在之前的一篇文章 中,介绍了assembleResponse函数(位于instance.cpp第224行),它会根据op操作枚举类型来调用相应的crud操作,枚举类型定义如下:
opReply = 1 , /* reply. responseTo is set. */
dbMsg = 1000 , /* generic msg command followed by a string */
dbUpdate = 2001 , /* update object */
dbInsert = 2002 ,
// dbGetByOID = 2003,
dbQuery = 2004 ,
dbGetMore = 2005 ,
dbDelete = 2006 ,
dbKillCursors = 2007
};
可以看到dbInsert = 2002 为插入操作枚举值,下面我们看一下assembleResponse在确定是插入操作时调用的方法,如下:
.....
try {
if ( op == dbInsert ) { // 添加记录操作
receivedInsert(m, currentOp);
}
else if ( op == dbUpdate ) { // 更新记录
receivedUpdate(m, currentOp);
}
else if ( op == dbDelete ) { // 删除记录
receivedDelete(m, currentOp);
}
else if ( op == dbKillCursors ) { // 删除Cursors(游标)对象
currentOp.ensureStarted();
logThreshold = 10 ;
ss << " killcursors " ;
receivedKillCursors(m);
}
else {
mongo::log() << " operation isn't supported: " << op << endl;
currentOp.done();
log = true ;
}
}
.....
}
}
从上面代码可以看出,系统在确定dbInsert操作时,调用了receivedInsert()方法(位于instance.cpp文件第570行),下面是该方法的定义:
DbMessage d(m); // 初始化数据库格式的消息
const char * ns = d.getns(); // 获取名空间,用于接下来insert数据
assert( * ns);
uassert( 10058 , " not master " , isMasterNs( ns ) );
op.debug().str << ns;
writelock lk(ns); // 声明写锁
if ( handlePossibleShardedMessage( m , 0 ) ) // 查看是不是sharding信息,如果是则处理
return ;
Client::Context ctx(ns);
int n = 0 ;
while ( d.moreJSObjs() ) { // 循环获取当前消息体中的BSONObj数据(数据库记录)
BSONObj js = d.nextJsObj();
uassert( 10059 , " object to insert too large " , js.objsize() <= BSONObjMaxUserSize);
{
// 声明BSONObj迭代器,以查看里面元素是否有更新操作,如set inc push pull 等
BSONObjIterator i( js );
while ( i.more() ) {
BSONElement e = i.next();
uassert( 13511 , " object to insert can't have $ modifiers " , e.fieldName()[ 0 ] != ' $ ' );
}
}
// 插入记录操作,god = false用于标识当前BSONObj对象为有效数据
theDataFileMgr.insertWithObjMod(ns, js, false );
logOp( " i " , ns, js); // 日志操作,包括master状态下及sharding分片情况
if ( ++ n % 4 == 0 ) {
// 在插入一些数据后,进行持久化操作,有关持久化部分参见我的这篇文章
// http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/03/21/1990344.html
getDur().commitIfNeeded();
}
}
globalOpCounters.incInsertInWriteLock(n); // 在写锁环境下添加已插入记录数(n),锁采用InterlockedIncrement实现数的原子性
}
上面的方法中,主要是在“写锁”环境下执行插入数据操作,并且在插入记录之前进行简单的数据对象检查,如长度和插入数据是否被修改,以确保数据的最终有效性。
最终上面代码会调用 insertWithObjMod()方法(位于pdfile.cpp 文件第1432行),该方法定义如下:
DiskLoc loc = insert( ns, o.objdata(), o.objsize(), god );
if ( ! loc.isNull() ) // 判断返回记录地址是否为空(记录是否插入成功)
o = BSONObj( loc.rec() ); // 如有效,则用记录地地址上的记录(record类型指针)绑定到o上
return loc;
}
该方法只是一个对插入操作及返回结果的封装,其中ns为数据对象的名空间,o就是要插入的数据对象(BSONObj),god用于标识当前BSONObj 对象是否为有效数据(false=有效),这里之所以要传入god这个参数,是因为在接下来的insert方法里同时支持添加名空间(及索引)和插入记录 操作(都会不断调用该方法),而在添加名空间时god=true。
下面我们看一下insert方法(pdfile.cpp 第1467行),因为其内容较长,请详见注释:
bool wouldAddIndex = false ;
massert( 10093 , " cannot insert into reserved $ collection " , god || isANormalNSName( ns ) );
uassert( 10094 , str::stream() << " invalid ns: " << ns , isValidNS( ns ) );
const char * sys = strstr(ns, " system. " );
if ( sys ) { // 对插入记录的ns进行判断,是否要插入保留的数据库名(system),如是则停止执行其它代码
uassert( 10095 , " attempt to insert in reserved database name 'system' " , sys != ns);
if ( strstr(ns, " .system. " ) ) {
// later:check for dba-type permissions here if have that at some point separate
if ( strstr(ns, " .system.indexes " ) ) // 判断是否创建索引
wouldAddIndex = true ;
else if ( legalClientSystemNS( ns , true ) )
;
else if ( ! god ) { // 表示obuf有数据,但这就意味着要向system下插入数据(把system当成数据表了)
out () << " ERROR: attempt to insert in system namespace " << ns << endl;
return DiskLoc();
}
}
else
sys = 0 ;
}
bool addIndex = wouldAddIndex && mayAddIndex; // 判断是否需要添加索引
NamespaceDetails * d = nsdetails(ns); // 获取ns的详细信息
if ( d == 0 ) {
addNewNamespaceToCatalog(ns); // 向system catalog添加新的名空间,它会再次调用当前insert()方法
/* todo: shouldn't be in the namespace catalog until after the allocations here work.
also if this is an addIndex, those checks should happen before this!
