使用Google Web Toolkit减轻AJAX的开发
2. Web模式:这种模式允许一个GWT应用来发布和执行本地的JavaScript和HTML,这些本地的JavaScripth和HTML使用GWT Java-to-JavaScript编译器从Java源文件中产生。
final com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button button = new com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button("Click me");
button.addClickListener(new com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.ClickListener() { public void onClick(com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Widget sender)
{ System.out.println("The 'Click me' button was clicked"); } });
com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel.get("MyContainerPanel").add(button);
同样的,所有的典型发生在服务器主机的行为都被称为服务器端过程。当一个应用和服务器相关联,它使用GWT的remote procedure call(RPC)框架来使浏览器(客户端)请求服务器端代码。
applicationCreator -out ./BookSearch com.example.client.BookSearch
|
在hosted模式下运行BookSearch skeleton应用,执行BookSearch-shell脚本。你会看到如下的图像:

现在,UI的布局已经完成,UI widgets可以被添加到里面去。
如下所示的是为BookSearch应用初始化UI布局所需要的代码:
public void onModuleLoad(){ private static final int VISIBLE_ROWS = 5;
public void onModuleLoad() { // Retrieve the panel for the booklist widget // RootPanel booklistPanel = RootPanel.get("booklist"); if (booklistPanel != null) { BookListWidget booklistWidget = new BookListWidget(VISIBLE_ROWS); booklistPanel.add(booklistWidget);
// Retrieve the panel for the searchterm widget // RootPanel searchtermPanel = RootPanel.get("searchterm"); if (searchtermPanel != null) { SearchTermWidget searchTermWidget = new SearchTermWidget(booklistWidget); searchtermPanel.add(searchTermWidget); } } }}所有的初始化代码都在BookSearch类的onModuleLoad()方法里。onModuleLoad()方法是com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint接口定义的唯一方法。这个方法在模块被载入的时候调用。请注意com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel类是如何通过他们的IDs来获取BookSearch.html元素的引用的。GWT依赖命令规则来定位widget类来映射HTML元素的IDs。例如,“booklist”HTML ID被用来定位被称为“BookListWidget”的widget。
创建应用的客户端行为
现在,应用的表格和结构已经建立起来了,应用的客户端行为就可以被创建了。我们的客户端行为被封装在三个主要的UI widget实例中:
1.
一个widget实例来处理search-term过程
2.
一个容器widget实例来盛装search-service提供器和可以翻页的清单
3.
一个翻页清单widget实例来合并一系列的widget实例来组成一个浏览bar和一个翻页的书籍清单
如下的代码显示了处理获取booklist和包含翻页清单的widget:
public class BookListWidget extends com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Composite{ private final PageableListWidget pageableListWidget; private String searchTerm = "";
/** * * @param visibleRows */ public BookListWidget(int visibleRows) { String[] columns = new String[]{"Title", "ISBN", "Edition", "MSRP"}; String[] styles = new String[]{"title", "isbn", "edition", "msrp"}; pageableListWidget = new PageableListWidget(bookSearchProvider, columns, styles, visibleRows); initWidget(pageableListWidget); }
protected void onLoad() { pageableListWidget.refresh(); }
/** * * @param searchTerm */ protected void setSearchTerm(String searchTerm) { if (this.searchTerm.equals(searchTerm)) { // No change // return; }
this.searchTerm = searchTerm;
pageableListWidget.refresh(); }}BookListWidget类继承com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Composite类来聚合UI组件以组合一个或多个相关的widgets。在这个例子中,只有一个嵌套的基于组合的widget,称为PageableListWidget被用到。
PageableListWidget类也继承自com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Composite类,包含多个子widgets,包括一个定制的navigation-bar widget和一个com.google.gwt.user.client.Grid widget来处理有关于书籍数据的清单。navigation-bar widget合并了一个com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.DockPanel widget的实例和几个com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button类的实例。
以下是PaneableListWidget类的示例代码:
public class PageableListWidget extends com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Composite{ private final RowDataAcceptor acceptor = new RowDataAcceptorImpl(); private final NavBar navbar = new NavBar(); private final DockPanel outer = new DockPanel(); private final SearchProvider provider; private int startRow = 0; private final Grid grid = new Grid();
