Java程序员面试题集(136-150)
摘要:这一部分主要是数据结构和算法相关的面试题目,虽然只有15道题目,但是包含的信息量还是很大的,很多题目背后的解题思路和算法是非常值得玩味的。
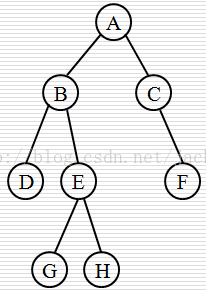
136、给出下面的二叉树先序、中序、后序遍历的序列?
答:先序序列:ABDEGHCF;中序序列:DBGEHACF;后序序列:DGHEBFCA。
补充:二叉树也称为二分树,它是树形结构的一种,其特点是每个结点至多有二棵子树,并且二叉树的子树有左右之分,其次序不能任意颠倒。二叉树的遍历序列按照访问根节点的顺序分为先序(先访问根节点,接下来先序访问左子树,再先序访问右子树)、中序(先中序访问左子树,然后访问根节点,最后中序访问右子树)和后序(先后序访问左子树,再后序访问右子树,最后访问根节点)。如果知道一棵二叉树的先序和中序序列或者中序和后序序列,那么也可以还原出该二叉树。
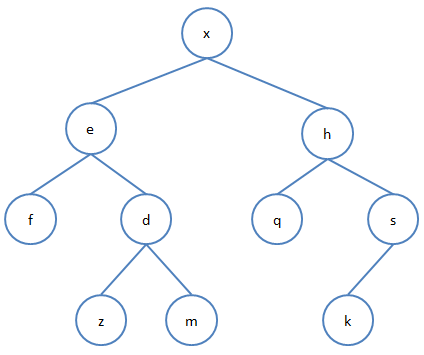
例如,已知二叉树的先序序列为:xefdzmhqsk,中序序列为:fezdmxqhks,那么还原出该二叉树应该如下图所示:
137、你知道的排序算法都哪些?用Java写一个排序系统。
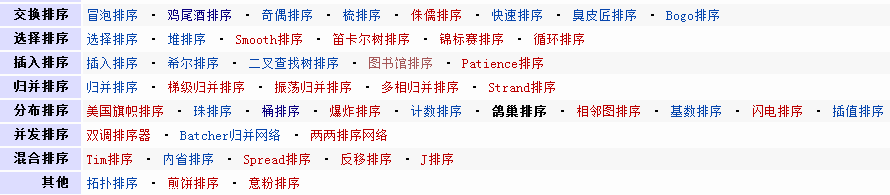
答:稳定的排序算法有:插入排序、选择排序、冒泡排序、鸡尾酒排序、归并排序、二叉树排序、基数排序等;不稳定排序算法包括:希尔排序、堆排序、快速排序等。
下面是关于排序算法的一个列表:
下面按照策略模式给出一个排序系统,实现了冒泡、归并和快速排序。
Sorter.java
package com.jackfrued.util;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* 排序器接口(策略模式: 将算法封装到具有共同接口的独立的类中使得它们可以相互替换)
* @author骆昊
*
*/
public interface Sorter {
/**
* 排序
* @param list 待排序的数组
*/
public <T extends Comparable<T>> void sort(T[] list);
/**
* 排序
* @param list 待排序的数组
* @param comp 比较两个对象的比较器
*/
public <T> void sort(T[] list, Comparator<T> comp);
}BubbleSorter.java
package com.jackfrued.util;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* 冒泡排序
* @author骆昊
*
*/
public class BubbleSorter implements Sorter {
@Override
public <T extends Comparable<T>> void sort(T[] list) {
boolean swapped = true;
for(int i = 1; i < list.length && swapped;i++) {
swapped= false;
for(int j = 0; j < list.length - i; j++) {
if(list[j].compareTo(list[j+ 1]) > 0 ) {
T temp = list[j];
list[j]= list[j + 1];
list[j+ 1] = temp;
swapped= true;
}
}
}
}
@Override
public <T> void sort(T[] list,Comparator<T> comp) {
boolean swapped = true;
for(int i = 1; i < list.length && swapped; i++) {
swapped = false;
for(int j = 0; j < list.length - i; j++) {
if(comp.compare(list[j], list[j + 1]) > 0 ) {
T temp = list[j];
list[j]= list[j + 1];
list[j+ 1] = temp;
swapped= true;
}
}
}
}
}MergeSorter.java
package com.jackfrued.util;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* 归并排序
* 归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法。
* 该算法是采用分治法(divide-and-conquer)的一个非常典型的应用,
* 先将待排序的序列划分成一个一个的元素,再进行两两归并,
* 在归并的过程中保持归并之后的序列仍然有序。
* @author骆昊
*
*/
public class MergeSorter implements Sorter {
@Override
public <T extends Comparable<T>> void sort(T[] list) {
T[] temp = (T[]) new Comparable[list.length];
mSort(list,temp, 0, list.length- 1);
}
private <T extends Comparable<T>> void mSort(T[] list, T[] temp, int low, int high) {
if(low == high) {
return ;
}
else {
int mid = low + ((high -low) >> 1);
mSort(list,temp, low, mid);
mSort(list,temp, mid + 1, high);
merge(list,temp, low, mid + 1, high);
}
}
private <T extends Comparable<T>> void merge(T[] list, T[] temp, int left, int right, int last) {
int j = 0;
int lowIndex = left;
int mid = right - 1;
int n = last - lowIndex + 1;
while (left <= mid && right <= last){
if (list[left].compareTo(list[right]) < 0){
temp[j++] = list[left++];
} else {
temp[j++] = list[right++];
}
}
while (left <= mid) {
temp[j++] = list[left++];
}
while (right <= last) {
temp[j++] = list[right++];
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
list[lowIndex + j] = temp[j];
}
}
@Override
public <T> void sort(T[] list, Comparator<T> comp) {
T[]temp = (T[])new Comparable[list.length];
mSort(list,temp, 0, list.length- 1, comp);
}
private <T> void mSort(T[] list, T[] temp, int low, int high, Comparator<T> comp) {
if(low == high) {
return ;
}
else {
int mid = low + ((high -low) >> 1);
mSort(list,temp, low, mid, comp);
mSort(list,temp, mid + 1, high, comp);
merge(list,temp, low, mid + 1, high, comp);
}
}
private <T> void merge(T[] list, T[]temp, int left, int right, int last, Comparator<T> comp) {
