最近一直整理着搜索引擎相关的主题,后续也准备多分享一些spring相关的技术。正所谓温故而知新,java bean内省模式对spring bean的影响非常深,真可谓是青出于蓝而胜于蓝。
目录
2.4 PropertyAccessor和BeanWrapper
1. JavaBean Introspector
Java的内省机制其实是基于JavaBean的,那么,什么是JavaBean哪?我们可以这样说,我们在项目中经常用到的Model可以充当JavaBean,其实我对于JavaBean的理解是它要满足以下几个特征:
- 有属性可以保存的成员变量
- 有空参构造方法
- 属性由对应get/set方法。
而内省(Introspector) 是Java语言对JavaBean类属性、事件的一种缺省处理方法。类User中有属性userName,那我们可以通过getUserName,setUserName来得到其值或者设置新的值。通过getUserName/setUserName来访问userName属性,这就是默认的规则。Sun JDK中提供了一套API用来访问某个属性的getter/setter方法,这就是内省。
1.1 BeanDescriptor
BeanDescriptor就是bean描述符,源码
package java.beans;
public class BeanDescriptor extends FeatureDescriptor {
private Reference<? extends Class<?>> beanClassRef;
private Reference<? extends Class<?>> customizerClassRef;
public BeanDescriptor(Class<?> var1) {
this(var1, (Class)null);
}
public BeanDescriptor(Class<?> var1, Class<?> var2) {
this.beanClassRef = getWeakReference(var1);
this.customizerClassRef = getWeakReference(var2);
String var3;
for(var3 = var1.getName(); var3.indexOf(46) >= 0; var3 = var3.substring(var3.indexOf(46) + 1)) {
;
}
this.setName(var3);
}
public Class<?> getBeanClass() {
return this.beanClassRef != null?(Class)this.beanClassRef.get():null;
}
public Class<?> getCustomizerClass() {
return this.customizerClassRef != null?(Class)this.customizerClassRef.get():null;
}
BeanDescriptor(BeanDescriptor var1) {
super(var1);
this.beanClassRef = var1.beanClassRef;
this.customizerClassRef = var1.customizerClassRef;
}
void appendTo(StringBuilder var1) {
appendTo(var1, "beanClass", this.beanClassRef);
appendTo(var1, "customizerClass", this.customizerClassRef);
}
}1.2 MethodDescriptor
MethodDescriptor就是方法描述符,
package java.beans;
public class MethodDescriptor extends FeatureDescriptor {
private final MethodRef methodRef = new MethodRef();
private String[] paramNames;
private List<WeakReference<Class<?>>> params;
private ParameterDescriptor parameterDescriptors[];
/**
* Constructs a <code>MethodDescriptor</code> from a
* <code>Method</code>.
*
* @param method The low-level method information.
*/
public MethodDescriptor(Method method) {
this(method, null);
}
/**
* Constructs a <code>MethodDescriptor</code> from a
* <code>Method</code> providing descriptive information for each
* of the method's parameters.
*
* @param method The low-level method information.
* @param parameterDescriptors Descriptive information for each of the
* method's parameters.
*/
public MethodDescriptor(Method method,
ParameterDescriptor parameterDescriptors[]) {
setName(method.getName());
setMethod(method);
this.parameterDescriptors = (parameterDescriptors != null)
? parameterDescriptors.clone()
: null;
}
}1.3 PropertyDescriptor
PropertyDescriptor就是字段描述符,
package java.beans;
public class PropertyDescriptor extends FeatureDescriptor {
private Reference<? extends Class<?>> propertyTypeRef;
private final MethodRef readMethodRef = new MethodRef();
private final MethodRef writeMethodRef = new MethodRef();
private Reference<? extends Class<?>> propertyEditorClassRef;
private boolean bound;
private boolean constrained;
// The base name of the method name which will be prefixed with the
// read and write method. If name == "foo" then the baseName is "Foo"
private String baseName;
private String writeMethodName;
private String readMethodName;
/**
* Constructs a PropertyDescriptor for a property that follows
* the standard Java convention by having getFoo and setFoo
* accessor methods. Thus if the argument name is "fred", it will
* assume that the writer method is "setFred" and the reader method
* is "getFred" (or "isFred" for a boolean property). Note that the
* property name should start with a lower case character, which will
* be capitalized in the method names.