*/
// 创建第一个数据库文件.
cc().database() -> allocExtent(ns, Extent::initialSize(len), false );
d = nsdetails(ns);
if ( ! god )
ensureIdIndexForNewNs(ns);
}
d -> paddingFits();
NamespaceDetails * tableToIndex = 0 ;
string tabletoidxns;
BSONObj fixedIndexObject;
if ( addIndex ) {
assert( obuf );
BSONObj io(( const char * ) obuf);
// 做索引准备工作,这里并不真正创建索引,只是进行参数检查,以及索引是否已存在等
if ( ! prepareToBuildIndex(io, god, tabletoidxns, tableToIndex, fixedIndexObject ) )
return DiskLoc();
if ( ! fixedIndexObject.isEmpty() ) {
obuf = fixedIndexObject.objdata();
len = fixedIndexObject.objsize();
}
}
const BSONElement * newId = & writeId;
int addID = 0 ;
if ( ! god ) {
// 检查对象 是否有_id字段,没有则添加
// Note that btree buckets which we insert aren't BSONObj's, but in that case god==true.
BSONObj io(( const char * ) obuf);
BSONElement idField = io.getField( " _id " );
uassert( 10099 , " _id cannot be an array " , idField.type() != Array );
if ( idField.eoo() /* 判断是否是结束元素 */ && ! wouldAddIndex && strstr(ns, " .local. " ) == 0 ) {
addID = len;
if ( writeId.eoo() ) {
// 初始化一个_id 随机值(因为_id可能是12 byte类型或其它类型)
idToInsert_.oid.init();
newId = & idToInsert; // 绑定初始化的_id值
}
len += newId -> size();
}
// 如果io对象中有时间戳元素时,并用当前时间进行更新
BSONElementManipulator::lookForTimestamps( io );
}
// 兼容旧的数据文件
DiskLoc extentLoc;
int lenWHdr = len + Record::HeaderSize;
lenWHdr = ( int ) (lenWHdr * d -> paddingFactor);
if ( lenWHdr == 0 ) {
assert( d -> paddingFactor == 0 );
* getDur().writing( & d -> paddingFactor) = 1.0 ;
lenWHdr = len + Record::HeaderSize;
}
// 在对新的对象分配空间前检查数据是否会造成索引冲突(唯一索引)
// capped标识是否是固定大小的集合类型,这种类型下系统会自动将过于陈旧的数据remove掉
// 注:此cap与nosql中常说的cap无太大关联
// nosql cap即:一致性,有效性,分区容忍性
// 参见这篇文章: http://blog.nosqlfan.com/html/1112.html ,
// http://blog.nosqlfan.com/html/96.html )
if ( d -> nIndexes && d -> capped && ! god ) {
checkNoIndexConflicts( d, BSONObj( reinterpret_cast < const char *> ( obuf ) ) );
}
DiskLoc loc = d -> alloc(ns, lenWHdr, extentLoc); // 为当前记录分配空间namespace.cpp __stdAlloc方法
if ( loc.isNull() ) { // 如果分配失效
if ( d -> capped == 0 ) { // cap大小未增加,即
log( 1 ) << " allocating new extent for " << ns << " padding: " << d -> paddingFactor << " lenWHdr: " << lenWHdr << endl;
// 尝试从空闲空间列表中分配空间
cc().database() -> allocExtent(ns, Extent::followupSize(lenWHdr, d -> lastExtentSize), false );
// 尝试再次为当前记录分配空间
loc = d -> alloc(ns, lenWHdr, extentLoc);
if ( loc.isNull() ) {
log() << " WARNING: alloc() failed after allocating new extent. lenWHdr: " << lenWHdr << " last extent size: " << d -> lastExtentSize << " ; trying again/n " ;
for ( int zzz = 0 ; zzz < 10 && lenWHdr > d -> lastExtentSize; zzz ++ ) { // 最多尝试循环10次分配空间
log() << " try # " << zzz << endl;
cc().database() -> allocExtent(ns, Extent::followupSize(len, d -> lastExtentSize), false );
loc = d -> alloc(ns, lenWHdr, extentLoc);
if ( ! loc.isNull() )
break ;
}
}
}
if ( loc.isNull() ) { // 最终未分配空间给对象
log() << " insert: couldn't alloc space for object ns: " << ns << " capped: " << d -> capped << endl;
assert(d -> capped);
return DiskLoc();
}
}
Record * r = loc.rec();
{
assert( r -> lengthWithHeaders >= lenWHdr );
r = (Record * ) getDur().writingPtr(r, lenWHdr); // 持久化插入记录信息
if ( addID ) {
/* a little effort was made here to avoid a double copy when we add an ID */
(( int & ) * r -> data) = * (( int * ) obuf) + newId -> size();
memcpy(r -> data + 4 , newId -> rawdata(), newId -> size()); // 拷贝_id字段到指定记录内存空间
memcpy(r -> data + 4 + newId -> size(), (( char * )obuf) + 4 , addID - 4 ); // 拷贝数据到指定内存空间
