This article describes the installation of Oracle 10g release 2 (10.2.0.1) RAC on Linux (Oracle Enterprise Linux 4.5) using NFS to provide the shared storage.
We can use NFS to provide shared storage for a RAC installation. In a production environment we would expect the NFS server to be a NAS, but for testing it can just as easily be another server, or even one of the RAC nodes itself.
To cut costs, this articles uses one of the RAC nodes as the source of the shared storage. Obviously, this means if that node goes down the whole database is lost, so it's not a sensible idea to do this if you are testing high availability. If you have access to a NAS or a third server you can easily use that for the shared storage, making the whole solution much more resilient. Whichever route you take, the fundamentals of the installation are the same.
This article was inspired by the blog postings of Kevin Closson .
Download SoftwareDownload the following software.
Operating System InstallationThis article uses Oracle Enterprise Linux 4.5, but it will work equally well on CentOS 4 or Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 4. A general pictorial guide to the operating system installation can be found here . More specifically, it should be a server installation with a minimum of 2G swap, firewall and secure Linux disabled and the following package groups installed:
-
- X Window System
- GNOME Desktop Environment
- Editors
- Graphical Internet
- Server Configuration Tools
- FTP Server
- Development Tools
- Legacy Software Development
- Administration Tools
- System Tools
RAC1:
-
- hostname: rac1.localdomain
- IP Address eth0: 192.168.2.101 (public address)
- Default Gateway eth0: 192.168.2.1 (public address)
- IP Address eth1: 192.168.0.101 (private address)
- Default Gateway eth1: none
-
- hostname: rac2.localdomain
- IP Address eth0: 192.168.2.102 (public address)
- Default Gateway eth0: 192.168.2.1 (public address)
- IP Address eth1: 192.168.0.102 (private address)
- Default Gateway eth1: none
Once the basic installation is complete, install the following packages whilst logged in as the root user.
# From Oracle Enterprise Linux 4.5 Disk 1cd /media/cdrecorder/CentOS/RPMSrpm -Uvh setarch-1*rpm -Uvh compat-libstdc++-33-3*rpm -Uvh make-3*rpm -Uvh glibc-2*cd /eject# From Oracle Enterprise Linux 4.5 Disk 2cd /media/cdrecorder/CentOS/RPMSrpm -Uvh openmotif-2*rpm -Uvh compat-db-4*rpm -Uvh gcc-3*cd /eject# From Oracle Enterprise Linux 4.5 Disk 3cd /media/cdrecorder/CentOS/RPMSrpm -Uvh libaio-0*rpm -Uvh rsh-*rpm -Uvh compat-gcc-32-3*rpm -Uvh compat-gcc-32-c++-3*rpm -Uvh openmotif21*cd /ejectOracle Installation PrerequisitesPerform the following steps whilst logged into the RAC1 virtual machine as the root user.
The /etc/hosts file must contain the following information.
127.0.0.1 localhost.localdomain localhost# Public192.168.2.101 rac1.localdomain rac1192.168.2.102 rac2.localdomain rac2#Private192.168.0.101 rac1-priv.localdomain rac1-priv192.168.0.102 rac2-priv.localdomain rac2-priv#Virtual192.168.2.111 rac1-vip.localdomain rac1-vip192.168.2.112 rac2-vip.localdomain rac2-vip#NAS192.168.2.101 nas1.localdomain nas1Notice that the NAS1 entry is actually pointing to the RAC1 node. If you are using a real NAS or a third server to provide your shared storage put the correct IP address into the file.
Add the following lines to the /etc/sysctl.conf file.
kernel.shmall = 2097152kernel.shmmax = 2147483648kernel.shmmni = 4096# semaphores: semmsl, semmns, semopm, semmnikernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128#fs.file-max = 65536net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000#net.core.rmem_default=262144#net.core.rmem_max=262144#net.core.wmem_default=262144#net.core.wmem_max=262144# Additional and amended parameters suggested by Kevin Clossonnet.core.rmem_default = 524288net.core.wmem_default = 524288net.core.rmem_max = 16777216net.core.wmem_max = 16777216net.ipv4.ipfrag_high_thresh=524288net.ipv4.ipfrag_low_thresh=393216net.ipv4.tcp_rmem=4096 524288 16777216net.ipv4.tcp_wmem=4096 524288 16777216net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps=0net.ipv4.tcp_sack=0net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling=1net.core.optmem_max=524287net.core.netdev_max_backlog=2500sunrpc.tcp_slot_table_entries=128sunrpc.udp_slot_table_entries=128net.ipv4.tcp_mem=16384 16384 16384Run the following command to change the current kernel parameters.
/sbin/sysctl -pAdd the following lines to the /etc/security/limits.conf file.