*
* @param propertyName The programmatic name of the property.
* @param beanClass The Class object for the target bean. For
* example sun.beans.OurButton.class.
* @exception IntrospectionException if an exception occurs during
* introspection.
*/
public PropertyDescriptor(String propertyName, Class<?> beanClass)
throws IntrospectionException {
this(propertyName, beanClass,
Introspector.IS_PREFIX + NameGenerator.capitalize(propertyName),
Introspector.SET_PREFIX + NameGenerator.capitalize(propertyName));
}
}1.4 ParameterDescriptor
ParameterDescriptor就是参数描述符
package java.beans;
public class ParameterDescriptor extends FeatureDescriptor {
/**
* Public default constructor.
*/
public ParameterDescriptor() {
}
/**
* Package private dup constructor.
* This must isolate the new object from any changes to the old object.
*/
ParameterDescriptor(ParameterDescriptor old) {
super(old);
}
}1.5 Introspector
Introspector将JavaBean中的属性封装起来进行操作(读取)。在程序把一个类当做JavaBean来看,就是调用Introspector.getBeanInfo()方法,得到BeanInfo对象。那修改怎么办?当然是只能反射了(java.lang.reflect)
| 构造器 | java.lang.reflect.Constructor<T> |
| 方法 | java.lang.reflect.Method |
| 字段 | java.lang.reflect.Field |
@Test
public void go_getDescriptor() throws IntrospectionException {
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(User.class);
System.out.println(beanInfo.getBeanDescriptor());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(beanInfo.getMethodDescriptors()));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors()));
}
@Test
public void go_setAge() throws IntrospectionException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
User userInfo = new User();
String age = "age";
Object ageValue = 19;
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(User.class);
PropertyDescriptor[] proDescrtptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
if (proDescrtptors != null && proDescrtptors.length > 0) {
for (PropertyDescriptor propDesc : proDescrtptors) {
if (propDesc.getName().equals(age)) {
Method methodSetUserName = propDesc.getWriteMethod();//很重要的原则
methodSetUserName.invoke(userInfo,ageValue);
Method methodGetUserName = propDesc.getReadMethod();
System.out.println(methodGetUserName.invoke(userInfo)); //output:19
break;
}
}
}
}go_getDescriptor的输出:
java.beans.BeanDescriptor[name=BeanInfo_test$User; beanClass=class com.example.introspector.BeanInfo_test$User]
[java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=getClass; method=public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=getUserName; method=public java.lang.String com.example.introspector.BeanInfo_test$User.getUserName()], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=setAge; method=public void com.example.introspector.BeanInfo_test$User.setAge(int)], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=getAge; method=public int com.example.introspector.BeanInfo_test$User.getAge()], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=wait; method=public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=notifyAll; method=public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=notify; method=public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=wait; method=public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=setUserName; method=public void com.example.introspector.BeanInfo_test$User.setUserName(java.lang.String)], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=hashCode; method=public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=wait; method=public final native void java.lang.Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=equals; method=public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)], java.beans.MethodDescriptor[name=toString; method=public java.lang.String java.lang.Object.toString()]]
[java.beans.PropertyDescriptor[name=age; propertyType=int; readMethod=public int com.example.introspector.BeanInfo_test$User.getAge(); writeMethod=public void com.example.introspector.BeanInfo_test$User.setAge(int)], java.beans.PropertyDescriptor[name=class; propertyType=class java.lang.Class; readMethod=public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()], java.beans.PropertyDescriptor[name=userName; propertyType=class java.lang.String; readMethod=public java.lang.String com.example.introspector.BeanInfo_test$User.getUserName(); writeMethod=public void com.example.introspector.BeanInfo_test$User.setUserName(java.lang.String)]]
这里思考个问题:如果ageValue="19",它就是非int,会报错(java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: argument type mismatch)该怎么办?其实是有解决方案的,继续往下看
1.6 属性变化监听
一般事件触发流程都是这样的:传递一个字符串(Text,它叫法更专业,所以类型的原生形态文本型)类型---》》》把这个Text类型转换为对应的Java数据类型并赋值---》》》事件发生(不同的属性对应不同的事件)
PropertyChangeEvent,事件
package java.beans;
public class PropertyChangeEvent extends EventObject {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7042693688939648123L;
/**
* Constructs a new {@code PropertyChangeEvent}.
