目录
1.unordered系列关联式容器
2.哈希
3.unordered_map和unordered_set哈希实现
4.代码总和
1.unordered系列关联式容器
1.1unordered系列
c++98的STL里面提供了底层为红黑树的关联式容器(set和map); 但是在结点数目很多的时候查询的效率就低了, 所以c++11里STL又提供了四个新的unordered的关联式容器;分别是unordered_map 和 unordered_set ; 以及unordered_multimap和unordered_multiset.
2.哈希
2.1哈希概念
(1)通过某种函数(HashFunc)使得元素的存储位置和它的关键码之间可以一一对应的映射关系;那么查找这个元素的时候就会很快.
(2)哈希方法中使用的转换函数就是哈希(散列)函数,构造出来的结构是哈希表(散列表).
2.2哈希函数
Hash(key) = key % capacity;
(1).直接定值法: 值和位置都有一个唯一的对应关系; but直接定值法会导致值的分布很散,空间浪费比较大.
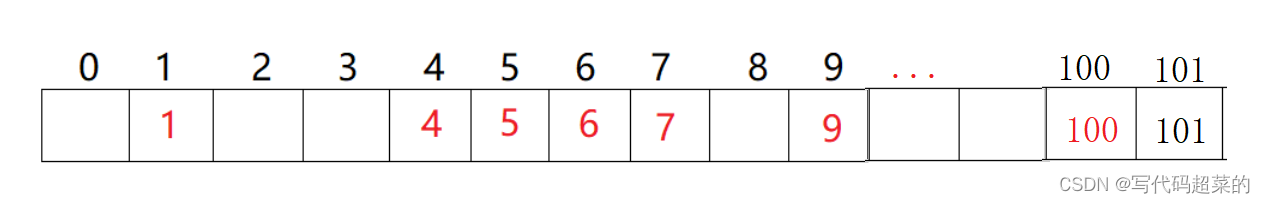
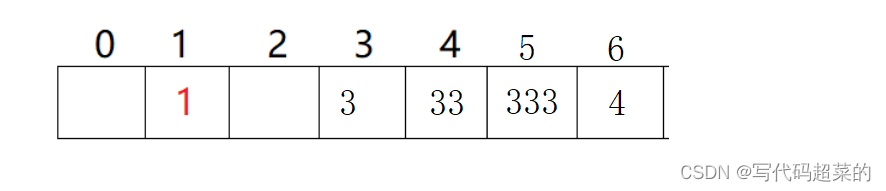
(2)除留余数法: hashi = key % len; key和位置建立关系.
肯定会造成不同值映射到同一个地方,就是造成哈希碰撞; 就只能够将这个值放到映射后面的其他位置.
(3)哈希函数设计的越好,产生的哈希碰撞就越少, 但非哈希碰撞能够避免.
2.3哈希冲突的解决
(1)闭散列(开放定值法): 当发生哈希冲突的时候, 如果哈希表没有满,那么就还有可以存放数据的位置,就将这个数据放到冲突位置的下一个空位置即可.
(2)开散列(拉链法): 首先对关键码用散列函数计算散列地址, 具有相同地址的关键码放到同一个子集合(桶), 各个桶里面的元素通过数据结构单链表进行连接, 链表的头节点放到哈希表中.
2.4哈希表的实现
2.4.1闭散列(开放定值法)
(1)哈希表的结构:首先是pair类型的数据; 以及哈希表的状态(这个结构对后面插入删除有很大作用);.
(2)闭散列又分为线性探测和二次探测;
线性探测:
插入数据就是如果发生哈希冲突就将这个数据放到下一个没有存放过数据的空位置;
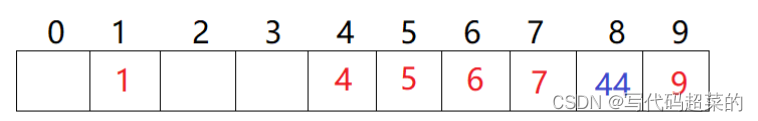
删除数据:不能随便删除数据, 因为如果删除数据可能影响后面数据的查找.比如删除4的话,那么查找44就会受到影响.所以线性探测都是采用伪删除方法(就是状态改变为delete).
