基于XQuery的Marklogic增删改查
摘要:任何复杂的数据库操作都离不开基本的增删改查操作,本节介绍在Marklogic8 API https://docs.marklogic.com下XQuery的基本语法。
建数据库
- 首先登陆Admin Page,找到Database.
- 点击create
- 填入database名字,语言选择中文zh(注意zh-Hant为繁体中文)其他选项全部取默认值。
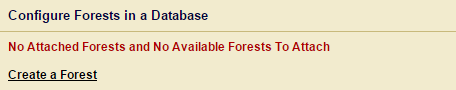
- 点击ok之后,出现提示,需要将database merge到forest。
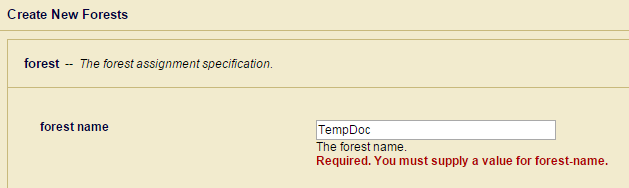
- 由于没有forest,点击Create a Forest,输入forest名字。
- 创建好的database,可以在qConsole中看到,之后的操作如果不做特殊说明,都在该数据库下进行。
插入文档
- API
xdmp:document-insert(
$uri as xs:string,
$root as node(),
[$permissions as element(sec:permission)*],
[$collections as xs:string*],
[$quality as xs:int?],
[$forest-ids as xs:unsignedLong*]
) as empty-sequence()- $uri : 文档存入的路径
- $root : 插入文档的内容
- 加中括号,表示该参数为可选参数
- $permissions : 插入的文档该有的权限。默认取
xdmp:default-permissions()权限。文档的创建者至少拥有文档的update权限。 - $collections : 插入的文档所属的collection。默认取
xdmp:default-collections()。 - $quality : 搜索时,该值影响搜索结果的相关性,正数增加相关性,负数减小相关性。默认值为0.
$forest-ids : 指定文档插入的forest。指定多个时,只插入其中一个,所指定的forest中至少有一个可以做update.。默认插入该数据库所merge的forest。
Marklogic权限是一个庞大而复杂的概念,有很多操作涉及到权限分配与管理。在讲解过程中,我使用是admin的权限操作,该账户拥有较高权限,暂且不提权限管理。在实际生产环境中,会加入各种类型的使用者,他们可能拥有完全不同的权限,这些内容在之后章节中会深入讲到。
- 举例
xquery version "1.0-ml";
declare namespace html = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml";
xdmp:document-insert("/books.xml",
<books>
<book id="1010596200" category="编程">
<title>Java编程思想</title>
<author>埃克尔</author>
<pubDate>2007-6-1</pubDate>
<pages>880</pages>
<price>30.0</price>
</book>
<book id="1010696100" category="文学">
<title>红楼梦</title>
<author>
<firstAuthor>曹雪芹</firstAuthor>
<secondAuthor>高鹗</secondAuthor>
</author>
<pubDate>2012-9-1</pubDate>
<pages>1606</pages>
<price>41.5</price>
</book>
</books>,
xdmp:default-permissions(),
xdmp:default-collections()
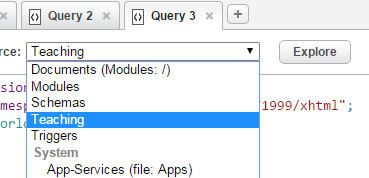
)在qConsole中键入如上代码,选择Content Source 为 Teaching,选择Query Type为Xquery , 点击Run, 即可看到输出your query returned an empty sequence 。如果有语法错误,会显示出来原因与大致出错位置。如果文档的uri是新的,会创建该文档,如果是存在的路径,则会覆盖原始文件。
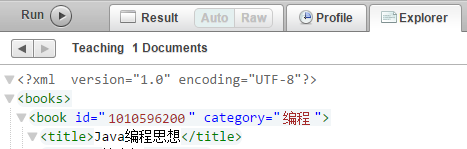
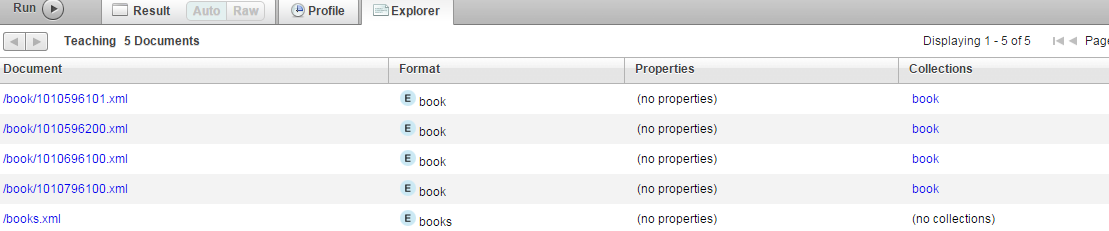
插入成功后,点击Explore

在列表中可以看到刚插入的文档名称
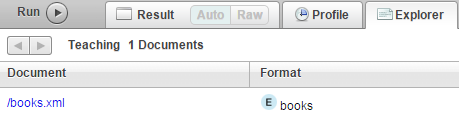
