稀疏数组
应用场景
应用场景:如下图存储五子棋盘数据。原数组中存在大量的无效数据,占据了大量的存储空间,真正有用的数据却少之又少压缩存储可以节省存储空间以避免资源的不必要的浪费,在数据序列化到磁盘时,压缩存储可以提高IO效率
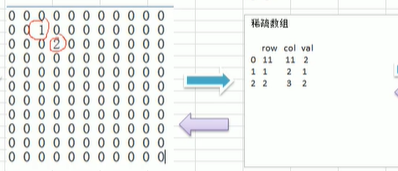
稀疏数组与二维数组间转换
以下代码为稀疏数组的作用以及与二维数组间转换
`package com.ghl.sparseArray;
/**
* @Date:2021/5/16
* @Author:GuoHeLong
* TODO 稀疏数组应用场景1:因为二维数组很多值默认是0,因此记录了很多无意义值->压缩二维数组节省空间其实稀疏数组是一种压缩后的数组,
原数组中存在大量的无效数据,占据了大量的存储空间,真正有用的数据却少之又少压缩存储可以节省存储空间以避免资源的不必要的浪费,在数据序列化到磁盘时,压缩存储可以提高IO效率
*
* TODO 稀疏数组结构(默认第一行记录原始二维数组结构)
* 一下用arr代表"二维数组"
* row column num
* arr的行长度 arr的列长度 arr中有效数据个数
* arr第一个有效值出现行 arr第一个有效值出现列 值
* arr第二个有效值出现行 arr第二个有效值出现列 值
*
* TODO 二维数组转稀疏:
* 1:遍历原始数组,得到有效数据的个数sum
* 2:根据sum创建稀疏数据sparse int[sum+1][3]
* 3: 二维数据有效数据存入稀疏数组
*
* TODO 稀疏数组转二维:
* 1:先读取稀疏数组第一行,根据第一行数据创建原始二维数据
* 2:读取稀疏数组后几行的数据,并赋值给二维数据即可
*/
public class Sparse01 {
//构建原始二维数组
public static int[][] createArray() {
//创建一个原始数组11*11 (可想象成五子棋盘)0表示无子,1:黑子,2:白子
int chessArr1[][] = new int[11][10];
chessArr1[1][2] = 1;
chessArr1[2][3] = 2;
chessArr1[4][5] = 2;
//输出原始数组
System.out.println("========================输出二维数组===============================");
printUtil(chessArr1);
return chessArr1;
}
//二维数组转稀疏数组
public static int[][] arryToSpare() {
int[][] array = createArray();
System.out.println("============================初始化稀疏数组================================");
//1)初始化稀疏数组
int sum = 0;
for (int[] ints : array) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
if (anInt > 0) {
sum++;
}
}
}
int spareArray[][] = new int[sum + 1][3];
spareArray[0][0] = array.length;
spareArray[0][1] = array[array.length - 1].length;
spareArray[0][2] = sum;
printUtil(spareArray);
System.out.println("============================二维数组->稀疏数组==============================");
//2)转换
int row = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array[i].length; j++) {
if (array[i][j] != 0) {
spareArray[row + 1][0] = i;
spareArray[row + 1][1] = j;
spareArray[row + 1][2] = array[i][j];
row++;
}
}
}
//输出稀疏数组
printUtil(spareArray);
return spareArray;
}
//稀疏数组转为二维数组
public static void sparseToArr() {
int[][] spare = arryToSpare();
//先恢复二维数组结构
int chessArr[][] = new int[spare[0][0]][spare[0][1]];
//赋值给二维数组
for (int i = 1; i < spare.length; i++) {
chessArr[spare[i][0]][spare[i][1]] = spare[i][2];
}
System.out.println("=================================稀疏数组->二维数组==================================");
printUtil(chessArr);
}
//打印工具
public static void printUtil(int[][] arrays) {
for (int[] ints : arrays) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", anInt);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建数组
//createArray();
//二维数组转稀疏数组
//arryToSpare();
//稀疏数组转二维数组
sparseToArr();
}
}
`
数组队列
应用场景示例:队列,挂号,排队等
简单的队列指针图

