问题描述:
Suppose that each coupon obtained is, independent of what has been previously obtained, equally likely to be any of m different types. Find the expected number of coupons one needs to obtain in order to have at least one of each type.
Hint: Let X be the number needed. It is useful to represent X by
X
=
∑
i
X
i
X = \sum_i X_i
X=i∑Xiwhere each
X
i
X_i
Xi is a geometric random variable.
(问题来源:《Introduction to Probability Models 10th Edition》习题2.42)
中文描述:
假设在一次抽奖活动中,你需要集齐 m 种卡片,每次抽中任意类型卡片的概率是相等的,即 1 m \frac{1}m m1 。那么要集齐所有类型,平均要抽多少次?
背景知识(几何分布):
这道题第一次做还是费一点脑力的,即便题目给了提示:考虑 m 个几何分布的和,但其实容易带来误导。
对于几何分布,大家都非常了解。每次试验成功的概率是 p,则直到第 n 次试验才第一次成功的概率服从几何分布 P(n):1
Suppose that independent trials, each having probability p of being a success, are performed until a success occurs. If we let X be the number of trials required until the first success, then X is said to be a geometric random variable with parameter p. Its probability mass function is given by
P
(
n
)
=
P
{
X
=
n
}
=
(
1
−
p
)
n
−
1
p
,
n
=
1
,
2
,
.
.
.
P(n) = P\{X = n\} = (1 − p)^{n−1}p, n = 1, 2, . . .
P(n)=P{X=n}=(1−p)n−1p,n=1,2,...
在本题中只需要用到它的期望:
E
[
X
]
=
∑
n
=
1
inf
n
p
(
1
−
p
)
n
−
1
=
1
/
p
E[X] = \sum_{n=1}^{\inf}np(1 − p)^{n−1}=1/p
E[X]=n=1∑infnp(1−p)n−1=1/p
也就是说平均需要 1/p 次试验才能成功,这非常直观明显,假设成功的概率是1/3,那平均尝试3次就能成功。
解答:
先从简单情况分析:
- 假设只有 1 种福卡,那只需要抽1次就集齐了。
- 假设有 2 种福卡呢?首先第一次一定可以抽中其中一种,那么问题就变成了:还需要抽多少次才能抽中第二种?显然这是几何分布问题:成功的概率 p = 1/2,那么平均还需要再抽2次,所以总体上看,平均抽奖 1+2 = 3次就能集齐两种福卡。
- 假设有 m 种福卡呢?大家应该明白了,我们一种一种来数。
首先,抽中第一种福卡,需要 1 次;
接着,我们希望抽中一种和之前不同的卡片,那么这个几何分布问题中成功的概率是 m − 1 m \frac{m-1}m mm−1, 即抽中剩余 m-1种的任意一种,失败的概率是 1 m \frac1m m1,即和第一次抽的一样。那么抽中第二种福卡,需要 1 m − 1 m = m m − 1 \frac1{\frac{m-1}m}=\frac{m}{m-1} mm−11=m−1m次;
接下来,规律自然就出来了,抽第三种福卡需要和之前两种不同,那么成功的概率是 m − 2 m \frac{m-2}m mm−2,所以抽中第三种福卡,需要 1 m − 2 m = m m − 2 \frac1{\frac{m-2}m}=\frac{m}{m-2} mm−21=m−2m次;
……
最后,抽中第m种福卡,需要 m 次。
所以,总共需要 ∑ i = 0 m − 1 m m − i = ∑ i = 1 m m i \sum_{i=0}^{m-1}\frac{m}{m-i}=\sum_{i=1}^{m}\frac{m}{i} i=0∑m−1m−im=i=1∑mim
你可能有些遗憾,只能写成级数形式,不过这就是最简形式了。
如果你怀疑它的正确性,我们下面来做个简单的仿真。
程序仿真:
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def sim(m):
count = 0
round = 1000 #重复次数
for i in range(round):
l = [0 for i in range(m)]
while True:
count = count+1
l[random.randint(0,m-1)] = 1
if sum(l[:]) == m: #全部集齐
break
return count/round
def func(m):
temp = [m/i for i in range(1,m+1)]
return sum(temp)
x = [i for i in range(1,10)]
y_simulation = [sim(i) for i in x]
y_target = [func(i) for i in x]
plt.plot(x,y_simulation,'b') #蓝线代表仿真结果
plt.plot(x,y_target,'or') #红点代表理论结果
plt.show()
实验结果:
横坐标 代表“福卡”种数
纵坐标 代表抽奖次数
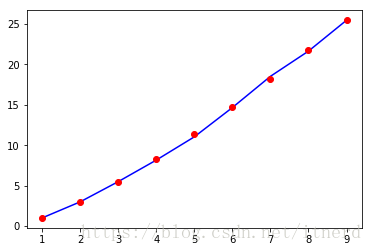
非常完美!
现在你知道在等概率条件下,集齐赢大奖 之类游戏要抽多少次了吧!当然,等概率条件在现实抽奖情况下往往是不存在的。 XD
《Introduction to Probability Models 10th Edition》p29 ↩︎


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