* soft nproc 2047* hard nproc 16384* soft nofile 1024* hard nofile 65536Add the following line to the /etc/pam.d/login file, if it does not already exist.
session required pam_limits.soDisable secure linux by editing the /etc/selinux/config file, making sure the SELINUX flag is set as follows.
SELINUX=disabledAlternatively, this alteration can be done using the GUI tool (Applications > System Settings > Security Level). Click on the SELinux tab and disable the feature.
Set the hangcheck kernel module parameters by adding the following line to the /etc/modprobe.conf file.
options hangcheck-timer hangcheck_tick=30 hangcheck_margin=180To load the module immediately, execute "modprobe -v hangcheck-timer".
Create the new groups and users.
groupadd oinstallgroupadd dbagroupadd operuseradd -g oinstall -G dba oraclepasswd oracleDuring the installation, both RSH and RSH-Server were installed. Enable remote shell and rlogin by doing the following.
chkconfig rsh onchkconfig rlogin onservice xinetd reloadCreate the /etc/hosts.equiv file as the root user.
touch /etc/hosts.equivchmod 600 /etc/hosts.equivchown root:root /etc/hosts.equivEdit the /etc/hosts.equiv file to include all the RAC nodes:
+rac1 oracle+rac2 oracle+rac1-priv oracle+rac2-priv oracleLogin as the oracle user and add the following lines at the end of the .bash_profile file.
# Oracle SettingsTMP=/tmp; export TMPTMPDIR=$TMP; export TMPDIRORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle; export ORACLE_BASEORACLE_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/10.2.0/db_1; export ORACLE_HOMEORACLE_SID=RAC1; export ORACLE_SIDORACLE_TERM=xterm; export ORACLE_TERMPATH=/usr/sbin:$PATH; export PATHPATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH; export PATHLD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib:/lib:/usr/lib; export LD_LIBRARY_PATHCLASSPATH=$ORACLE_HOME/JRE:$ORACLE_HOME/jlib:$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/jlib; export CLASSPATHif [ $USER = "oracle" ]; then if [ $SHELL = "/bin/ksh" ]; then ulimit -p 16384 ulimit -n 65536 else ulimit -u 16384 -n 65536 fifiRemember to set the ORACLE_SID to RAC2 on the second node.
Create Shared DisksFirst we need to set up some NFS shares. In this case we will do this on the RAC1 node, but you can do the on a NAS or a third server if you have one available. On the RAC1 node create the following directories.
mkdir /share1mkdir /share2Add the following lines to the /etc/exports file.
/share1 *(rw,sync,no_wdelay,insecure_locks,no_root_squash)/share2 *(rw,sync,no_wdelay,insecure_locks,no_root_squash)Run the following command to export the NFS shares.
chkconfig nfs onservice nfs restartOn both RAC1 and RAC2 create some mount points to mount the NFS shares to.
mkdir /u01mkdir /u02Add the following lines to the "/etc/fstab" file. The mount options are suggestions from Kevin Closson.
nas1:/share1 /u01 nfs rw,bg,hard,nointr,tcp,vers=3,timeo=300,rsize=32768,wsize=32768,actimeo=0 0 0nas1:/share2 /u02 nfs rw,bg,hard,nointr,tcp,vers=3,timeo=300,rsize=32768,wsize=32768,actimeo=0 0 0Mount the NFS shares on both servers.
mount /u01mount /u02Create the shared CRS Configuration and Voting Disk files.
touch /u01/crs_configurationtouch /u01/voting_diskCreate the directories in which the Oracle software will be installed.
mkdir -p /u01/crs/oracle/product/10.2.0/crsmkdir -p /u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1mkdir -p /u01/oradatachown -R oracle:oinstall /u01 /u02Install the Clusterware SoftwarePlace the clusterware and database software in the /u02 directory and unzip it.
cd /u02unzip 10201_clusterware_linux32.zipunzip 10201_database_linux32.zipLogin to RAC1 as the oracle user and start the Oracle installer.
cd /u02/clusterware./runInstallerOn the "Welcome" screen, click the "Next" button.

Accept the default inventory location by clicking the "Next" button.

Enter the appropriate name and path for the Oracle Home and click the "Next" button.
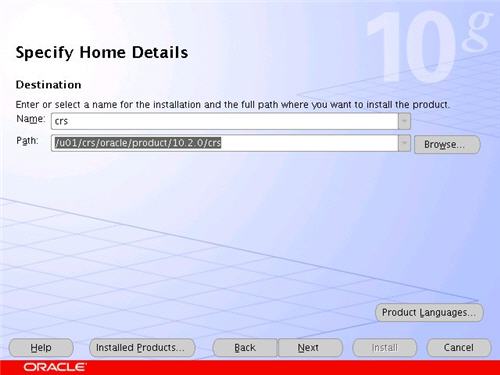
Wait while the prerequisite checks are done. If you have any failures correct them and retry the tests before clicking the "Next" button.