int j = 0;
int lowIndex = left;
int mid = right - 1;
int n = last - lowIndex + 1;
while (left <= mid && right <= last){
if (comp.compare(list[left], list[right]) <0) {
temp[j++] = list[left++];
} else {
temp[j++] = list[right++];
}
}
while (left <= mid) {
temp[j++] = list[left++];
}
while (right <= last) {
temp[j++] = list[right++];
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
list[lowIndex + j] = temp[j];
}
}
}QuickSorter.java
package com.jackfrued.util;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* 快速排序
* 快速排序是使用分治法(divide-and-conquer)依选定的枢轴
* 将待排序序列划分成两个子序列,其中一个子序列的元素都小于枢轴,
* 另一个子序列的元素都大于或等于枢轴,然后对子序列重复上面的方法,
* 直到子序列中只有一个元素为止
* @author Hao
*
*/
public class QuickSorter implements Sorter {
@Override
public <T extends Comparable<T>> void sort(T[] list) {
quickSort(list, 0, list.length- 1);
}
@Override
public <T> void sort(T[] list, Comparator<T> comp) {
quickSort(list, 0, list.length- 1, comp);
}
private <T extends Comparable<T>> void quickSort(T[] list, int first, int last) {
if (last > first) {
int pivotIndex = partition(list, first, last);
quickSort(list, first, pivotIndex - 1);
quickSort(list, pivotIndex, last);
}
}
private <T> void quickSort(T[] list, int first, int last,Comparator<T> comp) {
if (last > first) {
int pivotIndex = partition(list, first, last, comp);
quickSort(list, first, pivotIndex - 1, comp);
quickSort(list, pivotIndex, last, comp);
}
}
private <T extends Comparable<T>> int partition(T[] list, int first, int last) {
T pivot = list[first];
int low = first + 1;
int high = last;
while (high > low) {
while (low <= high && list[low].compareTo(pivot) <= 0) {
low++;
}
while (low <= high && list[high].compareTo(pivot) >= 0) {
high--;
}
if (high > low) {
T temp = list[high];
list[high]= list[low];
list[low]= temp;
}
}
while (high > first&& list[high].compareTo(pivot) >= 0) {
high--;
}
if (pivot.compareTo(list[high])> 0) {
list[first]= list[high];
list[high]= pivot;
return high;
}
else {
return low;
}
}
private <T> int partition(T[] list, int first, int last, Comparator<T> comp) {
T pivot = list[first];
int low = first + 1;
int high = last;
while (high > low) {
while (low <= high&& comp.compare(list[low], pivot) <= 0) {
low++;
}
while (low <= high&& comp.compare(list[high], pivot) >= 0) {
high--;
}
if (high > low) {
T temp = list[high];
list[high] = list[low];
list[low]= temp;
}
}
while (high > first&& comp.compare(list[high], pivot) >= 0) {
high--;
}
if (comp.compare(pivot,list[high]) > 0) {
list[first]= list[high];
list[high]= pivot;
return high;
}
else {
return low;
}
}
}138、写一个二分查找(折半搜索)的算法。
答:折半搜索,也称二分查找算法、二分搜索,是一种在有序数组中查找某一特定元素的搜索算法。搜素过程从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是要查找的元素,则搜素过程结束;如果某一特定元素大于或者小于中间元素,则在数组大于或小于中间元素的那一半中查找,而且跟开始一样从中间元素开始比较。如果在某一步骤数组为空,则代表找不到。这种搜索算法每一次比较都使搜索范围缩小一半。
package com.jackfrued.util;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class MyUtil {
public static <T extends Comparable<T>> int binarySearch(T[] x, T key) {
return binarySearch(x, 0, x.length- 1, key);
}
public static <T> int binarySearch(T[] x, T key, Comparator<T> comp) {
int low = 0;
int high = x.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int cmp = comp.compare(x[mid], key);
if (cmp < 0) {
low = mid + 1;
}
else if (cmp > 0) {
high = mid - 1;
}
else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
private static <T extends Comparable<T>> int binarySearch(T[] x, int low, int high, T key) {
if(low <= high) {
int mid = low + ((high -low) >> 1);
if(key.compareTo(x[mid]) == 0) {
return mid;
}
else if(key.compareTo(x[mid])< 0) {
return binarySearch(x,l ow, mid - 1, key);
}
else {
return binarySearch(x, mid + 1, high, key);
}
}
return -1;
}
