本文讲述了Tomcat的常见线程的功能、名称、线程池和配置等信息,其中源码来自于Tomcat 6.0.18。
Work线程
功能
HTTP请求的处理线程(非NIO)。当有新的http请求进来后,则会从线程池中获得一个线程Work对象,调用Work.assign函数,将新到的http请求分配给这个线程。
名称
名称是http-[IpAddr]-[Port]-[Number],如http-0.0.0.0-8080-1
这个可以从Http11Protocol中的setName函数和Worker中的start方法得知这个命名方式。
| 1 | public String getName() { |
| 2 | String encodedAddr = ""; |
| 3 | if (getAddress() != null) { |
| 4 | encodedAddr = "" + getAddress(); |
| 5 | if (encodedAddr.startsWith("/" )) |
| 6 | encodedAddr = encodedAddr.substring(1); |
| 7 | encodedAddr = URLEncoder. encode(encodedAddr) + "-"; |
| 8 | } |
| 9 | |
| 10 | return ("http-" + encodedAddr + endpoint.getPort()); |
| 11 | } |
| 12 | |
| 13 |
线程类:JIoEndpoint.Work
在JIoEndpoint.Work的run方法中调用await方法等待并获得下一个socket,传给handle进行处理。在await方法中,如果没有分配新的客户端请求socket, available变量会一直false,并会循环调用wait方法阻塞自己,同时释放Work对象的锁,直到Acceptor线程获得新的socket, 并调用Work.assign方法分配给该工作线程。 这时availble变量才为设置为true,并且await方法会返回分配的socket对象。
| 1 | protected class Worker implements Runnable { |
| 2 | |
| 3 | protected Thread thread = null; |
| 4 | |
| 5 | protected boolean available = false; |
| 6 | |
| 7 | protected Socket socket = null; |
| 8 | |
| 9 | /** |
| 10 | |
| 11 | * Process an incoming TCP/IP connection on the specified socket. Any |
| 12 | |
| 13 | * exception that occurs during processing must be logged and swallowed. |
| 14 | |
| 15 | * <b>NOTE</b> : This method is called from our Connector's thread. We |
| 16 | |
| 17 | * must assign it to our own thread so that multiple simultaneous |
| 18 | |
| 19 | * requests can be handled. |
| 20 | |
| 21 | * |
| 22 | |
| 23 | * @param socket TCP socket to process |
| 24 | |
| 25 | */ |
| 26 | |
| 27 | synchronized void assign(Socket socket ) { |
| 28 | |
| 29 | // Wait for the Processor to get the previous Socket |
| 30 | |
| 31 | while (available ) { |
| 32 | |
| 33 | try { |
| 34 | |
| 35 | wait(); |
| 36 | |
| 37 | } catch (InterruptedException e) { |
| 38 | |
| 39 | } |
| 40 | |
| 41 | } |
| 42 | |
| 43 | // Store the newly available Socket and notify our thread |
| 44 | |
| 45 | this.socket = socket ; |
| 46 | |
| 47 | available = true ; |
| 48 | |
| 49 | notifyAll(); |
| 50 | |
| 51 | } |
| 52 | |
| 53 | /** |
| 54 | |
| 55 | * 等待新分配的Socket |
| 56 | |
| 57 | */ |
| 58 | |
| 59 | private synchronized Socket await() { |
| 60 | |
| 61 | //等待Connector提供新的Socket |
| 62 | |
| 63 | while (!available ) { |
| 64 | |
| 65 | try { |
| 66 | |
| 67 | wait(); |
| 68 | |
| 69 | } catch (InterruptedException e) { |
| 70 | |
| 71 | } |
| 72 | |
| 73 | } |
| 74 | |