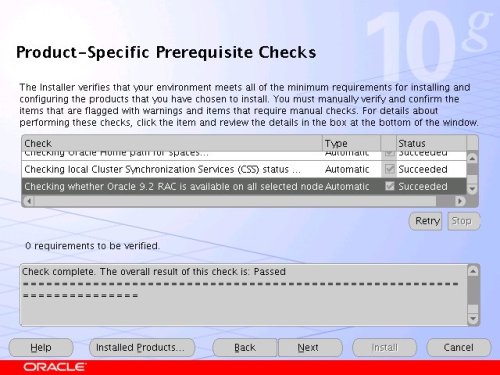
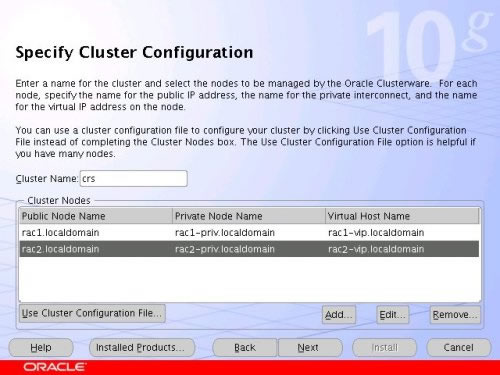
The "Specify Cluster Configuration" screen shows only the RAC1 node in the cluster. Click the "Add" button to continue.
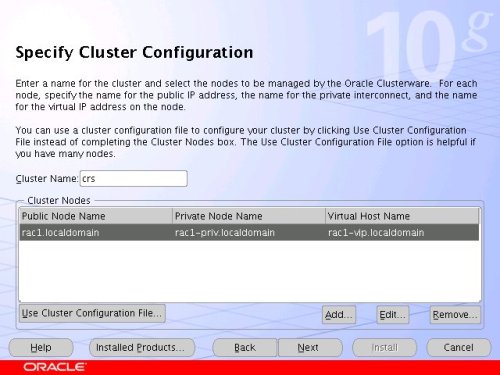
Enter the details for the RAC2 node and click the "OK" button.
Click the "Next" button to continue.
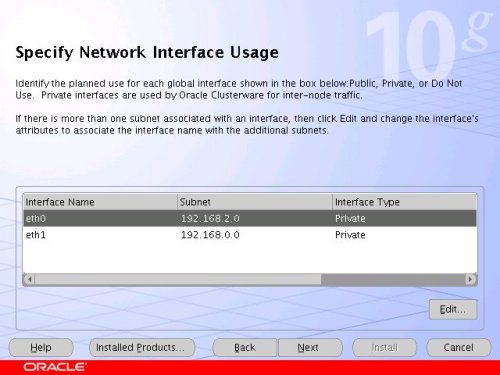
The "Specific Network Interface Usage" screen defines how each network interface will be used. Highlight the "eth0" interface and click the "Edit" button.
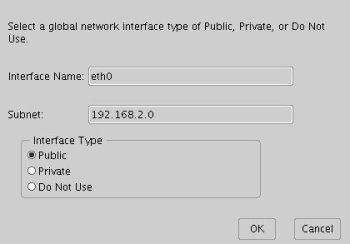
Set the "eht0" interface type to "Public" and click the "OK" button.
Leave the "eth1" interface as private and click the "Next" button.
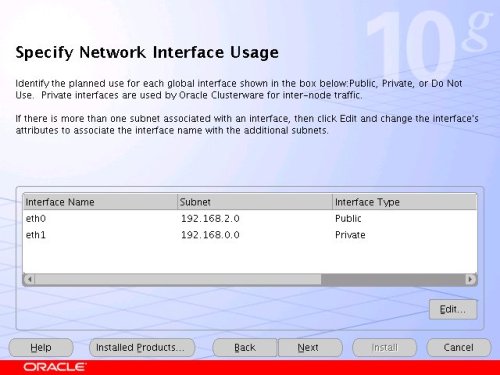
Click the "External Redundancy" option, enter "/u01/ocr_configuration" as the OCR Location and click the "Next" button. To have greater redundancy we would need to define another shared disk for an alternate location.

Click the "External Redundancy" option, enter "/u01/voting_disk" as the Voting Disk Location and click the "Next" button. To have greater redundancy we would need to define another shared disk for an alternate location.

On the "Summary" screen, click the "Install" button to continue.
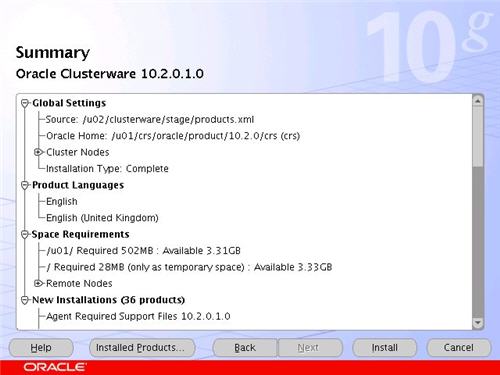
Wait while the installation takes place.

