https://github.com/android10/Android-CleanArchitecture
这个项目很多的代码,实现了很简单的列表跳转功能。
首先是 Data 层,负责获取数据。
/**
* 一个简单的实体类
*/
public class User {
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
/**
* 获取用户信息的类
* 接口可以让我们更专注于功能
*/
public interface UserRepository {
/**
* 功能1 获取用户列表
*
* @param userListCallback the user list callback
*/
void getUserList(UserListCallback userListCallback);
/**
* 功能2 获取用户信息
*
* @param userId the user id
* @param userCallback the user callback
*/
void getUserById(final String userId, UserDetailsCallback userCallback);
// /**
// * Callback 是什么?
// * 最常用 OnClickListener 就是一个 Callback,.onClick 则是回调函数。
// * 这是暴露给外部的入口。
// * 帮助我们在某一个时刻(比如当用户信息加载完毕,或者是被点击时)执行某段代码段。
// * 回调函数需要向外部提供一些参数(比如 User)。
// */
/**
* The interface User list callback.
*/
interface UserListCallback {
/**
* On user list loaded.
*
* @param usersCollection the users collection
*/
void onUserListLoaded(List<User> usersCollection);
/**
* On error.
*
* @param errorBundle the error bundle
*/
void onError(ErrorBundle errorBundle);
}
/**
* The interface User details callback.
*/
interface UserDetailsCallback {
/**
* On user loaded.
*
* @param user the user
*/
void onUserLoaded(User user);
/**
* On error.
*
* @param errorBundle the error bundle
*/
void onError(ErrorBundle errorBundle);
}
}public class UserRepositoryImpl implements UserRepository {
static private List<User> userCollection = new ArrayList<>();
static {
User user = new User();
user.setId("1");
user.setName("Li");
userCollection.add(user);
user = new User();
user.setId("2");
user.setName("Shang");
userCollection.add(user);
}
@Override
public void getUserList(UserListCallback userListCallback) {
// 直接返回数据集,正常的实现应该是费时操作。
userListCallback.onUserListLoaded(userCollection);
}
@Override
public void getUserById(String userId, UserDetailsCallback userCallback) {
// 如果找到对应用户则返回
boolean exist = false;
for (User user : userCollection) {
if (userId.equals(user.getId())) {
userCallback.onUserLoaded(user);
exist = true;
break;
}
}
// 否则返回一个填充对象
if (!exist) {
User user = new User();
user.setId("-1");
user.setName("Clean");
userCallback.onUserLoaded(user);
}
}
}
然后是 Domain 层
/**
* Common interface for an Interactor {@link java.lang.Runnable} declared in the application.
* This interface represents a execution unit for different use cases (this means any use case
* in the application should implement this contract).
* <p>
* By convention each Interactor implementation will return the result using a Callback that should
* be executed in the UI thread.
*/
public interface Interactor extends Runnable {
/**
* Everything inside this method will be executed asynchronously.
*/
void run();
}
/**
* The interface Get user details use case.
*/
public interface GetUserDetailsUseCase extends Interactor {
/**
* The interface Callback.
*/
interface Callback {
/**
* On user data loaded.
*
* @param user the user
*/
void onUserDataLoaded(User user);
/**
* On error.
*
* @param errorBundle the error bundle
*/
void onError(ErrorBundle errorBundle);
}
/**
* Execute.
*
* @param userId the user id
* @param callback the callback
*/
public void execute(String userId, Callback callback);
}这两个类,注释一堆,看不到实质,看其实现。
/**
* This class is an implementation of {@link GetUserDetailsUseCase} that represents a use case for
* retrieving data related to an specific {@link User}.
*/
public class GetUserDetailsUseCaseImpl implements GetUserDetailsUseCase {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
private final ThreadExecutor threadExecutor;
private final PostExecutionThread postExecutionThread;
private String userId;
private GetUserDetailsUseCase.Callback callback;
/**
* Constructor of the class.
*
* @param userRepository A {@link UserRepository} as a source for retrieving data.
* @param threadExecutor {@link ThreadExecutor} used to execute this use case in a background
* thread.
* @param postExecutionThread {@link PostExecutionThread} used to post updates when the use case
* has been executed.