}
else {
if ( obuf )
memcpy(r -> data, obuf, len); // 直接拷贝数据到记录字段r
}
}
{
Extent * e = r -> myExtent(loc);
if ( e -> lastRecord.isNull() ) { // 如果未尾记录为空,本人理解:即之前未插入过记录
Extent::FL * fl = getDur().writing(e -> fl());
fl -> firstRecord = fl -> lastRecord = loc;
r -> prevOfs = r -> nextOfs = DiskLoc::NullOfs;
}
else {
Record * oldlast = e -> lastRecord.rec(); // 否则将新记录添加到最后一条记录的后面
r -> prevOfs = e -> lastRecord.getOfs();
r -> nextOfs = DiskLoc::NullOfs;
getDur().writingInt(oldlast -> nextOfs) = loc.getOfs();
getDur().writingDiskLoc(e -> lastRecord) = loc;
}
}
/* 持久化操作并更新相应统计信息 */
{
NamespaceDetails::Stats * s = getDur().writing( & d -> stats);
s -> datasize += r -> netLength();
s -> nrecords ++ ;
}
// 在god时会清空stats信息,同时会添加一个 btree bucket(占据存储空间)
if ( ! god )
NamespaceDetailsTransient::get_w( ns ).notifyOfWriteOp(); // 在写操作时清空缓存,优化查询优化
if ( tableToIndex ) {
uassert( 13143 , " can't create index on system.indexes " , tabletoidxns.find( " .system.indexes " ) == string ::npos );
BSONObj info = loc.obj();
bool background = info[ " background " ].trueValue();
if ( background && cc().isSyncThread() ) {
/* don't do background indexing on slaves. there are nuances. this could be added later but requires more code. */
log() << " info: indexing in foreground on this replica; was a background index build on the primary " << endl;
background = false ;
}
int idxNo = tableToIndex -> nIndexes;
IndexDetails & idx = tableToIndex -> addIndex(tabletoidxns.c_str(), ! background); // 清空临时缓存信息; 同时递增索引数量
getDur().writingDiskLoc(idx.info) = loc;
try {
buildAnIndex(tabletoidxns, tableToIndex, idx, idxNo, background); // 创建索引
}
catch ( DBException & e ) {
// 保存异常信息,并执行dropIndexes
LastError * le = lastError. get ();
int savecode = 0 ;
string saveerrmsg;
if ( le ) {
savecode = le -> code;
saveerrmsg = le -> msg;
}
else {
savecode = e.getCode();
saveerrmsg = e.what();
}
// 回滚索引操作(drop索引)
string name = idx.indexName();
BSONObjBuilder b;
string errmsg;
bool ok = dropIndexes(tableToIndex, tabletoidxns.c_str(), name.c_str(), errmsg, b, true );
if ( ! ok ) {
log() << " failed to drop index after a unique key error building it: " << errmsg << ' ' << tabletoidxns << ' ' << name << endl;
}
assert( le && ! saveerrmsg.empty() );
raiseError(savecode,saveerrmsg.c_str());
throw ;
}
}
/* 将记录数据添加到索引信息(btree)中 */
if ( d -> nIndexes ) {
try {
BSONObj obj(r -> data);
indexRecord(d, obj, loc);
}
catch ( AssertionException & e ) {
// _id index 键值重复
if ( tableToIndex || d -> capped ) {
massert( 12583 , " unexpected index insertion failure on capped collection " , ! d -> capped );
string s = e.toString();
s += " : on addIndex/capped - collection and its index will not match " ;
uassert_nothrow(s.c_str());
error() << s << endl;
}
else {
// 回滚上述操作
_deleteRecord(d, ns, r, loc);
throw ;
}
}
}
// out() << " inserted at loc:" << hex << loc.getOfs() << " lenwhdr:" << hex << lenWHdr << dec << ' ' << ns << endl;
return loc;
}
正如之前所说,该方法会完成添加名空间,添加索引,添加数据记录(memcpy调用)。其中名空间的添加方法addNewNamespaceToCatalog 比较简单,下面主要介绍一下索引的创建过程,这里分为了两步:
1.创建索引树(b树)
2.将数据(主要是地址)添加到索引(树)中
先看一下创建索引过程:
tlog() << " building new index on " << idx.keyPattern() << " for " << ns << ( background ? " background " : "" ) << endl;
Timer t;
unsigned long long n;
if ( background ) {
log( 2 ) << " buildAnIndex: background=true/n " ;
}
assert( ! BackgroundOperation::inProgForNs(ns.c_str()) ); // should have been checked earlier, better not be...