| 75 | //通知Connector我们已经接收到这个Socket |
| 76 | |
| 77 | Socket socket = this.socket ; |
| 78 | |
| 79 | available = false ; |
| 80 | |
| 81 | notifyAll(); |
| 82 | |
| 83 | return (socket); |
| 84 | |
| 85 | } |
| 86 | |
| 87 | /** |
| 88 | |
| 89 | * 后台线程,监听进入的TCP/IP连接,并传递给合适的处理模块 |
| 90 | |
| 91 | */ |
| 92 | |
| 93 | public void run() { |
| 94 | |
| 95 | // Process requests until we receive a shutdown signal |
| 96 | |
| 97 | //处理请求直到我们接收到shutdown信号 |
| 98 | |
| 99 | while (running ) { |
| 100 | |
| 101 | //等待下一个分配的socket |
| 102 | |
| 103 | Socket socket = await(); |
| 104 | |
| 105 | if (socket == null) |
| 106 | |
| 107 | continue; |
| 108 | |
| 109 | //设置socket的选项,并处理socket |
| 110 | |
| 111 | if (!setSocketOptions(socket) || !handler.process(socket)) { |
| 112 | |
| 113 | // 关闭socket |
| 114 | |
| 115 | try { |
| 116 | |
| 117 | socket.close(); |
| 118 | |
| 119 | } catch (IOException e) { |
| 120 | |
| 121 | } |
| 122 | |
| 123 | } |
| 124 | |
| 125 | // Finish up this request |
| 126 | |
| 127 | socket = null; |
| 128 | |
| 129 | //回收线程 |
| 130 | |
| 131 | recycleWorkerThread( this); |
| 132 | |
| 133 | } |
| 134 | |
| 135 | } |
| 136 | |
| 137 | /** |
| 138 | |
| 139 | * 开启后台处理线程 |
| 140 | |
| 141 | */ |
| 142 | |
| 143 | public void start() { |
| 144 | |
| 145 | thread = new Thread(this); |
| 146 | |
| 147 | thread.setName(getName() + "-" + (++curThreads)); |
| 148 | |
| 149 | thread.setDaemon(true); |
| 150 | |
| 151 | thread.start(); |
| 152 | |
| 153 | } |
| 154 | |
| 155 | } |
| 156 | |
| 157 |
所属线程池
所属线程池实现功能比较简单,是内嵌到JIoEndpoint类中的实现。基本数据结构是一个工作线程栈JIoEndpoint.WorkerStack。
线程池主要属性
curThreadsBusy:当前繁忙线程数
curThreads:当前工作线程数
maxThreads:最大工作线程数
线程池启动
这个线程池实现功能比较简单,不需要太多启动功能。可以从JIoEndpoint类的start方法看到,启动初始化需要做的事是分配线程栈worker空间。
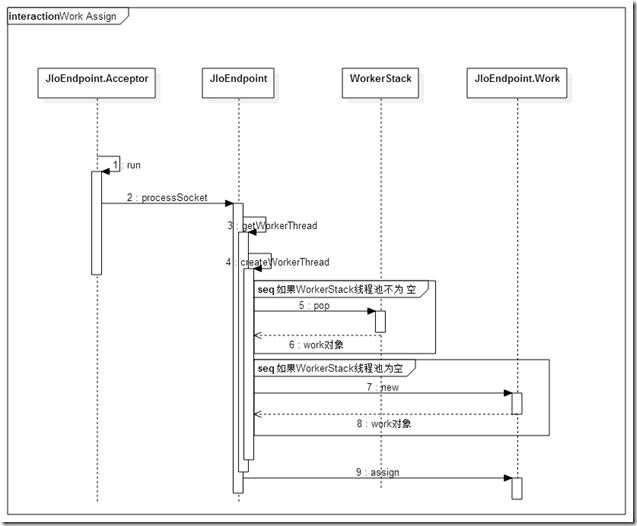
任务分配时序图
任务分配
通过JIoEndPoint中createWorkerThread方法获得一个工作线程。如在工作线程栈workers中获得一个线程对象,如果线程栈已经是空的,并且当前线程数量curThreads还小于最大线程数maxThreads,那么就创建一个新的工作线程。然后调用Work.assign方法分配给工作线程。
| 1 | protected Worker createWorkerThread() { |
| 2 | |
| 3 | //获得工作线程栈workers的锁 |
| 4 | |
| 5 | synchronized (workers ) { |
| 6 | |
| 7 | //如果工作线程栈里有线程则返回栈顶工作线程 |
| 8 | |
| 9 | if (workers .size() > 0) { |
| 10 | |
| 11 | curThreadsBusy++; |
| 12 | |
| 13 | return workers .pop(); |
| 14 | |
| 15 | } |
| 16 | |
| 17 | //如果工作线程栈里没有线程,maxThreads大于0且当前线程数小于最大线程数,则创建一个新的线程 |
| 18 | |
| 19 | if ((maxThreads > 0) && (curThreads < maxThreads)) { |
| 20 | |
| 21 | curThreadsBusy++; |
| 22 | |
| 23 | return (newWorkerThread()); |
| 24 | |
| 25 | } else { |
