一、实验目的
1. 了解TPM安全芯片的组成和作用
2. 掌握计算平台信任链扩展的原理及作用
3. 掌握IMA的工作原理及作用
二、实验内容
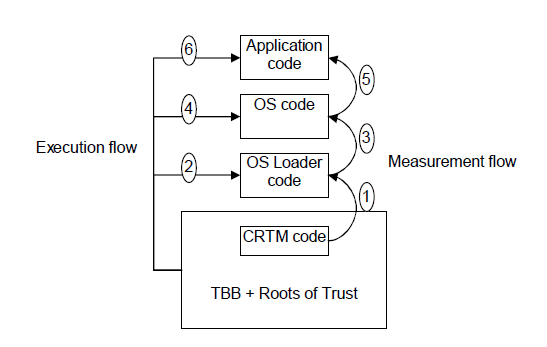
信任链扩展的准则是“Measure before load”,即在加载下一阶段组件并把控制权移交给它之前首先对其进行度量,记录组件度量值并使用TPM将此度量值保护起来。
下图是计算平台信任链扩展原型图:
1.扩展Linux操作系统为其增加IMA功能,使信任链由OS层扩展到用户应用层。
2.编写以下代码加载或运行,观察IMA是如何作用的:
(1)用户应用程序
(2)共享库
(3)内核模块
三、实验过程、结果
实验步骤:
1. 在VMware Workstation 11上创建Ubuntu 14.04 x64虚拟机,Ubuntu 14.04的内核本身已经集成了IMA相关代码,因此不需要再编译和加载新内核。同时Ubuntu 14.04也已经mount了securityfs文件系统,因此以下命令也省略:
mount -tsecurityfs securityfs /sys/kernel/security
2. 通过以下命令查看IMA记录的应用度量值:
cat/sys/kernel/security/ima/ascii_runtime_measurements
3. 编写以下代码加载或运行,观察IMA是如何作用的:
(1)用户应用程序
编写任意C应用程序testima_exe,编译并运行,观察ima securityfs的变化。程序的编译和运行可参考如下命令:
gcctestima_exe.c -o testima_exe
./testima_exe
testima_exe.c源码:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Test IMA!\n");
return 0;
}
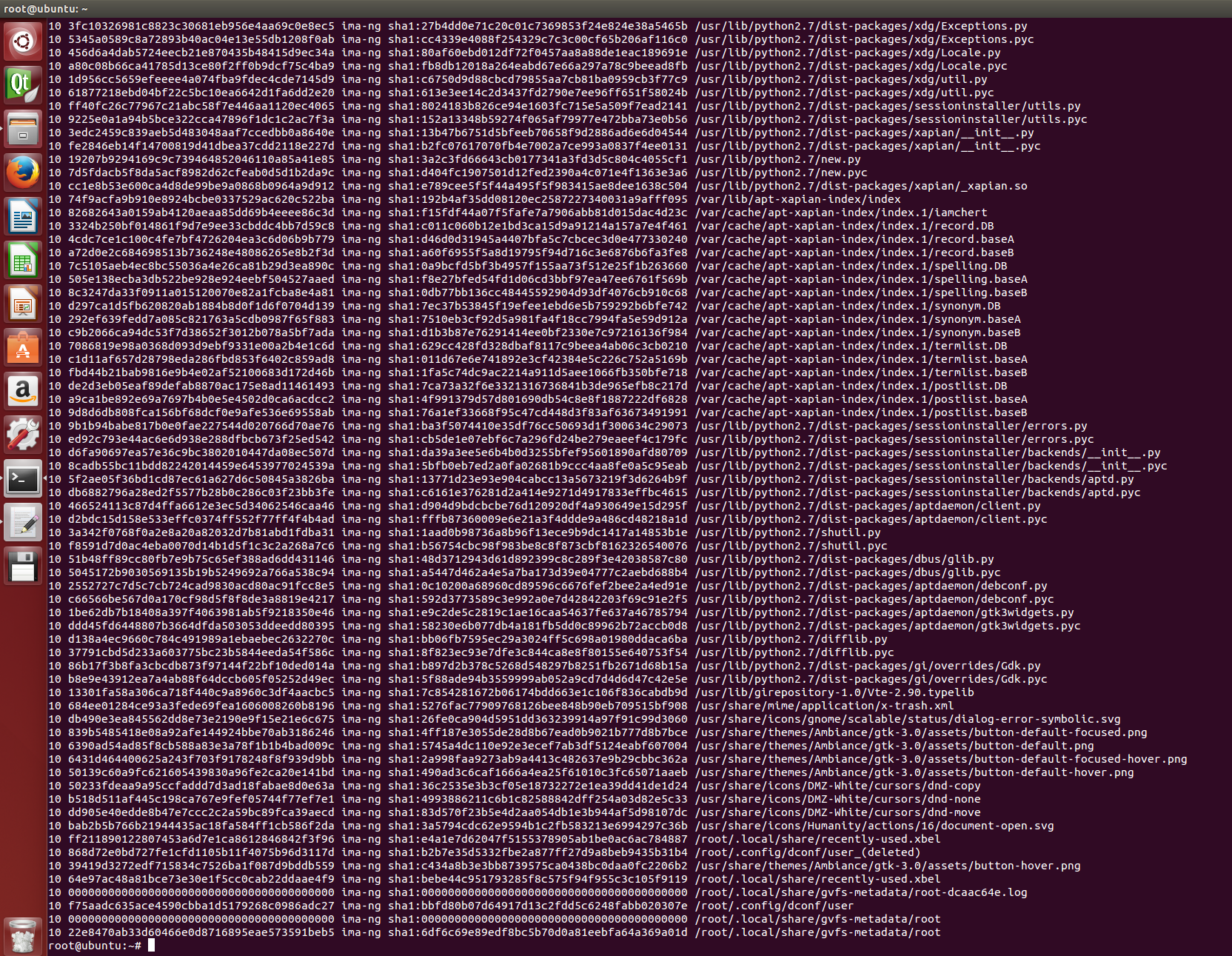
在没有运行任何程序时,运行cat/sys/kernel/security/ima/ascii_runtime_measurements命令后,结果如下图所示。
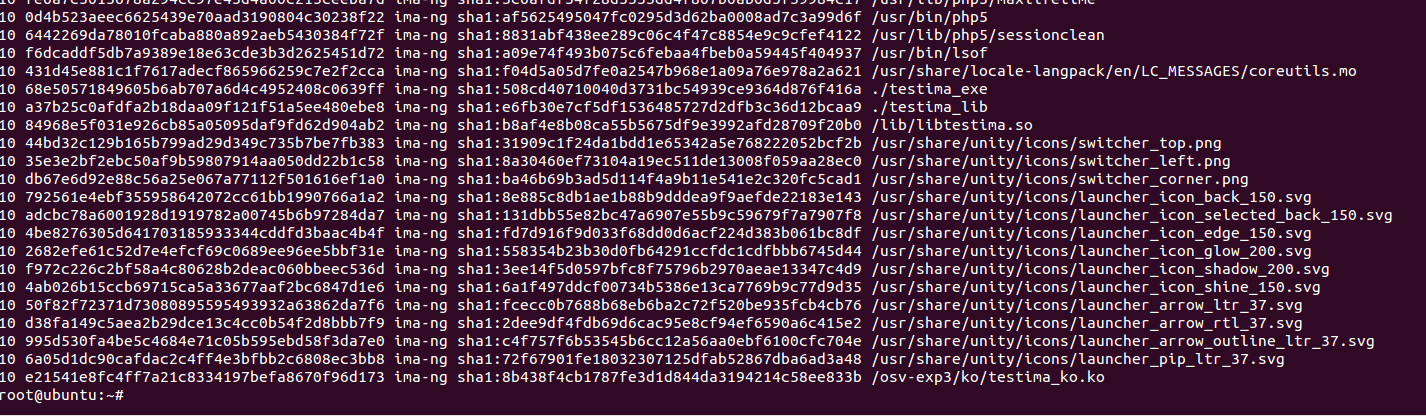
