题目链接
题目
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 97615 | Accepted: 21702 |
Description
We use Cartesian coordinate system, defining the coasting is the x-axis. The sea side is above x-axis, and the land side below. Given the position of each island in the sea, and given the distance of the coverage of the radar installation, your task is to write a program to find the minimal number of radar installations to cover all the islands. Note that the position of an island is represented by its x-y coordinates.
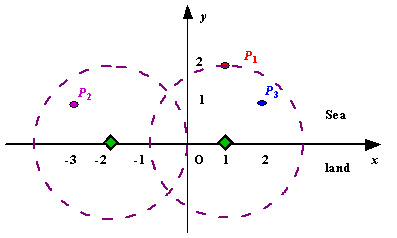
Figure A Sample Input of Radar Installations
Input
The input is terminated by a line containing pair of zeros
Output
Sample Input
3 2 1 2 -3 1 2 1 1 2 0 2 0 0
Sample Output
Case 1: 2 Case 2: 1
Source
题意
建立坐标轴,坐标轴的上边分布着小岛,每个小岛有在坐标系中的坐标(x,y),y是一定大于等于0的,也就是说所有的小岛都在x轴的上面或者x轴上。现在我们只能在x轴上放雷达,每个雷达的范围是一个圆形,半径为d。要求在x轴上最少能放几个雷达使得雷达能辐射到所有的小岛。小岛的坐标值一定是2个整数,雷达的放置位置一定要在x轴上(暗示雷达的坐标是浮点数)。
输入小岛数量n,辐射半径d,n个小岛的坐标值。输出雷达的最少数量。如果某个小岛无论怎样都不能被雷达辐射,那么输出-1。
题解
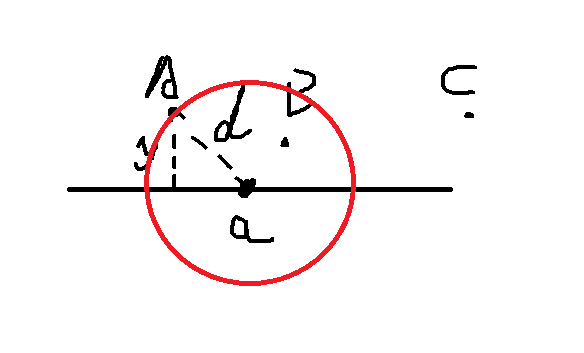
刚看这个题果断WA了,考虑以小岛的x坐标进行排序,从最左边开始,看最远的雷达能放在哪里,然后一个一个小岛进行遍历,如果能被该雷达辐射,就继续遍历后面的小岛,如果不能被辐射,就将新的雷达放在这个小岛的最右边。图例:
那么这样是错误的,假如2个小岛,覆盖B岛的雷达只能放在最下方,也就是说y = d这样的情况,那么这里的雷达可以覆盖A岛,但是按照上面的考虑方法,在A岛最远处的雷达却无法辐射到B岛,例:
这样,答案是1,可是求的结果是2,果断错误。
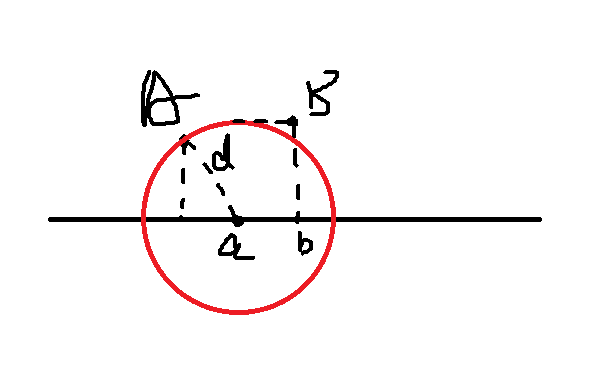
我们需要将问题转换,上面的方法是从小岛位置出发,看雷达放在哪里比较合适。反过来,我们利用勾股定理可以得到为了能覆盖这个小岛,雷达可以放置的位置区间。每个小岛都对应一个雷达的放置区间。那么利用贪心的思想,我们利用区间的重叠,在重叠位置放置雷达,就可以满足1个雷达覆盖最多的小岛,反过来就是覆盖全部小岛需要的最少雷达。
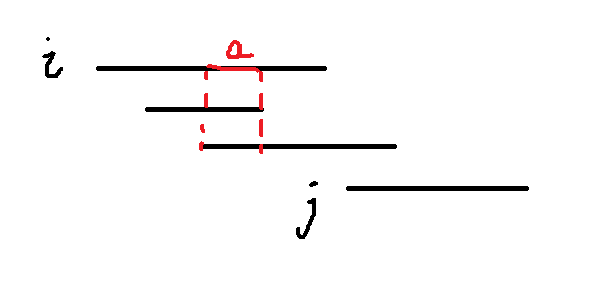
这样,我们就可以求出所有的区间范围,并且储存所有的数据,按照区间起点从左到右的顺序进行排序,可以得到区间范围图。接下来就是找重叠区间了。我们想一下贪心,找重复区间的时候,每次从左到右分析区间,如果新的区间与之前的区间全部有重合部分,说明可以用1个雷达;反之,如果跟任意一个区间没有重合区间,就需要一个新的雷达。图例:
有4个小岛,区间如上图所示。明显看出前3个区间有a区间是重叠的,在这个区间中任意位置放一个雷达就可以覆盖前3个小岛。那么第4个小岛向前进行比较:第三个小岛有重叠区间,第二个小岛完全不重叠。也就是说,第一个雷达无论如何都不能再覆盖3个小岛的情况下覆盖第4个小岛。那么第4个小岛就只能再建一个雷达了。