| 26 | |
| 27 | //如果maxThreads小于0,则说明没有限制,创建新的线程 |
| 28 | |
| 29 | if (maxThreads < 0) { |
| 30 | |
| 31 | curThreadsBusy++; |
| 32 | |
| 33 | return (newWorkerThread()); |
| 34 | |
| 35 | } else { |
| 36 | |
| 37 | return (null); |
| 38 | |
| 39 | } |
| 40 | |
| 41 | } |
| 42 | |
| 43 | } |
| 44 | |
| 45 | } |
| 46 | |
| 47 |
工作线程回收
JIoEndPoint中recycleWorkerThread方法是回收工作线程,当http请求处理完成,则调用该方法回收工作线程。该方法首先获得worker对象锁,然后调用workers.push方法将工作线程压入工作线程栈中,接着将当前繁忙线程数减1,最后调用workers.notify方法。
| 1 | protected void recycleWorkerThread(Worker workerThread) { |
| 2 | |
| 3 | synchronized (workers ) { |
| 4 | |
| 5 | workers.push(workerThread); |
| 6 | |
| 7 | curThreadsBusy--; |
| 8 | |
| 9 | workers.notify(); |
| 10 | |
| 11 | } |
| 12 | } |
配置
在Tomcat中配置文件Server.xml中的Connector属性配置最大线程数maxThreads。
例如:
<Connector port="8080"
maxThreads="150"
……/>
Acceptor线程
功能
获得HTTP请求socket。并从工作线程池中获得一个线程,将socket分配给一个工作线程。
名称
http-[IPAddr]-[Port]-Acceptor-[Number],如http-0.0.0.0-8080-Acceptor-1
线程类:JIoEndpoint.Acceptor
所属线程池
无
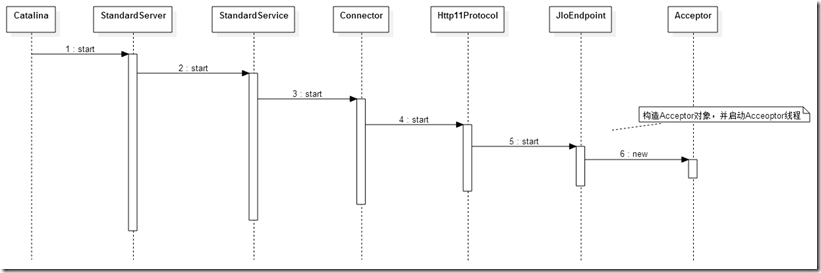
启动时序图
在启动时会开启Accepter线程,时序图如下:
线程启动
如上时序图,在Tomcat启动过程会调用JIoEndpoint类的start方法,会创建并启动acceptorThreadCount个Acceptor线程。
| 1 | public void start() throws Exception { |
| 2 | |
| 3 | // Initialize socket if not done before |
| 4 | |
| 5 | if (!initialized ) { |
| 6 | |
| 7 | init(); |
| 8 | |
| 9 | } |
| 10 | |
| 11 | if (!running ) { |
| 12 | |
| 13 | running = true ; |
| 14 | |
| 15 | paused = false ; |
| 16 | |
| 17 | //如果没有配置executor线程池,则创建工作线程栈worker, 就是上例中的线程池的工作线程栈。 |
| 18 | |
| 19 | if (executor == null) { |
| 20 | |
| 21 | workers = new WorkerStack(maxThreads); |
| 22 | |
| 23 | } |
| 24 | |
| 25 | //启动acceptor线程 |
| 26 | |
| 27 | for (int i = 0; i < acceptorThreadCount; i++) { |
| 28 | |
| 29 | Thread acceptorThread = new Thread(new Acceptor(), getName() + "-Acceptor-" + i); |
| 30 | |
| 31 | acceptorThread.setPriority( threadPriority); |
| 32 | |
| 33 | acceptorThread.setDaemon( daemon); |
| 34 | |
| 35 | acceptorThread.start(); |
| 36 | |
| 37 | } |
| 38 | |
| 39 | } |
| 40 | |
| 41 | } |
属性
acceptorThreadCount:开启的acceptor线程数,从源码看到这个值并没有通过配置设置,而是固定的值为1
配置
无
Main主线程
功能
完成装配、初始化和启动,之后会开启SocketServer,并循环等待命令,如shutdown。
名称:Main
线程类:Main主线程
所属线程池:
无
catalina-exec线程
功能
StandardThreadExecutor的工作线程,功能和Work线程类似。如果为Connector配置了Executor,则会使用该线程处理http请求。
线程类:ThreadPoolExecutor.Work
所属线程池:StandardThreadExecutor
类名是org.apache.catalina.core.StandardThreadExecutor,该线程池类通过代理设计模式对Java Concurrent包中的线程池ThreadPoolExecutor进行简单的封装。并实现了Lifecycle接口,以及增加了发送消息的功能。
属性