运行cat /sys/kernel/security/ima/ascii_runtime_measurements命令后,观察到结果如下图所示,./testima_exe出现在最后一行,可见运行C应用程序会导致IMA度量值变化。
(2)共享库
编写Linux共享库libtestima,并编写C应用程序testima_lib链接此共享库,编译并运行,观察ima securityfs的变化。参考命令如下:
gcc-o libtestima.so -fPIC -shared libtestima.c
cplibtestima.so /lib
gcctestima_lib.c -o testima_lib -l testima
./testima_liblibtestima.c源码:
#include <stdio.h>
void print_testima()
{
printf("Test IMA from lib!\n");
}
testima_lib.c源码:
extern void print_testima();
int main()
{
print_testima();
return 0;
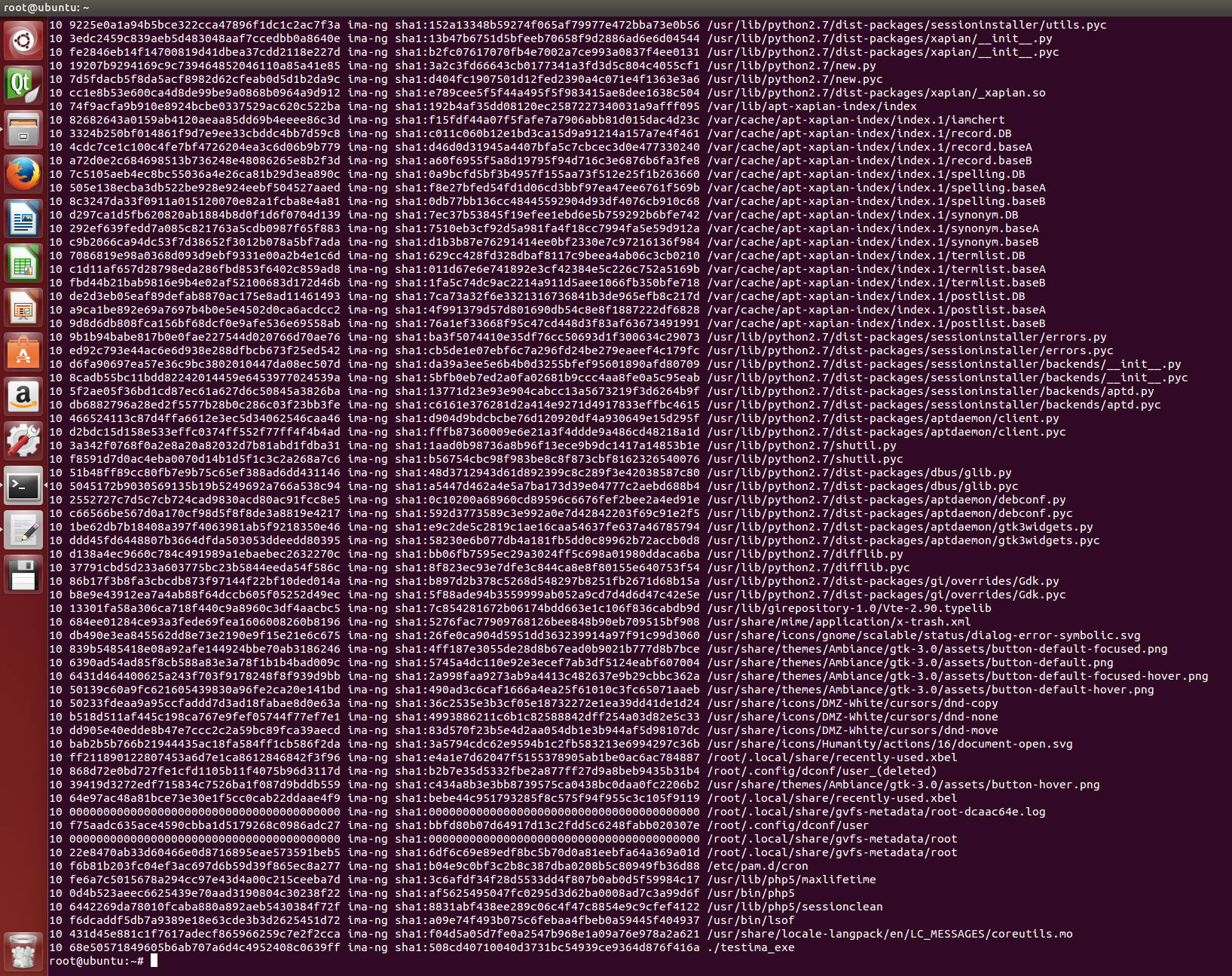
}运行cat /sys/kernel/security/ima/ascii_runtime_measurements命令后,观察到结果如下图所示,./testima_lib和/lib/libtestima.so出现在最后两行,可见运行加载lib会导致IMA度量值变化。
(3)内核模块
编写Linux内核模块testima_ko,编译并加载,观察ima securityfs的变化。参考命令如下:
make
insmodtestima_ko.ko
dmesg
rmmodtestima_ko.ko
dmesgtestima_ko.c源码:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
static int __init hello_init(void)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "Hello testima_ko!\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit hello_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "Goodbye testima_ko!\n");