assert( d -> indexBuildInProgress == 0 );
assertInWriteLock();
RecoverableIndexState recoverable( d );
if ( inDBRepair || ! background ) { // 当数据库在repair时或非后台工作方式下
n = fastBuildIndex(ns.c_str(), d, idx, idxNo); // 创建索引
assert( ! idx.head.isNull() );
}
else {
BackgroundIndexBuildJob j(ns.c_str()); // 以后台方式创建索引
n = j.go(ns, d, idx, idxNo);
}
tlog() << " done for " << n << " records " << t.millis() / 1000.0 << " secs " << endl;
}
创建索引方法会要据创建方式(是否是后台线程等),使用不同的方法,这里主要讲解非后台方式,也就是上面的fastBuildIndex方法(pdfile.cpp第1101行),其定义如下(内容详见注释):
CurOp * op = cc().curop(); // 设置当前操作指针,用于设置操作信息
Timer t;
tlog( 1 ) << " fastBuildIndex " << ns << " idxNo: " << idxNo << ' ' << idx.info.obj().toString() << endl;
bool dupsAllowed = ! idx.unique();
bool dropDups = idx.dropDups() || inDBRepair;
BSONObj order = idx.keyPattern();
getDur().writingDiskLoc(idx.head).Null();
if ( logLevel > 1 ) printMemInfo( " before index start " );
/* 获取并排序所有键值 ----- */
unsigned long long n = 0 ;
shared_ptr < Cursor > c = theDataFileMgr.findAll(ns);
BSONObjExternalSorter sorter(order);
sorter.hintNumObjects( d -> stats.nrecords );
unsigned long long nkeys = 0 ;
ProgressMeterHolder pm( op -> setMessage( " index: (1/3) external sort " , d -> stats.nrecords , 10 ) );
while ( c -> ok() ) {
BSONObj o = c -> current();
DiskLoc loc = c -> currLoc();
BSONObjSetDefaultOrder keys;
idx.getKeysFromObject(o, keys); // 从对象中获取键值信息
int k = 0 ;
for ( BSONObjSetDefaultOrder::iterator i = keys.begin(); i != keys.end(); i ++ ) {
if ( ++ k == 2 ) { // 是否是多键索引
d -> setIndexIsMultikey(idxNo);
}
sorter.add( * i, loc); // 向排序器添加键值和记录位置信息
nkeys ++ ;
}
c -> advance();
n ++ ;
pm.hit();
if ( logLevel > 1 && n % 10000 == 0 ) {
printMemInfo( " /t iterating objects " );
}
};
pm.finished();
if ( logLevel > 1 ) printMemInfo( " before final sort " );
sorter.sort();
if ( logLevel > 1 ) printMemInfo( " after final sort " );
log(t.seconds() > 5 ? 0 : 1 ) << " /t external sort used : " << sorter.numFiles() << " files " << " in " << t.seconds() << " secs " << endl;
list < DiskLoc > dupsToDrop;
/* 创建索引 */
{
BtreeBuilder btBuilder(dupsAllowed, idx); // 实例化b树索引对象
// BSONObj keyLast;
auto_ptr < BSONObjExternalSorter::Iterator > i = sorter.iterator(); // 初始化迭代器用于下面遍历
assert( pm == op -> setMessage( " index: (2/3) btree bottom up " , nkeys , 10 ) );
while ( i -> more() ) {
RARELY killCurrentOp.checkForInterrupt(); // 检查冲突如shutdown或kill指令
BSONObjExternalSorter::Data d = i -> next();
try {
btBuilder.addKey(d.first, d.second); // 向b树索引对象中添加索引键值和记录位置信息
}
catch ( AssertionException & e ) {
if ( dupsAllowed ) {
// unknow exception??
throw ;
}
if ( e.interrupted() )
throw ;
if ( ! dropDups )
throw ;
/* we could queue these on disk, but normally there are very few dups, so instead we
keep in ram and have a limit.
*/
dupsToDrop.push_back(d.second);
uassert( 10092 , " too may dups on index build with dropDups=true " , dupsToDrop.size() < 1000000 );
}
pm.hit();
}
pm.finished();
op -> setMessage( " index: (3/3) btree-middle " );