*
* @param source the bean that fired the event
* @param propertyName the programmatic name of the property that was changed
* @param oldValue the old value of the property
* @param newValue the new value of the property
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code source} is {@code null}
*/
public PropertyChangeEvent(Object source, String propertyName,
Object oldValue, Object newValue) {
super(source);
this.propertyName = propertyName;
this.newValue = newValue;
this.oldValue = oldValue;
}
}PropertyChangeListener,监听器
package java.beans;
public interface PropertyChangeListener extends java.util.EventListener {
/**
* This method gets called when a bound property is changed.
* @param evt A PropertyChangeEvent object describing the event source
* and the property that has changed.
*/
void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent evt);
}PropertyEditor,事件源
package java.beans;
public interface PropertyEditor {
void setAsText(String text) throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException;
Object getValue();
}
public class PropertyEditorSupport implements PropertyEditor {
public void setAsText(String text) throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException {
if (value instanceof String) {
setValue(text);
return;
}
throw new java.lang.IllegalArgumentException(text);
}
public void setValue(Object value) {
this.value = value;
firePropertyChange();
}
public void firePropertyChange() {
java.util.Vector<PropertyChangeListener> targets;
synchronized (this) {
if (listeners == null) {
return;
}
targets = unsafeClone(listeners);
}
// Tell our listeners that "everything" has changed.
PropertyChangeEvent evt = new PropertyChangeEvent(source, null, null, null);
for (int i = 0; i < targets.size(); i++) {
PropertyChangeListener target = targets.elementAt(i);
target.propertyChange(evt);
}
}
}实例代码
Test
public void go_setAgeToListener() throws IntrospectionException {
User userInfo = new User();
String age = "age";
String ageValue = "19";
BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(User.class);
PropertyDescriptor[] proDescrtptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();
for (PropertyDescriptor propDesc : proDescrtptors) {
if (propDesc.getName().equals(age)) {
propDesc.setPropertyEditorClass(IntegerEditor.class);//很重要,也可以自定义
PropertyEditor propertyEditor = propDesc.createPropertyEditor(null);
propertyEditor.addPropertyChangeListener(x -> {
PropertyEditor source = (PropertyEditor) x.getSource();
Method methodSetUserName = propDesc.getWriteMethod();
try {
System.out.println("newValue:" + source.getValue());
methodSetUserName.invoke(userInfo, source.getValue());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
propertyEditor.setAsText(ageValue);
break;
}
}
}2. spring bean

2.1 PropertyEditorRegistry
属性编辑器的注册表,实现类就老厉害了

public class PropertyEditorRegistrySupport implements PropertyEditorRegistry {
private static Class<?> pathClass;
private static Class<?> zoneIdClass;
private ConversionService conversionService;
private boolean defaultEditorsActive = false;
private boolean configValueEditorsActive = false;
private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> defaultEditors;
private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> overriddenDefaultEditors;
private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> customEditors;
private Map<String, PropertyEditorRegistrySupport.CustomEditorHolder> customEditorsForPath;
private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> customEditorCache;
public PropertyEditorRegistrySupport() {
}
public void setConversionService(ConversionService conversionService) {
this.conversionService = conversionService;
}
public ConversionService getConversionService() {
return this.conversionService;
}
protected void registerDefaultEditors() {
this.defaultEditorsActive = true;
}
public void useConfigValueEditors() {
this.configValueEditorsActive = true;
}
public void overrideDefaultEditor(Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor propertyEditor) {
if(this.overriddenDefaultEditors == null) {
this.overriddenDefaultEditors = new HashMap();
}
this.overriddenDefaultEditors.put(requiredType, propertyEditor);
}
public PropertyEditor getDefaultEditor(Class<?> requiredType) {
if(!this.defaultEditorsActive) {
return null;
} else {
if(this.overriddenDefaultEditors != null) {
PropertyEditor editor = (PropertyEditor)this.overriddenDefaultEditors.get(requiredType);
if(editor != null) {
return editor;
}
}
if(this.defaultEditors == null) {
this.createDefaultEditors();
}
return (PropertyEditor)this.defaultEditors.get(requiredType);
}
}
//这里处理xml中常规的转换
private void createDefaultEditors() {
this.defaultEditors = new HashMap(64);