minSpareThreads:最小空闲线程数
maxThreads:最大线程数
maxIdleTime:最大空闲时间
配置
在Server.xml文件中配置Executor节点,支持如下属性,
| Name | Executor的名称 |
| namePrefix | 工作线程前缀 |
| maxThreads | 最大线程数 |
| minSpareThreads | 最小空闲线程数 |
| maxIdleTime | 最大空闲时间 |
并在Connector节点配置executor,并指定为Executor的名称。
例如:
<Executor name="tomcatThreadPool" namePrefix="catalina-exec-" maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="4" maxIdleTime="200"/>
<Connector Address="0.0.0.0" port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"executor="tomcatThreadPool".../>
TP-Processor线程
功能
AJP协议中Servlet容器的处理线程
名称
TP-Processor-[Number],例如TP-Processor-1
线程类:ThreadPool.ControlRunnable
所属线程池:org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPool
该线程池还会启动一个TP-Monitor线程监控空闲线程。在TheadPool会有一个ControlRunnable数组保存线程池中的工作线程。使用该线程池需要先调用start方法,进行ControlRunnable数组初始化,minSpareThreads个空闲线程的创建,以及TP-Monitor线程的启动。
属性
maxThreads:最大线程数
minSpareThreads:最小空闲线程数
maxSpareThreads: 最大空闲线程数
线程池的启动
通过ThreadPool.start方法,该方法会分配线程数组pool,并打开minSpareThreads空线程。如果最大空闲线程数小于最大线程数,则启动TP-Monitor线程。
| 1 | public synchronized void start() { |
| 2 | |
| 3 | stopThePool=false ; |
| 4 | |
| 5 | currentThreadCount = 0; |
| 6 | |
| 7 | currentThreadsBusy = 0; |
| 8 | |
| 9 | adjustLimits(); |
| 10 | |
| 11 | pool = new ControlRunnable[maxThreads]; |
| 12 | |
| 13 | //启动minSpareThreads空闲线程 |
| 14 | |
| 15 | openThreads( minSpareThreads); |
| 16 | |
| 17 | //如果最大空闲线程数小于最大线程数,则启动TP-Monitor线程 |
| 18 | |
| 19 | if (maxSpareThreads < maxThreads) { |
| 20 | |
| 21 | monitor = new MonitorRunnable(this); |
| 22 | |
| 23 | } |
| 24 | |
| 25 | } |
任务分配
使用ThreadPool.runIt来运行新的任务,在该方法中,会调用findControlRunnable方法来获得一个工作线程。需要注意的是调用方不需要调用额外的方法来回收线程。当ControlRunnable线程完成指定的任务会自动将线程回收到线程池中。
findControlRunnable是ThreadPool线程池的关键方法,它提供了从线程池中获得一个工作线程,并将相应的计数调整,如 tpOpen,currentThreadsBusy。
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | |
| 3 | * Executes a given Runnable on a thread in the pool, block if needed. |
| 4 | |
| 5 | */ |
| 6 | |
| 7 | public void runIt(ThreadPoolRunnable r) { |
| 8 | |
| 9 | if(null == r) { |
| 10 | |
| 11 | throw new NullPointerException(); |
| 12 | |
| 13 | } |
| 14 | |
| 15 | //从线程池中获得一个工作线程 |
| 16 | |
| 17 | ControlRunnable c = findControlRunnable(); |
| 18 | |
| 19 | //运行任务 |
| 20 | |
| 21 | c.runIt(r); |
| 22 | |
| 23 | } |
| 24 | |
| 25 | private ControlRunnable findControlRunnable() { |
| 26 | |
| 27 | ControlRunnable c= null; |
| 28 | |
| 29 | if ( stopThePool ) { |
| 30 | |
| 31 | throw new IllegalStateException(); |
| 32 | |
| 33 | } |
| 34 | |