/** * Navigation Bar widget */ private class NavBar extends Composite implements ClickListener { public final DockPanel bar = new DockPanel(); public final Button gotoFirst = new Button("First", this); public final Button gotoNext = new Button("Next", this); public final Button gotoPrev = new Button("Prev", this); public final HTML status = new HTML();
public NavBar() { initWidget(bar); bar.setStyleName("navbar"); status.setStyleName("status");
HorizontalPanel buttons = new HorizontalPanel(); buttons.add(gotoFirst); buttons.add(gotoPrev); buttons.add(gotoNext); bar.add(buttons, DockPanel.EAST); bar.setCellHorizontalAlignment(buttons, DockPanel.ALIGN_RIGHT); bar.add(status, DockPanel.CENTER); bar.setVerticalAlignment(DockPanel.ALIGN_MIDDLE); bar.setCellHorizontalAlignment(status, HasAlignment.ALIGN_RIGHT); bar.setCellVerticalAlignment(status, HasAlignment.ALIGN_MIDDLE); bar.setCellWidth(status, "100%");
// Initially disable prev & first buttons // gotoPrev.setEnabled(false); gotoFirst.setEnabled(false); }
public void onClick(Widget sender) {
// handle nav-bar button clicks } }
public PageableListWidget(SearchProvider provider,
String[] columns, String[] columnStyles, int rowCount) {
this.provider = provider; initWidget(outer); grid.setStyleName("table"); outer.add(navbar, DockPanel.NORTH); outer.add(grid, DockPanel.CENTER); initTable(columns, columnStyles, rowCount); setStyleName("BookSearch-PageableListWidget"); }
/** * * @param columns * @param columnStyles * @param rowCount */ private void initTable(String[] columns, String[] columnStyles, int rowCount) { // Set up the header row to one greater than the number of visible rows // grid.resize(rowCount + 1, columns.length); for (int i = 0, n = columns.length; i < n; i++) { grid.setText(0, i, columns[i]); if (columnStyles != null) { grid.getCellFormatter().setStyleName(0, i, columnStyles[i] + " header"); } }
}
public void refresh() { // Disable buttons temporarily to stop the user from overrunning the table // navbar.gotoFirst.setEnabled(false); navbar.gotoPrev.setEnabled(false); navbar.gotoNext.setEnabled(false);
setStatusText("Please wait...");
// update table updateTable(startRow, getDataFromService()); }
private void updateTable(int startRow, String[][] data) { int destRowCount = getDataRowCount(); int destColCount = grid.getCellCount(0); assert (data.length <= destRowCount) : "Too many rows";
int srcRowIndex = 0; int srcRowCount = data.length; int destRowIndex = 1; // skip navbar row for (; srcRowIndex < srcRowCount; ++srcRowIndex, ++destRowIndex) { String[] srcRowData = data[srcRowIndex]; assert (srcRowData.length == destColCount) : " Column count mismatch"; for (int srcColIndex = 0; srcColIndex < destColCount; ++srcColIndex) { String cellHTML = srcRowData[srcColIndex]; grid.setText(destRowIndex, srcColIndex, cellHTML); } }
// Clear any remaining table rows // boolean isLastPage = false; for (; destRowIndex < destRowCount + 1; ++destRowIndex) { isLastPage = true; for (int destColIndex = 0; destColIndex < destColCount; ++destColIndex) { grid.clearCell(destRowIndex, destColIndex); } }
// Synchronize the nav buttons // navbar.gotoNext.setEnabled(!isLastPage); navbar.gotoFirst.setEnabled(startRow > 0); navbar.gotoPrev.setEnabled(startRow > 0); }
public void setRowCount(int rows) { grid.resizeRows(rows); }
private int getDataRowCount() { return grid.getRowCount() - 1; } }SearchTermWidget继承自com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Composite类,包含一个label,一个text box,和一个button。Text box包含搜索项,button发动每一次的搜索。
以下是SearchTermWidget类的代码:
public class SearchTermWidget extends com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Composite{ private final HorizontalPanel outer = new HorizontalPanel(); private BookListWidget booklistWidget = null; private TextBox searchTermTxtBox = null;
public SearchTermWidget(final BookListWidget booklist) { initWidget(outer); setStyleName("BookSearch-SearchTermWidget");