}说明:两个版本一个用递归实现,一个用循环实现。需要注意的是计算中间位置时不应该使用(high+ low) / 2的方式,因为加法运算可能导致整数越界,这里应该使用一下三种方式之一:low+ (high – low) / 2或low + (high – low) >> 1或(low + high) >>> 1(注:>>>是逻辑右移,不带符号位的右移)
139、统计一篇英文文章中单词个数。
答:
import java.io.FileReader;
public class WordCounting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt")) {
int counter = 0;
boolean state = false;
int currentChar;
while((currentChar= fr.read()) != -1) {
if(currentChar== ' ' || currentChar == '\n'
|| currentChar == '\t' || currentChar == '\r') {
state = false;
}
else if(!state) {
state = true;
counter++;
}
}
System.out.println(counter);
}
catch(Exceptione) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
补充:这个程序可能有很多种写法,这里选择的是Dennis M. Ritchie和Brian W. Kernighan老师在他们不朽的著作《The C Programming Language》中给出的代码,向两位老师致敬。下面的代码也是如此。
140、输入年月日,计算该日期是这一年的第几天。
答:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DayCounting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] data = {
{31,28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31},
{31,29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}
};
Scanner sc = newScanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入年月日(1980 11 28): ");
int year = sc.nextInt();
int month = sc.nextInt();
int date = sc.nextInt();
int[] daysOfMonth = data[(year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0)?1 : 0];
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < month -1; i++) {
sum += daysOfMonth[i];
}
sum += date;
System.out.println(sum);
sc.close();
}
}141、约瑟夫环:15个基督教徒和15个非教徒在海上遇险,必须将其中一半的人投入海中,其余的人才能幸免于难,于是30个人围成一圈,从某一个人开始从1报数,报到9的人就扔进大海,他后面的人继续从1开始报数,重复上面的规则,直到剩下15个人为止。结果由于上帝的保佑,15个基督教徒最后都幸免于难,问原来这些人是怎么排列的,哪些位置是基督教徒,哪些位置是非教徒。
答:
public class Josephu {
private static final int DEAD_NUM = 9;
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean[] persons = new boolean[30];
for(int i = 0; i < persons.length; i++) {
persons[i] = true;
}
int counter = 0;
int claimNumber = 0;
int index = 0;
while(counter < 15) {
if(persons[index]) {
claimNumber++;
if(claimNumber == DEAD_NUM) {
counter++;
claimNumber= 0;
persons[index]= false;
}
}
index++;
if(index >= persons.length) {
index= 0;
}
}
for(boolean p : persons) {
if(p) {
System.out.print("基");
}
else {
System.out.print("非");
}
}
}
}142、回文素数:所谓回文数就是顺着读和倒着读一样的数(例如:11,121,1991…),回文素数就是既是回文数又是素数(只能被1和自身整除的数)的数。编程找出11~9999之间的回文素数。
答:
public class PalindromicPrimeNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 11; i <= 9999; i++) {
if(isPrime(i) && isPalindromic(i)) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
public static boolean isPrime(int n) {
for(int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++) {
if(n % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static boolean isPalindromic(int n) {
int temp = n;
int sum = 0;
while(temp > 0) {
sum= sum * 10 + temp % 10;
temp/= 10;
}
return sum == n;
}
}143、全排列:给出五个数字12345的所有排列。
答:
public class FullPermutation {
public static void perm(int[] list) {
perm(list,0);
}
private static void perm(int[] list, int k) {
if (k == list.length) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
System.out.print(list[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}else{
for (int i = k; i < list.length; i++) {
swap(list, k, i);
perm(list, k + 1);
swap(list, k, i);
}
}
}
private static void swap(int[] list, int pos1, int pos2) {
int temp = list[pos1];
list[pos1] = list[pos2];
list[pos2] = temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] x = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
perm(x);
}
}
144、对于一个有N个整数元素的一维数组,找出它的子数组(数组中下标连续的元素组成的数组)之和的最大值。
答:下面给出几个例子(最大子数组用粗体表示):
1) 数组:{ 1, -2, 3,5, -3, 2 },结果是:8
2) 数组:{ 0, -2, 3, 5, -1, 2 },结果是:9
3) 数组:{ -9, -2,-3, -5, -3 },结果是:-2
可以使用动态规划的思想求解:
public class MaxSum {