Once the install is complete, run the orainstRoot.sh and root.sh scripts on both nodes as directed on the following screen.
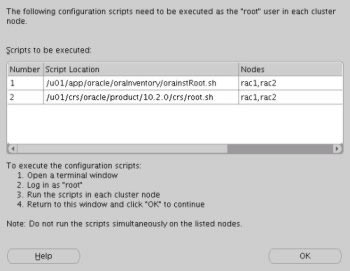
The output from the orainstRoot.sh file should look something like that listed below.
# cd /u01/app/oracle/oraInventory# ./orainstRoot.shChanging permissions of /u01/app/oracle/oraInventory to 770.Changing groupname of /u01/app/oracle/oraInventory to oinstall.The execution of the script is complete#The output of the root.sh will vary a little depending on the node it is run on. The following text is the output from the RAC1 node.
# cd /u01/crs/oracle/product/10.2.0/crs# ./root.shWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle/product/10.2.0' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle/product' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01' is not owned by rootChecking to see if Oracle CRS stack is already configured/etc/oracle does not exist. Creating it now.Setting the permissions on OCR backup directorySetting up NS directoriesOracle Cluster Registry configuration upgraded successfullyWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle/product/10.2.0' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle/product' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01' is not owned by rootassigning default hostname rac1 for node 1.assigning default hostname rac2 for node 2.Successfully accumulated necessary OCR keys.Using ports: CSS=49895 CRS=49896 EVMC=49898 and EVMR=49897.node <nodenumber>: <nodename> <private interconnect name> <hostname>node 1: rac1 rac1-priv rac1node 2: rac2 rac2-priv rac2Creating OCR keys for user 'root', privgrp 'root'..Operation successful.Now formatting voting device: /u01/voting_diskFormat of 1 voting devices complete.Startup will be queued to init within 90 seconds.Adding daemons to inittabExpecting the CRS daemons to be up within 600 seconds.CSS is active on these nodes. rac1CSS is inactive on these nodes. rac2Local node checking complete.Run root.sh on remaining nodes to start CRS daemons.#Ignore the directory ownership warnings. We should really use a separate directory structure for the clusterware so it can be owned by the root user, but it has little effect on the finished results.
The output from the RAC2 node is listed below.
# /u01/crs/oracle/product/10.2.0/crs# ./root.shWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle/product/10.2.0' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle/product' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01' is not owned by rootChecking to see if Oracle CRS stack is already configured/etc/oracle does not exist. Creating it now.Setting the permissions on OCR backup directorySetting up NS directoriesOracle Cluster Registry configuration upgraded successfullyWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle/product/10.2.0' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle/product' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs/oracle' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01/crs' is not owned by rootWARNING: directory '/u01' is not owned by rootclscfg: EXISTING configuration version 3 detected.clscfg: version 3 is 10G Release 2.assigning default hostname rac1 for node 1.assigning default hostname rac2 for node 2.Successfully accumulated necessary OCR keys.Using ports: CSS=49895 CRS=49896 EVMC=49898 and EVMR=49897.node <nodenumber>: <nodename> <private interconnect name> <hostname>node 1: rac1 rac1-priv rac1node 2: rac2 rac2-priv rac2clscfg: Arguments check out successfully.NO KEYS WERE WRITTEN. Supply -force parameter to override.-force is destructive and will destroy any previous clusterconfiguration.Oracle Cluster Registry for cluster has already been initializedStartup will be queued to init within 90 seconds.Adding daemons to inittabExpecting the CRS daemons to be up within 600 seconds.CSS is active on these nodes. rac1 rac2CSS is active on all nodes.Waiting for the Oracle CRSD and EVMD to startWaiting for the Oracle CRSD and EVMD to startWaiting for the Oracle CRSD and EVMD to startWaiting for the Oracle CRSD and EVMD to startWaiting for the Oracle CRSD and EVMD to startWaiting for the Oracle CRSD and EVMD to startWaiting for the Oracle CRSD and EVMD to startOracle CRS stack installed and running under init(1M)Running vipca(silent) for configuring nodeappsThe given interface(s), "eth0" is not public. Public interfaces should be used to configure virtual IPs.#Here you can see that some of the configuration steps are omitted as they were done by the first node. In addition, the final part of the script ran the Virtual IP Configuration Assistant (VIPCA) in silent mode, but it failed. This is because my public IP addresses are actually within the "192.168.255.255" range which is a private IP range. If you were using "legal" IP addresses you would not see this and you could ignore the following VIPCA steps.
Run the VIPCA manually as the root user on the RAC2 node using the following command.