数组实现单向队列
简单代码示例
/**
* @Date:2021/5/17
* @Author:GuoHeLong
*/
public class ArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个队列
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(3);
char key = ' ';//用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
//输出一个菜单
while (loop){
System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit): 退出队列");
System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get): 从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key){
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输入一个数字");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n",res);
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
try {
int res = queue.headQueue();
System.out.println("头部数据为:"+res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
}
}
}
//使用数组模拟队列
static class ArrayQueue {
private int maxSize; //表示数组最大容量
private int front; //队列头
private int rear; //队列尾
private int[] arr; //该数组用于存放数据,模拟队列
//创建队列的容器
public ArrayQueue(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize = arrMaxSize;
arr = new int[arrMaxSize];
front = -1; //指向队列头部,分析出front是指向队列头的前一个位置
rear = -1; //指向队列尾的具体的数据(就是队列最后一个数据)
}
//判断队列满
public boolean isFull() {
return rear == maxSize - 1;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
//添加队列到队列
public void addQueue(int n) {
//判断队列是否满
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满,不能加入数据···");
return;
}
rear++; //让rear后移
arr[rear] = n;
}
//出队列
public int getQueue() {
//判断队列空
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据");
}
front++; //front后移
return arr[front];
}
//显示队列的所有数据
public void showQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列空的没有数据...");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i, arr[i]);
}
}
//查看队列头数据
public int headQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,没有数据");
}
return arr[front + 1];
}
}
}
数组实现双向队列
以上代码虽然简单实现了队列。但是只能使用一次不能达到复用效果,造成内存空间的浪费


public class CircleArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个队列
CircleArray queue = new CircleArray(3);
char key = ' ';//用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
//输出一个菜单
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit): 退出队列");
System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get): 从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case 's':
queue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("输入一个数字");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
try {
int res = queue.headQueue();
System.out.println("头部数据为:" + res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
}
}
}
static class CircleArray {
private int maxSize; // 表示数组的最大容量
// front 变量的含义做一个调整: front 就指向队列的第一个元素, 也就是说 arr[front] 就是队列的第一个元素
// front 的初始值 = 0
private int front;
// rear 变量的含义做一个调整:rear 指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置. 因为希望空出一个空间做为约定.
// rear 的初始值 = 0
private int rear; // 队列尾
private int[] arr; // 该数据用于存放数据, 模拟队列
public CircleArray(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize = arrMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
}
// 判断队列是否满
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
// 添加数据到队列
public void addQueue(int n) {
// 判断队列是否满
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列满,不能加入数据~");
return;
}
// 直接将数据加入
arr[rear] = n;
// 将 rear 后移, 这里必须考虑取模
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
System.out.println("===========此时rear指针为"+rear);
}
// 获取队列的数据, 出队列
public int getQueue() {
// 判断队列是否空
if (isEmpty()) {
// 通过抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据");
}
// 这里需要分析出 front是指向队列的第一个元素
// 1. 先把 front 对应的值保留到一个临时变量
// 2. 将 front 后移, 考虑取模
// 3. 将临时保存的变量返回
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
System.out.println("===========此时front指针为"+front);
return value;
}
// 显示队列的所有数据
public void showQueue() {
// 遍历
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列空的,没有数据~~");
return;
}
// 思路:从front开始遍历,遍历多少个元素
// 动脑筋
for (int i = front; i < front + size(); i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i % maxSize, arr[i % maxSize]);
}
}
// 求出当前队列有效数据的个数
public int size() {
// rear = 2
// front = 1
// maxSize = 3
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
// 显示队列的头数据, 注意不是取出数据
public int headQueue() {
// 判断
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空的,没有数据~~");
}
return arr[front];
}
}
}






















 1365
1365











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