log(t.seconds() > 10 ? 0 : 1 ) << " /t done building bottom layer, going to commit " << endl;
btBuilder.commit(); // 提交创建索引操作,该方法会完成最终构造Btree索引操作
wassert( btBuilder.getn() == nkeys || dropDups );
}
log( 1 ) << " /t fastBuildIndex dupsToDrop: " << dupsToDrop.size() << endl;
// 删除索引中已出现的重复记录
for ( list < DiskLoc > ::iterator i = dupsToDrop.begin(); i != dupsToDrop.end(); i ++ )
theDataFileMgr.deleteRecord( ns, i -> rec(), * i, false , true );
return n;
}
上面方法主要对要创建的索引信息进行提取,并封装到一个BtreeBuilder中,顾名思义,该对象用于进行b树的创建(因为索引也是一个b树),当信息收集排序完成后,就开始创建索引,如下:
void BtreeBuilder::commit() {
buildNextLevel(first);
committed = true ;
}
void BtreeBuilder::buildNextLevel(DiskLoc loc) {
int levels = 1 ;
while ( 1 ) {
if ( loc.btree() -> tempNext().isNull() ) {
// 在当前层级上只有一个 bucket
getDur().writingDiskLoc(idx.head) = loc;
break ;
}
levels ++ ;
DiskLoc upLoc = BtreeBucket::addBucket(idx); // 添加bucket并实例化上一层DiskLoc
DiskLoc upStart = upLoc;
BtreeBucket * up = upLoc.btreemod(); // 获取上一层的bucket指针
DiskLoc xloc = loc;
while ( ! xloc.isNull() ) {
RARELY {
getDur().commitIfNeeded();
b = cur.btreemod();
up = upLoc.btreemod();
}
BtreeBucket * x = xloc.btreemod();
BSONObj k;
DiskLoc r;
x -> popBack(r,k); // 弹出当前bucket中最右边的键
bool keepX = ( x -> n != 0 ); // 当前bucket中元素个数是否为0
DiskLoc keepLoc = keepX ? xloc : x -> nextChild;
// 压入上面弹出的最右边的键值,该键值为当前up(bucket)中最大值
if ( ! up -> _pushBack(r, k, ordering, keepLoc) )
{
// 当前 bucket 已满,则新创建一个addBucket
DiskLoc n = BtreeBucket::addBucket(idx);
up -> tempNext() = n;
upLoc = n;
up = upLoc.btreemod();
up -> pushBack(r, k, ordering, keepLoc);
}
DiskLoc nextLoc = x -> tempNext(); // get next in chain at current level
if ( keepX ) { // 表示当前结点非顶层结点,则设置它的父结点
x -> parent = upLoc;
}
else {
if ( ! x -> nextChild.isNull() )
x -> nextChild.btreemod() -> parent = upLoc;
x -> deallocBucket( xloc, idx ); // 删除xloc bucket
}
xloc = nextLoc; // 指向当前层的下个元素
}
loc = upStart; // 升级当前结点
mayCommitProgressDurably();
}
if ( levels > 1 )
log( 2 ) << " btree levels: " << levels << endl;
}
上面的buildNextLevel方法自下而上根据之前抽取的键值逐层构造一个b树。这里有一个问题需要注意一下,因为mongodb使用 bucket来作为b树中的一个层次结点或叶子结点容器(如下图),bucket最大尺寸为8192字节,c。有关b树索引的文章可以参见这篇文章 :,
mongodb目前关于B树索引的文档 :http://blog.nosqlfan.com/html/758.html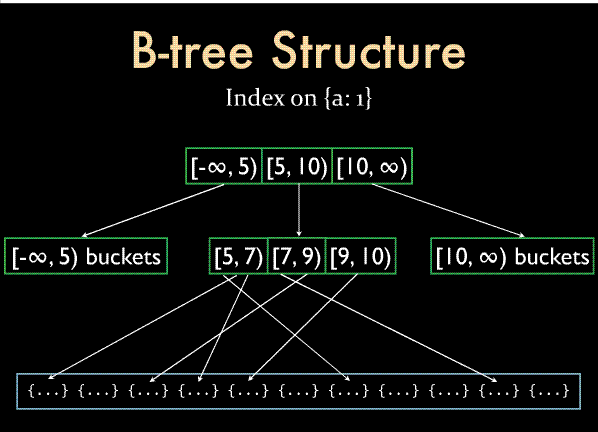
当初始化了b树索引及空间信息之后,下面就会将数据绑定到相应信息结点上了,也就是DataFileMgr::insert方法(pdfile.cpp文件)的如下代码:
if ( d -> nIndexes ) {
try {
BSONObj obj(r -> data);
indexRecord(d, obj, loc);
}
......
}
上面的indexRecord方法会将键值和数据(包括存储位置)添加到索引中(其中参数d包括之前创建的B树索引信息), 该方法定义如下(pdfile.cpp 第1355行):
static void indexRecord(NamespaceDetails * d, BSONObj obj, DiskLoc loc) {
int n = d -> nIndexesBeingBuilt(); // 获取已(及正在)构建的索引数
for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ) {
try {
bool unique = d -> idx(i).unique();
// 内联函数(inline):将索引和记录相关信息初始化到btree中
_indexRecord(d, i /* 索引顺序位 */ , obj, loc, /* dupsAllowed */ ! unique);
}
catch ( DBException & ) {
/* 如果发生异常,则进行回滚操作
note <= i (not < i) is important here as the index we were just attempted
may be multikey and require some cleanup.