# cd /u01/crs/oracle/product/10.2.0/crs/bin# ./vipcaClick the "Next" button on the VIPCA welcome screen.

Highlight the "eth0" interface and click the "Next" button.

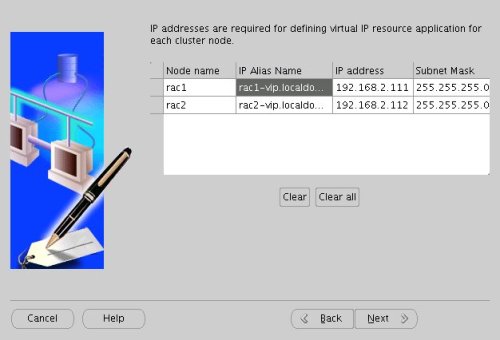
Enter the vitual IP alias and address for each node. Once you enter the first alias, the remaining values should default automatically. Click the "Next" button to continue.
Accept the summary information by clicking the "Finish" button.
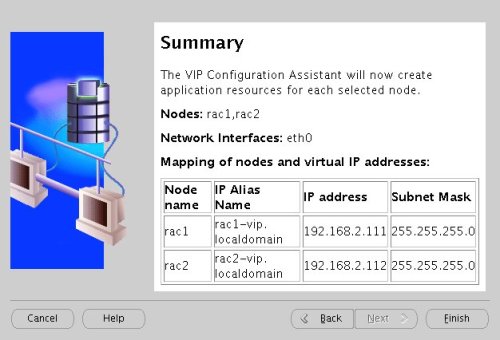
Wait until the configuration is complete, then click the "OK" button.

Accept the VIPCA results by clicking the "Exit" button.
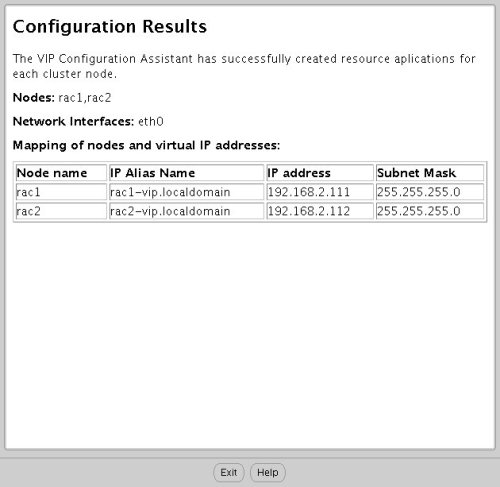
You should now return to the "Execute Configuration Scripts" screen on RAC1 and click the "OK" button.

Wait for the configuration assistants to complete.
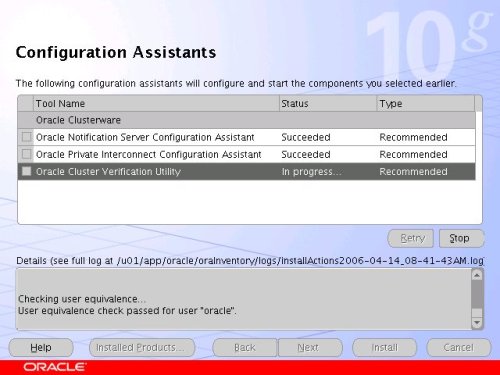
When the installation is complete, click the "Exit" button to leave the installer.
The clusterware installation is now complete.
Install the Database SoftwareLogin to RAC1 as the oracle user and start the Oracle installer.
cd /u02/database./runInstallerOn the "Welcome" screen, click the "Next" button.
Select the "Enterprise Edition" option and click the "Next" button.
Enter the name and path for the Oracle Home and click the "Next" button.
Select the "Cluster Install" option and make sure both RAC nodes are selected, the click the "Next" button.
Wait while the prerequisite checks are done. If you have any failures correct them and retry the tests before clicking the "Next" button.
Select the "Install database Software only" option, then click the "Next" button.
On the "Summary" screen, click the "Install" button to continue.
Wait while the database software installs.
Once the installation is complete, wait while the configuration assistants run.
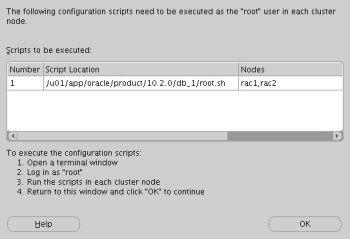
Execute the "root.sh" scripts on both nodes, as instructed on the "Execute Configuration scripts" screen, then click the "OK" button.