| 35 | //从线程池中获得一个空闲线程 |
| 36 | |
| 37 | synchronized(this ) { |
| 38 | |
| 39 | //当前繁忙线程和当前线程数相同,则表示所有的开启线程都是繁忙的。 |
| 40 | |
| 41 | while (currentThreadsBusy == currentThreadCount) { |
| 42 | |
| 43 | //如果当前线程数比最大线程数小 |
| 44 | |
| 45 | if (currentThreadCount < maxThreads) { |
| 46 | |
| 47 | // Not all threads were open, |
| 48 | |
| 49 | // Open new threads up to the max number of idel threads |
| 50 | |
| 51 | |
| 52 | int toOpen = currentThreadCount + minSpareThreads; |
| 53 | |
| 54 | openThreads(toOpen); |
| 55 | |
| 56 | } else { |
| 57 | |
| 58 | logFull(log, currentThreadCount, maxThreads ); |
| 59 | |
| 60 | //线程数已经满了,等待线程成为空闲线程 |
| 61 | |
| 62 | try { |
| 63 | |
| 64 | this.wait(); |
| 65 | |
| 66 | } |
| 67 | |
| 68 | // was just catch Throwable -- but no other |
| 69 | |
| 70 | // exceptions can be thrown by wait, right? |
| 71 | |
| 72 | // So we catch and ignore this one, since |
| 73 | |
| 74 | // it'll never actually happen, since nowhere |
| 75 | |
| 76 | // do we say pool.interrupt(). |
| 77 | |
| 78 | catch(InterruptedException e) { |
| 79 | |
| 80 | log.error("Unexpected exception" , e); |
| 81 | |
| 82 | } |
| 83 | |
| 84 | if( log .isDebugEnabled() ) { |
| 85 | |
| 86 | log.debug("Finished waiting: CTC=" +currentThreadCount + |
| 87 | |
| 88 | ", CTB=" + currentThreadsBusy ); |
| 89 | |
| 90 | } |
| 91 | |
| 92 | // Pool was stopped. Get away of the pool. |
| 93 | |
| 94 | if( stopThePool ) { |
| 95 | |
| 96 | break; |
| 97 | |
| 98 | } |
| 99 | |
| 100 | } |
| 101 | |
| 102 | } |
| 103 | |
| 104 | //线程池已经关闭,离开线程池 |
| 105 | |
| 106 | if(0 == currentThreadCount || stopThePool) { |
| 107 | |
| 108 | throw new IllegalStateException(); |
| 109 | |
| 110 | } |
| 111 | |
| 112 | //到了这里,表示有空闲线程可用 |
| 113 | |
| 114 | //取出数组pool中最后一个线程 |
| 115 | |
| 116 | int pos = currentThreadCount - currentThreadsBusy - 1; |
| 117 | |
| 118 | c = pool[pos]; |
| 119 | |
| 120 | pool[pos] = null; |
| 121 | |
| 122 | //繁忙线程数加1 |
| 123 | |
| 124 | currentThreadsBusy++; |
| 125 | |
| 126 | } |
| 127 | |
| 128 | return c; |
| 129 | |
| 130 | } |
| 131 | |
| 132 | /** |
| 133 | |
| 134 | *开启线程 |
| 135 | |
| 136 | * @param toOpen 我们将要开启的线程数 |
| 137 | |
| 138 | */ |
| 139 | |
| 140 | protected void openThreads(int toOpen) { |
| 141 | |
| 142 | if(toOpen > maxThreads ) { |
| 143 | |
| 144 | toOpen = maxThreads; |
| 145 | |
| 146 | } |
| 147 | |
| 148 | //创建空闲线程 |
| 149 | |
| 150 | for(int i = currentThreadCount ; i < toOpen ; i++) { |
| 151 | |
| 152 | //需要减去currentThreadsBusy, 因为繁忙线程已经从pool数组中移出 |
