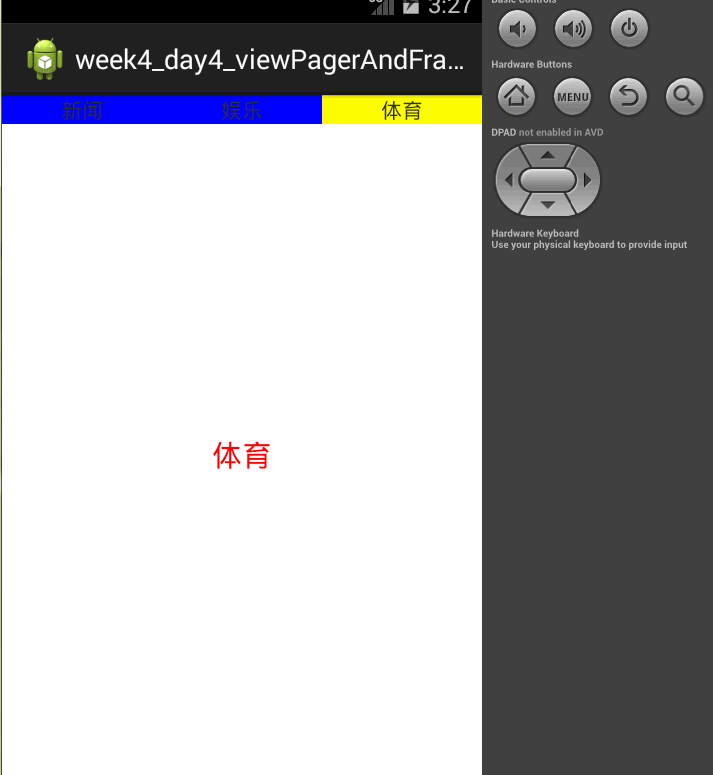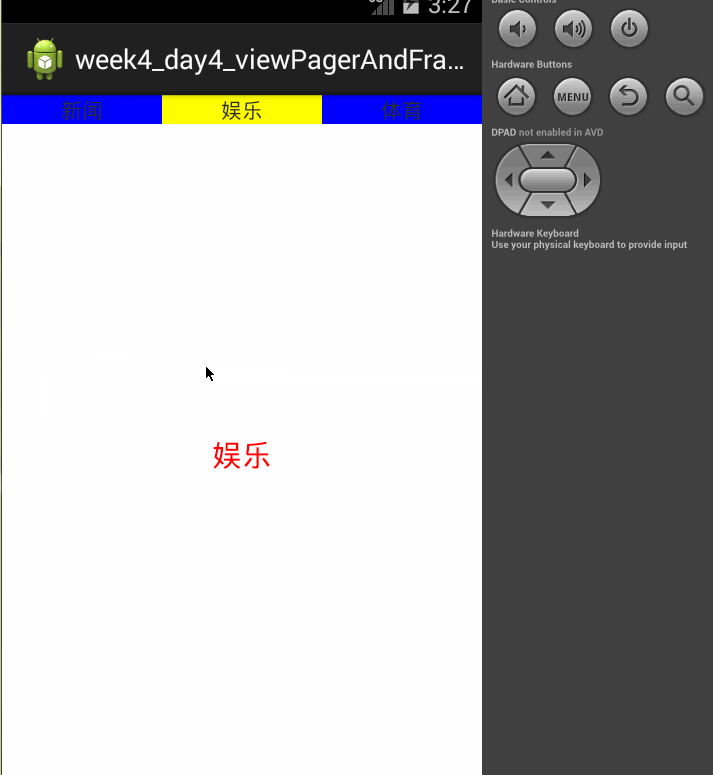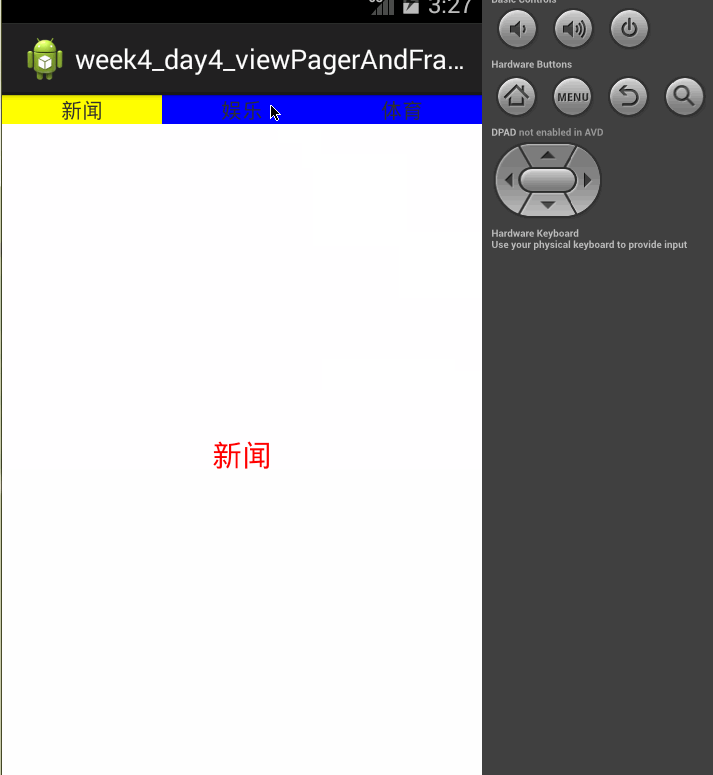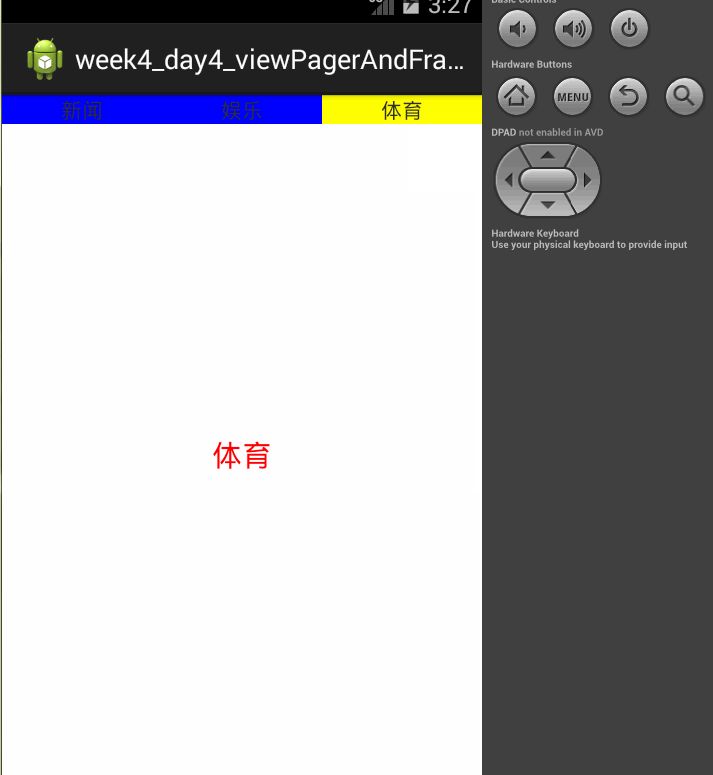
页面效果
逻辑代码--MainActivity
package com.example.week4_day4_viewpagerandfragment;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager.OnPageChangeListener;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
private ViewPager viewPager;//声明ViewPager
private List<Fragment> list;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);//加载布局
viewPager = (ViewPager) findViewById(R.id.viewpager);//得到ViewPager对象
initFragment();//调用Fragment
tab();//导航栏
//绑定适配器
viewPager
.setAdapter(new MyFragmentAdapter(getSupportFragmentManager(),list) );
//导航栏绑定数据源
viewPager.setOnPageChangeListener(new OnPageChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onPageSelected(int arg0) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
tvs[i].setBackgroundColor(Color.BLUE);
}
tvs[arg0].setBackgroundColor(Color.YELLOW);
}
@Override
public void onPageScrolled(int arg0, float arg1, int arg2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void onPageScrollStateChanged(int arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
});
}
public void initFragment() {
list = new ArrayList<Fragment>();
MyFragment fragment1 = new MyFragment();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("index", 1);
fragment1.setArguments(bundle);
MyFragment fragment2 = new MyFragment();
bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("index",2);
fragment2.setArguments(bundle);
MyFragment fragment3 = new MyFragment();
bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("index", 3);
fragment3.setArguments(bundle);
list.add(fragment1);
list.add(fragment2);
list.add(fragment3);
}
private TextView[] tvs;
//导航栏
public void tab(){
LinearLayout layout=(LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.linear1);
tvs=new TextView[3];
for (int i = 0; i < tvs.length; i++) {
tvs[i]=(TextView) layout.getChildAt(i);