*/
public GetUserDetailsUseCaseImpl(UserRepository userRepository, ThreadExecutor threadExecutor,
PostExecutionThread postExecutionThread) {
if (userRepository == null || threadExecutor == null || postExecutionThread == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Constructor parameters cannot be null!!!");
}
this.userRepository = userRepository;
this.threadExecutor = threadExecutor;
this.postExecutionThread = postExecutionThread;
}
@Override
public void execute(String userId, Callback callback) {
if (userId == null || callback == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid parameter!!!");
}
this.userId = userId;
this.callback = callback;
this.threadExecutor.execute(this);
}
@Override
public void run() {
this.userRepository.getUserById(this.userId, this.repositoryCallback);
}
private final UserRepository.UserDetailsCallback repositoryCallback =
new UserRepository.UserDetailsCallback() {
@Override
public void onUserLoaded(User user) {
notifyGetUserDetailsSuccessfully(user);
}
@Override
public void onError(ErrorBundle errorBundle) {
notifyError(errorBundle);
}
};
private void notifyGetUserDetailsSuccessfully(final User user) {
this.postExecutionThread.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callback.onUserDataLoaded(user);
}
});
}
private void notifyError(final ErrorBundle errorBundle) {
this.postExecutionThread.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callback.onError(errorBundle);
}
});
}
}UseCase 的作用就是另一线程查询,查询完成后切换到主线程执行外部传入的 Callback。
这一层就是完成了线程切换的工作。
最后是 Presentation 表现层。
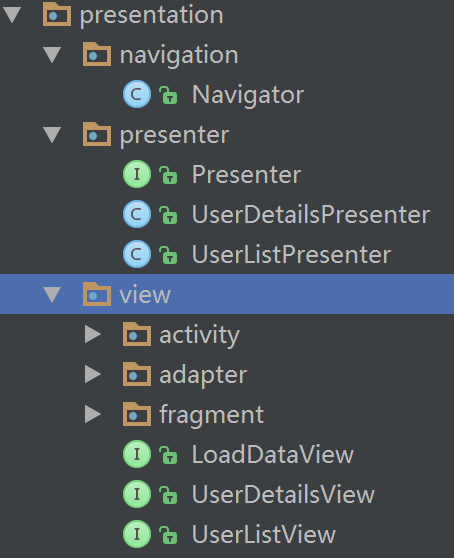
Navigator 是作者把跳转抽象出的一个类,看 Presenter。
/**
* Interface representing a Presenter in a model view presenter (MVP) pattern.
*/
public interface Presenter {
}/**
* {@link Presenter} that controls communication between views and models of the presentation
* layer.
*/
public class UserDetailsPresenter implements Presenter {
/**
* id used to retrieve user details
*/
private String userId;
private final UserDetailsView viewDetailsView;
private final GetUserDetailsUseCase getUserDetailsUseCase;
public UserDetailsPresenter(UserDetailsView userDetailsView,
GetUserDetailsUseCase getUserDetailsUseCase) {
if (userDetailsView == null || getUserDetailsUseCase == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Constructor parameters cannot be null!!!");
}
this.viewDetailsView = userDetailsView;
this.getUserDetailsUseCase = getUserDetailsUseCase;
}
/**
* Initializes the presenter by start retrieving user details.
*/
public void initialize(String userId) {
this.userId = userId;
this.loadUserDetails();
}
/**
* Loads user details.
*/
private void loadUserDetails() {
this.hideViewRetry();
this.showViewLoading();
this.getUserDetails();
}
private void showViewLoading() {
this.viewDetailsView.showLoading();
}
private void hideViewLoading() {
this.viewDetailsView.hideLoading();
}
private void showViewRetry() {
this.viewDetailsView.showRetry();
}
private void hideViewRetry() {
this.viewDetailsView.hideRetry();
}
private void showErrorMessage(ErrorBundle errorBundle) {
}
private void showUserDetailsInView(User user) {
this.viewDetailsView.renderUser(user);
}
private void getUserDetails() {
this.getUserDetailsUseCase.execute(this.userId, this.userDetailsCallback);
}
private final GetUserDetailsUseCase.Callback userDetailsCallback = new GetUserDetailsUseCase.Callback() {
@Override
public void onUserDataLoaded(User user) {
UserDetailsPresenter.this.showUserDetailsInView(user);
UserDetailsPresenter.this.hideViewLoading();
}
@Override
public void onError(ErrorBundle errorBundle) {
UserDetailsPresenter.this.hideViewLoading();
UserDetailsPresenter.this.showErrorMessage(errorBundle);
UserDetailsPresenter.this.showViewRetry();
}
};
}
private final UserDetailsView viewDetailsView;
private final GetUserDetailsUseCase getUserDetailsUseCase;那么 Presener 的工作就是,View 渲染的逻辑。
initialize 是他的入口。
最后看一个 View
/**
* Fragment that shows details of a certain user.
