"
android:textSize="30sp"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_middle"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#00ff00"
android:textColor="#ffff00"
android:text="@string/middle"
android:textSize="30sp"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_top"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#0000ff"
android:textColor="#ffff00"
android:text="@string/top"
android:textSize="30sp"/>
</FrameLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/but_switch_color"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="doSwitchColor"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="@string/switch_color"
/>
</LinearLayout>
打开字符串资源文件strings.xml输入:

具体代码:
<resources>
<string name="app_name">帧式</string>
<string name="top">顶层</string>
<string name="middle">中层</string>
<string name="bottom">底层</string>
<string name="switch_color">切换颜色</string>
</resources>
打开主界面MainActivity文件
输入:
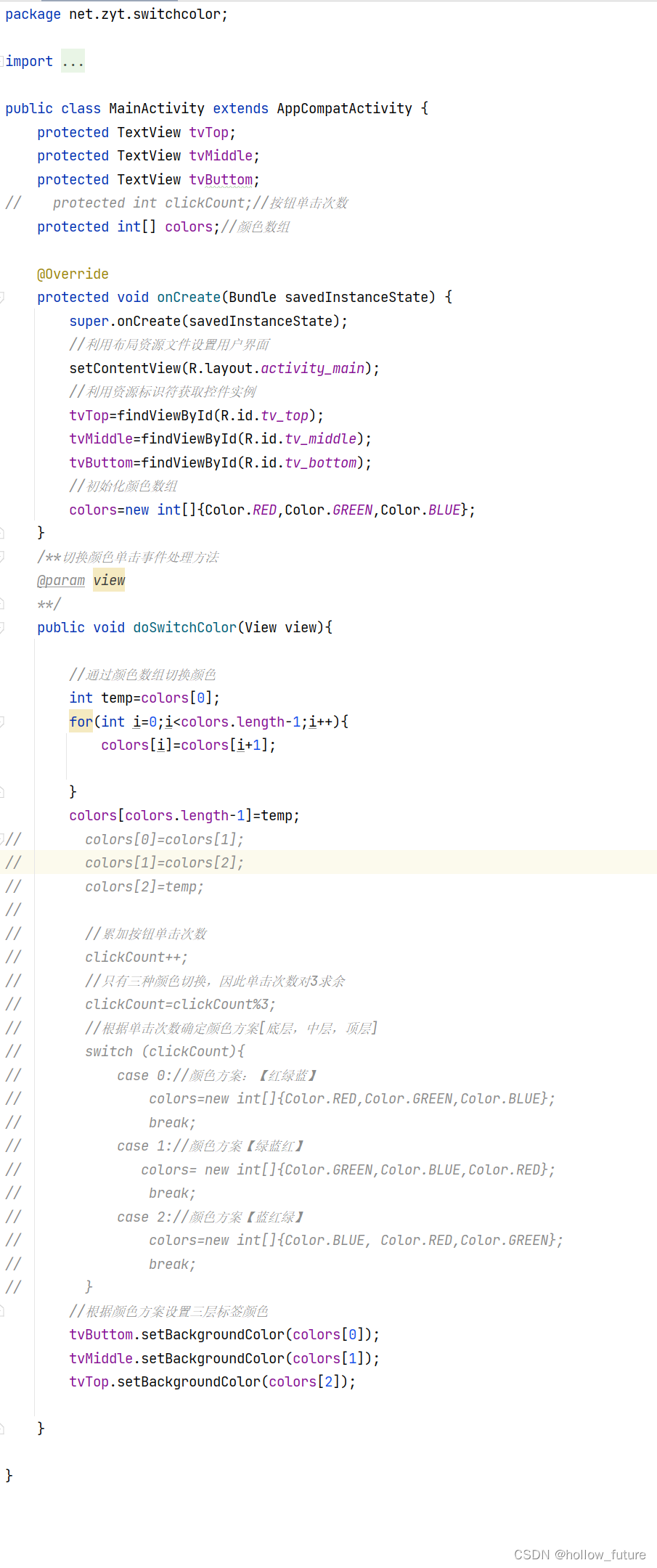
具体代码:
package net.zyt.switchcolor;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
protected TextView tvTop;
protected TextView tvMiddle;
protected TextView tvButtom;
protected int[] colors;//颜色数组
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//利用布局资源文件设置用户界面
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//利用资源标识符获取控件实例
tvTop=findViewById(R.id.tv_top);
tvMiddle=findViewById(R.id.tv_middle);
tvButtom=findViewById(R.id.tv_bottom);
//初始化颜色数组
colors=new int[]{Color.RED,Color.GREEN,Color.BLUE};
}
/**切换颜色单击事件处理方法
@param view
**/
public void doSwitchColor(View view){
//通过颜色数组切换颜色
int temp=colors[0];
for(int i=0;i<colors.length-1;i++){
colors[i]=colors[i+1];
}
colors[colors.length-1]=temp;
//根据颜色方案设置三层标签颜色
tvButtom.setBackgroundColor(colors[0]);
tvMiddle.setBackgroundColor(colors[1]);
tvTop.setBackgroundColor(colors[2]);
}
}
运行代码最后效果:





 博客介绍了Android帧式布局的相关内容。帧式布局是层叠式布局,后添加控件会层叠在先添加的控件上。还给出了常用属性,并通过新建文件、修改布局资源文件、输入代码等步骤进行案例演示,展示了运行代码后的效果。
博客介绍了Android帧式布局的相关内容。帧式布局是层叠式布局,后添加控件会层叠在先添加的控件上。还给出了常用属性,并通过新建文件、修改布局资源文件、输入代码等步骤进行案例演示,展示了运行代码后的效果。
















 966
966

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