this.booklistWidget = booklist;
Label lbl = new Label("Search term: "); lbl.setHeight("1.5em");
searchTermTxtBox = new TextBox(); searchTermTxtBox.setHeight("1em"); searchTermTxtBox.setText("");
Button searchBtn = new Button("Search", new ClickListener() { public void onClick(Widget sender) { booklistWidget.setSearchTerm(searchTermTxtBox.getText());
} }); searchBtn.setHeight("1.5em");
HorizontalPanel hp = new HorizontalPanel(); hp.setHorizontalAlignment(HasAlignment.ALIGN_CENTER);
hp.add(lbl); hp.add(searchTermTxtBox); hp.add(searchBtn);
outer.add(hp); outer.setCellVerticalAlignment(hp, HasAlignment.ALIGN_MIDDLE); outer.setCellHorizontalAlignment(hp, HasAlignment.ALIGN_CENTER); }}现在,应用已经准备好了来调用服务器端的服务。
创建应用的服务器端行为
现在服务器端的功能能够被添加到应用中来。对于BookSearch应用,一个远程的API被调用以获取给定搜索词相对应的书籍清单。GWT提供一个RPC框架来使得客户端获取服务并且被调用以完成实际的搜索。
BookSearch应用的相互通信如下图所示:
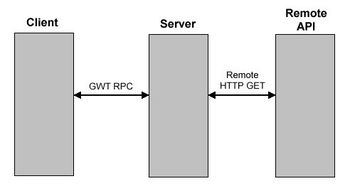
图3点击可查看大图
实现服务器端代码的第一步是为搜索服务定义一个接口。这个接口必须继承com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.RemoteService接口,并且包含能够被GWT客户端代码调用的方法。
如下的代码就是搜索服务的接口。它的唯一方法是获取搜索词作为输入并且返回包含相对应的数据清单的Book对象的数组。
public interface SearchService extends com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.RemoteService{ Book[] getBooks(String searchTerm, int startIndex, int maxCount);}由JavaScript发起的AJAX调用是异步的;因而,一个对应于RemoteService接口的异步接口必须被定义。异步接口的方法签名通过一个或多个额外的com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback的参数类型来匹配那些远程接口,它在异步服务完成之后被调用。由于callback对象会用来和响应通信,返回类型也是可变的。
如下的清单展示了SearchService的异步接口:
public interface SearchServiceAsync{ void getBooks(String searchTerm, int startIndex, int maxCount, com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback callback); }AsyncCallback类有两个方法:onSuccess()和onFailure(),他们在远程服务成功或失败的时候被调用。
为SearchService类的异步实现类现在被创建了。实际搜索动作被执行的逻辑是使用Apache HTTPClient框架来远程调用HTTP GET方法,search-related API。在本例中,search API由Safari Books online提供,并且由URL:http://my.safaribooksonline.com/xmlapi/?search=调用。由Safari Books Online search API返回的结果是一个XML文档。这个文档由使用Java API for XML Processing(JAXP)框架来作为一个DOM(Document Object Model)文档来处理。
如下的代码显示了使用Apache Commons HttpClient类调用search API和使用JAXP API来作为DOM文档处理结果的过程:
HttpClient client = new HttpClient(); GetMethod get = new GetMethod(url);
org.w3c.dom.Document xmlDoc = null;
try { // Invoke the remote search API int resultCode = client.executeMethod(get);
if (resultCode == 200) { InputStream in = get.getResponseBodyAsStream(); // Build the DOM document from the response stream DocumentBuilder builder = builderFactory.newDocumentBuilder(); xmlDoc = builder.parse(in); } else { throw new IOException("HTTP error with response code: " + resultCode); } } finally { // Release the connection get.releaseConnection(); }一旦DOM文档被创建,它的单个的元素就可以被用来找到元素以添加到books的清单中去,像如下代码所示:
org.w3c.dom.NodeList nodeList = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book"); if (nodeList != null) { int len = nodeList.getLength(); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { org.w3c.dom.Element bookElement = (org.w3c.dom.Element)nodeList.item(i);
org.w3c.dom.Element title = (org.w3c.dom.Element) bookElement.getElementsByTagName("title").item(0); String titleStr = (title != null ? title.getTextContent() : ""); org.w3c.dom.Element isbn = (org.w3c.dom.Element) bookElement.getElementsByTagName("isbn").item(0); String isbnStr = (isbn != null ? isbn.getTextContent() : "");
org.w3c.dom.Element edition = (org.w3c.dom.Element) bookElement.getElementsByTagName("edition").item(0); String editionStr = (edition != null ? edition.getTextContent() : "");
org.w3c.dom.Element msrp = (org.w3c.dom.Element) bookElement.getElementsByTagName("msrp").item(0); String msrpStr = (msrp != null ? msrp.getTextContent() : "");
books.add(new Book(titleStr, isbnStr, editionStr, msrpStr)); }通过search service类和接口的实现,客户端类能够调用服务并且处理它的响应。
从客户端代码调用search service
通过search service类和接口的实现,客户端类能够调用服务并且处理它的响应。步骤如下:
1.