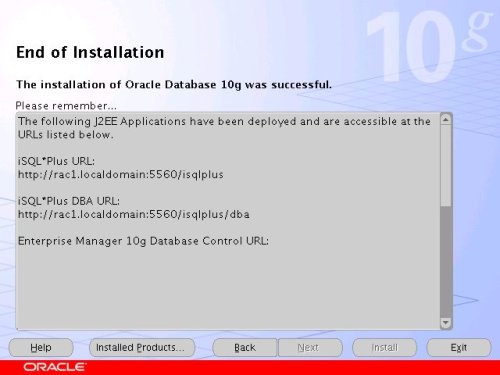
When the installation is complete, click the "Exit" button to leave the installer.
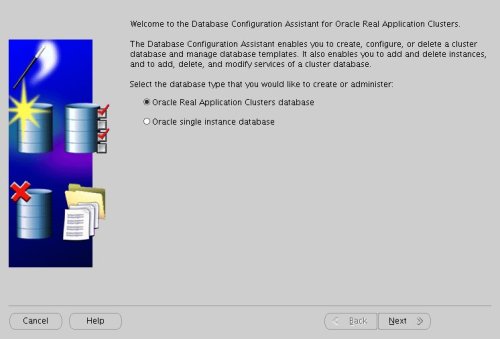
Create a Database using the DBCALogin to RAC1 as the oracle user and start the Database Configuration Assistant.
dbcaOn the "Welcome" screen, select the "Oracle Real Application Clusters database" option and click the "Next" button.
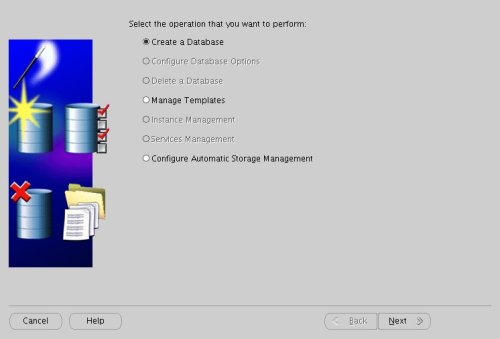
Select the "Create a Database" option and click the "Next" button.
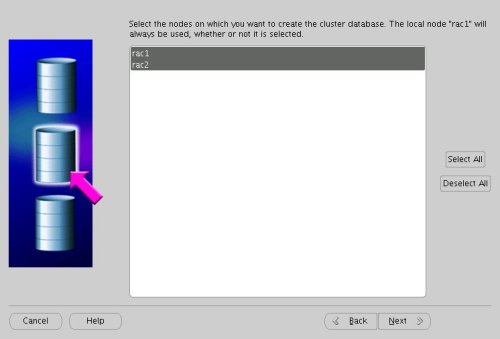
Highlight both RAC nodes and click the "Next" button.
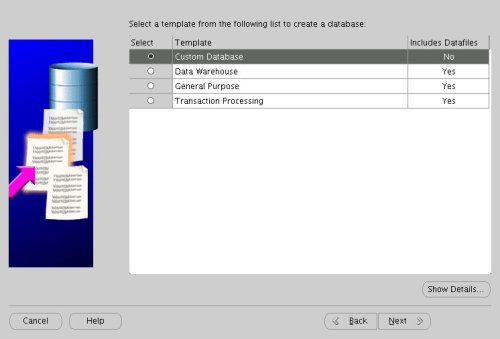
Select the "Custom Database" option and click the "Next" button.
Enter the values "RAC.WORLD" and "RAC" for the Global Database Name and SID Prefix respectively, then click the "Next" button.

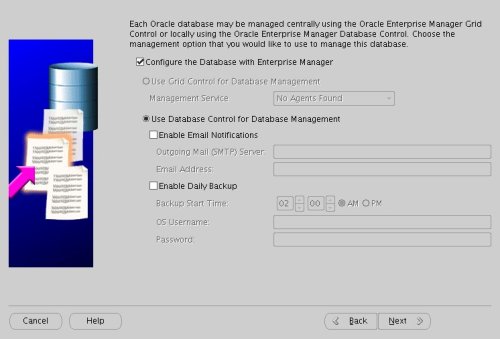
Accept the management options by clicking the "Next" button. If you are attempting the installation on a server with limited memory, you may prefer not to configure Enterprise Manager at this time.
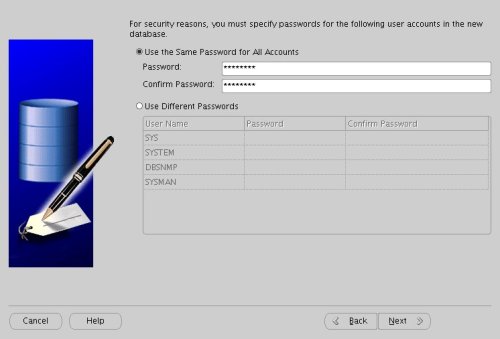
Enter database passwords then click the "Next" button.
