IO流是指在计算机中进行输入和输出操作的一种方式,用于读取和写入数据。IO流主要用于处理数据传输,可以将数据从一个地方传送到另一个地方,例如从内存到硬盘,从网络到内存等。IO流在编程中非常常见,特别是在文件操作和网络通信中。
一、IO流小知识
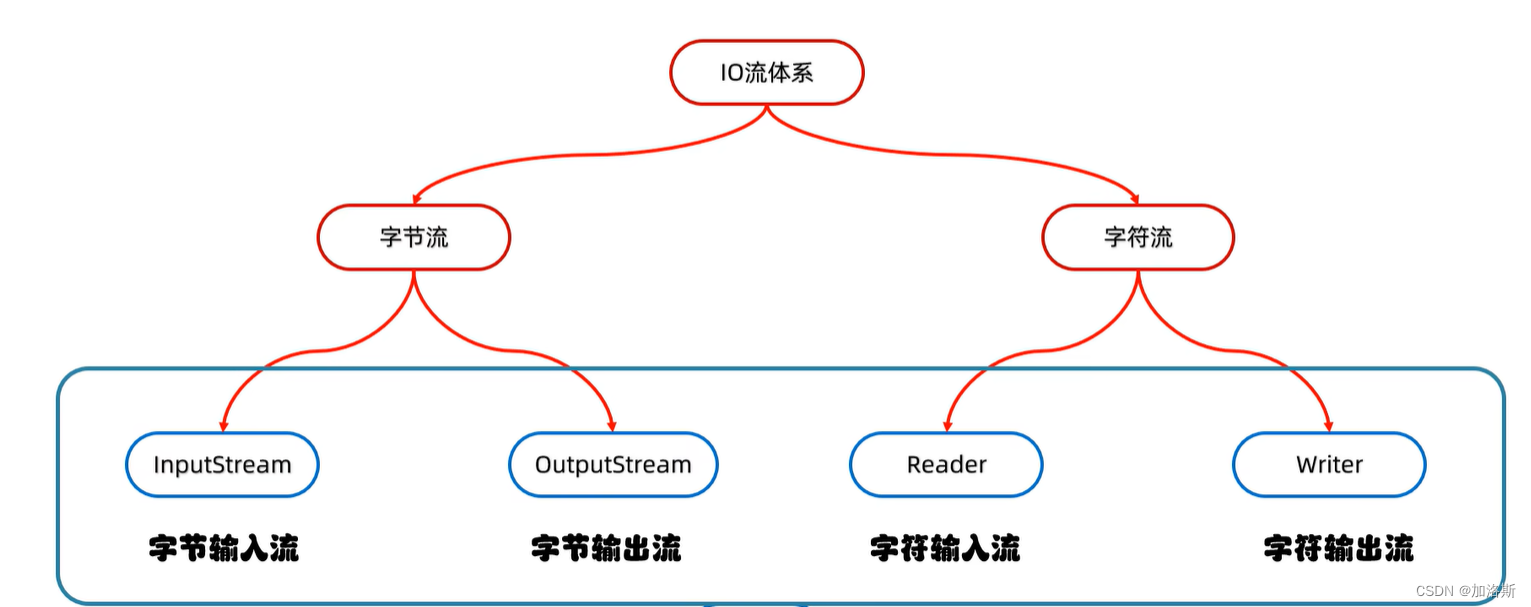
1.1、 IO流的分类
IO流主要分为以下几类:
-
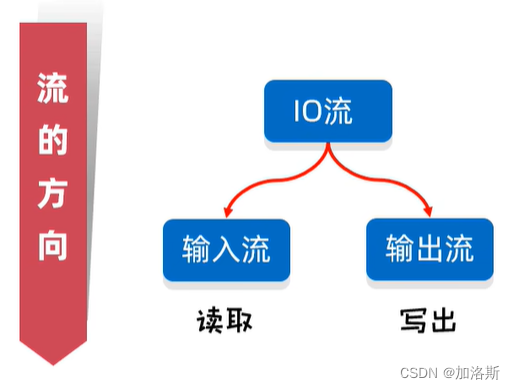
按数据流方向分类:
- 输入流(Input Stream):从外部设备读取数据到内存,例如从文件读取数据。
- 输出流(Output Stream):将数据从内存写入到外部设备,例如将数据写入文件。
-
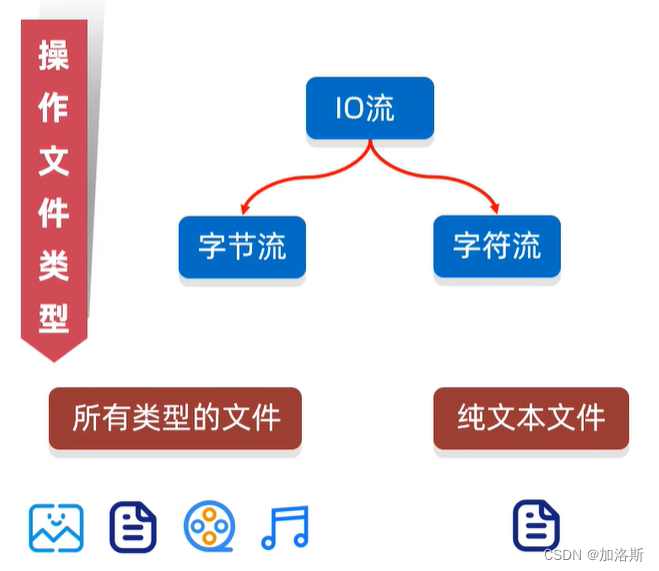
按数据类型分类:
-
字节流(Byte Stream):以字节为单位传输数据,常用于处理二进制数据。例如图片、视频等。常见的字节流类有:
- 输入字节流:
InputStream及其子类(如FileInputStream、BufferedInputStream等) - 输出字节流:
OutputStream及其子类(如FileOutputStream、BufferedOutputStream等)
- 输入字节流:
-
字符流(Character Stream):以字符为单位传输数据,常用于处理文本数据。例如文本文件。常见的字符流类有:
- 输入字符流:
Reader及其子类(如FileReader、BufferedReader等) - 输出字符流:
Writer及其子类(如FileWriter、BufferedWriter等)
- 输入字符流:
-
1.2、常见的IO流类
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream:用于读取和写入文件的字节流。FileReader和FileWriter:用于读取和写入文件的字符流。BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream:带有缓冲区的字节流,可以提高读写效率。BufferedReader和BufferedWriter:带有缓冲区的字符流,可以提高读写效率。InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter:将字节流转换为字符流,通常用于处理编码问题。
二、字节流
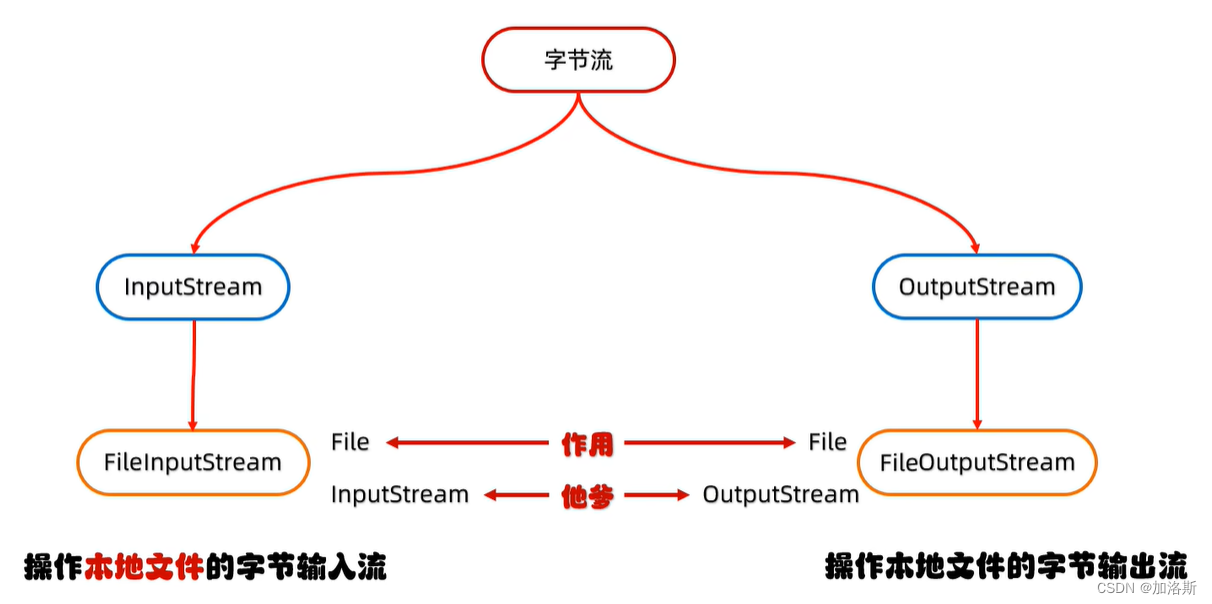
2.1、字节输出流:FileOutputStream
操作本地文件的字节输出流,可以把程序中的数据写到本地文件中。他的操作方法分为三步:
- 创建字节流输出对象
- 写入数据
- 释放资源
字节输出流的细节:
- 创建字节输出流对象
- 参数是字符串表示的路径或者是File对象都是可以的
- 如果文件不存在会创建一个新的文件,但是要保证父级路径是存在的。