线性探测的优缺点:
优点:简单实现;
缺点: 一旦产生哈希碰撞的数据很多, 就会数据的堆积,那么搜索的效率就会很低.
二次探测:
当表的数据已经超过负载因子并且为质数; 那么可以将哈希碰撞的数据重新映射到新表中在将数据重新排放.
有数学验证:
当表的长度为质数且表负载因子不超过0.5时,新的表项一定能够插入,而且任
何一个位置都不会被探查两次。因此只要表中有一半的空位置,就不会存在表满的问题。在搜索时可以不考虑表装满的情况,但在插入时必须确保表的装载因子a不超过0.5,如果超出必须考虑增容。
enum status
{
EMPTY,
EXIST,
DELETE
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashDate
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
status _s;
};(2)哈希表的插入(包括查找和扩容):
查找:首先可以判断一下这个值是否存在,存在就无需插入,不存在再插入; 通过key;先找到hashi下标,如果这个值的状态不为空(可能为delete或者exist); 那么再判断是否为exist和值是否相等,相等就返回,不相等就继续小标查找.最后还没找到就返回nullptr.
插入 扩容: 扩容这里采用负载因子来检查, 就是用来减少哈希冲突的, 但是负载因子如果太大,就很容易冲突加剧, 效率就低, 负载因子太小冲突降低但是空间利用率就低了.所以合适的负载因子很重要,一般设置为0.7.而且扩容不是采用在原本空间扩容而是在新空间扩,原本的数据也要挪过来.
插入数据: 先使用哈希函数找到下标,然后判断状态为非exist,最后插入数据即可.
HashDate<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = _kv.first % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._s != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._s == EXIST && _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
return nullptr;
} bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first)) //先判断这个值是否存在
return false;
//负载因子;
if (_n * 10 / _tables.size() == 7)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K, V> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i]._s == EXIST)
{
newHT.Insert(_table[i]._kv);
}
}
_table.swap(newHT._tables);
}
//哈希函数
size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._s == EXIST)//如果存在就跳过
{
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
//空位置或者删除位置就填写数据
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._s = EXIST;
_n++;
return true;
}2.4.2 哈希桶( Hash_bucket)
由于线性探测(闭散列)如果哈希冲突很多,搜索效率降低,那么我们想到开散列(拉链法),在每个表里面存放头节点,然后挂单链表.
(1)哈希桶的结构(HashNode):
HashNode里面包含着next指针以及数据data;
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode<T>* next;
T _data;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
,next(nullptr)
{}
};(2)哈希桶的指针(__HTIterator):
1. 首先就是因为有使用到HashTable, 所以提前进行前置声明.
2. 迭代器的构造有const类型和非const类型的.
3. operator++: 因为哈希表挂的单链表, 那么迭代到下一个链表可能是非空(后面还有结点);还有就是已经遍历完了一个桶,那么就要找下一个桶. 然后前面传hashi就是这个用的, 找到哈希下标, 如果结点挂链表就赋给node, 直到遍历完还没有就nullptr;
4. operator* : 返回数据, 返回类型Ref就是T&;
5. operator->: 返回地址, 返回类型Ptr就是T*;
6. operator!= : 结点不相同.
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
struct __HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef __HTIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyOfT, Hash> self;
Node* _node;
const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* _pht;
size_t _hashi;
__HTIterator(Node* node, HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* pht, size_t hashi)
:_node(node)
, _pht(pht)
, _hashi(hashi)
{}
__HTIterator(Node* node,const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* pht, size_t hashi)
:_node(node)
, _pht(pht)
, _hashi(hashi)
{}
//返回值为迭代器iterator.
self& operator++()
{
//桶里面还有下一个结点
if (_node->next)
{
_node = _node->next;
}
else//当前桶已经走完那么就到下一个桶
{
_hashi++;
while (_hashi < _pht->_tables.size())
{
if (_pht->_tables[_hashi])
{
_node = _pht->_tables[_hashi];
break;
}
++_hashi;
}
if (_hashi == _pht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
//Ref == T&
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//Ptr == T*
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};(3)哈希桶(HashTable):
1 迭代器的begin():
因为是单链表结构, 先遍历哈希表, 找到有链表连接的第一个结点然后返回iterator, 如果最后没找到就是nullptr.