private static int max(int x, int y) {
return x > y? x: y;
}
public static int maxSum(int[] array) {
int n = array.length;
int[] start = new int[n];
int[] all = new int[n];
all[n - 1] = start[n - 1] = array[n - 1];
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0;i--) {
start[i] = max(array[i], array[i] + start[i + 1]);
all[i] = max(start[i], all[i + 1]);
}
return all[0];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] x1 = { 1, -2, 3, 5,-3, 2 };
int[] x2 = { 0, -2, 3, 5,-1, 2 };
int[] x3 = { -9, -2, -3,-5, -3 };
System.out.println(maxSum(x1)); // 8
System.out.println(maxSum(x2)); // 9
System.out.println(maxSum(x3)); //-2
}
}145、用递归实现字符串倒转
答:
public class StringReverse {
public static String reverse(String originStr) {
if(originStr == null || originStr.length()== 1) {
return originStr;
}
return reverse(originStr.substring(1))+ originStr.charAt(0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(reverse("hello"));
}
}
146、输入一个正整数,将其分解为素数的乘积。
答:
public class DecomposeInteger {
private static List<Integer> list = newArrayList<Integer>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("请输入一个数: ");
Scanner sc = newScanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
decomposeNumber(n);
System.out.print(n + " = ");
for(int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " * ");
}
System.out.println(list.get(list.size() - 1));
}
public static void decomposeNumber(int n) {
if(isPrime(n)) {
list.add(n);
list.add(1);
}
else {
doIt(n, (int)Math.sqrt(n));
}
}
public static void doIt(int n, int div) {
if(isPrime(div) && n % div == 0) {
list.add(div);
decomposeNumber(n / div);
}
else {
doIt(n, div - 1);
}
}
public static boolean isPrime(int n) {
for(int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n);i++) {
if(n % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}147、一个有n级的台阶,一次可以走1级、2级或3级,问走完n级台阶有多少种走法。
答:可以通过递归求解。
public class GoSteps {
public static int countWays(int n) {
if(n < 0) {
return 0;
}
else if(n == 0) {
return 1;
}
else {
return countWays(n - 1) + countWays(n - 2) + countWays(n -3);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(countWays(5)); // 13
}
}148、写一个算法判断一个英文单词的所有字母是否全都不同(不区分大小写)。
答:
public class AllNotTheSame {
public static boolean judge(String str) {
String temp = str.toLowerCase();
int[] letterCounter = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i <temp.length(); i++) {
int index = temp.charAt(i)- 'a';
letterCounter[index]++;
if(letterCounter[index] > 1) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(judge("hello"));
System.out.print(judge("smile"));
}
}149、有一个已经排好序的整数数组,其中存在重复元素,请将重复元素删除掉,例如,A= [1, 1, 2, 2, 3],处理之后的数组应当为A= [1, 2, 3]。
答:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class RemoveDuplication {
public static int[] removeDuplicates(int a[]) {
if(a.length <= 1) {
return a;
}
int index = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if(a[index] != a[i]) {
a[++index] = a[i];
}
}
int[] b = new int[index + 1];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, b, 0, b.length);
return b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 1, 2, 2, 3};
a = removeDuplicates(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}150、给一个数组,其中有一个重复元素占半数以上,找出这个元素。
答:
public class FindMost {
public static <T> T find(T[] x){
T temp = null;
for(int i = 0, nTimes = 0; i< x.length;i++) {
if(nTimes == 0) {
temp= x[i];
nTimes= 1;
}
else {
if(x[i].equals(temp)) {
nTimes++;
}
else {
nTimes--;
}
}
}
return temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[]strs = {"hello","kiss","hello","hello","maybe"};
System.out.println(find(strs));
}
}























 157
157

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