*/
for ( int j = 0 ; j <= i; j ++ ) {
try {
_unindexRecord(d -> idx(j), obj, loc, false );
}
catch (...) {
log( 3 ) << " unindex fails on rollback after unique failure/n " ;
}
}
throw ;
}
}
}
上面的_indexRecord为内联函数(pdfile.cpp)(inline关键字参见C++说明),该参数声明如下:
IndexDetails & idx = d -> idx(idxNo); //
BSONObjSetDefaultOrder keys;
idx.getKeysFromObject(obj, keys); // 从对象信息中获取键属性信息
BSONObj order = idx.keyPattern();
Ordering ordering = Ordering::make(order); // 初始化排序方式用于下面传参
int n = 0 ;
for ( BSONObjSetDefaultOrder::iterator i = keys.begin(); i != keys.end(); i ++ ) {
if ( ++ n == 2 ) {
d -> setIndexIsMultikey(idxNo); // 设置多键值索引
}
assert( ! recordLoc.isNull() );
try {
idx.head /* DiskLoc */ .btree() /* BtreeBucket */ -> bt_insert(idx.head, recordLoc, // 执行向btree中添加记录和绑定索引信息的操作
* i, ordering, dupsAllowed, idx);
}
catch (AssertionException & e) {
if ( e.getCode() == 10287 && idxNo == d -> nIndexes ) {
DEV log() << " info: caught key already in index on bg indexing (ok) " << endl;
continue ;
}
if ( ! dupsAllowed ) {
// 重复键值异常
throw ;
}
problem() << " caught assertion _indexRecord " << idx.indexNamespace() << endl;
}
}
}
上面方法最终会执行b树插入方法bt_insert(btree.cpp文件1622行),如下(详情见注释):
const BSONObj & key, const Ordering & order, bool dupsAllowed,
IndexDetails & idx, bool toplevel) const {
if ( toplevel ) { // 如果是顶级节点(如果是通过构造索引方式调用 ,则toplevel=true)
// 判断键值是否过界(因为其会存储在system.indexs中),其中:KeyMax = 8192 / 10 .mongodb开发团队可能会在更高版本中扩大该值
if ( key.objsize() > KeyMax ) {
problem() << " Btree::insert: key too large to index, skipping " << idx.indexNamespace() << ' ' << key.objsize() << ' ' << key.toString() << endl;
return 3 ;
}
}
// 执行添加操作
int x = _insert(thisLoc, recordLoc, key, order, dupsAllowed, DiskLoc(), DiskLoc(), idx);
assertValid( order ); // assert排序方式是否有效
return x;
}
上面代码紧接着会调用btree.cpp文件的内部方法_insert(btree.cpp文件 1554行):
const BSONObj & key, const Ordering & order, bool dupsAllowed,
const DiskLoc lChild, const DiskLoc rChild, IndexDetails & idx) const {
if ( key.objsize() > KeyMax ) {
problem() << " ERROR: key too large len: " << key.objsize() << " max: " << KeyMax << ' ' << key.objsize() << ' ' << idx.indexNamespace() << endl;
return 2 ;
}
assert( key.objsize() > 0 );
int pos;
// 在btree bucket中使用二分查询,查看键值是否已在所索引信息中
bool found = find(idx, key, recordLoc, order, pos /* 返回该索引信息所在或应该在的位置 */ , ! dupsAllowed);
if ( insert_debug ) {
out () << " " << thisLoc.toString() << ' . ' << " _insert " <<
key.toString() << ' / ' << recordLoc.toString() <<
" l: " << lChild.toString() << " r: " << rChild.toString() << endl;
out () << " found: " << found << " pos: " << pos << " n: " << n << endl;
}
if ( found ) {
const _KeyNode & kn = k(pos); // 获取指定磁盘位置的节点信息,_KeyNode
if ( kn.isUnused() ) { // 查看已存在的键结点是否已使用
log( 4 ) << " btree _insert: reusing unused key " << endl;
massert( 10285 , " _insert: reuse key but lchild is not null " , lChild.isNull());
massert( 10286 , " _insert: reuse key but rchild is not null " , rChild.isNull());
kn.writing().setUsed();
return 0 ;
}
DEV {
log() << " _insert(): key already exists in index (ok for background:true)/n " ;
log() << " " << idx.indexNamespace() << " thisLoc: " << thisLoc.toString() << ' /n ' ;
log() << " " << key.toString() << ' /n ' ;
log() << " " << " recordLoc: " << recordLoc.toString() << " pos: " << pos << endl;
log() << " old l r: " << childForPos(pos).toString() << ' ' << childForPos(pos + 1 ).toString() << endl;
log() << " new l r: " << lChild.toString() << ' ' << rChild.toString() << endl;
}
alreadyInIndex(); // 提示键值结点已在索引中,不必再创建,并抛出异常
}
DEBUGGING out () << " TEMP: key: " << key.toString() << endl;
DiskLoc child = childForPos(pos); // 查询当前pos的子结点信息,以寻找插入位置
if ( insert_debug )
out () << " getChild( " << pos << " ): " << child.toString() << endl;
if ( child.isNull() || ! rChild.isNull() /* 在当前buckets中插入,即 'internal' 插入 */ ) {
insertHere(thisLoc, pos, recordLoc, key, order, lChild, rChild, idx); // 在当前buckets中插入
return 0 ;
}
// 如果有子结点,则在子结点上执行插入操作
return child.btree() -> bt_insert(child, recordLoc, key, order, dupsAllowed, idx, /* toplevel */ false );
}
上面_insert方法首先会使用二分法查找要插入的记录是否已存在于索引中,同时会返回一个插入点(pos),如不存在则会进一步在插入点位置查看找 元素以决定是在当前bucket中插入,还是在当前pos位置的(右)子结点(bucket)上插入(这会再次递归调用上面的bt_insert方法), 这里我们假定在当前bucket插入,则会执行insertHere方法(btree.cpp文件1183行),它的定义如下:
* insert a key in this bucket, splitting if necessary.
* @keypos - where to insert the key in range 0..n. 0=make leftmost, n=make rightmost.