- 如果文件已经存在,则会清空文件
- 写数据
- write方法的参数是整数,但是实际上写到本地文件中的是整数在ASCII上对应的字符
- 释放资源
- 每次使用完流之后都要释放资源
其成员方法如下:
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public void write(int b) | 写入单个字节 |
public void write(byte[] b) | 写入字节数组 |
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 写入指定字节数组的一部分 |
public void close() | 关闭文件输出流 |
protected void finalize() | 确保文件输出流被关闭 |
public FileChannel getChannel() | 返回与此文件输出流相关的通道 |
public void flush() | 刷新此文件输出流的缓冲 |
演示代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建对象就相当于创建一个通路 只有通路才能输入输出数据
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\password123456\\Desktop\\资料\\IO流\\a.txt");
fos.write(97);
fos.close();
}
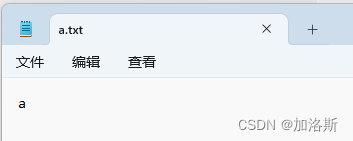
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] buf = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\password123456\\Desktop\\资料\\IO流\\a.txt");
fos.write(buf);
// 数组名 起始索引 长度
fos.write(buf,1,2);
fos.close();
}
2.2、换行与续写
换行符:
- window:
“\r\n” - linux::
"\n" - mac::
"\r"
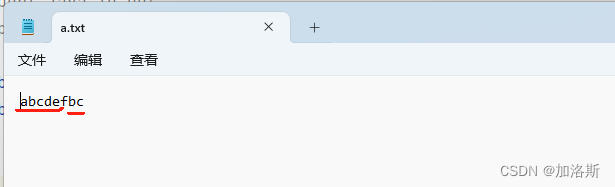
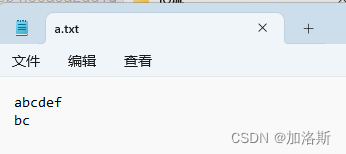
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
byte[] buf = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\password123456\\Desktop\\资料\\IO流\\a.txt");
fos.write(buf);
String wrap = "\r\n";
