http://www.cnblogs.com/tt_mc/category/279401.html
Android Looper和Handler
Message:消息,其中包含了消息ID,消息处理对象以及处理的数据等,由MessageQueue统一列队,终由Handler处理。
Handler:处理者,负责Message的发送及处理。使用Handler时,需要实现handleMessage(Message msg)方法来对特定的Message进行处理,例如更新UI等。
MessageQueue:消息队列,用来存放Handler发送过来的消息,并按照FIFO规则执行。当然,存放Message并非实际意义的保存,而是将Message以链表的方式串联起来的,等待Looper的抽取。
Looper:消息泵,不断地从MessageQueue中抽取Message执行。因此,一个MessageQueue需要一个Looper。
Thread:线程,负责调度整个消息循环,即消息循环的执行场所。
class LooperThread extends Thread { public Handler mHandler; public void run() { Looper.prepare(); mHandler = new Handler() { public void handleMessage(Message msg) { // process incoming messages here } }; Looper.loop(); } }这样你的线程就具有了消息处理机制了,在Handler中进行消息处理。
Activity是一个UI线程,运行于主线程中,Android系统在启动的时候会为Activity创建一个消息队列和消息循环(Looper)。详细实现请参考ActivityThread.java文件Android应用程序进程在启动的时候,会在进程中加载ActivityThread类,并且执行这个类的main函数,应用程序的消息循环过程就是在这个main函数里面实现的public final class ActivityThread { ...... public static final void main(String[] args) { ...... Looper.prepareMainLooper(); ...... ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread(); thread.attach(false); ...... Looper.loop(); ...... thread.detach(); ...... } }这个函数做了两件事情,一是在主线程中创建了一个ActivityThread实例,二是通过Looper类使主线程进入消息循环中,这里我们只关注后者。首先看Looper.prepareMainLooper函数的实现,这是一个静态成员函数,定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Looper.java文件中:
2 // 没找到合适的分析代码的办法,只能这么来了。每个重要行的上面都会加上注释
3 // 功能方面的代码会在代码前加上一段分析
4 public class Looper {
5 // static变量,判断是否打印调试信息。
6 private static final boolean DEBUG = false;
7 private static final boolean localLOGV = DEBUG ? Config.LOGD : Config.LOGV;
8
9 // sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().
10 // 线程本地存储功能的封装,TLS,thread local storage,什么意思呢?因为存储要么在栈上,例如函数内定义的内部变量。要么在堆上,例如new或者malloc出来的东西
11 // 但是现在的系统比如Linux和windows都提供了线程本地存储空间,也就是这个存储空间是和线程相关的,一个线程内有一个内部存储空间,这样的话我把线程相关的东西就存储到
12 // 这个线程的TLS中,就不用放在堆上而进行同步操作了。
13 private static final ThreadLocal sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
14 // 消息队列,MessageQueue,看名字就知道是个queue..
15 final MessageQueue mQueue;
16 volatile boolean mRun;
17 // 和本looper相关的那个线程,初始化为null
18 Thread mThread;
19 private Printer mLogging = null;
20 // static变量,代表一个UI Process(也可能是service吧,这里默认就是UI)的主线程
21 private static Looper mMainLooper = null;
22
23 /** Initialize the current thread as a looper.
24 * This gives you a chance to create handlers that then reference
25 * this looper, before actually starting the loop. Be sure to call
26 * { @link #loop()} after calling this method, and end it by calling
27 * { @link #quit()}.
28 */
29 // 往TLS中设上这个Looper对象的,如果这个线程已经设过了looper的话就会报错
30 // 这说明,一个线程只能设一个looper
31 public static final void prepare() {
32 if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
33 throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
34 }
35 sThreadLocal.set( new Looper());
36 }
37
38 /** Initialize the current thread as a looper, marking it as an application's main
39 * looper. The main looper for your application is created by the Android environment,
40 * so you should never need to call this function yourself.
41 * { @link #prepare()}
42 */
43 // 由framework设置的UI程序的主消息循环,注意,这个主消息循环是不会主动退出的
44 //
45 public static final void prepareMainLooper() {
46 prepare();
47 setMainLooper(myLooper());
48 // 判断主消息循环是否能退出....
49 // 通过quit函数向looper发出退出申请
50 if (Process.supportsProcesses()) {
51 myLooper().mQueue.mQuitAllowed = false;
52 }
53 }
54
55 private synchronized static void setMainLooper(Looper looper) {
56 mMainLooper = looper;
57 }
58
59 /** Returns the application's main looper, which lives in the main thread of the application.
60 */
61 public synchronized static final Looper getMainLooper() {
62 return mMainLooper;
63 }
64
65 /**
66 * Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call
67 * { @link #quit()} to end the loop.
68 */
69 // 消息循环,整个程序就在这里while了。
70 // 这个是static函数喔!
71 public static final void loop() {
72 Looper me = myLooper(); // 从该线程中取出对应的looper对象
73 MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; // 取消息队列对象...
74 while ( true) {
75 Message msg = queue.next(); // might block取消息队列中的一个待处理消息..
76 // if (!me.mRun) { // 是否需要退出?mRun是个volatile变量,跨线程同步的,应该是有地方设置它。
77 // break;
78 // }
79 if (msg != null) {
80 if (msg.target == null) {
81 // No target is a magic identifier for the quit message.