点击对应文档,可以看到内容
更新文档
更新主要有4种类型:
1. 在节点之后插入节点
xdmp:node-insert-after(
$sibling as node(),
$new as node()
) as empty-sequence()例如我们要在上例中添加出版社的信息到出版日期之后
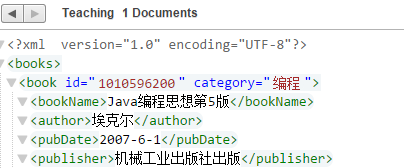
xdmp:node-insert-after(doc("/books.xml")/books/book[title="Java编程思想"]/pubDate, <publisher>机械工业出版社出版</publisher>)可以看到已经添加了所要的数据
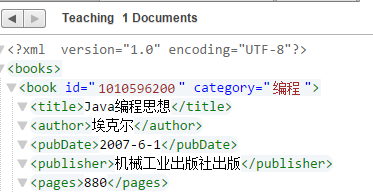
2. 在节点之前插入节点
xdmp:node-insert-before(
$sibling as node(),
$new as node()
) as empty-sequence()和xdmp:node-insert-after不同的就是插入节点在之前,就不举例了。
3. 插入子节点
xdmp:node-insert-child(
$parent as node(),
$new as node()
) as empty-sequence()例如我们要给页码添加一个子节点-开本
xdmp:node-insert-child(doc("/books.xml")/books/book[title="Java编程思想"]/pages, <format>1/16</format> ) 看一下是不是在pages下多了一个子节点format
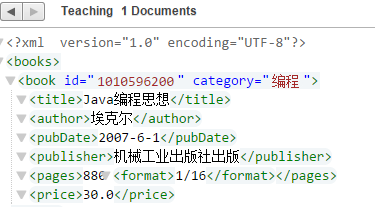
4. 节点更换
xdmp:node-replace(
$old as node(),
$new as node()
) as empty-sequence()例如要将书的标题title更新为bookName
xdmp:node-replace(doc("/books.xml")/books/book[title="Java编程思想"]/title, <bookName>Java编程思想第5版</bookName> )查询数据
Marklogic 的查询功能相当丰富,API cts的大部分方法都为查询服务,还有search,方法不多,但是有些很重要。本节主要介绍cts的部分query函数和search下比较重要的函数。
为了更切合生产环境,现在准备如下数据:
xquery version "1.0-ml";
declare namespace html = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml";
xdmp:document-insert("/book/1010596200.xml",
<book id="1010596200" category="编程">
<title>Java编程思想</title>
<author>埃克尔</author>
<pubDate>2007-6-1</pubDate>
<pages>880</pages>
<price>30.0</price>
</book>,
xdmp:default-permissions(),
"book"
)xquery version "1.0-ml";
declare namespace html = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml";
xdmp:document-insert("/book/1010696100.xml",
<book id="1010696100" category="文学">
<title>红楼梦</title>
<author>
<firstAuthor>曹雪芹</firstAuthor>
<secondAuthor>高鹗</secondAuthor>
</author>
<pubDate>2012-9-1</pubDate>
<pages>1606</pages>
<price>41.5</price>
</book>,
xdmp:default-permissions(),
"book"
)xquery version "1.0-ml";
declare namespace html = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml";
xdmp:document-insert("/book/1010796100.xml",
<book id="1010796100" category="教育">
<title>资格考试</title>
<author>教育集团</author>