2 迭代器的end():
结构规定,返回nullptr且hashi为-1.
3.HashTable析构:
将哈希表挂的链表都delete. 哈希表的结点置空.
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
friend struct __HTIterator;
public:
typedef __HTIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> iterator;
typedef __HTIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyOfT, Hash> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i])
{
return iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
}
return end();
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i])
{
return iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
}
return end();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}
HashTable()
{
_tables.resize(10);//初始化容量
}
~HashTable()
{
//结点的析构
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}(4)哈希桶插入数据
1. 首先进行数据的查找, 如果存在就不需要插入,反之则要;
2. hf和kot都是仿函数,处理数据的.
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& date)
{
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
//查找数据在否,不在就创建,在就不需要了.
iterator it = Find(kot(date));
if (it != end())
return make_pair(it, false);
//负载因子为1;
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
vector<Node*> newTables;
newTables.resize(_tables.size() * 2, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->next;
//重新使用哈希函数进行映射.
size_t hashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newTables.size();
cur->next = newTables[i];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(newTables);
}
size_t hashi = hf(kot(date)) % _tables.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(date);
//头插
newnode->next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this, hashi), true);
}(5)哈希桶的查找:
通过key进行查找, 首先通过hashi进行查找到在哈希表的那个位置, 然后再根据cur链表进行遍历查找到date和key相同的结点.
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
return iterator(cur, this, hashi);
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return end();
}(6)哈希桶的删除
删除也是先找到要删除的结点, 定义prev结点和cur结点, 如果找到且prev非空那么就是将prev置给cur->next; prev为空就将_tables[hashi] 置给cur->next; 没找到就一直遍历链表.
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_date) == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->next;
}
else
{
prev->next = cur->next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return false;
}(7)计算桶的大小
bucketsize是计算每个桶的大小;
bucketlen是计算每个桶的大小并且给sum.
maxbucketlen是计算最大的桶的大小;
averagebucketlen是计算平均每个桶的大小.
//计算桶的各种大小
void some()
{
size_t bucketSize = 0;//一个桶的大小
size_t maxbucketLen = 0;
size_t sum = 0;
double averagebucketlen = 0.0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
if (cur)
{
bucketSize++;
}
size_t bucketLen = 0;
while (cur)
{
bucketLen++;
cur = cur->next;
}
sum += bucketLen;//计算全部桶的大小
if (bucketLen > maxbucketLen)
{
maxbucketLen = bucketLen;
}
}
averagebucketlen = (double)sum / (double)bucketSize;
printf("all bucketSize:%d\n", _tables.size());
printf("bucketSize:%d\n", bucketSize);
printf("maxBucketLen:%d\n", maxBucketLen);
printf("averageBucketLen:%lf\n\n", averageBucketLen);
}
3.unordered_map和unordered_set哈希实现.
3.1unordered_map
(1) 直接从HashTable.h文件里面去拿begin, end, insert, find, erase...
(2) unordered_map的时候对应HashTable里面的函数模板的参数,尤其是仿函数.
#pragma once
#include"HashTable.h"
namespace study1
{
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
const V& operator[](const K& key)const
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
iterator earse(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};
void test_map()
{
unordered_map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", ""));
dict.insert(make_pair("string", ""));
dict.insert(make_pair("insert", ""));
for (auto& kv : dict)
{
kv.second += 'x';
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
string arr[] = { "香蕉", "哈密瓜", "香蕉", "西瓜", "桃子" };
unordered_map<string, int> cout_map;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
cout_map[e]++;
}
for (auto& kv : cout_map)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
}3.2unordered_set
同理处理完unordered_map, unordered_set也是一样的处理,只是接口和仿函数修改一点.