82 return;
83 }
84 if (me.mLogging!= null) me.mLogging.println(
85 ">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " "
86 + msg.callback + ": " + msg.what
87 );
88 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
89 if (me.mLogging!= null) me.mLogging.println(
90 "<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " "
91 + msg.callback);
92 msg.recycle();
93 }
94 }
95 }
96
97 /**
98 * Return the Looper object associated with the current thread. Returns
99 * null if the calling thread is not associated with a Looper.
100 */
101 // 返回和线程相关的looper
102 public static final Looper myLooper() {
103 return (Looper)sThreadLocal.get();
104 }
105
106 /**
107 * Control logging of messages as they are processed by this Looper. If
108 * enabled, a log message will be written to <var>printer</var>
109 * at the beginning and ending of each message dispatch, identifying the
110 * target Handler and message contents.
111 *
112 * @param printer A Printer object that will receive log messages, or
113 * null to disable message logging.
114 */
115 // 设置调试输出对象,looper循环的时候会打印相关信息,用来调试用最好了。
116 public void setMessageLogging(Printer printer) {
117 mLogging = printer;
118 }
119
120 /**
121 * Return the { @link MessageQueue} object associated with the current
122 * thread. This must be called from a thread running a Looper, or a
123 * NullPointerException will be thrown.
124 */
125 public static final MessageQueue myQueue() {
126 return myLooper().mQueue;
127 }
128 // 创建一个新的looper对象,
129 // 内部分配一个消息队列,设置mRun为true
130 private Looper() {
131 mQueue = new MessageQueue();
132 mRun = true;
133 mThread = Thread.currentThread();
134 }
135
136 public void quit() {
137 Message msg = Message.obtain();
138 // NOTE: By enqueueing directly into the message queue, the
139 // message is left with a null target. This is how we know it is
140 // a quit message.
141 mQueue.enqueueMessage(msg, 0);
142 }
143
144 /**
145 * Return the Thread associated with this Looper.
146 */
147 public Thread getThread() {
148 return mThread;
149 }
150 // 后面就简单了,打印,异常定义等。
151 public void dump(Printer pw, String prefix) {
152 pw.println(prefix + this);
153 pw.println(prefix + "mRun=" + mRun);
154 pw.println(prefix + "mThread=" + mThread);
155 pw.println(prefix + "mQueue=" + ((mQueue != null) ? mQueue : "(null"));
156 if (mQueue != null) {
157 synchronized (mQueue) {
158 Message msg = mQueue.mMessages;
159 int n = 0;
160 while (msg != null) {
161 pw.println(prefix + " Message " + n + ": " + msg);
162 n++;
163 msg = msg.next;
164 }
165 pw.println(prefix + "(Total messages: " + n + ")");
166 }
167 }
168 }
169
170 public String toString() {
171 return "Looper{"
172 + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode( this))
173 + "}";
174 }
175
176 static class HandlerException extends Exception {
177
178 HandlerException(Message message, Throwable cause) {
179 super(createMessage(cause), cause);
180 }
181
182 static String createMessage(Throwable cause) {
183 String causeMsg = cause.getMessage();
184 if (causeMsg == null) {
185 causeMsg = cause.toString();
186 }
187 return causeMsg;
188 }
189 }
190 }
2 ..........
3 // handler默认构造函数
4 public Handler() {
5 // 这个if是干嘛用的暂时还不明白,涉及到java的深层次的内容了应该
6 if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {
7 final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();
8 if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&
9 (klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {
10 Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +
11 klass.getCanonicalName());
12 }
13 }
14 // 获取本线程的looper对象
15 // 如果本线程还没有设置looper,这回抛异常
16 mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
17 if (mLooper == null) {
18 throw new RuntimeException(
19 "Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
20 }
21 // 无耻啊,直接把looper的queue和自己的queue搞成一个了
22 // 这样的话,我通过handler的封装机制加消息的话,就相当于直接加到了looper的消息队列中去了
23 mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
24 mCallback = null;
25 }
26 // 还有好几种构造函数,一个是带callback的,一个是带looper的
27 // 由外部设置looper
28 public Handler(Looper looper) {
29 mLooper = looper;
30 mQueue = looper.mQueue;
31 mCallback = null;
32 }
33 // 带callback的,一个handler可以设置一个callback。如果有callback的话,
34 // 凡是发到通过这个handler发送的消息,都有callback处理,相当于一个总的集中处理
35 // 待会看dispatchMessage的时候再分析
36 public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback) {
37 mLooper = looper;
38 mQueue = looper.mQueue;
39 mCallback = callback;
40 }
41 //
42 // 通过handler发送消息
43 // 调用了内部的一个sendMessageDelayed
44 public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg)
45 {
46 return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);
47 }
48 // FT,又封装了一层,这回是调用sendMessageAtTime了
49 // 因为延时时间是基于当前调用时间的,所以需要获得绝对时间传递给sendMessageAtTime
50 public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis)
51 {
52 if (delayMillis < 0) {
53 delayMillis = 0;
54 }
55 return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
56 }
57
58
59 public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis)
60 {
61 boolean sent = false;
62 MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
63 if (queue != null) {
64 // 把消息的target设置为自己,然后加入到消息队列中
65 // 对于队列这种数据结构来说,操作比较简单了
66 msg.target = this;
67 sent = queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
68 }
69 else {
70 RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
71 this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");
72 Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);
73 }
74 return sent;
75 }
76 // 还记得looper中的那个消息循环处理吗
77 // 从消息队列中得到一个消息后,会调用它的target的dispatchMesage函数
78 // message的target已经设置为handler了,所以
79 // 最后会转到handler的msg处理上来
80 // 这里有个处理流程的问题
81 public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
82 // 如果msg本身设置了callback,则直接交给这个callback处理了
83 if (msg.callback != null) {
84 handleCallback(msg);
85 } else {
86 // 如果该handler的callback有的话,则交给这个callback处理了---相当于集中处理
87 if (mCallback != null) {
88 if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
89 return;
90 }
91 }
92 // 否则交给派生处理,基类默认处理是什么都不干
93 handleMessage(msg);
94 }
95 }
96 ..........