<pubDate>2016-1-15</pubDate>
<pages>900</pages>
<price>80.8</price>
</book>,
xdmp:default-permissions(),
"book"
)xdmp:document-insert("/book/1010596101.xml",
<book id="1010596101" category="编程">
<title>java核心技术</title>
<author>霍斯特曼</author>
<pubDate>2014-01</pubDate>
<pages>704</pages>
<price>80.8</price>
</book>,
xdmp:default-permissions(),
"book"
)点击Expore,应该可以看到下图:
- 举例
let $query := cts:and-query((
cts:not-query(cts:word-query("思想")),
cts:element-word-query(xs:QName("title"),"java"),
cts:element-value-query(xs:QName("pages"),"704")
))
let $result := cts:search(/book,$query)
return $result这里有大量的查询操作,通过方法名基本可以知道该方法的功能,我就不列出所有的API了,可以到https://docs.marklogic.com/cts 查看详细的说明,接下来大致介绍一下常用的query函数。
cts:search(
$expression as node()*,
$query as cts:query?,
[$options as (cts:order|xs:string)*],
[$quality-weight as xs:double?],
[$forest-ids as xs:unsignedLong*]
) as node()*查询主要有两个参数,第一个传入文档节点,可以是某目录下所有文档,可以是整个Content Source;第二个是query语句,是整个查询的精髓。之后大量的xquery代码都是在组装这个query语句,query语句由各种查询条件合并而来,如查询符合某元素值的cts:element-value-query,查询符合某属性的cts:element-attribute-value-query,查询不符合某条件的cts:not-query等等。
下面3个函数使用的时候需要注意各自的不同:
cts:element-value-query(
$element-name as xs:QName*,
[$text as xs:string*],
[$options as xs:string*],
[$weight as xs:double?]
) as cts:element-value-query这里指定了元素的值,说明只有元素的值完全符合条件才会返回数据,可以理解为此时为“exact”匹配,当然$options可以设置是否大小写敏感,是否空格敏感。
cts:search(//book,cts:element-value-query(xs:QName("title"),"java核心技术")) 会返回id=1010596101的book,但是将其中的“java核心技术”改为“Java核心技术”,只是有一个大小写不同,则查询不到结果。
如果只指定元素名,而不指定其值,则返回包含该元素的所有文档。
cts:search(//book,cts:element-value-query(xs:QName("title")))会返回所有数据,因为每一条数据都包含title元素。
cts:element-word-query(
$element-name as xs:QName*,
$text as xs:string*,
[$options as xs:string*],
[$weight as xs:double?]
) as cts:element-word-query这里必须指定元素名和一个word, 只要该词出现在这一元素的值中,则会返回数据。
cts:search(//book,cts:element-word-query(xs:QName("title"),"java"))
这里会返回id=1010596101 和id= 1010596200两条数据。后者的标题中”java”有大写字母,但是可以识别到。
cts:element-range-query(
$element-name as xs:QName*,
$operator as xs:string,
$value as xs:anyAtomicType*,
[$options as xs:string*],
[$weight as xs:double?]