创建SearchServiceAsync类的实例,如下:searchService = (SearchServiceAsync)GWT.create(SearchService.class);
2.
在SearchServiceAsync类的实例中设置entry point URL,如下:
ServiceDefTarget target = (ServiceDefTarget)searchService;String moduleRelativeURL = GWT.getModuleBaseURL() + "booksearch"; target.setServiceEntryPoint(moduleRelativeURL);
3.
在SearchTermWidget类的search按钮的onClick方法中添加逻辑,通过在SearchTermWidget类中的text box中发现的搜索词来更新相对应的BookListWidget类,如下:
Button searchBtn = new Button("Search", new ClickListener() { public void onClick(Widget sender) { booklistWidget.setSearchTerm (searchTermTxtBox.getText()); } });
4.
通过调用它的refresh方法来更新PageableListWidget实例的UI
5.
通过调用updateRowData方法使用新的搜索词来更新BookSearchProvider,该updateRowData方法会调用search service的getBooks方法
6.
通过getBooks方法,search service执行并且调用AsyncCallback实例的onFailure或者onSuccess方法:
searchService.getBooks(searchTerm, startRow, maxRows, new AsyncCallback() { public void onFailure(Throwable caught) { // handle failures }
public void onSuccess(Object result) { // update com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Grid // Widget with results } });当onSuccess方法被调用,com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Grid widget的实例会被新的book清单所更新。
下图所显示的是应用的主页,使用“Java”搜索词从Safari Books Online API获取的书籍清单显示在页面上:
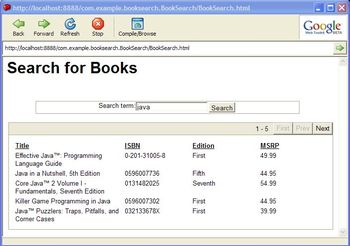
图4点击可查看大图
小结
Google Web Toolkit是AJAX应用开发的一个Java开发框架。GWT简化了基于AJAX的RPC通信的大量技术细节,并且为构建富UIs提供了一个widget组件库。
GWT允许开发人员在Java环境下使用通用的Java开发工具实现和调试基于AJAX的应用,然后编译和发布应用为客户端的HTML和JavaScript,或者服务器端的Java。
GWT用Java将客户端和服务器端代码融合到一起作为一个普通的语言。这个通用的环境在一些特性如调试方面有一些缺点。例如,GWT完全依赖于JavaScript的实用性。如果JavaScript不可用,UI就不会工作。还有,传统Web客户端开发技术所暴露的安全上的漏洞,GWT由于在客户端和服务器端都使用Java开发,使得弱点会被隐藏起来,这样会导致一个对运行期安全的一个错误感觉。
GWT的工作形成了一个黑盒框架,这消除了很多共有的Web应用开发的挑战,它使得开发人员朝向一个AJAX模式的开发模型。然而,这种黑盒的环境使得集成其他非AJAX技术变得复杂。因而,GWT大部分适用于围绕一个富GUI,简单页面模型的Web应用设计。
作者简历
Jeff Hanson在软件工业有着二十年的经验,包括在Novell作为Windows OpenDoc项目的高级工程师和Route 66框架的首席架构师。无数的文章和书籍的作者,他现在是eReinsure.com的首席架构师,为基于Java EE的再保险系统创建Web服务框架和平台。
资源
·
下载本文的代码:
http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-12-2006/gwt/jw-12-gwt.zip
·
GWT:
http://code.google.com/webtoolkit/download.html
·
一些最近关于AJAX编程的文章, read these following JavaWorld articles:
o
For an alternative to AJAX, read "Dynamic Webpages with JSON," Ajay Raina and John Jimenez (November 2006):
http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-11-2006/jw-1115-json.html
o
"Pump Some AJAX into Your JSF Application," Peter Wang (September 2006):
http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-09-2006/jw-0911-jsf.html
o
"AjaxChat: Chatting, the AJAX Way!" Frank W. Zammetti (September 2006):
http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-09-2006/jw-0911-ajax.html
o
"AJAX Made Simple with DWR," Cloves Carneiro Jr. (June 2005):
http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-06-2005/jw-0620-dwr.html
·
Browse through the articles in JavaWorld's User Interface Design Research Center:
http://www.javaworld.com/channel_content/jw-ui-index.html




















 3885
3885











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