this.defaultEditors.put(Charset.class, new CharsetEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(Class.class, new ClassEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(Class[].class, new ClassArrayEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(Currency.class, new CurrencyEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(File.class, new FileEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(InputStream.class, new InputStreamEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(InputSource.class, new InputSourceEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(Locale.class, new LocaleEditor());
if(pathClass != null) {
this.defaultEditors.put(pathClass, new PathEditor());
}
this.defaultEditors.put(Pattern.class, new PatternEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(Properties.class, new PropertiesEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(Reader.class, new ReaderEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(Resource[].class, new ResourceArrayPropertyEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(TimeZone.class, new TimeZoneEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(URI.class, new URIEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(URL.class, new URLEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(UUID.class, new UUIDEditor());
if(zoneIdClass != null) {
this.defaultEditors.put(zoneIdClass, new ZoneIdEditor());
}
this.defaultEditors.put(Collection.class, new CustomCollectionEditor(Collection.class));
this.defaultEditors.put(Set.class, new CustomCollectionEditor(Set.class));
this.defaultEditors.put(SortedSet.class, new CustomCollectionEditor(SortedSet.class));
this.defaultEditors.put(List.class, new CustomCollectionEditor(List.class));
this.defaultEditors.put(SortedMap.class, new CustomMapEditor(SortedMap.class));
this.defaultEditors.put(byte[].class, new ByteArrayPropertyEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(char[].class, new CharArrayPropertyEditor());
this.defaultEditors.put(Character.TYPE, new CharacterEditor(false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Character.class, new CharacterEditor(true));
this.defaultEditors.put(Boolean.TYPE, new CustomBooleanEditor(false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Boolean.class, new CustomBooleanEditor(true));
this.defaultEditors.put(Byte.TYPE, new CustomNumberEditor(Byte.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Byte.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Byte.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(Short.TYPE, new CustomNumberEditor(Short.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Short.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Short.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(Integer.TYPE, new CustomNumberEditor(Integer.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Integer.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Integer.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(Long.TYPE, new CustomNumberEditor(Long.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Long.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Long.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(Float.TYPE, new CustomNumberEditor(Float.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Float.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Float.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(Double.TYPE, new CustomNumberEditor(Double.class, false));
this.defaultEditors.put(Double.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Double.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(BigDecimal.class, new CustomNumberEditor(BigDecimal.class, true));
this.defaultEditors.put(BigInteger.class, new CustomNumberEditor(BigInteger.class, true));
if(this.configValueEditorsActive) {
StringArrayPropertyEditor sae = new StringArrayPropertyEditor();
this.defaultEditors.put(String[].class, sae);
this.defaultEditors.put(short[].class, sae);
this.defaultEditors.put(int[].class, sae);
this.defaultEditors.put(long[].class, sae);
}
}
}2.2 PropertyEditorRegistrar
它是PropertyEditorRegistry中的defaultEditors的功能拓展
//它本身是null实现,实现类BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper是真正的实现(向PropertyEditorRegistry中添加DataBinder到customEditors,DataBinder就老厉害了(想想springmvc的@RequestBody就懂了))
public class DefaultPropertyEditorRegistrar implements PropertyEditorRegistrar {
private Map<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> customEditors;
/**
* Register the custom editors with the given registry.
*
* @see org.springframework.beans.PropertyEditorRegistrar#registerCustomEditors(org.springframework.beans.PropertyEditorRegistry)
*/
@Override
public void registerCustomEditors(PropertyEditorRegistry registry) {
if (this.customEditors != null) {
for (Entry<Class<?>, PropertyEditor> entry : customEditors.entrySet()) {
registry.registerCustomEditor(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
/**
* Specify the {@link PropertyEditor custom editors} to register.
*
*
* @param customEditors a map of Class to PropertyEditor (or class name to
* PropertyEditor).