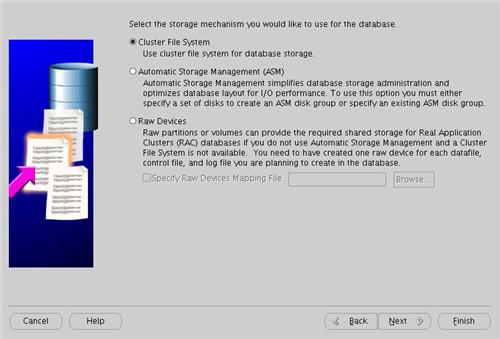
Select the "Cluster File System" option, then click the "Next" button.
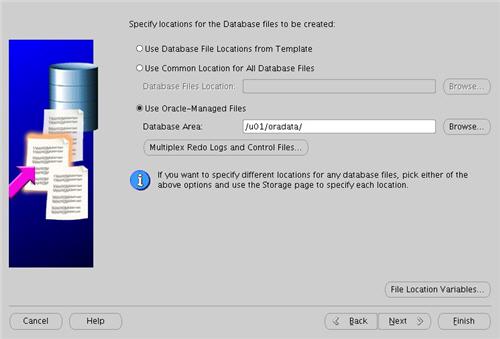
Select the "Use Oracle-Managed Files" option and enter "/u01/oradata/" as the database location, then click the "Next" button.
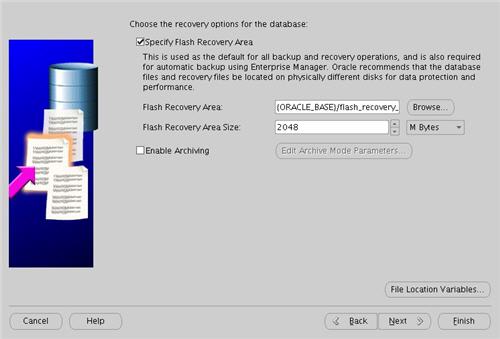
Check the "Specify Flash Recovery Area" option and accept the default location by clicking the "Next" button.
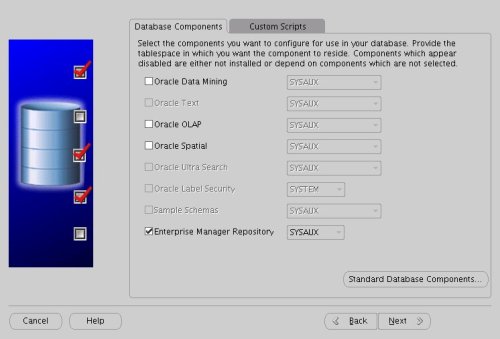
Uncheck all but the "Enterprise Manager Repository" option, then click the "Standard Database Components..." button.
Uncheck all but the "Oracle JVM" option, then click the "OK" button, followed by the "Next" button on the previous screen. If you are attempting the installation on a server with limited memory, you may prefer not to install the JVM at this time.
Accept the current database services configuration by clicking the "Next" button.
Select the "Custom" memory management option and accept the default settings by clicking the "Next" button.
Accept the database storage settings by clicking the "Next" button.
Accept the database creation options by clicking the "Finish" button.
Accept the summary information by clicking the "OK" button.
Wait while the database is created.
Once the database creation is complete you are presented with the following screen. Make a note of the information on the screen and click the "Exit" button.
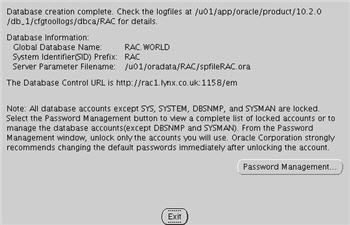
The RAC database creation is now complete.
TNS ConfigurationOnce the installation is complete, the "$ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/listener.ora" file in the shared $ORACLE_HOME will contain the following entries.
LISTENER_RAC2 = (DESCRIPTION_LIST = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = rac2-vip.lynx.co.uk)(PORT = 1521)(IP = FIRST)) ) (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = 192.168.2.102)(PORT = 1521)(IP = FIRST)) ) (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC)) ) ) )LISTENER_RAC1 = (DESCRIPTION_LIST = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = rac1-vip.lynx.co.uk)(PORT = 1521)(IP = FIRST)) ) (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = 192.168.2.101)(PORT = 1521)(IP = FIRST)) ) (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC)) ) ) )The shared "$ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora" file will contain the following entries.
RAC = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = rac1-vip.lynx.co.uk)(PORT = 1521)) (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = rac2-vip.lynx.co.uk)(PORT = 1521)) (LOAD_BALANCE = yes) (CONNECT_DATA = (SERVER = DEDICATED) (SERVICE_NAME = RAC.WORLD) ) )LISTENERS_RAC = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = rac1-vip.lynx.co.uk)(PORT = 1521)) (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = rac2-vip.lynx.co.uk)(PORT = 1521)) )RAC2 = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = rac2-vip.lynx.co.uk)(PORT = 1521)) (CONNECT_DATA = (SERVER = DEDICATED) (SERVICE_NAME = RAC.WORLD) (INSTANCE_NAME = RAC2) ) )RAC1 = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = rac1-vip.lynx.co.uk)(PORT = 1521)) (CONNECT_DATA = (SERVER = DEDICATED) (SERVICE_NAME = RAC.WORLD) (INSTANCE_NAME = RAC1) ) )This configuration allows direct connections to specific instance, or using a load balanced connection to the main service.