| 153 | |
| 154 | pool[i - currentThreadsBusy ] = new ControlRunnable( this); |
| 155 | |
| 156 | } |
| 157 | |
| 158 | currentThreadCount = toOpen; |
| 159 | |
| 160 | } |
工作线程回收
通过ThreadPool.returnController方法回收线程。该方法会将繁忙线程数currentThreadsBusy减1,并将线程回收到线程数组中。
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | |
| 3 | * 将线程返还线程池 |
| 4 | |
| 5 | */ |
| 6 | protected synchronized void returnController (ControlRunnable c) { |
| 7 | |
| 8 | if(0 == currentThreadCount || stopThePool) { |
| 9 | |
| 10 | c.terminate(); |
| 11 | |
| 12 | return; |
| 13 | |
| 14 | } |
| 15 | |
| 16 | // atomic |
| 17 | |
| 18 | currentThreadsBusy--; |
| 19 | |
| 20 | //将线程回收到pool数组中 |
| 21 | |
| 22 | pool[currentThreadCount - currentThreadsBusy - 1] = c; |
| 23 | |
| 24 | //notify会唤醒在等待线程资源 |
| 25 | |
| 26 | notify(); |
| 27 | |
| 28 | } |
配置
在Server.xml文件中配置Connector属性
| maxThreads | 最大线程数 |
| minSpareThreads | 最小空闲线程数 |
| maxSpareThreads | 最大空闲线程数 |
例如:
<Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" maxThreads="800" minSpareThreads="50" maxSpareThreads="500" />
TP-Monitor线程
功能
监控ThreadPool线程池的空闲线程,回收比最大空闲线程数多出的空闲线程。
线程类:ThreadPool.MonitorRunnable
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | |
| 3 | * 定期清理空闲线程 |
| 4 | |
| 5 | */ |
| 6 | |
| 7 | public static class MonitorRunnable implements Runnable { |
| 8 | |
| 9 | ThreadPool p; |
| 10 | |
| 11 | Thread t; |
| 12 | |
| 13 | int interval =WORK_WAIT_TIMEOUT; |
| 14 | |
| 15 | boolean shouldTerminate ; |
| 16 | |
| 17 | MonitorRunnable(ThreadPool p) { |
| 18 | |
| 19 | this.p =p; |
| 20 | |
| 21 | this.start(); |
| 22 | |
| 23 | } |
| 24 | |
| 25 | public void start() { |
| 26 | |
| 27 | shouldTerminate = false ; |
| 28 | |
| 29 | t = new Thread(this); |
| 30 | |
| 31 | t.setDaemon( p.getDaemon() ); |
| 32 | |
| 33 | t.setName( p.getName() + "-Monitor"); |
| 34 | |
| 35 | t.start(); |
| 36 | |
| 37 | } |
| 38 | |
| 39 | public void setInterval(int i ) { |
| 40 | |
| 41 | this.interval =i; |
| 42 | |
| 43 | } |
| 44 | |
| 45 | public void run() { |
| 46 | |
| 47 | while(true ) { |
| 48 | |
| 49 | try { |
| 50 | |
| 51 | //Wait一段时间 |
| 52 | |
| 53 | synchronized(this ) { |
| 54 | |
| 55 | this.wait(interval ); |
| 56 | |
| 57 | } |
| 58 | |
| 59 | // Check if should terminate. |
| 60 | |
| 61 | // termination happens when the pool is shutting down. |
| 62 | |
| 63 | if(shouldTerminate ) { |
| 64 | |
| 65 | break; |
| 66 | |
| 67 | } |
| 68 | |
| 69 | //回收空闲线程 |
| 70 | |
| 71 | p.checkSpareControllers(); |
| 72 | |