97 }
生成
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage();
msg.what = what;
msg.sendToTarget();
发送
MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
if (queue != null) {
msg.target = this;
sent = queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
}
在Handler.java的sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis)方法中,我们看到,它找到它所引用的MessageQueue,然后将Message的target设定成自己(目的是为了在处理消息环节,Message能找到正确的Handler),再将这个Message纳入到消息队列中。
抽取
Looper me = myLooper();
MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
while (true) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg != null) {
if (msg.target == null) {
// No target is a magic identifier for the quit message.
return;
}
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
msg.recycle();
}
}
在Looper.java的loop()函数里,我们看到,这里有一个死循环,不断地从MessageQueue中获取下一个(next方法)Message,然后通过Message中携带的target信息,交由正确的Handler处理(dispatchMessage方法)。
处理
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
handleMessage(msg);
}
在Handler.java的dispatchMessage(Message msg)方法里,其中的一个分支就是调用handleMessage方法来处理这条Message,而这也正是我们在职责处描述使用Handler时需要实现handleMessage(Message msg)的原因。
至于dispatchMessage方法中的另外一个分支,我将会在后面的内容中说明。
至此,我们看到,一个Message经由Handler的发送,MessageQueue的入队,Looper的抽取,又再一次地回到Handler的怀抱。而绕的这一圈,也正好帮助我们将同步操作变成了异步操作。
3)剩下的部分,我们将讨论一下Handler所处的线程及更新UI的方式。
在主线程(UI线程)里,如果创建Handler时不传入Looper对象,那么将直接使用主线程(UI线程)的Looper对象(系统已经帮我们创建了);在其它线程里,如果创建Handler时不传入Looper对象,那么,这个Handler将不能接收处理消息。在这种情况下,通用的作法是:
class LooperThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// process incoming messages here
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
}
在创建Handler之前,为该线程准备好一个Looper(Looper.prepare),然后让这个Looper跑起来(Looper.loop),抽取Message,这样,Handler才能正常工作。
因此,Handler处理消息总是在创建Handler的线程里运行。而我们的消息处理中,不乏更新UI的操作,不正确的线程直接更新UI将引发异常。因此,需要时刻关心Handler在哪个线程里创建的。
如何更新UI才能不出异常呢?SDK告诉我们,有以下4种方式可以从其它线程访问UI线程:
· Activity.runOnUiThread(Runnable)
· View.post(Runnable)
· View.postDelayed(Runnable, long)
· Handler
其中,重点说一下的是View.post(Runnable)方法。在post(Runnable action)方法里,View获得当前线程(即UI线程)的Handler,然后将action对象post到Handler里。在Handler里,它将传递过来的action对象包装成一个Message(Message的callback为action),然后将其投入UI线程的消息循环中。在Handler再次处理该Message时,有一条分支(未解释的那条)就是为它所设,直接调用runnable的run方法。而此时,已经路由到UI线程里,因此,我们可以毫无顾虑的来更新UI。
4) 几点小结
· Handler的处理过程运行在创建Handler的线程里
· 一个Looper对应一个MessageQueue
· 一个线程对应一个Looper
· 一个Looper可以对应多个Handler
· 不确定当前线程时,更新UI时尽量调用post方法
Android中的Looper类,是用来封装消息循环和消息队列的一个类,用于在android线程中进行消息处理。handler其实可以看做是一个工具类,用来向消息队列中插入消息的。
(1) Looper类用来为一个线程开启一个消息循环。
默认情况下android中新诞生的线程是没有开启消息循环的。(主线程除外,主线程系统会自动为其创建Looper对象,开启消息循环。)
Looper对象通过MessageQueue来存放消息和事件。一个线程只能有一个Looper,对应一个MessageQueue。
(2) 通常是通过Handler对象来与Looper进行交互的。Handler可看做是Looper的一个接口,用来向指定的Looper发送消息及定义处理方法。
默认情况下Handler会与其被定义时所在线程的Looper绑定,比如,Handler在主线程中定义,那么它是与主线程的Looper绑定。
mainHandler = new Handler() 等价于new Handler(Looper.myLooper()).
Looper.myLooper():获取当前进程的looper对象,类似的 Looper.getMainLooper() 用于获取主线程的Looper对象。
(3) 在非主线程中直接new Handler() 会报如下的错误:
E/AndroidRuntime( 6173): Uncaught handler: thread Thread-8 exiting due to uncaught exception
E/AndroidRuntime( 6173): java.lang.RuntimeException: Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()
原因是非主线程中默认没有创建Looper对象,需要先调用Looper.prepare()启用Looper。
(4) Looper.loop(); 让Looper开始工作,从消息队列里取消息,处理消息。
注意:写在Looper.loop()之后的代码不会被执行,这个函数内部应该是一个循环,当调用mHandler.getLooper().quit()后,loop才会中止,其后的代码才能得以运行。
(5) 基于以上知识,可实现主线程给子线程(非主线程)发送消息。
把下面例子中的mHandler声明成类成员,在主线程通过mHandler发送消息即可。
Android官方文档中Looper的介绍:
Class used to run a message loop for a thread. Threads by default do not have a message loop associated with them; to create one, call prepare() in the thread that is to run the loop, and then loop() to have it process messages until the loop is stopped.
