16.3 字符串IO
istringstream / ostringstream : stringstream
16.3.1 istringstream类
从流中提取数据,支持 >> 操作,这里字符串可以包括多个单词,单词之间使用空格分开
初始化:使用字符串进行初始化 构造函数:istringstream::istringstream(string str);
使用:我们可以使用分解点获取不同的数据,完成 字符串 到 其他类型 的转换
16.3.2 ostringstream类
把其他类型的数据写入流(往流中写入数据),支持<<操作
初始化:使用字符串进行初始化,构造函数:ostringstream::ostringstream(string str);
16.3.3 stringstream类
是对istringstream和ostringstream类的综合,支持<<, >>操作符,可以进行字符串到其它类型的快速转换
初始化:使用字符串进行初始化 构造函数:stringstream::stringstream(string str);
作用:1、stringstream通常是用来做数据转换的
2、将文件的所有数据一次性读入内存
注意:stringstream sst 成员函数
sst.str("") 常用来初始化/覆盖 字符串或清空 << 追加字符串
sst.clear() 清除错误状态
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str1,str2,str3;
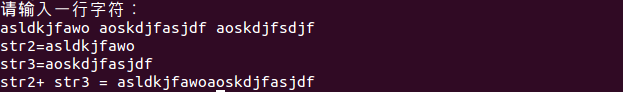
cout << "请输入一行字符:" << endl;
getline(cin,str1);
istringstream is(str1);
is >> str2;
is >> str3;
cout << "str2=" << str2 << endl << "str3=" << str3 << endl;
ostringstream os;
os << str2 << str3;
cout << "str2+ str3 = " << os.str()<< endl;
cout << os.str()[1];
return 0;
}输出结果:
关于sstringstream内存消耗问题参见:
http://www.cnblogs.com/gamesky/archive/2013/01/09/2852356.html
16.4 文件IO
ofstream是从内存到硬盘,ifstream是从硬盘到内存
16.4.1打开文件
在fstream类中,有一个成员函数open(),就是用来打开文件的,或者使用构造函数,声明如下:void open(const char* filename,int mode,int access);
void fstream(const char* filename,int mode,int access);
参数:filename: 要打开的文件名
mode: 要打开文件的方式
access: 打开文件的属性
ios::app: 以追加的方式打开文件
ios::ate: 文件打开后定位到文件尾,ios:app就包含有此属性
ios::binary: 以二进制方式打开文件,缺省的方式是文本方式。两种方式的区别见前文
ios::in: 文件以输入方式打开(文件数据输入到内存)
ios::out: 文件以输出方式打开(内存数据输出到文件)
ios::nocreate: 不建立文件,所以文件不存在时打开失败
ios::noreplace:不覆盖文件,所以打开文件时如果文件存在失败
ios::trunc: 如果文件存在,把文件长度设为0
打开文件的属性取值是:(可加)
0:普通文件,打开访问1:只读文件
2:隐含文件
4:系统文件
16.4.2 关闭文件
打开的文件使用完成后一定要关闭,fstream提供了成员函数close()来完成此操作,如:file1.close();就把file1相连的文件关闭。
16.4.3 读写文件
读写文件分为文本文件和二进制文件的读取,对于文本文件的读取比较简单,用插入器和析取器就可以了;而对于二进制的读取就要复杂些,下要就详细的介绍这两种方式1、文本文件的读写
文本文件的读写很简单:用插入器(<<)向文件输出;用析取器(>>)从文件输入。
2、二进制文件的读写
put()
ofstream &put(char ch) 如file1.put('c');就是向流写一个字符'c'。
ifstream &get(char &ch);功能是从流中读取一个字符,结果保存在引用ch,如果到文件尾,返回空字符。
int get();这种形式是从流中返回一个字符,如果到达文件尾,返回EOF,ifstream &get(char *buf,int num,char delim='\n');这种形式把字符读入由 buf 指向的数组,直到读入了 num 个字符或遇到了由 delim 指定的字符,如果没使用 delim 这个参数,将使用缺省值换行符'\n'。
read(unsigned char *buf,int num);
write(const unsigned char *buf,int num);
read()从文件中读取 num 个字符到 buf 指向的缓存中,如果在还未读入 num 个字符时就到了文件尾,可以用成员函数 int gcount();来取得实际读取的字符数;而 write() 从buf 指向的缓存写 num 个字符到文件中,值得注意的是缓存的类型是 unsigned char *,有时可能需要类型转换。