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
Makefile源码:
obj-m := testima_ko.o
all:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean
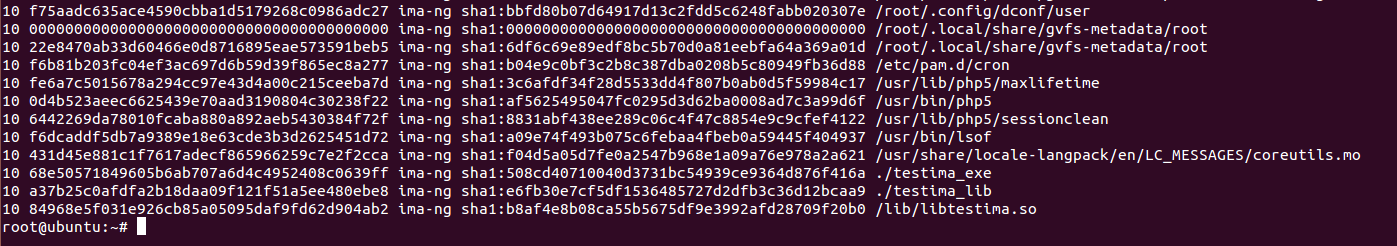
运行cat/sys/kernel/security/ima/ascii_runtime_measurements命令后,观察到结果如下图所示,/osv-exp3/ko/testima_ko.ko出现在最后一行,可见加载内核模块会导致IMA度量值变化。
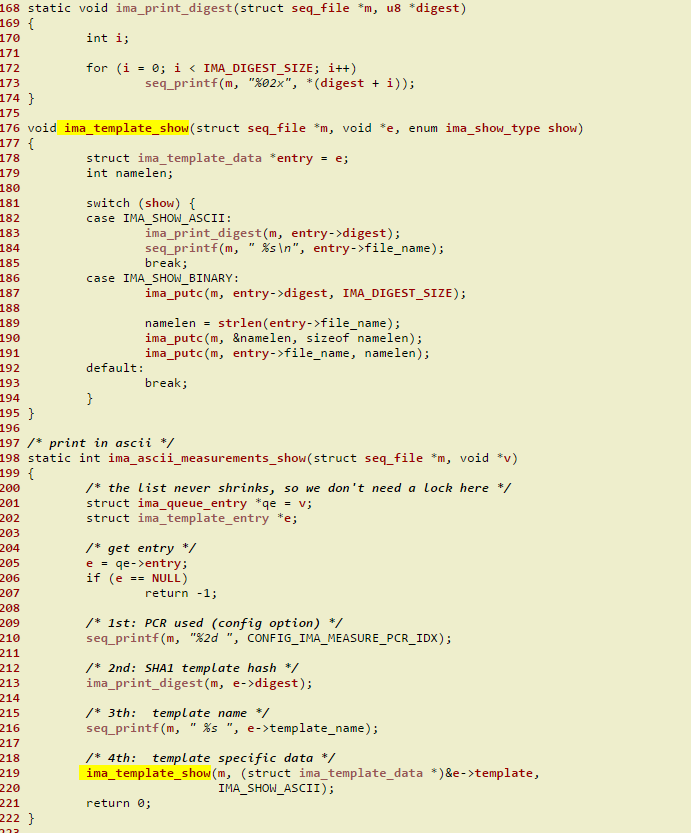
通过查看IMA源码,我们发现以上图片中显示的度量日志的含义为:
linux/security/integrity/ima/ima_fs.c
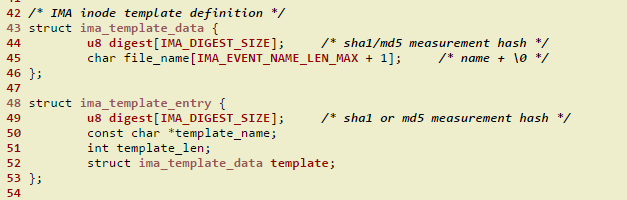
从上图中,我们可以发现,ima-ng左边那列是ima_template_entry结构的digest成员,右边那列是ima_template_data结构的digest成员,而ima_template_data结构是包含在ima_template_entry里面的,具体定义位置如下:
linux/security/integrity/ima/ima.h
我们称左边这列为“列表项度量值”,右边这列为“模板数据度量值”。
“列表项度量值”是最终TPM芯片硬件度量以及挑战者软件度量所采用的度量值,其值只包括对文件内容的SHA1值;
“模板数据度量值”并没有在代码里实际用到,包括文件内容以及文件信息(如文件名)总体计算出的SHA1值。
Tspi_TPM_PcrExtend函数是文章中TPM_Extend函数的实现,代码位于TPM软件栈的TSPI部分,这部分代码不是Linux标准的一部分,需要额外安装,网上有源码:
https://github.com/srajiv/trousers/blob/master/src/tspi/tspi_pcr_extend.c
TSS_RESULT
Tspi_TPM_PcrExtend(TSS_HTPM hTPM, /* in */
UINT32 ulPcrIndex, /* in */
UINT32 ulPcrDataLength, /* in */
BYTE *pbPcrData, /* in */
TSS_PCR_EVENT *pPcrEvent, /* in */
UINT32 * pulPcrValueLength, /* out */
BYTE ** prgbPcrValue) /* out */
{
TCPA_PCRVALUE outDigest;
TSS_RESULT result;
BYTE *extendData;
TPM_DIGEST digest;
UINT32 number;
TSS_HCONTEXT tspContext;
Trspi_HashCtx hashCtx;
if (pulPcrValueLength == NULL || prgbPcrValue == NULL)
return TSPERR(TSS_E_BAD_PARAMETER);
if (ulPcrDataLength > 0 && pbPcrData == NULL)
return TSPERR(TSS_E_BAD_PARAMETER);
if ((result = obj_tpm_get_tsp_context(hTPM, &tspContext)))
return result;
if (pPcrEvent) {
/* Create data to extend according to the TSS 1.2 spec section 2.6.2
* 'TSS_PCR_EVENT', in the 'rgbPcrValue' parameter description. */
result = Trspi_HashInit(&hashCtx, TSS_HASH_SHA1);
result |= Trspi_Hash_UINT32(&hashCtx, ulPcrIndex);
result |= Trspi_HashUpdate(&hashCtx, ulPcrDataLength, pbPcrData);