* @see CustomEditorConfigurer#setCustomEditors(Map)
*/
public void setCustomEditors(Map<? extends Object, ? extends PropertyEditor> customEditors) {
this.customEditors = new HashMap<Class<?>, PropertyEditor>();
for (Entry<? extends Object, ? extends PropertyEditor> entry : customEditors.entrySet()) {
Object key = entry.getKey();
Class<?> requiredType = null;
if (key instanceof Class<?>) {
requiredType = (Class<?>) key;
}
else if (key instanceof String) {
String className = (String) key;
requiredType = ClassUtils.resolveClassName(className, getClass().getClassLoader());
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid key [" + key
+ "] for custom editor: needs to be Class or String.");
}
PropertyEditor value = entry.getValue();
this.customEditors.put(requiredType, value);
}
}
}
//处理xml中Resource、URL、File...、向PropertyEditorRegistry中添加registry.registerCustomEditor或overrideDefaultEditor(requiredType, editor)
public class ResourceEditorRegistrar implements PropertyEditorRegistrar {
private static Class<?> pathClass;
static {
try {
pathClass = ClassUtils.forName("java.nio.file.Path", ResourceEditorRegistrar.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Java 7 Path class not available
pathClass = null;
}
}
private final PropertyResolver propertyResolver;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
/**
* Create a new ResourceEditorRegistrar for the given {@link ResourceLoader}
* and {@link PropertyResolver}.
* @param resourceLoader the ResourceLoader (or ResourcePatternResolver)
* to create editors for (usually an ApplicationContext)
* @param propertyResolver the PropertyResolver (usually an Environment)
* @see org.springframework.core.env.Environment
* @see org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext
*/
public ResourceEditorRegistrar(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, PropertyResolver propertyResolver) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
this.propertyResolver = propertyResolver;
}
/**
* Populate the given {@code registry} with the following resource editors:
* ResourceEditor, InputStreamEditor, InputSourceEditor, FileEditor, URLEditor,
* URIEditor, ClassEditor, ClassArrayEditor.
*/
@Override
public void registerCustomEditors(PropertyEditorRegistry registry) {
ResourceEditor baseEditor = new ResourceEditor(this.resourceLoader, this.propertyResolver);
doRegisterEditor(registry, Resource.class, baseEditor);
doRegisterEditor(registry, ContextResource.class, baseEditor);
doRegisterEditor(registry, InputStream.class, new InputStreamEditor(baseEditor));
doRegisterEditor(registry, InputSource.class, new InputSourceEditor(baseEditor));
doRegisterEditor(registry, File.class, new FileEditor(baseEditor));
if (pathClass != null) {
doRegisterEditor(registry, pathClass, new PathEditor(baseEditor));
}
doRegisterEditor(registry, Reader.class, new ReaderEditor(baseEditor));
doRegisterEditor(registry, URL.class, new URLEditor(baseEditor));
ClassLoader classLoader = this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader();
doRegisterEditor(registry, URI.class, new URIEditor(classLoader));
doRegisterEditor(registry, Class.class, new ClassEditor(classLoader));
doRegisterEditor(registry, Class[].class, new ClassArrayEditor(classLoader));
if (this.resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
doRegisterEditor(registry, Resource[].class,
new ResourceArrayPropertyEditor((ResourcePatternResolver) this.resourceLoader, this.propertyResolver));
}
}
/**
* Override default editor, if possible (since that's what we really mean to do here);
* otherwise register as a custom editor.
*/
private void doRegisterEditor(PropertyEditorRegistry registry, Class<?> requiredType, PropertyEditor editor) {
if (registry instanceof PropertyEditorRegistrySupport) {
((PropertyEditorRegistrySupport) registry).overrideDefaultEditor(requiredType, editor);
}
else {
registry.registerCustomEditor(requiredType, editor);
}
}
