
策略模式(Strategy)目的是,定义一系列算法,将每个算法封装起来,并让他们可以相互替换。策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户而变化。 状态图为:
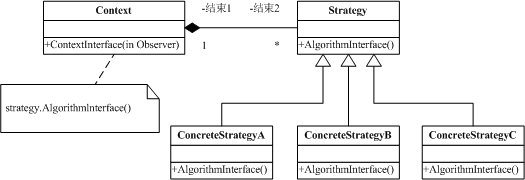
我们使用策略模式为多个对象封装不同的排序算法,允许客户动态改变不同的排序策略。
实现代码:
//
SortStrategy.h
class SortStrategy
{
public :
SortStrategy();
virtual ~ SortStrategy();
virtual void Sort( int * pArray, int nSize) = 0 ;
};
// SortStrategy.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " SortStrategy.h "
SortStrategy::SortStrategy()
{
}
SortStrategy:: ~ SortStrategy()
{
}
// QuickSort.h
#include " SortStrategy.h "
class QuickSort : public SortStrategy
{
public :
QuickSort();
virtual ~ QuickSort();
void Sort( int * pArray, int nSize);
private :
void Sort( int * pArray, int nLow, int nHigh);
void Swap( int & nA, int & nB);
int Partition( int * pArray, int nLow, int nHigh);
};
// QuickSort.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " QuickSort.h "
QuickSort::QuickSort()
{
}
QuickSort:: ~ QuickSort()
{
}
void QuickSort::Sort( int * pArray, int nSize)
{
Sort(pArray, 0 , nSize);
}
void QuickSort::Sort( int * pArray, int nLow, int nHigh)
{
int i;
if (nLow < nHigh)
{
i = Partition(pArray, nLow, nHigh);
Sort(pArray, 0 , i - 1 );
Sort(pArray, i + 1 , nHigh);
}
}
void QuickSort::Swap( int & nA, int & nB)
{
int x;
x = nA;
nA = nB;
nB = x;
}
int QuickSort::Partition( int * pArray, int nLow, int nHigh)
{
int i = nLow - 1 ;
int j;
for (j = nLow; j < nHigh; ++ j)
{
if (pArray[j] < pArray[nHigh])
{
Swap(pArray[ ++ i], pArray[j]);
}
}
Swap(pArray[i + 1 ], pArray[nHigh]);
return i + 1 ;
}
// BubbleSort.h
#include " SortStrategy.h "
class BubbleSort : public SortStrategy
{
public :
BubbleSort();
virtual ~ BubbleSort();
void Sort( int * , int nSize);
private :
void Swap( int & nA, int & nB);
};
// BubbleSort.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " BubbleSort.h "
BubbleSort::BubbleSort()
{
}
BubbleSort:: ~ BubbleSort()
{
}
void BubbleSort::Sort( int * pArray, int nSize)
{
for ( int i = nSize - 1 ; i >= 0 ; -- i)
{
for ( int j = 0 ; j <= i; ++ j)
{
if (pArray[i] > pArray[j])
{
Swap(pArray[i], pArray[j]);
}
}
}
}
void BubbleSort::Swap( int & nA, int & nB)
{
int x;
x = nA;
nA = nB;
nB = x;
}
// SortedList.h
class SortStrategy;
class SortedList
{
public :
SortedList();
virtual ~ SortedList();
void SetSortStrategy(SortStrategy * );
void Sort( int * , int nSize);
void Display();
private :
SortStrategy * m_pStrategy;
int * m_pArray;
int m_nSize;
};
// SortedList.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " SortedList.h "
#include " SortStrategy.h "
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
SortedList::SortedList()
{
}
SortedList:: ~ SortedList()
{
if (m_pStrategy != NULL)
{
delete m_pStrategy;
m_pStrategy = NULL;
}
}
void SortedList::SetSortStrategy(SortStrategy * pStrategy)
{
m_pStrategy = pStrategy;
}
void SortedList::Sort( int * nArray, int nSize)
{
m_pArray = nArray;
m_nSize = nSize;
m_pStrategy -> Sort(m_pArray, nSize);
}
void SortedList::Display()
{
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m_nSize; ++ i)
{
cout << m_pArray[i] << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
}
// main.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " SortedList.h "
#include " QuickSort.h "
#include " BubbleSort.h "
int main( int argc, char * argv[])
{
int nArray[] = { 8 , 7 , 10 , 15 , 4 , 3 , 20 , 13 };
int nSize = sizeof nArray / sizeof nArray[ 0 ];
SortedList sort;
SortStrategy * pStrategy = new QuickSort;
sort.SetSortStrategy(pStrategy);
sort.Sort(nArray, nSize);
printf( " 快速排序: " );
sort.Display();
pStrategy = new BubbleSort;
sort.SetSortStrategy(pStrategy);
sort.Sort(nArray, nSize);
printf( " 冒泡排序: " );