tvs[i].setTag(i);
tvs[i].setBackgroundColor(Color.BLUE);
tvs[i].setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
viewPager.setCurrentItem((Integer) v.getTag());
}
});
tvs[0].setBackgroundColor(Color.YELLOW);
}
}
}
package com.example.week4_day4_viewpagerandfragment;
import java.util.List;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentPagerAdapter;
/**
* 自定义FragmentPagerAdapter的适配器
* 专门存放Fragment数据
*
*/
public class MyFragmentAdapter extends FragmentPagerAdapter {
private List<Fragment> list;
public MyFragmentAdapter(FragmentManager fm,List<Fragment> list) {
super(fm);
this.list=list;
}
/**
* 根据指定下标返回对应的Fragment对象
*/
@Override
public Fragment getItem(int arg0) {
return list.get(arg0);
}
/**
* 适配器中Fragment的数量
*/
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
}
package com.example.week4_day4_viewpagerandfragment;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public class MyFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView tv;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
Bundle bundle = getArguments();
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.item, null);
tv = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv);
if (bundle != null) {
int tab = bundle.getInt("index");
switch (tab) {
case 1:
tv.setText("新闻");
break;
case 2:
tv.setText("娱乐");
break;
case 3:
tv.setText("体育");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return view;
}
}
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linear1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="新闻" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="娱乐" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="体育" />
</LinearLayout>
<android.support.v4.view.ViewPager
android:id="@+id/viewpager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:textColor="#ff0000"
android:textSize="20sp"/>
</RelativeLayout>






















 169
169

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