| 73 | } catch(Throwable t) { |
| 74 | |
| 75 | ThreadPool. log.error("Unexpected exception" , t); |
| 76 | |
| 77 | } |
| 78 | |
| 79 | } |
| 80 | |
| 81 | } |
| 82 | |
| 83 | public void stop() { |
| 84 | |
| 85 | this.terminate(); |
| 86 | |
| 87 | } |
| 88 | |
| 89 | /** 停止monitor线程 |
| 90 | |
| 91 | */ |
| 92 | |
| 93 | public synchronized void terminate() { |
| 94 | |
| 95 | shouldTerminate = true ; |
| 96 | |
| 97 | this.notify(); |
| 98 | |
| 99 | } |
| 100 | |
| 101 | } |
ThreadPool.checkSpareControllers方法,用来被TP-Monitor线程调用回收工作线程。
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | |
| 3 | * 被TP-Monitor线程用来回收线程 |
| 4 | |
| 5 | */ |
| 6 | |
| 7 | protected synchronized void checkSpareControllers() { |
| 8 | |
| 9 | if(stopThePool ) { |
| 10 | |
| 11 | return; |
| 12 | |
| 13 | } |
| 14 | |
| 15 | //如果当前空闲线程数大于最大空闲线程数 |
| 16 | |
| 17 | if((currentThreadCount - currentThreadsBusy) > maxSpareThreads) { |
| 18 | |
| 19 | //回收比最大空闲线程数多出的空闲线程 |
| 20 | |
| 21 | int toFree = currentThreadCount - |
| 22 | |
| 23 | currentThreadsBusy - |
| 24 | |
| 25 | maxSpareThreads; |
| 26 | |
| 27 | for(int i = 0 ; i < toFree ; i++) { |
| 28 | |
| 29 | ControlRunnable c = pool[currentThreadCount - currentThreadsBusy - 1]; |
| 30 | |
| 31 | c.terminate(); |
| 32 | |
| 33 | pool[currentThreadCount - currentThreadsBusy - 1] = null; |
| 34 | |
| 35 | currentThreadCount --; |
| 36 | |
| 37 | } |
| 38 | |
| 39 | } |
| 40 | |
| 41 | } |
所属线程池
ThreadPool线程池
ContainerBackgroundProcessor线程
功能
容器后台线程,只有设置backgroundProcessorDelay大于0的容器才会启动ContainerBackgroundProcessor线程。该线程会调用当前容器的backgroundProcess方法,并且递归调用 backgroundProcessorDelay值小于等于0的子容器的方法。
从源码中看到只有StandardEngine设置了这个backgroundProcessorDelay值为10,所以只有StandardEngine容器启动ContainerBackgroundProcessor线程, 而其它StandardHost, StandardContext设置的值都是-1。
| 1 | /** |
| 2 | |
| 3 | * 创建一个新的StandardEngine组件,并绑定默认的基础Valve。 |
| 4 | |
| 5 | */ |
| 6 | |
| 7 | public StandardEngine() { |
| 8 | |
| 9 | super(); |
| 10 | |
| 11 | pipeline.setBasic(new StandardEngineValve()); |
| 12 | |
| 13 | /* Set the jmvRoute using the system property jvmRoute */ |
| 14 | |
| 15 | try { |
| 16 | |
| 17 | setJvmRoute(System. getProperty("jvmRoute")); |
| 18 | |
| 19 | } catch(Exception ex) { |
| 20 | |
| 21 | } |
| 22 | |
| 23 | // Engine将拥有reloading线程 |
| 24 | |
| 25 | backgroundProcessorDelay = 10; |
| 26 | |
| 27 | } |
线程类:ContainerBase.ContainerBackgroundProcessor
| 1 | /* |
| 2 | |
| 3 | * ContainerBase的保护线程类,调用当前容器的backgroundProcess方法,并在一个固定延时后, |
| 4 | |
| 5 | * 用它的子容器的backgroundProcess方法 |