sort.Display();
return 0 ;
}
class SortStrategy
{
public :
SortStrategy();
virtual ~ SortStrategy();
virtual void Sort( int * pArray, int nSize) = 0 ;
};
// SortStrategy.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " SortStrategy.h "
SortStrategy::SortStrategy()
{
}
SortStrategy:: ~ SortStrategy()
{
}
// QuickSort.h
#include " SortStrategy.h "
class QuickSort : public SortStrategy
{
public :
QuickSort();
virtual ~ QuickSort();
void Sort( int * pArray, int nSize);
private :
void Sort( int * pArray, int nLow, int nHigh);
void Swap( int & nA, int & nB);
int Partition( int * pArray, int nLow, int nHigh);
};
// QuickSort.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " QuickSort.h "
QuickSort::QuickSort()
{
}
QuickSort:: ~ QuickSort()
{
}
void QuickSort::Sort( int * pArray, int nSize)
{
Sort(pArray, 0 , nSize);
}
void QuickSort::Sort( int * pArray, int nLow, int nHigh)
{
int i;
if (nLow < nHigh)
{
i = Partition(pArray, nLow, nHigh);
Sort(pArray, 0 , i - 1 );
Sort(pArray, i + 1 , nHigh);
}
}
void QuickSort::Swap( int & nA, int & nB)
{
int x;
x = nA;
nA = nB;
nB = x;
}
int QuickSort::Partition( int * pArray, int nLow, int nHigh)
{
int i = nLow - 1 ;
int j;
for (j = nLow; j < nHigh; ++ j)
{
if (pArray[j] < pArray[nHigh])
{
Swap(pArray[ ++ i], pArray[j]);
}
}
Swap(pArray[i + 1 ], pArray[nHigh]);
return i + 1 ;
}
// BubbleSort.h
#include " SortStrategy.h "
class BubbleSort : public SortStrategy
{
public :
BubbleSort();
virtual ~ BubbleSort();
void Sort( int * , int nSize);
private :
void Swap( int & nA, int & nB);
};
// BubbleSort.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " BubbleSort.h "
BubbleSort::BubbleSort()
{
}
BubbleSort:: ~ BubbleSort()
{
}
void BubbleSort::Sort( int * pArray, int nSize)
{
for ( int i = nSize - 1 ; i >= 0 ; -- i)
{
for ( int j = 0 ; j <= i; ++ j)
{
if (pArray[i] > pArray[j])
{
Swap(pArray[i], pArray[j]);
}
}
}
}
void BubbleSort::Swap( int & nA, int & nB)
{
int x;
x = nA;
nA = nB;
nB = x;
}
// SortedList.h
class SortStrategy;
class SortedList
{
public :
SortedList();
virtual ~ SortedList();
void SetSortStrategy(SortStrategy * );
void Sort( int * , int nSize);
void Display();
private :
SortStrategy * m_pStrategy;
int * m_pArray;
int m_nSize;
};
// SortedList.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " SortedList.h "
#include " SortStrategy.h "
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
SortedList::SortedList()
{
}
SortedList:: ~ SortedList()
{
if (m_pStrategy != NULL)
{
delete m_pStrategy;
m_pStrategy = NULL;
}
}
void SortedList::SetSortStrategy(SortStrategy * pStrategy)
{
m_pStrategy = pStrategy;
}
void SortedList::Sort( int * nArray, int nSize)
{
m_pArray = nArray;
m_nSize = nSize;
m_pStrategy -> Sort(m_pArray, nSize);
}
void SortedList::Display()
{
for ( int i = 0 ; i < m_nSize; ++ i)
{
cout << m_pArray[i] << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
}
// main.cpp
#include " stdafx.h "
#include " SortedList.h "
#include " QuickSort.h "
#include " BubbleSort.h "
int main( int argc, char * argv[])
{
int nArray[] = { 8 , 7 , 10 , 15 , 4 , 3 , 20 , 13 };
int nSize = sizeof nArray / sizeof nArray[ 0 ];
SortedList sort;
SortStrategy * pStrategy = new QuickSort;
sort.SetSortStrategy(pStrategy);
sort.Sort(nArray, nSize);
printf( " 快速排序: " );
sort.Display();
pStrategy = new BubbleSort;
sort.SetSortStrategy(pStrategy);
sort.Sort(nArray, nSize);
printf( " 冒泡排序: " );
sort.Display();
return 0 ;
}
代码中,我们使用快速排序从小到大排序,使用冒泡排序从大到小排序,场景为SortedList,由它来决定执行哪一个排序。
最后输出为:
快速排序:3 4 7 8 10 13 15 20
冒泡排序:20 15 13 10 8 7 4 3






















 272
272

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