Most interaction with a message loop is through the Handler class.
This is a typical example of the implementation of a Looper thread, using the separation of prepare() and loop() to create an initial Handler to communicate with the Looper.
01 | class LooperThreadextends Thread { |
02 | publicHandler mHandler; |
03 | |
04 | publicvoid run() { |
05 | Looper.prepare(); |
06 | |
07 | mHandler =new Handler() { |
08 | publicvoid handleMessage(Message msg) { |
09 | // process incoming messages here |
10 | } |
11 | }; |
12 | |
13 | Looper.loop(); |
14 | } |
15 | } |
Android应用程序消息处理机制(Looper、Handler)分析
Android应用程序是通过消息来驱动的,系统为每一个应用程序维护一个消息队例,应用程序的主线程不断地从这个消息队例中获取消息(Looper),然后对这些消息进行处理(Handler),这样就实现了通过消息来驱动应用程序的执行,本文将详细分析Android应用程序的消息处理机制。前面我们学习Android应用程序中的Activity启动(Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析和Android应用程序内部启动Activity过程(startActivity)的源代码分析)、Service启动(Android系统在新进程中启动自定义服务过程(startService)的原理分析和Android应用程序绑定服务(bindService)的过程源代码分析)以及广播发送(Android应用程序发送广播(sendBroadcast)的过程分析)时,它们都有一个共同的特点,当ActivityManagerService需要与应用程序进行并互时,如加载Activity和Service、处理广播待,会通过Binder进程间通信机制来知会应用程序,应用程序接收到这个请求时,它不是马上就处理这个请求,而是将这个请求封装成一个消息,然后把这个消息放在应用程序的消息队列中去,然后再通过消息循环来处理这个消息。这样做的好处就是消息的发送方只要把消息发送到应用程序的消息队列中去就行了,它可以马上返回去处理别的事情,而不需要等待消息的接收方去处理完这个消息才返回,这样就可以提高系统的并发性。实质上,这就是一种异步处理机制。
这样说可能还是比较笼统,我们以Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析一文中所介绍的应用程序启动过程的一个片断来具体看看是如何这种消息处理机制的。在这篇文章中,要启动的应用程序称为Activity,它的默认Activity是MainActivity,它是由Launcher来负责启动的,而Launcher又是通过ActivityManagerService来启动的,当ActivityManagerService为这个即将要启的应用程序准备好新的进程后,便通过一个Binder进程间通信过程来通知这个新的进程来加载MainActivity,如下图所示:
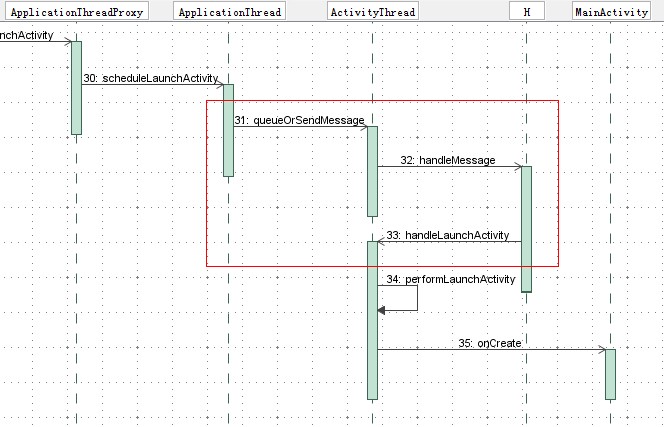
它对应Android应用程序启动过程中的Step 30到Step 35,有兴趣的读者可以回过头去参考Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析一文。这里的Step 30中的scheduleLaunchActivity是ActivityManagerService通过Binder进程间通信机制发送过来的请求,它请求应用程序中的ActivityThread执行Step 34中的performLaunchActivity操作,即启动MainActivity的操作。这里我们就可以看到,Step 30的这个请求并没有等待Step 34这个操作完成就返回了,它只是把这个请求封装成一个消息,然后通过Step 31中的queueOrSendMessage操作把这个消息放到应用程序的消息队列中,然后就返回了。应用程序发现消息队列中有消息时,就会通过Step 32中的handleMessage操作来处理这个消息,即调用Step 33中的handleLaunchActivity来执行实际的加载MainAcitivy类的操作。
了解Android应用程序的消息处理过程之后,我们就开始分样它的实现原理了。与Windows应用程序的消息处理过程一样,Android应用程序的消息处理机制也是由消息循环、消息发送和消息处理这三个部分组成的,接下来,我们就详细描述这三个过程。
1. 消息循环
在消息处理机制中,消息都是存放在一个消息队列中去,而应用程序的主线程就是围绕这个消息队列进入一个无限循环的,直到应用程序退出。如果队列中有消息,应用程序的主线程就会把它取出来,并分发给相应的Handler进行处理;如果队列中没有消息,应用程序的主线程就会进入空闲等待状态,等待下一个消息的到来。在Android应用程序中,这个消息循环过程是由Looper类来实现的,它定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Looper.java文件中,在分析这个类之前,我们先看一下Android应用程序主线程是如何进入到这个消息循环中去的。
在Android应用程序进程启动过程的源代码分析一文中,我们分析了Android应用程序进程的启动过程,Android应用程序进程在启动的时候,会在进程中加载ActivityThread类,并且执行这个类的main函数,应用程序的消息循环过程就是在这个main函数里面实现的,我们来看看这个函数的实现,它定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- public static final void main(String[] args) {
- ......