* NOTE this function may free some data, and as a result the value passed for keypos may
* be invalid after calling insertHere()
*/
void BtreeBucket::insertHere( const DiskLoc thisLoc, int keypos,
const DiskLoc recordLoc, const BSONObj & key, const Ordering & order,
const DiskLoc lchild, const DiskLoc rchild, IndexDetails & idx) const {
if ( insert_debug )
out () << " " << thisLoc.toString() << " .insertHere " << key.toString() << ' / ' << recordLoc.toString() << ' '
<< lchild.toString() << ' ' << rchild.toString() << " keypos: " << keypos << endl;
DiskLoc oldLoc = thisLoc;
// 根据keypos插入相应位置并将数据memcpy到内存指定位置
if ( ! basicInsert(thisLoc, keypos, recordLoc, key, order) ) {
// 如果插入无效,表示当前bucket已满,则分割记录并放到新创建的bucket中
thisLoc.btreemod() -> split(thisLoc, keypos, recordLoc, key, order, lchild, rchild, idx);
return ;
}
{ // 持久化当前thisLoc的结点信息并根据插入位置(是否最后一个key),来更新当前thisLoc(及后面key结点)的子结点信息
const _KeyNode * _kn = & k(keypos);
_KeyNode * kn = (_KeyNode * ) getDur().alreadyDeclared((_KeyNode * ) _kn); // already declared intent in basicInsert()
if ( keypos + 1 == n ) { // n为pack(打包后)存储的记录数,这里"判断等于n"表示为最后(last)一个key
if ( nextChild != lchild ) { // 如果是最后元素,那么"当前最高键值的右子结点应该与要插入的左子结点相同
out () << " ERROR nextChild != lchild " << endl;
out () << " thisLoc: " << thisLoc.toString() << ' ' << idx.indexNamespace() << endl;
out () << " keyPos: " << keypos << " n: " << n << endl;
out () << " nextChild: " << nextChild.toString() << " lchild: " << lchild.toString() << endl;
out () << " recordLoc: " << recordLoc.toString() << " rchild: " << rchild.toString() << endl;
out () << " key: " << key.toString() << endl;
dump();
assert( false );
}
kn -> prevChildBucket = nextChild; // "当前最高键值的右子结点”绑定到持久化结点的左子结点
assert( kn -> prevChildBucket == lchild );
nextChild.writing() = rchild; // 持久化"当前最高键值的右子结点”,并将“要插入结点”的右子结点绑定到
if ( ! rchild.isNull() ) // 如果有右子结点,则更新右子结点的父结点信息为当前thisLoc
rchild.btree() -> parent.writing() = thisLoc;
}
else {
// 如果keypos位置不是最后一个
kn -> prevChildBucket = lchild; // 将左子结点绑定到keypos位置结点的左子结点上
if ( k(keypos + 1 ).prevChildBucket != lchild ) { // 这时左子结点应该与下一个元素的左子结点相同
out () << " ERROR k(keypos+1).prevChildBucket != lchild " << endl;
out () << " thisLoc: " << thisLoc.toString() << ' ' << idx.indexNamespace() << endl;
out () << " keyPos: " << keypos << " n: " << n << endl;
out () << " k(keypos+1).pcb: " << k(keypos + 1 ).prevChildBucket.toString() << " lchild: " << lchild.toString() << endl;
out () << " recordLoc: " << recordLoc.toString() << " rchild: " << rchild.toString() << endl;
out () << " key: " << key.toString() << endl;
dump();
assert( false );
}
const DiskLoc * pc = & k(keypos + 1 ).prevChildBucket; // 获取keypos后面元素的左子结点信息
* getDur().alreadyDeclared((DiskLoc * ) pc) = rchild; // 将右子结点绑定到下一个元素(keypos+1)的左子结点上declared in basicInsert()
if ( ! rchild.isNull() ) // 如果有右子结点,则更新右子结点的父结点信息为当前thisLoc
rchild.btree() -> parent.writing() = thisLoc;
}
return ;
}
}
该方法中会调用一个叫basicInsert的方法,它主要会在当前bucket中指定位置(keypos)添加记录信息,同时持久化该结点信息,如下:
bool BucketBasics::basicInsert( const DiskLoc thisLoc, int & keypos, const DiskLoc recordLoc, const BSONObj & key, const Ordering & order) const {
assert( keypos >= 0 && keypos <= n );
// 判断bucket剩余的空间是否满足当前数据需要的存储空间
int bytesNeeded = key.objsize() + sizeof (_KeyNode);
if ( bytesNeeded > emptySize ) {
_pack(thisLoc, order, keypos); // 如不够用,进行一次整理打包操作,以为bucket中整理更多空间
if ( bytesNeeded > emptySize ) // 如还不够用,则返回
return false ;
}
BucketBasics * b; // 声明Bucket管理对象指针,该对象提供了Bucket存储管理的基本操作和属性,如insert,_pack等
{
const char * p = ( const char * ) & k(keypos);
const char * q = ( const char * ) & k(n + 1 );
// declare that we will write to [k(keypos),k(n)]
// todo: this writes a medium amount to the journal. we may want to add a verb "shift" to the redo log so
// we can log a very small amount.