result |= Trspi_Hash_UINT32(&hashCtx, pPcrEvent->eventType);
result |= Trspi_HashUpdate(&hashCtx, pPcrEvent->ulEventLength, pPcrEvent->rgbEvent);
if ((result |= Trspi_HashFinal(&hashCtx, (BYTE *)&digest.digest)))
return result;
extendData = (BYTE *)&digest.digest;
}
else {
if (ulPcrDataLength != TPM_SHA1_160_HASH_LEN)
return TSPERR(TSS_E_BAD_PARAMETER);
extendData = pbPcrData;
}
if ((result = TCS_API(tspContext)->Extend(tspContext, ulPcrIndex, *(TPM_DIGEST *)extendData,
&outDigest)))
return result;
/* log the event structure if its passed in */
if (pPcrEvent) {
/* Set the PCR index in the event struct */
pPcrEvent->ulPcrIndex = ulPcrIndex;
if ((pPcrEvent->rgbPcrValue = calloc_tspi(tspContext,
TPM_SHA1_160_HASH_LEN)) == NULL) {
LogError("malloc of %d bytes failed.", TPM_SHA1_160_HASH_LEN);
return TSPERR(TSS_E_OUTOFMEMORY);
}
memcpy(pPcrEvent->rgbPcrValue, (BYTE *)&digest.digest, TPM_SHA1_160_HASH_LEN);
pPcrEvent->ulPcrValueLength = TPM_SHA1_160_HASH_LEN;
/* Set the version info in the event struct */