fos.write(wrap.getBytes());
// 数组名 起始索引 长度
fos.write(buf,1,2);
fos.close();
}
我们说了FileOutputStream创建对象,如果文件已经存在,则会清空文件。但是在我们创建FileOutputStream对象的时候,除了地址参数,其实还有一个续写参数:
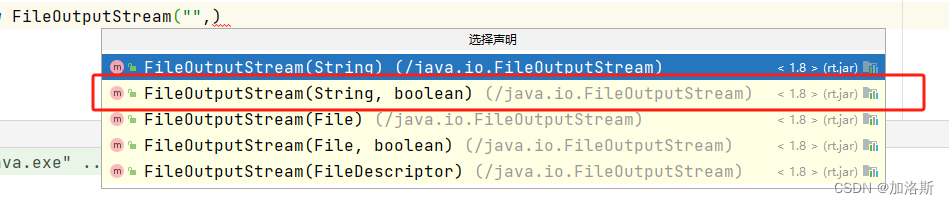
只不过他的默认值是false,只要改为true,就进入到了续写模式。

2.3、字节输入流:FileInputStream
操作本地文件的字节输入流,可以把本地文件中的数据读取到程序中来
步骤:
- 创建字节流输入对象
- 读入数据
- 释放资源
其成员方法如下:
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
public int read() | 从输入流读取一个字节 |
public int read(byte[] b) | 从输入流读取一定数量的字节,并将其存储到缓冲区数组 b 中 |
public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 从输入流中读取最多 len 个字节的数据,并将其存储到缓冲区数组 b 中,从偏移量 off 开始存储 |
public long skip(long n) | 跳过和丢弃输入流中最多 n 个字节的数据 |
public int available() | 返回可以从此输入流中读取的字节数 |
public void close() | 关闭此文件输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源 |
protected void finalize() | 确保在垃圾回收时关闭文件输入流 |
public FileChannel getChannel() | 返回与此文件输入流相关的通道 |
public FileDescriptor getFD() | 返回文件描述符,表示与此文件输入流相关的连接 |
根据上面的读取细节,我们可以写一个循环读取:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream ios = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\password123456\\Desktop\\资料\\IO流\\a.txt");
int a;
while ((a=ios.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)a);
}
ios.close();
}
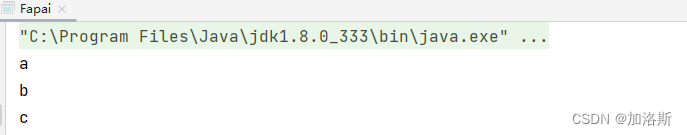