$ sqlplus / as sysdbaSQL*Plus: Release 10.2.0.1.0 - Production on Tue Apr 18 12:27:11 2006Copyright (c) 1982, 2005, Oracle. All rights reserved.Connected to:Oracle Database 10g Enterprise Edition Release 10.2.0.1.0 - ProductionWith the Partitioning, Real Application Clusters, OLAP and Data Mining optionsSQL> CONN sys/password@rac1 AS SYSDBAConnected.SQL> SELECT instance_name, host_name FROM v$instance;INSTANCE_NAME HOST_NAME---------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------RAC1 rac1.localdomainSQL> CONN sys/password@rac2 AS SYSDBAConnected.SQL> SELECT instance_name, host_name FROM v$instance;INSTANCE_NAME HOST_NAME---------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------RAC2 rac2.localdomainSQL> CONN sys/password@rac AS SYSDBAConnected.SQL> SELECT instance_name, host_name FROM v$instance;INSTANCE_NAME HOST_NAME---------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------RAC1 rac1.localdomainSQL>Check the Status of the RACThere are several ways to check the status of the RAC. The srvctl utility shows the current configuration and status of the RAC database.
$ srvctl config database -d RACrac1 RAC1 /u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1rac2 RAC2 /u01/app/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1$$ srvctl status database -d RACInstance RAC1 is running on node rac1Instance RAC2 is running on node rac2$The V$ACTIVE_INSTANCES view can also display the current status of the instances.
$ sqlplus / as sysdbaSQL*Plus: Release 10.2.0.1.0 - Production on Tue Apr 18 12:15:15 2006Copyright (c) 1982, 2005, Oracle. All rights reserved.Connected to:Oracle Database 10g Enterprise Edition Release 10.2.0.1.0 - ProductionWith the Partitioning, Real Application Clusters, OLAP and Data Mining optionsSQL> SELECT * FROM v$active_instances;INST_NUMBER INST_NAME----------- ------------------------------------------------------------ 1 rac1.localdomain:RAC1 2 rac2.localdomain:RAC2SQL>Finally, the GV$ allow you to display global information for the whole RAC.
SQL> SELECT inst_id, username, sid, serial# FROM gv$session WHERE username IS NOT NULL; INST_ID USERNAME SID SERIAL#---------- ------------------------------ ---------- ---------- 1 SYS 127 2 1 SYS 128 28 1 SYS 130 10 1 SYS 131 4 1 SYS 133 9 1 DBSNMP 134 27 1 DBSNMP 135 1 1 SYS 153 122 2 SYSMAN 120 243 2 DBSNMP 122 37 2 DBSNMP 124 93 INST_ID USERNAME SID SERIAL#---------- ------------------------------ ---------- ---------- 2 SYSMAN 125 2 2 SYSMAN 127 6 2 SYS 128 26 2 SYS 129 30 2 SYS 130 3 2 SYS 133 149 2 SYSMAN 134 58 2 SYS 136 3219 rows selected.SQL>If you have configured Enterprise Manager, it can be used to view the configuration and current status of the database.
Direct and Asynchronous I/ORemember to use direct I/O and asynchronous I/O to improve performance. Direct I/O has been supported over NFS for some time, but support for asynchronous I/O over NFS was only introduced in RHEL 4 Update 3 (and its clones), so you need to use an up to date version of your Linux distribution to take advantage of this feature.
You can get details about this Direct and Asynchronous I/O by following the link.
For more information see:
-
- Oracle 10g RAC On Linux Using VMware Server
- Oracle Database 10g Release 2 (10.2.0.1) RAC Installation On Windows 2003 Using VMware Server
- Build Your Own Oracle RAC 10g Release 2 Cluster on Linux and FireWire
- Installation Guide for Linux x86 (10.2)
- Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation Guide for Linux (10.2)
- Direct and Asynchronous I/O
- 提供Oracle管理/故障处理/优化/安装/RAC/备份恢复技术服务,提供专业的Oracle培训和咨询服务。
- 邮件: inthirties@gmail.com
- MSN: inthirties@hotmail.com
- QQ: inthirties@qq.com
- 电话: 13828706466
- 技术博客 http://blog.csdn.net/inthirties
- 个人站点 http://blog.inthirties.com


























 429
429

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










