1024. Permutations
Time Limit: 2.0 second
Memory Limit: 16 MB
Memory Limit: 16 MB
Background
We remind that the permutation of some final set is a one-to-one mapping of the set onto itself. Less formally, that is a way to reorder elements of the set. For example, one can define a permutation of the set {1,2,3,4,5} as follows:
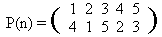
This record defines a permutation P as follows: P(1) = 4, P(2) = 1, P(3) = 5, etc.
What is the value of the expression P(P(1))? It’s clear, that P(P(1)) = P(4) = 2. And P(P(3)) = P(5) = 3. One can easily see that if P(
n) is a permutation then P(P(
n)) is a permutation as well. In our example (check it by yourself)
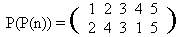
It is natural to denote this permutation by P
2(
n) = P(P(
n)). In a general form the definition is as follows: P(
n) = P
1(
n), P
k(
n) = P(P
k-1(
n)).
Among the permutations there is a very important one — that moves nothing:
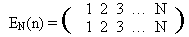
It is clear that for every
k the following relation is satisfied: (E
N)
k = E
N. The following less trivial statement is correct (we won’t prove it here, you may prove it yourself incidentally):
Let P(n) be some permutation of an N elements set. Then there exists a positive integer k, that Pk = EN.
The least positive integer
k such that P
k = E
N is called an order of the permutation P.
Problem
The problem that your program should solve is formulated now in a very simple manner:
“Given a permutation find its order.”
Input
The first line contains the only integer
N (1 ≤
N ≤ 1000), that is a number of elements in the set that is rearranged by this permutation. In the second line there are
N integers of the range from 1 up to
N, separated by a space, that define a permutation — the numbers P(1), P(2),…, P(
N).
Output
You should write the order of the permutation. You may consider that an answer shouldn’t exceed 10
9.
Sample
| input | output |
|---|---|
5 4 1 5 2 3 | 6 |
一开始理解错了题目意思,泪奔。。。
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
int lcm(int a, int b)
{
return a / gcd(a, b) * b;
}
int main()
{
int i, n, ans = 1, temp;
int a[1001], b[1001];
cin>>n;
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
b[i] = 1;
}
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
temp = a[i];
while (temp != i)
{
temp = a[temp];
b[i]++;
}
}
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
ans = lcm(ans, b[i]);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}





















 208
208

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