| 6 | |
| 7 | */ |
| 8 | |
| 9 | protected class ContainerBackgroundProcessor implements Runnable { |
| 10 | |
| 11 | public void run() { |
| 12 | |
| 13 | while (!threadDone ) { |
| 14 | |
| 15 | try { |
| 16 | |
| 17 | Thread. sleep(backgroundProcessorDelay * 1000L); |
| 18 | |
| 19 | } catch (InterruptedException e) { |
| 20 | |
| 21 | ; |
| 22 | |
| 23 | } |
| 24 | |
| 25 | if (!threadDone ) { |
| 26 | |
| 27 | //获得当前容器,作为父容器 |
| 28 | |
| 29 | Container parent = (Container) getMappingObject(); |
| 30 | |
| 31 | ClassLoader cl = |
| 32 | |
| 33 | Thread. currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); |
| 34 | |
| 35 | if (parent.getLoader() != null) { |
| 36 | |
| 37 | cl = parent.getLoader().getClassLoader(); |
| 38 | |
| 39 | } |
| 40 | |
| 41 | //处理父容器和所有的子容器 |
| 42 | |
| 43 | processChildren(parent, cl); |
| 44 | |
| 45 | } |
| 46 | |
| 47 | } |
| 48 | |
| 49 | } |
| 50 | |
| 51 | //处理父容器和所有的子容器 |
| 52 | |
| 53 | protected void processChildren(Container container, ClassLoader cl) { |
| 54 | |
| 55 | try { |
| 56 | |
| 57 | //如果父容器的loader不为null,则将当前线程的上下文类加载器contextClassLoader设置为父容器 |
| 58 | |
| 59 | //的loader的类加载器 |
| 60 | |
| 61 | if (container.getLoader() != null) { |
| 62 | |
| 63 | Thread. currentThread().setContextClassLoader |
| 64 | |
| 65 | (container.getLoader().getClassLoader()); |
| 66 | |
| 67 | } |
| 68 | |
| 69 | //调用父容器的backgroundProcess方法 |
| 70 | |
| 71 | container.backgroundProcess(); |
| 72 | |
| 73 | } catch (Throwable t) { |
| 74 | |
| 75 | log.error("Exception invoking periodic operation: " , t); |
| 76 | |
| 77 | } finally { |
| 78 | |
| 79 | Thread. currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl); |
| 80 | |
| 81 | } |
| 82 | |
| 83 | //获得父容器的所有子容器 |
| 84 | |
| 85 | Container[] children = container.findChildren(); |
| 86 | |
| 87 | for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) { |
| 88 | |
| 89 | //如果子容器的backgroundProcessorDelay小于等于0,则递归处理子容器 |
| 90 | |
| 91 | if (children[i].getBackgroundProcessorDelay() <= 0) { |
| 92 | |
| 93 | processChildren(children[i], cl); |
| 94 | |
| 95 | } |
| 96 | |
| 97 | } |
| 98 | |
| 99 | } |
| 100 | |
| 101 | } |
所属线程池
无










 本文详细解析了Tomcat服务器中的各种线程模型,包括Work线程、Acceptor线程、Main主线程、catalina-exec线程、TP-Processor线程、TP-Monitor线程及ContainerBackgroundProcessor线程的功能、命名、线程类、所属线程池及其配置。
本文详细解析了Tomcat服务器中的各种线程模型,包括Work线程、Acceptor线程、Main主线程、catalina-exec线程、TP-Processor线程、TP-Monitor线程及ContainerBackgroundProcessor线程的功能、命名、线程类、所属线程池及其配置。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