以上就是算法的思想,实现的时候注意:当确定j小岛无法跟从i到j的小岛全部重合,那么应有语句:i = j。也就是说开始了新的一轮比较,看j小岛能与j-n的小岛中有多少个能重叠。所以博主使用了3层的for循环,第一层循环i,第二层标记j,第三层k在i-j之间遍历,让j与k进行比较,看是否j与i-j内所有小岛都能有重合。
C++ 代码 32ms
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<math.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<utility>
#include<queue>
#define TIME std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define LL long long
#define MAX 310
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
struct det{
double begin,end;
bool operator<(const det &c) const{
return begin < c.begin;
}
}dets[1010];
int main() {
TIME;
int N = 1;
while(cin){
int n,d;
cin >> n >> d;
if(n == 0 && d == 0) break;
int x,y;
int err = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
cin >> x >> y;
if(y > d){
err = 1;
}else{
double length = sqrt((double)d*d - (double)y*y);
dets[i].begin = 1.0*x - length;
dets[i].end = 1.0*x + length;
}
}
cout << "Case " << N << ": ";
if(err == 1){
cout << -1 << endl;
}else{
sort(dets,dets + n);
int radar = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
if(i == n-1){
radar++;
}else{
int flag = 0;
for(int j = i+1;j < n;j++){
for(int k = j-1;k >= i;k--){
if(dets[j].end < dets[k].begin || dets[j].begin > dets[k].end){
i = j-1;
radar++;
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if(flag == 1){
break;
}
}
}
}
cout << radar << endl;
}
N++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}代码的一些解释
1.考虑到小岛一定不能被雷达覆盖的情况,唯一可能就是小岛的y > d,这样在输入数据的时候就可以进行判断,如果无解就不用再处理任何数据了,读取所有数据后直接输出-1。
2.j指向的是新的区间,看是否能被当前雷达覆盖,换而言之是看是否有必要新建一个雷达。所以要建新雷达的时候要赋值,i = j。所以可能存在这样的情况,i = n-1,也就是说j已经不再循环了。如果这样结束程序,答案会比正确答案少1,因为最后一个或n个小岛没有出现令radar自加1的情况,所以要进行一次判断。
3.博主代码中是i = j-1,这是因为出里循环到外循环的时候i会自加1,如果直接i = j,那么实际上j岛被跳过了,从j+1岛开始计算了。






















 158
158











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