- Looper.prepareMainLooper();
- ......
- ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
- thread.attach(false);
- ......
- Looper.loop();
- ......
- thread.detach();
- ......
- }
- }
首先看Looper.prepareMainLooper函数的实现,这是一个静态成员函数,定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Looper.java文件中:
- public class Looper {
- ......
- private static final ThreadLocal sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
- final MessageQueue mQueue;
- ......
- /** Initialize the current thread as a looper.
- * This gives you a chance to create handlers that then reference
- * this looper, before actually starting the loop. Be sure to call
- * {@link #loop()} after calling this method, and end it by calling
- * {@link #quit()}.
- */
- public static final void prepare() {
- if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
- throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
- }
- sThreadLocal.set(new Looper());
- }
- /** Initialize the current thread as a looper, marking it as an application's main
- * looper. The main looper for your application is created by the Android environment,
- * so you should never need to call this function yourself.
- * {@link #prepare()}
- */
- public static final void prepareMainLooper() {
- prepare();
- setMainLooper(myLooper());
- if (Process.supportsProcesses()) {
- myLooper().mQueue.mQuitAllowed = false;
- }
- }
- private synchronized static void setMainLooper(Looper looper) {
- mMainLooper = looper;
- }
- /**
- * Return the Looper object associated with the current thread. Returns
- * null if the calling thread is not associated with a Looper.
- */
- public static final Looper myLooper() {
- return (Looper)sThreadLocal.get();
- }
- private Looper() {
- mQueue = new MessageQueue();
- mRun = true;
- mThread = Thread.currentThread();
- }
- ......
- }
- public class MessageQueue {
- ......
- private int mPtr; // used by native code
- private native void nativeInit();
- MessageQueue() {
- nativeInit();
- }
- ......
- }
- static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj) {
- NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = new NativeMessageQueue();
- if (! nativeMessageQueue) {
- jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Unable to allocate native queue");
- return;
- }
- android_os_MessageQueue_setNativeMessageQueue(env, obj, nativeMessageQueue);
- }
- NativeMessageQueue::NativeMessageQueue() {
- mLooper = Looper::getForThread();
- if (mLooper == NULL) {
- mLooper = new Looper(false);
- Looper::setForThread(mLooper);
- }
- }
这个Looper的创建过程也很重要,不过我们暂时放一放,先分析完android_os_MessageQueue_nativeInit函数的执行,它创建了本地消息队列NativeMessageQueue对象之后,接着调用android_os_MessageQueue_setNativeMessageQueue函数来把这个消息队列对象保存在前面我们在Java层中创建的MessageQueue对象的mPtr成员变量里面:
- static void android_os_MessageQueue_setNativeMessageQueue(JNIEnv* env, jobject messageQueueObj,
- NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue) {
- env->SetIntField(messageQueueObj, gMessageQueueClassInfo.mPtr,
- reinterpret_cast<jint>(nativeMessageQueue));
- }
我们再回到NativeMessageQueue的构造函数中,看看JNI层的Looper对象的创建过程,即看看它的构造函数是如何实现的,这个Looper类实现在frameworks/base/libs/utils/Looper.cpp文件中:
- Looper::Looper(bool allowNonCallbacks) :
- mAllowNonCallbacks(allowNonCallbacks),
- mResponseIndex(0) {
- int wakeFds[2];
- int result = pipe(wakeFds);
- ......
- mWakeReadPipeFd = wakeFds[0];
- mWakeWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];
- ......
- #ifdef LOOPER_USES_EPOLL
- // Allocate the epoll instance and register the wake pipe.
- mEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);
- ......
- struct epoll_event eventItem;
- memset(& eventItem, 0, sizeof(epoll_event)); // zero out unused members of data field union
- eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
- eventItem.data.fd = mWakeReadPipeFd;
- result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeReadPipeFd, & eventItem);
- ......
- #else
- ......
- #endif
- ......
- }
- int wakeFds[2];
- int result = pipe(wakeFds);
- ......
- mWakeReadPipeFd = wakeFds[0];
- mWakeWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];
要使用Linux系统的epoll机制,首先要通过epoll_create来创建一个epoll专用的文件描述符:
- mEpollFd = epoll_create(EPOLL_SIZE_HINT);
接着还要通过epoll_ctl函数来告诉epoll要监控相应的文件描述符的什么事件:
- struct epoll_event eventItem;
- memset(& eventItem, 0, sizeof(epoll_event)); // zero out unused members of data field union
- eventItem.events = EPOLLIN;
- eventItem.data.fd = mWakeReadPipeFd;
- result = epoll_ctl(mEpollFd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, mWakeReadPipeFd, & eventItem);
C++层的这个Looper对象创建好了之后,就返回到JNI层的NativeMessageQueue的构造函数,最后就返回到Java层的消息队列MessageQueue的创建过程,这样,Java层的Looper对象就准备好了。有点复杂,我们先小结一下这一步都做了些什么事情:
A. 在Java层,创建了一个Looper对象,这个Looper对象是用来进入消息循环的,它的内部有一个消息队列MessageQueue对象mQueue;
B. 在JNI层,创建了一个NativeMessageQueue对象,这个NativeMessageQueue对象保存在Java层的消息队列对象mQueue的成员变量mPtr中;
C. 在C++层,创建了一个Looper对象,保存在JNI层的NativeMessageQueue对象的成员变量mLooper中,这个对象的作用是,当Java层的消息队列中没有消息时,就使Android应用程序主线程进入等待状态,而当Java层的消息队列中来了新的消息后,就唤醒Android应用程序的主线程来处理这个消息。
回到ActivityThread类的main函数中,在上面这些工作都准备好之后,就调用Looper类的loop函数进入到消息循环中去了:
- public class Looper {
- ......