我们再来看一种错误的写法:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream ios = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\password123456\\Desktop\\资料\\IO流\\a.txt");
int a;
while (ios.read()!=-1){
a = ios.read();
System.out.println((char)a);
}
ios.close();
}
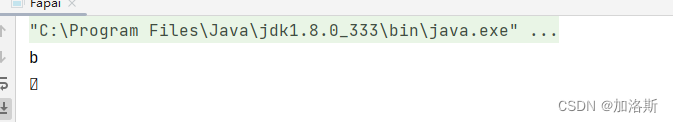
这样的写法自然是错的,还记得我们之前学过的迭代器吗?每一个next都会移动指针,这里也是一样的,每一个read也会移动指针,第一次移动是判断,第二次移动是赋值,所以一次循环会移动两次指针。
三、文件拷贝
第一种方法:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream ios = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\password123456\\Desktop\\资料\\IO流\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\password123456\\Desktop\\资料\\IO流\\b.txt");
int a;
while ((a=ios.read())!=-1){
fos.write(a);
}
ios.close();
fos.close();
}
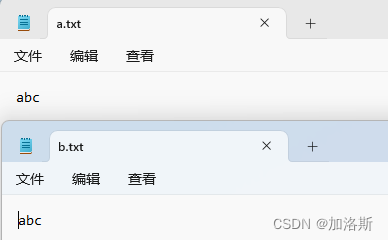
这种方法效率非常的慢,来看第二种方法:这种方法非常的好。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream ios = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\password123456\\Desktop\\资料\\IO流\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\password123456\\Desktop\\资料\\IO流\\b.txt");
int len;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];
while ((len = ios.read(buffer))!=-1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
fos.close();
ios.close();
}























 233
233











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