}2.3 CustomEditorConfigurer
可以自定义PropertyEditorRegistry、PropertyEditor,它其实是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor
public class CustomEditorConfigurer implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, Ordered {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE; // default: same as non-Ordered
private PropertyEditorRegistrar[] propertyEditorRegistrars;
private Map<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>> customEditors;
public void setOrder(int order) {
this.order = order;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return this.order;
}
public void setPropertyEditorRegistrars(PropertyEditorRegistrar[] propertyEditorRegistrars) {
this.propertyEditorRegistrars = propertyEditorRegistrars;
}
public void setCustomEditors(Map<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>> customEditors) {
this.customEditors = customEditors;
}
//beanFactory中添加PropertyEditorRegistrar和PropertyEditor
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
if (this.propertyEditorRegistrars != null) {
for (PropertyEditorRegistrar propertyEditorRegistrar : this.propertyEditorRegistrars) {
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(propertyEditorRegistrar);
}
}
if (this.customEditors != null) {
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>> entry : this.customEditors.entrySet()) {
Class<?> requiredType = entry.getKey();
Class<? extends PropertyEditor> propertyEditorClass = entry.getValue();
beanFactory.registerCustomEditor(requiredType, propertyEditorClass);
}
}
}
}
2.4 PropertyAccessor和BeanWrapper
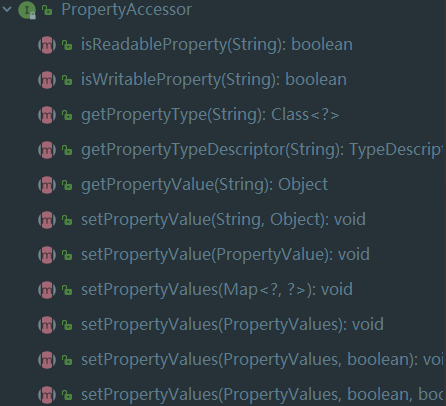
PropertyAccessor接口定义了各种访问属性的方法。
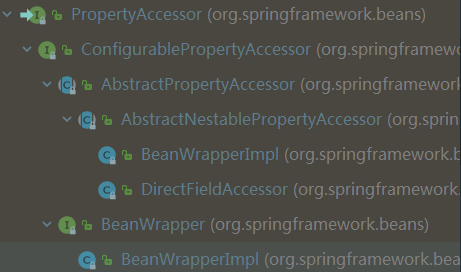
- BeanWrapperImpl,对属性取值赋值依赖 setter/getter方法,必须通过readMethod.invoke等反射方式进行,遵循javabean规约
- DirectFieldAccessor,4.1版本中引入,执行直接字段访问而不是通过Java Bean的getter(效率更高,特别是实现嵌套遍历字段),在springmvc中有@Validated和BindingResult bindingResult是配对出现,实际就是通过DataBinder.getBindingResult()填充,真正是由DirectFieldBindingResult完成的。
@RequestMapping(value = "/addStudent", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addStudent(@ModelAttribute("student") @Validated Student student,
BindingResult bindingResult, Model model) {
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
return "student";
}
model.addAttribute("name", student.getName());
model.addAttribute("age", student.getAge());
model.addAttribute("id", student.getId());
return "student_result";
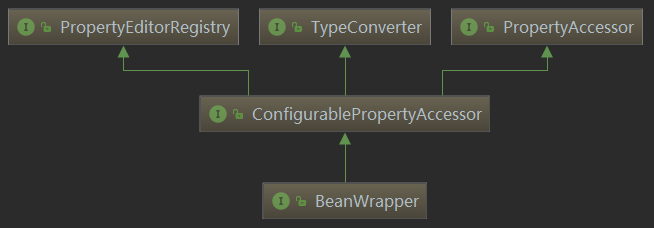
}BeanWrapper接口还继承了PropertyAccessor, propertyEditorRegistry, TypeConverter、ConfigurablePropertyAccessor接口,所以它是一个功能强大的综合体。
/**
* The central interface of Spring's low-level JavaBeans infrastructure.
*
* <p>Typically not used directly but rather implicitly via a
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} or a
* {@link org.springframework.validation.DataBinder}.
*/BeanWrapper是spring中对JavaBeans遵循的规约,间接服务于BeanFactory和DataBinder
private static class GetterBean {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
if (this.name == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("name property must be set");
}
return name;
}
}
//BeanWrapperImpl
@Test
public void setterDoesNotCallGetter() {
GetterBean target = new GetterBean();
BeanWrapper accessor = new BeanWrapperImpl(target);
accessor.setPropertyValue("name", "tom");
assertTrue("Set name to tom", target.getName().equals("tom"));
}
//DirectFieldAccessor
@Test
public void setterDoesNotCallGetter() {
TestBean bean = new TestBean() {
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
String name = "alex";
};
//嵌套设置/访问对象字段数据
DirectFieldAccessor accessor = new DirectFieldAccessor(bean);
//如果嵌套对象为null,字段创建
accessor.setAutoGrowNestedPaths(true);
//设置字段值
accessor.setPropertyValue("name", "zhangsan");
//读取字段值
System.out.println(accessor.getPropertyValue("name"));
}总结,springBean其实是集成拓展了javaBean的内省解决方案,但在它的基础上做了增强。
























 432
432











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