#pragma once
#include"HashTable.h"
namespace study2
{
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _hf.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _hf.end();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _hf.begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _hf.end();
}
pair<const_iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
auto ret = _hf.Insert(key);
return pair<const_iterator, bool>(const_iterator(ret.first._node, ret.first._pht, ret.first._hashi), ret.second);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _hf.Find(key);
}
iterator erase(const K& key)
{
return _hf.Erase(key);
}
private:
Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash> _hf;
};
void test_set()
{
unordered_set<int> us;
us.insert(5);
us.insert(15);
us.insert(52);
us.insert(3);
unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin();
while (it != us.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : us)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}4.代码总和
4.1Hash_Bucket的代码:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//仿函数
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
//BKDR;是一种算法用来查找的方法,避免哈希碰撞的,比较高效.
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto e : key)
{
hash *= 31;
hash += e;
}
return hash;
}
};
namespace open_address
{
enum status
{
EMPTY,
EXIST,
DELETE
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashDate
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
status _s;
};
//丢到全局去,因为hash_bucket也要使用.
//template<class K>
//struct HashFunc
//{
// //重载()
// size_t operator()(const K& key)
// {
// return (size_t)key;
// }
//};
//template<>
//struct HashFunc<string>
//{
// //重载()string
// size_t operator()(const string& key)
// {
// size_t hash = 0;
// for (auto e : key)
// {
// hash *= 31;
// hash += e;
// }
// cout << key << ":" << hash << endl;
// return hash;
// }
//};
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
HashTable()
{
_tables.resize(10); //空间初始化先开10个空间;
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first)) //先判断这个值是否存在
return false;
//负载因子;用来扩容操作,扩容直接开新的空间,还要将原来的数据移动到新空间,不用担心原来表是否释放,自动调用析构函数
if (_n * 10 / _tables.size() == 7)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K, V> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i]._s == EXIST)
{
newHT.Insert(_tables[i]._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
//HashFunc
Hash hf;
//哈希函数
size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._s == EXIST)//如果存在就跳过
{
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
//空位置或者删除位置就填写数据
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._s = EXIST;
_n++;
return true;
}
HashDate<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._s != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._s == EXIST && _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
return NULL;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashDate<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_s = DELETE;
_n--;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void print()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i]._s == EXIST)
{
printf("[%d]-> %d\n", i, _tables[i]._kv.first);
}
else if (_tables[i]._s == EMPTY)
{
printf("[%d]-> E\n", i);
}
else
{
printf("[%d]-> D\n", i);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
size_t Size()const
{
return _n;
}
bool Empty() const
{
return _n == 0;
}
private:
vector< HashDate<K, V>> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;//存储关键字的个数;
};
void TsetHT1()
{
HashTable<int, int> ht;
int a[] = { 4, 14, 24, 34, 5, 7, 1 };
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
//ht.print();
ht.Insert(make_pair(3, 3));
ht.Insert(make_pair(3, 3));
ht.Insert(make_pair(-3, -3));
ht.print();
ht.Erase(3);
ht.print();
if (ht.Find(3))
{
cout << "3存在" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "3不存在" << endl;
}
cout << ht.Size() << endl;
}
}
namespace Hash_bucket
{
template<class T>
struct HashNode
{
HashNode<T>* next;
T _data;
HashNode(const T& data)
:_data(data)
,next(nullptr)
{}
};
//前置声明
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
class HashTable;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
struct __HTIterator
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
typedef __HTIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyOfT, Hash> self;
Node* _node;
const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* _pht;
size_t _hashi;
__HTIterator(Node* node, HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* pht, size_t hashi)
:_node(node)
, _pht(pht)
, _hashi(hashi)
{}
__HTIterator(Node* node,const HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash>* pht, size_t hashi)
:_node(node)
, _pht(pht)
, _hashi(hashi)
{}
//返回值为迭代器iterator.