注意:使用string时格式应为:read(string.c_str(),string.size()),而不是直接使用string和sizeof(string),string是一个类的对象,里面封装了指针。
16.4.4 检测EOF
成员函数eof()用来检测是否到达文件尾,如果到达文件尾返回非0值,否则返回0。原型是int eof();
例: if(in.eof()) ShowMessage("已经到达文件尾!");
16.4.5 文件定位
和C的文件操作方式不同的是,C++ I/O系统管理两个与一个文件相联系的指针。一个是读指针,它说明输入操作在文件中的位置;另一个是写指针,它下次写操作的位置。每次执行输入或输出时,相应的指针自动变化。所以,C++的文件定位分为读位置和写位置的定位,对应的成员函数是seekg()和seekp()。seekg()是设置读位置, seekp是设置写位置(注意:在fstream中,读指针与写指针始终相同)。它们最通用的形式如下:istream &seekg(streamoff offset,seek_dir origin);-->tellg() 返回读指针所在位置
ostream &seekp(streamoff offset,seek_dir origin);-->tellp() 返回写指针所在位置
ios::beg: 文件开头
ios::cur: 文件当前位置
ios::end: 文件结尾
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string path = "../Desktop/write.txt";
ifstream fin("./conIO.cpp");
ofstream fou(path.c_str());//此处形参为 const char*(C风格字符串)
if(!fin) cout << "write.txt打开失败!" << endl;
if(!fou) cout << "charIO.cpp打开失败!" << endl;
char ch;
while(fin.get(ch))//用while(fin>>ch)会跳过所有空白字符
{
cout << ch;
fou << ch;
}//while(fin) {fin.get(ch);fout<<ch;} 这样复制最后会多一个字符
fin.clear();
fin.close();
fou.close();
return 0;
}
二进制加密程序:
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
void encode(char *ch,int cnt)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i < cnt ; i++)
++ch[i];
}
void decode(char *ch ,int cnt)
{
int i = 0;
for(;i < cnt ; i++)
{
--ch[i];
}
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 3||(!strcmp(argv[1],"-e")&&!strcmp(argv[1],"-d")))
{
cout << argv[0] << " -e/-d filename" << endl;
return -1;
}
//生成输出文件
string str0 = argv[2];
string str1 = strcmp(argv[1],"-e")?"decode":"encode";//注意:strcmp返回值为1/0/-1
string filename = str1+"_"+str0 ;
fstream fin(filename.c_str(),ios::out);//(内存-->文件)
//只有ios::out才可以自动生成文件,ios::out|ios::in是不可以的
fstream fout(argv[2],ios::in|ios::binary); //(文件-->内存)
if(!fin)
{
cout << "打开" << filename << "失败!" << endl;
return 1;
}
if(!fout)
{
cout << "打开" <<argv[2] << "失败!" << endl;
return 2;
}
void (*p)(char*,int) = strcmp(argv[1],"-e")?decode:encode;//定义函数指针
bool temp[100],state;
int bytes,pos1,pos2;
while(state)
{
fout.read((char*)temp,sizeof(temp));
if(!fout) //注意当read读取不足sizeof(temp)时,fout状态置false
{
fout.clear();
state = 0;
}
bytes = fout.gcount();
p((char*)temp,bytes);
fin.write((char*)temp,bytes);
}
fout.clear();
fout.close();
fin.close();
return 0;
}






















 1112
1112

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