memcpy(&pPcrEvent->versionInfo, &VERSION_1_1, sizeof(TCPA_VERSION));
if ((result = RPC_LogPcrEvent(tspContext, *pPcrEvent, &number)))
return result;
}
*prgbPcrValue = calloc_tspi(tspContext, sizeof(TPM_PCRVALUE));
if (*prgbPcrValue == NULL) {
LogError("malloc of %zd bytes failed.", sizeof(TPM_PCRVALUE));
return TSPERR(TSS_E_OUTOFMEMORY);
}
memcpy(*prgbPcrValue, &outDigest, sizeof(TPM_PCRVALUE));
*pulPcrValueLength = sizeof(TPM_PCRVALUE);
return result;
}从以上Tspi_TPM_PcrExtend函数的定义中可以看出,TPM扩展所采用的SHA1值是digest.digest变量,并没有用到digest.template.digest变量,因此当前TPM扩展采用的是“列表项度量值”。
四、实验总结
1. 实验收获:
学到了很多IMA方面的知识,也进一步熟悉了Linux操作系统的命令用法。
2. 总结实验过程中遇到的问题及解决方法:
IMA功能默认未启动,cat /sys/kernel/security/ima/ascii_runtime_measurements命令不返回正确结果。
解决方案:
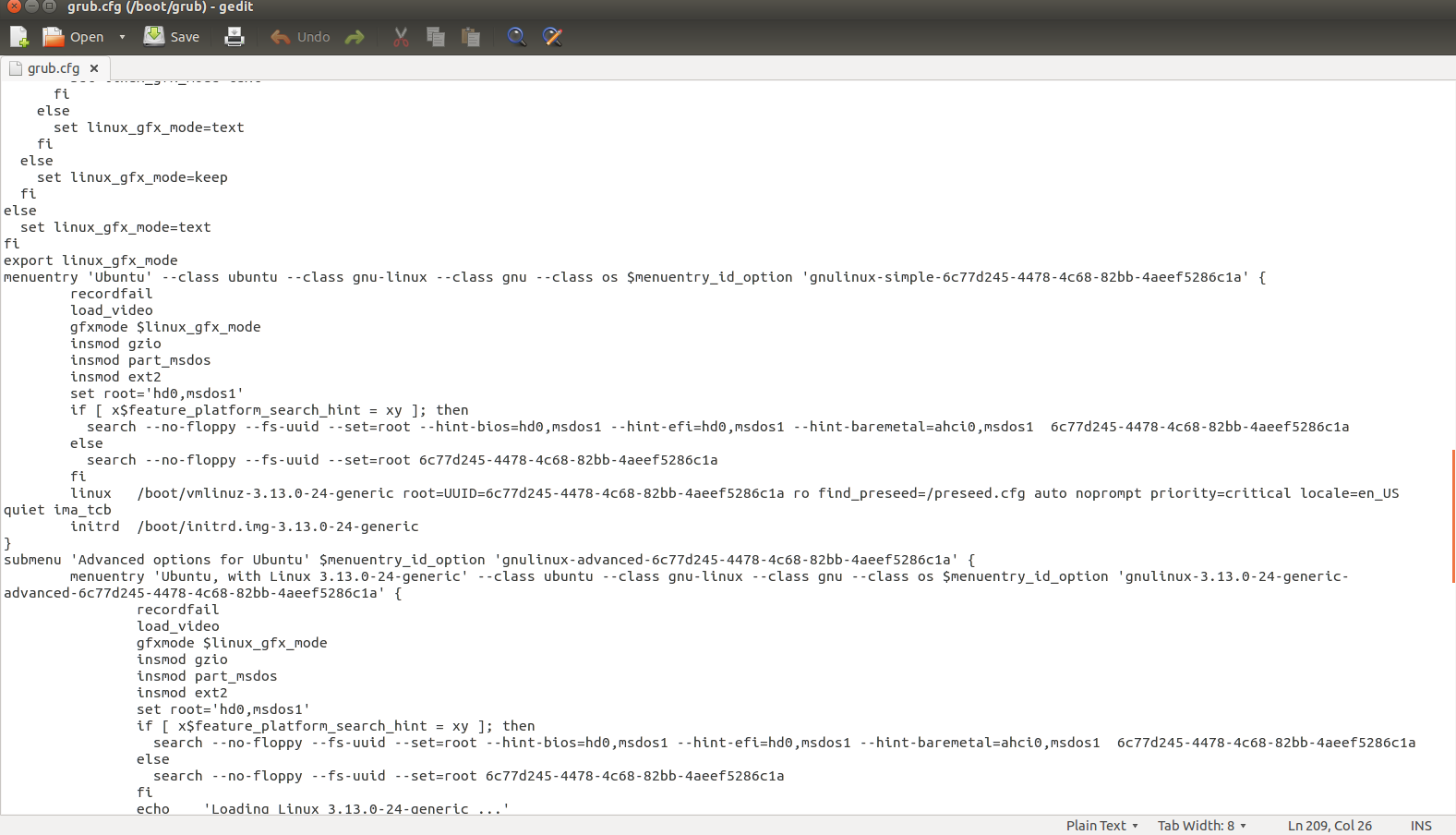
修改/boot/grub/grub.cfg文件,在“menuentry 'Ubuntu'”后面添加“quiet ima_tcb”来启用IMA功能(如下图所示),再重启机器即可。
3. 总结实验的不足之处,以及进一步的改进措施:
对Linux操作系统的命令还不够熟练,需要进一步操作。

























 1665
1665

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