- public static final void loop() {
- Looper me = myLooper();
- MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
- ......
- while (true) {
- Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
- ......
- if (msg != null) {
- if (msg.target == null) {
- // No target is a magic identifier for the quit message.
- return;
- }
- ......
- msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
- ......
- msg.recycle();
- }
- }
- }
- ......
- }
这个函数最关键的地方便是从消息队列中获取下一个要处理的消息了,即MessageQueue.next函数,它实现frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/MessageQueue.java文件中:
- public class MessageQueue {
- ......
- final Message next() {
- int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration
- int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
- for (;;) {
- if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) {
- Binder.flushPendingCommands();
- }
- nativePollOnce(mPtr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
- synchronized (this) {
- // Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found.
- final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
- final Message msg = mMessages;
- if (msg != null) {
- final long when = msg.when;
- if (now >= when) {
- mBlocked = false;
- mMessages = msg.next;
- msg.next = null;
- if (Config.LOGV) Log.v("MessageQueue", "Returning message: " + msg);
- return msg;
- } else {
- nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- }
- } else {
- nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
- }
- // If first time, then get the number of idlers to run.
- if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0) {
- pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();
- }
- if (pendingIdleHandlerCount == 0) {
- // No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.
- mBlocked = true;
- continue;
- }
- if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {
- mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];
- }
- mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);
- }
- // Run the idle handlers.
- // We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.
- for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {
- final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];
- mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler
- boolean keep = false;
- try {
- keep = idler.queueIdle();
- } catch (Throwable t) {
- Log.wtf("MessageQueue", "IdleHandler threw exception", t);
- }
- if (!keep) {
- synchronized (this) {
- mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);
- }
- }
- }
- // Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again.
- pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0;
- // While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered
- // so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting.
- nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
- }
- }
- ......
- }
执行下面语句是看看当前消息队列中有没有消息:
- nativePollOnce(mPtr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
当前nativePollOnce返回后,就去看看消息队列中有没有消息:
- final Message msg = mMessages;
- if (msg != null) {
- final long when = msg.when;
- if (now >= when) {
- mBlocked = false;
- mMessages = msg.next;
- msg.next = null;
- if (Config.LOGV) Log.v("MessageQueue", "Returning message: " + msg);
- return msg;
- } else {
- nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- }
- } else {
- nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
- }
- nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
这里计算出来的等待时间都是在下次调用nativePollOnce时使用的。
这里说的等待,是空闲等待,而不是忙等待,因此,在进入空闲等待状态前,如果应用程序注册了IdleHandler接口来处理一些事情,那么就会先执行这里IdleHandler,然后再进入等待状态。IdlerHandler是定义在MessageQueue的一个内部类:
- public class MessageQueue {
- ......
- /**
- * Callback interface for discovering when a thread is going to block
- * waiting for more messages.
- */
- public static interface IdleHandler {
- /**
- * Called when the message queue has run out of messages and will now
- * wait for more. Return true to keep your idle handler active, false
- * to have it removed. This may be called if there are still messages
- * pending in the queue, but they are all scheduled to be dispatched
- * after the current time.
- */
- boolean queueIdle();
- }
- ......
- }
回到MessageQueue函数中,它接下来就是在进入等待状态前,看看有没有IdleHandler是需要执行的:
- // If first time, then get the number of idlers to run.
- if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0) {
- pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size();
- }
- if (pendingIdleHandlerCount == 0) {
- // No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more.
- mBlocked = true;
- continue;
- }
- if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) {
- mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)];
- }
- mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers);
接下来就是执行这些注册了的IdleHanlder了:
- // Run the idle handlers.
- // We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration.
- for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) {
- final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i];
- mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler
- boolean keep = false;
- try {
- keep = idler.queueIdle();
- } catch (Throwable t) {
- Log.wtf("MessageQueue", "IdleHandler threw exception", t);
- }
- if (!keep) {
- synchronized (this) {
- mIdleHandlers.remove(idler);
- }
- }
- }
- // While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered
- // so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting.
- nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
- static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativePollOnce(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj,
- jint ptr, jint timeoutMillis) {
- NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = reinterpret_cast<NativeMessageQueue*>(ptr);
- nativeMessageQueue->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
- }
- void NativeMessageQueue::pollOnce(int timeoutMillis) {
- mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
- }
- int Looper::pollOnce(int timeoutMillis, int* outFd, int* outEvents, void** outData) {
- int result = 0;
- for (;;) {
- ......
- if (result != 0) {
- ......
- return result;
- }
- result = pollInner(timeoutMillis);
- }
- }
函数pollInner的定义如下:
- int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {
- ......
- int result = ALOOPER_POLL_WAKE;
- ......
- #ifdef LOOPER_USES_EPOLL
- struct epoll_event eventItems[EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS];
- int eventCount = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, eventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
- bool acquiredLock = false;
- #else
- ......