) as cts:element-range-query这里还要传一个操作符(支持的操作符[<, <=, >, >= ,!=, =]),既然有操作符,当然就是为了做比较,这个函数可以返回符合某一范围的所有数据,较为常用的是找出某一时间点之前或之后的数据,或者在某一数值范围内的数据。
cts:search(//book,cts:element-range-query(xs:QName("price"),">",50.0)) 可以找出价格大于50元的书籍信息。
但是当我们在qConsole中运行时,却得到一个错误提示: No decimal element range index for price。原来element-range-query是需要range index的,那这个index从哪里来呢?
marklogic 8 设置range index
下面介绍一下marklogic 8 如何设置element range index:
1. 登陆Admin Page . 地址:hostname:8001, 我的地址是:http://localhost:8001/
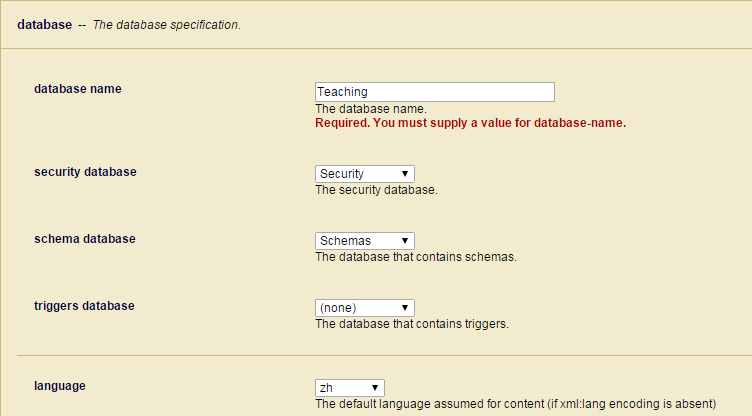
2. 点击Databases, 点击数据库名,这里点击Teaching,这个数据库是我之前创建的,如果你还没有这个数据库,请参照之前的方法自行创建。
3. 点击 Element Range Indexes ,右侧页面会展示当前数据库中存在的index。可以看到默认是存在两组inedxes的。
4. 点击Add 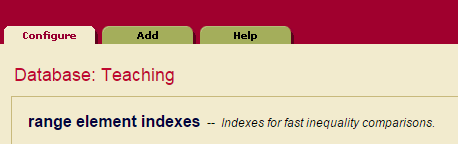
5. 编辑index
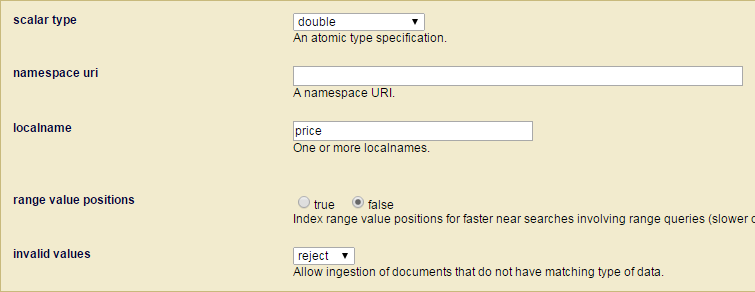
说明:
- scalar type: 数据类型,主要是一些数值,日期,字符串,url类型
- namespace uri: 要绑定元素的命名空间
- localname: 要绑定元素的名称
- range value positions: 可以加快查询速度,但是会加长加载数据时间、使数据库庞大,一般取false
- invalid values: 如何处理无效数据,一般选择拒绝接受无效数据。
- 举例
xdmp:document-insert("/book/1010896100.xml",
<book id="1010896100" category="儿童">
<bookName>安徒生童话</bookName>
<author>安徒生</author>
<pubDate>2016-01-25</pubDate>
<publisher>同心出版社</publisher>
<pages>122</pages>
<price>17元</price>
</book>
)当你已经在price上设置了index为double类型,上例将报错 Invalid lexical value。原来我插入的数据为17元,不符合所要求的数据类型,而我将无效数据的处理设置为reject,因此报错,如果设置值为ignore,则不会报错,可以把数据插入到数据库,但是不建议这样,将不合规的数据插入 后cts:search(//book,cts:element-range-query(xs:QName("price"),">",50.0)) 就会报错。
关于查询,还有一个search函数库:
search:search(
$qtext as xs:string+,
[$options as element(search:options)?],
[$start as xs:unsignedLong?],
[$page-length as xs:unsignedLong?]