b = (BucketBasics * ) getDur().writingAtOffset(( void * ) this , p - ( char * ) this , q - p);
// 如已有3个结点,目前要插到第三个结点之间,则对每三个元素进行迁移,
// e.g. n==3, keypos==2
// 1 4 9
// ->
// 1 4 _ 9
for ( int j = n; j > keypos; j -- ) // make room
b -> k(j) = b -> k(j - 1 );
}
getDur().declareWriteIntent( & b -> emptySize, 12 ); // [b->emptySize..b->n] is 12 bytes and we are going to write those
b -> emptySize -= sizeof (_KeyNode); // 将当前bucket中的剩余空闲空间减少
b -> n ++ ; // 已有结点数加1
_KeyNode & kn = b -> k(keypos);
kn.prevChildBucket.Null(); // 设置当前结点的左子结点为空
kn.recordLoc = recordLoc; // 绑定结点记录信息
kn.setKeyDataOfs(( short ) b -> _alloc(key.objsize()) ); // 设置结点数据偏移信息
char * p = b -> dataAt(kn.keyDataOfs()); // 实例化指向磁盘数据(journal文件)位置(含偏移量)的指针
getDur().declareWriteIntent(p, key.objsize()); // 持久化结点数据信息
memcpy(p, key.objdata(), key.objsize()); // 将当前结点信息复制到p指向的地址空间
return true ;
}
如果上面方法调用失效,则意味着当前 bucket中已有可用空间插入新记录,这时系统会调用 split(btree.cpp文件 1240行)方法来进行bucket分割,以创建新的bucket并将信息塞入其中,如下:
assertWritable();
if ( split_debug )
out () << " " << thisLoc.toString() << " .split " << endl;
int split = splitPos( keypos ); // 找到要迁移的数据位置
DiskLoc rLoc = addBucket(idx); // 添加一个新的BtreeBucket
BtreeBucket * r = rLoc.btreemod();
if ( split_debug )
out () << " split: " << split << ' ' << keyNode(split).key.toString() << " n: " << n << endl;
for ( int i = split + 1 ; i < n; i ++ ) {
KeyNode kn = keyNode(i);
r -> pushBack(kn.recordLoc, kn.key, order, kn.prevChildBucket); // 向新bucket中迁移过剩数据
}
r -> nextChild = nextChild; // 绑定新bucket的右子结点
r -> assertValid( order );
if ( split_debug )
out () << " new rLoc: " << rLoc.toString() << endl;
r = 0 ;
rLoc.btree() -> fixParentPtrs(rLoc); // 设置当前bucket树的父指针信息
{
KeyNode splitkey = keyNode(split); // 获取内存中分割点位置所存储的数据
nextChild = splitkey.prevChildBucket; // 提升splitkey 键,它的子结点将会是 thisLoc (l) 和 rLoc (r)
if ( split_debug ) {
out () << " splitkey key: " << splitkey.key.toString() << endl;
}
// 将 splitkey 提升为父结点
if ( parent.isNull() ) {
// 如果无父结点时,则创建一个,并将
DiskLoc L = addBucket(idx);
BtreeBucket * p = L.btreemod();
p -> pushBack(splitkey.recordLoc, splitkey.key, order, thisLoc);
p -> nextChild = rLoc; // 将分割的bucket为了当前
p -> assertValid( order );
parent = idx.head.writing() = L; // 将splitkey 提升为父结点
if ( split_debug )
out () << " we were root, making new root: " << hex << parent.getOfs() << dec << endl;
rLoc.btree() -> parent.writing() = parent;
}
else {
// set this before calling _insert - if it splits it will do fixParent() logic and change the value.
rLoc.btree() -> parent.writing() = parent;
if ( split_debug )
out () << " promoting splitkey key " << splitkey.key.toString() << endl;
// 提升splitkey键,它的左子结点 thisLoc, 右子点rLoc
parent.btree() -> _insert(parent, splitkey.recordLoc, splitkey.key, order, /* dupsallowed */ true , thisLoc, rLoc, idx);
}
}
int newpos = keypos;
// 打包压缩数据(pack,移除无用数据),以提供更多空间
truncateTo(split, order, newpos); // note this may trash splitkey.key. thus we had to promote it before finishing up here.
// add our new key, there is room now
{
if ( keypos <= split ) { // 如果还有空间存储新键
if ( split_debug )
out () << " keypos<split, insertHere() the new key " << endl;
insertHere(thisLoc, newpos, recordLoc, key, order, lchild, rchild, idx); // 再次向当前bucket中添加记录
}
else { // 如压缩之后依旧无可用空间,则向新创建的bucket中添加节点
int kp = keypos - split - 1 ;
assert(kp >= 0 );
rLoc.btree() -> insertHere(rLoc, kp, recordLoc, key, order, lchild, rchild, idx);
}
}
if ( split_debug )
out () << " split end " << hex << thisLoc.getOfs() << dec << endl;
}
好了,今天的内容到这里就告一段落了,在接下来的文章中,将会介绍客户端发起Delete操作时,Mongodb的执行流程和相应实现部分。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2011/03/30/1999699.html
作者: daizhj, 代震军
微博: http://t.sina.com.cn/daizhj
Tags: mongodb,c++,btree





















 1257
1257











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