- #endif
- if (eventCount < 0) {
- if (errno == EINTR) {
- goto Done;
- }
- LOGW("Poll failed with an unexpected error, errno=%d", errno);
- result = ALOOPER_POLL_ERROR;
- goto Done;
- }
- if (eventCount == 0) {
- ......
- result = ALOOPER_POLL_TIMEOUT;
- goto Done;
- }
- ......
- #ifdef LOOPER_USES_EPOLL
- for (int i = 0; i < eventCount; i++) {
- int fd = eventItems[i].data.fd;
- uint32_t epollEvents = eventItems[i].events;
- if (fd == mWakeReadPipeFd) {
- if (epollEvents & EPOLLIN) {
- awoken();
- } else {
- LOGW("Ignoring unexpected epoll events 0x%x on wake read pipe.", epollEvents);
- }
- } else {
- ......
- }
- }
- if (acquiredLock) {
- mLock.unlock();
- }
- Done: ;
- #else
- ......
- #endif
- ......
- return result;
- }
- int eventCount = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, eventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
当mEpollFd所监控的文件描述符发生了要监控的IO事件后或者监控时间超时后,线程就从epoll_wait返回了,否则线程就会在epoll_wait函数中进入睡眠状态了。返回后如果eventCount等于0,就说明是超时了:
- if (eventCount == 0) {
- ......
- result = ALOOPER_POLL_TIMEOUT;
- goto Done;
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < eventCount; i++) {
- int fd = eventItems[i].data.fd;
- uint32_t epollEvents = eventItems[i].events;
- if (fd == mWakeReadPipeFd) {
- if (epollEvents & EPOLLIN) {
- awoken();
- } else {
- LOGW("Ignoring unexpected epoll events 0x%x on wake read pipe.", epollEvents);
- }
- } else {
- ......
- }
- }
函数awoken的实现很简单,它只是把管道中的内容都读取出来:
- void Looper::awoken() {
- ......
- char buffer[16];
- ssize_t nRead;
- do {
- nRead = read(mWakeReadPipeFd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
- } while ((nRead == -1 && errno == EINTR) || nRead == sizeof(buffer));
- }
这样,消息的循环过程就分析完了,这部分逻辑还是比较复杂的,它利用Linux系统中的管道(pipe)进程间通信机制来实现消息的等待和处理,不过,了解了这部分内容之后,下面我们分析消息的发送和处理就简单多了。
2. 消息的发送
应用程序的主线程准备就好消息队列并且进入到消息循环后,其它地方就可以往这个消息队列中发送消息了。我们继续以文章开始介绍的Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析一文中的应用程序启动过为例,说明应用程序是如何把消息加入到应用程序的消息队列中去的。
在Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析这篇文章的Step 30中,ActivityManagerService通过调用ApplicationThread类的scheduleLaunchActivity函数通知应用程序,它可以加载应用程序的默认Activity了,这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java文件中:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
- ......
- // we use token to identify this activity without having to send the
- // activity itself back to the activity manager. (matters more with ipc)
- public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
- ActivityInfo info, Bundle state, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults,
- List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward) {
- ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord();
- r.token = token;
- r.ident = ident;
- r.intent = intent;
- r.activityInfo = info;
- r.state = state;
- r.pendingResults = pendingResults;
- r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents;
- r.startsNotResumed = notResumed;
- r.isForward = isForward;
- queueOrSendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
- ......
- // if the thread hasn't started yet, we don't have the handler, so just
- // save the messages until we're ready.
- private final void queueOrSendMessage(int what, Object obj) {
- queueOrSendMessage(what, obj, 0, 0);
- }
- ......
- private final void queueOrSendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2) {
- synchronized (this) {
- ......
- Message msg = Message.obtain();
- msg.what = what;
- msg.obj = obj;
- msg.arg1 = arg1;
- msg.arg2 = arg2;
- mH.sendMessage(msg);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final class H extends Handler {
- ......
- public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
- ......
- switch (msg.what) {
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
这个H类就是通过其成员函数handleMessage函数来处理消息的了,后面我们分析消息的处理过程时会看到。
ActivityThread类的这个mH成员变量是什么时候创建的呢?我们前面在分析应用程序的消息循环时,说到当应用程序进程启动之后,就会加载ActivityThread类的main函数里面,在这个main函数里面,在通过Looper类进入消息循环之前,会在当前进程中创建一个ActivityThread实例:
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- public static final void main(String[] args) {
- ......
- ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
- thread.attach(false);
- ......
- }
- }
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- final H mH = new H();
- ......
- }
- public class Handler {
- ......
- public Handler() {
- ......
- mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
- ......
- mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
- ......
- }
- final MessageQueue mQueue;
- final Looper mLooper;
- ......
- }
- public class Looper {
- ......
- public static final Looper myLooper() {
- return (Looper)sThreadLocal.get();
- }
- ......
- }
有了这个Handler对象mH后,就可以通过它来往应用程序的消息队列中加入新的消息了。回到前面的queueOrSendMessage函数中,当它准备好了一个Message对象msg后,就开始调用mH.sendMessage函数来发送消息了,这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Handler.java文件中:
- public class Handler {
- ......
- public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg)
- {
- return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);
- }
- public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis)
- {
- if (delayMillis < 0) {
- delayMillis = 0;
- }
- return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);
- }
- public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis)
- {
- boolean sent = false;
- MessageQueue queue = mQueue;
- if (queue != null) {
- msg.target = this;
- sent = queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
- }
- else {
- ......