) as element(search:response)举例search:search("java"), 但是在qConsole中运行时,报错Prefix search has no namespace binding。这是因为search不是Marklogic 8 的内嵌函数,我们需要手动引入
import module namespace search = "http://marklogic.com/appservices/search" 关于Marklogic的build-in函数,大致有cts、fn、math、rdf、sc、sem、spell、sql、xdmp等。
at "/MarkLogic/appservices/search/search.xqy";
这一API重要的参数不在于qtext, 而是options,这些内容将在后面重点讲到,此处跳过。
search:parse(
$qtext as xs:string+,
[$options as element(search:options)?],
[$output as xs:string?]
) as element()?主要用来解析自定义的query,比如你想用TITLE:java核心技术这种形式表示查询标题为”java核心技术”的书籍,可以用下面代码来处理自定义的逻辑:
- 举例
xquery version "1.0-ml";
declare namespace html = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml";
import module namespace search = "http://marklogic.com/appservices/search"
at "/MarkLogic/appservices/search/search.xqy";
let $q := "TITLE:java核心技术"
let $query := search:parse($q,
<options xmlns="http://marklogic.com/appservices/search">
<constraint name="TITLE">
<value>
<element name="title"/>
</value>
</constraint>
</options>
)
let $query := cts:query($query)
let $result := cts:search(/book,$query)
return $result将参数$q改为TITLE:红楼梦, 逻辑是一样的。这里的constraint是一个很有用的概念,它可以将查询限定在某些条件下,在做一些复杂查询时可以事半功倍。
- 举例
search:suggest(
$qtext as xs:string+,
[$options as element(search:options)?],
[$limit as xs:unsignedInt?],
[$cursor-position as xs:unsignedInt?],
[$focus as xs:positiveInteger?],
[$query as element(search:query)*]
) as xs:string*这个API可以用来做词汇联想,比如在一些搜索界面,输入一个字或词后,会自动提示可能输入的情况,方便用户输入。
- $qtext :Sting数组,默认第一个字符串是用来关联查询的关键词,用focus参数可以更改位置。剩下的字符串解析为cts:query,然后用cts:and-query链接,并将结果作为constraint去匹配词库。
- $options : 定义查询语法并控制查询条件,参见search:search的 options
- $limit : 返回值的个数,默认10条
- $cursor-position : 用来确定哪些查询text用来关联匹配
- $focus : 用来确定qtext中的关键词
- $query : 一个限定qtext查询范围的query
xquery version "1.0-ml";
import module namespace search = "http://marklogic.com/appservices/search"
at "/MarkLogic/appservices/search/search.xqy";
let $options :=
<search:options xmlns="http://marklogic.com/appservices/search">
<default-suggestion-source>
<range type="xs:string" collation="http://marklogic.com/collation/" >
<element name="title"/>
</range>
</default-suggestion-source>
</search:options>
return search:suggest("java", $options)在运行上面代码之前,需要先在数据库中将title配置上range index,因为对title用到的是range query。上例返回的是一个 {“java核心技术”,“Java编程思想”} 数组,可见用“java”在“title”上搜索时,Marklogic能提供相应的建议。
删除文档
Marklogic的删除操作常用的有文档删除和节点删除:
1 . 文档删除只需要文档的uri即可,删除成功后返回your query returned an empty sequence. 如果该文档不存在,则返回Document not found
xdmp:document-delete(
$uri as xs:string
) as empty-sequence()- 举例
xquery version "1.0-ml";
xdmp:document-delete("/book/1010896100.xml")2 . 节点删除需要节点的xpath,删除成功后返回your query returned an empty sequence. 如果所删除的节点不存在,返回同样的提示信息。
xdmp:node-delete(
$old as node()
) as empty-sequence()- 举例
xquery version "1.0-ml";
declare namespace html = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml";
xdmp:node-delete(doc("/book/1010896100.xml")/book/publisher)




























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