*/
public class UserDetailsFragment extends BaseFragment implements UserDetailsView {
private static final String ARGUMENT_KEY_USER_ID = "org.android10.ARGUMENT_USER_ID";
private String userId;
private UserDetailsPresenter userDetailsPresenter;
private TextView tv_fullname;
private TextView tv_email;
private TextView tv_followers;
private TextView tv_description;
private RelativeLayout rl_progress;
private RelativeLayout rl_retry;
private Button bt_retry;
public UserDetailsFragment() {
super();
}
public static UserDetailsFragment newInstance(int userId) {
UserDetailsFragment userDetailsFragment = new UserDetailsFragment();
Bundle argumentsBundle = new Bundle();
argumentsBundle.putInt(ARGUMENT_KEY_USER_ID, userId);
userDetailsFragment.setArguments(argumentsBundle);
return userDetailsFragment;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.initialize();
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View fragmentView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_user_details, container, false);
this.tv_fullname = (TextView) fragmentView.findViewById(R.id.tv_fullname);
this.tv_email = (TextView) fragmentView.findViewById(R.id.tv_email);
this.tv_followers = (TextView) fragmentView.findViewById(R.id.tv_followers);
this.tv_description = (TextView) fragmentView.findViewById(R.id.tv_description);
this.rl_progress = (RelativeLayout) fragmentView.findViewById(R.id.rl_progress);
this.rl_retry = (RelativeLayout) fragmentView.findViewById(R.id.rl_retry);
this.bt_retry = (Button) fragmentView.findViewById(R.id.bt_retry);
this.bt_retry.setOnClickListener(this.retryOnClickListener);
return fragmentView;
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
this.userDetailsPresenter.initialize(this.userId);
}
@Override
void initializePresenter() {
// All these dependency initialization could have been avoided using a
// dependency injection framework. But in this case are used this way for
// LEARNING EXAMPLE PURPOSE.
ThreadExecutor threadExecutor = JobExecutor.getInstance();
PostExecutionThread postExecutionThread = UIThread.getInstance();
UserRepository userRepository = new UserRepositoryImpl();
GetUserDetailsUseCase getUserDetailsUseCase = new GetUserDetailsUseCaseImpl(userRepository,
threadExecutor, postExecutionThread);
this.userDetailsPresenter =
new UserDetailsPresenter(this, getUserDetailsUseCase);
}
@Override
public void renderUser(User user) {
if (user != null) {
this.tv_fullname.setText(user.getName());
}
}
@Override
public void showLoading() {
this.rl_progress.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
this.getActivity().setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(true);
}
@Override
public void hideLoading() {
this.rl_progress.setVisibility(View.GONE);
this.getActivity().setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(false);
}
@Override
public void showRetry() {
this.rl_retry.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
@Override
public void hideRetry() {
this.rl_retry.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
@Override
public void showError(String message) {
this.showToastMessage(message);
}
@Override
public Context getContext() {
return getActivity().getApplicationContext();
}
/**
* Initializes fragment's private members.
*/
private void initialize() {
this.userId = getArguments().getString(ARGUMENT_KEY_USER_ID);
}
/**
* Loads all users.
*/
private void loadUserDetails() {
if (this.userDetailsPresenter != null) {
this.userDetailsPresenter.initialize(this.userId);
}
}
private final View.OnClickListener retryOnClickListener = new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
UserDetailsFragment.this.loadUserDetails();
}
};
}View 中会初始化 Presenter,并在合适的时候启动它。
View 负责实现渲染功能,但具体渲染逻辑是在 Presenter 中实现的。





















 1746
1746











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