- }
- return sent;
- }
- ......
- }
在sendMessageAtTime函数,首先得到应用程序的消息队列mQueue,这是在Handler对象构造时初始化好的,前面已经分析过了,接着设置这个消息的目标对象target,即这个消息最终是由谁来处理的:
- msg.target = this;
函数最后调用queue.enqueueMessage来把这个消息加入到应用程序的消息队列中去,这个函数实现在frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/MessageQueue.java文件中:
- public class MessageQueue {
- ......
- final boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
- ......
- final boolean needWake;
- synchronized (this) {
- ......
- msg.when = when;
- //Log.d("MessageQueue", "Enqueing: " + msg);
- Message p = mMessages;
- if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
- msg.next = p;
- mMessages = msg;
- needWake = mBlocked; // new head, might need to wake up
- } else {
- Message prev = null;
- while (p != null && p.when <= when) {
- prev = p;
- p = p.next;
- }
- msg.next = prev.next;
- prev.next = msg;
- needWake = false; // still waiting on head, no need to wake up
- }
- }
- if (needWake) {
- nativeWake(mPtr);
- }
- return true;
- }
- ......
- }
第一种情况比较简单,只要把消息放在消息队列头就可以了:
- msg.next = p;
- mMessages = msg;
- needWake = mBlocked; // new head, might need to wake up
- Message prev = null;
- while (p != null && p.when <= when) {
- prev = p;
- p = p.next;
- }
- msg.next = prev.next;
- prev.next = msg;
- needWake = false; // still waiting on head, no need to wake up
- static void android_os_MessageQueue_nativeWake(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jint ptr) {
- NativeMessageQueue* nativeMessageQueue = reinterpret_cast<NativeMessageQueue*>(ptr);
- return nativeMessageQueue->wake();
- }
- void NativeMessageQueue::wake() {
- mLooper->wake();
- }
- void Looper::wake() {
- ......
- ssize_t nWrite;
- do {
- nWrite = write(mWakeWritePipeFd, "W", 1);
- } while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
- .......
- }
这时候既然管道中有内容可读了,应用程序的主线程就会从这里的Looper类的pollInner函数返回到JNI层的nativePollOnce函数,最后返回到Java层中的MessageQueue.next函数中去,这里它就会发现消息队列中有新的消息需要处理了,于就会处理这个消息。
3. 消息的处理
前面在分析消息循环时,说到应用程序的主线程是在Looper类的loop成员函数中进行消息循环过程的,这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Looper.java文件中:
- public class Looper {
- ......
- public static final void loop() {
- Looper me = myLooper();
- MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
- ......
- while (true) {
- Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
- ......
- if (msg != null) {
- if (msg.target == null) {
- // No target is a magic identifier for the quit message.
- return;
- }
- ......
- msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
- ......
- msg.recycle();
- }
- }
- }
- ......
- }
我们继续以前面分析消息的发送时所举的例子来分析消息的处理过程。前面说到,在Android应用程序启动过程源代码分析这篇文章的Step 30中,ActivityManagerService通过调用ApplicationThread类的scheduleLaunchActivity函数通知应用程序,它可以加载应用程序的默认Activity了,而ApplicationThread类的scheduleLaunchActivity函数最终把这个请求封装成一个消息,然后通过ActivityThread类的成员变量mH来把这个消息加入到应用程序的消息队列中去。现在要对这个消息进行处理了,于是就会调用H类的dispatchMessage函数进行处理。
H类没有实现自己的dispatchMessage函数,但是它继承了父类Handler的dispatchMessage函数,这个函数定义在frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ Handler.java文件中:
- public class Handler {
- ......
- public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
- if (msg.callback != null) {
- handleCallback(msg);
- } else {
- if (mCallback != null) {
- if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
- return;
- }
- }
- handleMessage(msg);
- }
- }
- ......
- }
- public final class ActivityThread {
- ......
- private final class H extends Handler {
- ......
- public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
- ......
- switch (msg.what) {
- case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
- ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
- r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
- r.activityInfo.applicationInfo);
- handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
- } break;
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
- ......
- }
至此,我们就从消息循环、消息发送和消息处理三个部分分析完Android应用程序的消息处理机制了,为了更深理解,这里我们对其中的一些要点作一个总结:
A. Android应用程序的消息处理机制由消息循环、消息发送和消息处理三个部分组成的。
B. Android应用程序的主线程在进入消息循环过程前,会在内部创建一个Linux管道(Pipe),这个管道的作用是使得Android应用程序主线程在消息队列为空时可以进入空闲等待状态,并且使得当应用程序的消息队列有消息需要处理时唤醒应用程序的主线程。
C. Android应用程序的主线程进入空闲等待状态的方式实际上就是在管道的读端等待管道中有新的内容可读,具体来说就是是通过Linux系统的Epoll机制中的epoll_wait函数进行的。
D. 当往Android应用程序的消息队列中加入新的消息时,会同时往管道中的写端写入内容,通过这种方式就可以唤醒正在等待消息到来的应用程序主线程。
E. 当应用程序主线程在进入空闲等待前,会认为当前线程处理空闲状态,于是就会调用那些已经注册了的IdleHandler接口,使得应用程序有机会在空闲的时候处理一些事情。























 166
166

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