self& operator++()
{
//桶里面还有下一个结点
if (_node->next)
{
_node = _node->next;
}
else//当前桶已经走完那么就到下一个桶
{
_hashi++;
while (_hashi < _pht->_tables.size())
{
if (_pht->_tables[_hashi])
{
_node = _pht->_tables[_hashi];
break;
}
++_hashi;
}
if (_hashi == _pht->_tables.size())
{
_node = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
//Ref == T&
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//Ptr == T*
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<T> Node;
template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
friend struct __HTIterator;
public:
typedef __HTIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> iterator;
typedef __HTIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyOfT, Hash> const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i])
{
return iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
}
return end();
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i])
{
return iterator(_tables[i], this, i);
}
}
return end();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return iterator(nullptr, this, -1);
}
HashTable()
{
_tables.resize(10);//初始化容量
}
~HashTable()
{
//结点的析构
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& date)
{
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
//查找数据在否,不在就创建,在就不需要了.
iterator it = Find(kot(date));
if (it != end())
return make_pair(it, false);
//负载因子为1;
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
vector<Node*> newTables;
newTables.resize(_tables.size() * 2, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->next;
//重新使用哈希函数进行映射.
size_t hashi = hf(kot(cur->_data)) % newTables.size();
cur->next = newTables[i];
newTables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(newTables);
}
size_t hashi = hf(kot(date)) % _tables.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(date);
//头插
newnode->next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this, hashi), true);
}
iterator Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
{
return iterator(cur, this, hashi);
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return end();
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Hash hf;
KeyOfT kot;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_date) == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->next;
}
else
{
prev->next = cur->next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return false;
}
//计算桶的各种大小
void some()
{
size_t bucketSize = 0;//一个桶的大小
size_t maxbucketLen = 0;
size_t sum = 0;
double averagebucketlen = 0.0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
if (cur)
{
bucketSize++;
}
size_t bucketLen = 0;
while (cur)
{
bucketLen++;
cur = cur->next;
}
sum += bucketLen;//计算全部桶的大小
if (bucketLen > maxbucketLen)
{
maxbucketLen = bucketLen;
}
}
averagebucketlen = (double)sum / (double)bucketSize;
printf("all bucketSize:%d\n", _tables.size());
printf("bucketSize:%d\n", bucketSize);
printf("maxBucketLen:%d\n", maxbucketLen);
printf("averageBucketLen:%lf\n\n", averagebucketlen);
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
}4.2 unordered_set代码:
#pragma once
#include"HashTable.h"
namespace study2
{
template<class K, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _hf.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _hf.end();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _hf.begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _hf.end();
}
pair<const_iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
auto ret = _hf.Insert(key);
return pair<const_iterator, bool>(const_iterator(ret.first._node, ret.first._pht, ret.first._hashi), ret.second);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _hf.Find(key);
}
iterator erase(const K& key)
{
return _hf.Erase(key);
}
private:
Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash> _hf;
};
void test_set()
{
unordered_set<int> us;
us.insert(5);
us.insert(15);
us.insert(52);
us.insert(3);
unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin();
while (it != us.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : us)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}4.3 unordered_map的代码:
#pragma once
#include"HashTable.h"
namespace study1
{
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _ht.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _ht.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _ht.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
const V& operator[](const K& key)const
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Find(key);
}
iterator earse(const K& key)
{
return _ht.Erase(key);
}
private:
Hash_bucket::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
};
void test_map()
{
unordered_map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", ""));
dict.insert(make_pair("string", ""));
dict.insert(make_pair("insert", ""));
for (auto& kv : dict)
{
kv.second += 'x';
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
string arr[] = { "香蕉", "哈密瓜", "香蕉", "西瓜", "桃子" };
unordered_map<string, int> cout_map;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
cout_map[e]++;
}
for (auto& kv : cout_map)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
}后言:
博主在这里讨个三联.xdm麻烦给博主个一键三联, 多支持支持,博主更加有动力更新更好的文章.谢谢xdm.






















 847
847

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








